Evaluation of swelling-shrinkage of expansive soil based on subjective and objective weighting and efficiency coefficient methods
-
摘要:
膨胀土胀缩等级的分类是治理膨胀土工作中的首要问题, 为了精确评价膨胀土胀缩性, 便于现场安全施工, 防灾减灾, 将功效系数法应用于膨胀土胀缩等级的分类问题中。选用液限、胀缩总率、塑性指数、天然含水率和自由膨胀率为评价指标, 采用德尔菲法和熵权法相结合的主客观赋权确定各指标的权重系数, 通过计算样本总功效系数值来确定最终评价结果, 建立了一个新的膨胀土胀缩等级评价模型, 选取19组膨胀土实测数据进行了模型检验, 其中有15组数据与其他方法进行了对比分析, 有4组数据与实际情况进行对比分析。研究结果表明: 与模糊数学、物元可拓法、变权靶心贴近度法和未知测度法对比分析的15组数据准确率达到93.3%;与实际情况对比的4组数据准确率达到了100%。研究成果证明了功效系数法用于膨胀土胀缩等级划分的合理性和有效性, 对膨胀土现场安全施工具有指导意义。
Abstract:Objective Classifying the swelling-shrinkage degree of expansive soil is a critical issue in their management of expansive soil. To prevent and mitigate engineering disasters, accurate evaluation of the swelling-shrinkage for expansive soil is essential. This study applies the efficacy coefficient method to classify the swelling-shrinkage grade of expansive soil.
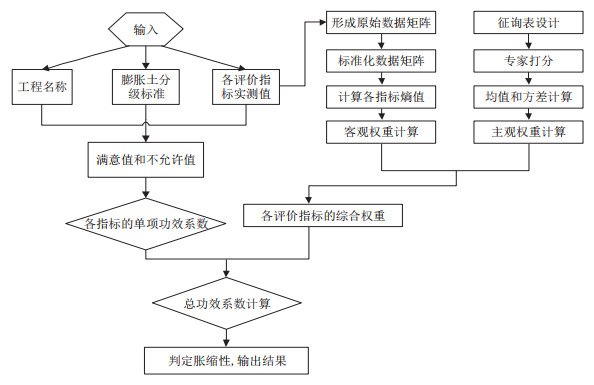
Methods Five factors(the liquid limit, total swell-shrink ratio, plastic index, water content, and free swelling ratio) are selected as evaluation indices to comprehensively assess the swelling-shrinkage characteristics. The weight coefficients of these indices are determined using both objective and subjective weighting method, namely the Delphi method and information entropy theory. The final classification is obtained by calculating the total efficacy coefficient of the sample. A new model for evaluating the swelling-shrinkage grade of expansive soil is established using the efficacy coefficient method in combination with the subjective and objective weighting approach. The model is tested on 19 sets of field test data from relevant literature, with 15 groups of data compared to other methods and 4 groups of data compared to actual situation.
Results The accuracy of the model, when compared with extension theory, the variable weight and the unascertained measurement method, reached 93.3% for the 15 groups of data. For the 4 groups of data compared with the real-world conditions, the accuracy reached 100%.
Conclusion The proposed model is both reasonable and effective in classifying the swelling-shrinkage grade of expansive soil, offering valuable guidance for the safe construction of expansive soil projects.
-
胀缩等级 液限/% 胀缩总率/% 塑性指数/% 天然含水率/% 自由膨胀率/% Ⅰ(极高) [55, 59] [6, 8] [35, 45] [5, 15) [85, 99] Ⅱ(高) [50, 55) [4, 6) [25, 35) [15, 25) [70, 85) Ⅲ(中) [45, 50) [2, 4) [18, 25) [25, 35) [55, 70) Ⅳ(低) [40, 45) [0.7, 2) [12, 18) [35, 45] [40, 55) 表 2 膨胀土评价指标的满意值和不允许值
Table 2. Satisfactory value and unacceptable value of the evaluation indices of expansive soil
评价指标 液限/% 胀缩总率/% 塑性指数/% 天然含水率/% 自由膨胀率/% 满意值 59 8 45 5 99 不允许值 40 0.7 12 45 40 表 3 各评价因子主观权重
Table 3. Subjective weights of each evaluation factor
指标 液限 胀缩总率 塑性指数 天然含水率 自由膨胀率 a1 3 10 6 8 4 a2 4 9 7 9 4 a3 3 10 5 9 4 信息熵Ei 3.333 3 9.666 7 6.000 0 8.666 7 4.000 0 方差δ2 0.333 3 0.333 3 1.000 0 0.333 3 0.000 0 主观权重ωia 0.105 3 0.305 2 0.189 5 0.273 7 0.126 3 注:a1, a2, a3分别为第1,2,3位专家评分 表 4 各评价因子客观权重
Table 4. Objective weights of each evaluation factor
指标 液限 胀缩总率 塑性指数 天然含水率 自由膨胀率 信息熵Ei 0.995 8 0.963 5 0.981 6 0.965 6 0.991 9 偏差度Di 0.004 2 0.036 5 0.018 4 0.034 4 0.008 1 客观熵权ωib 0.041 8 0.359 6 0.180 9 0.338 4 0.079 4 表 5 膨胀土评价指标的主客观赋权
Table 5. Combined subjective and objective weights of expansive soil evaluation indices
指标 液限 胀缩总率 塑性指数 天然含水率 自由膨胀率 主观权重ωia 0.105 3 0.305 2 0.189 5 0.273 7 0.126 3 客观权重ωib 0.041 8 0.359 6 0.180 9 0.338 4 0.079 4 综合权重ωi 0.073 6 0.332 4 0.185 2 0.306 1 0.102 8 表 6 膨胀等级分析
Table 6. Expansion grade analysis
胀缩等级 总功效系数 说明 Ⅰ(极高) ≥90 胀缩性极高,灾害风险很高 Ⅱ(高) [80, 90) 胀缩性高,灾害风险高 Ⅲ(中) [70, 80) 胀缩性中等,灾害风险低 Ⅳ(低) [60, 70) 胀缩性弱,灾害风险极低 表 7 膨胀土胀缩等级计算结果与其他方法对比分析
Table 7. Comparison and analysis of the calculation results of the swelling-shrinking grade of expansive soil with other methods
样本序号 评价指标[23-24] 总功效系数 膨胀土胀缩等级 液限/% 胀缩总率/% 塑性指数/% 天然含水率/% 自由膨胀率/% 本研究 可拓法[25] 改进可拓法[26] 变权靶心贴近度法[27] 未知测度法[12] 样本1 60 7.0 36.0 20 80.0 90.906 Ⅰ Ⅰ Ⅰ Ⅰ Ⅰ 样本2 50 5.0 36.0 27 66.0 82.753 Ⅱ Ⅱ Ⅱ Ⅱ Ⅱ 样本3 47 4.0 24.0 29 70.0 76.865 Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ 样本4 57 6.0 25.0 33 61.0 80.000 Ⅱ Ⅱ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅱ 样本5 66 7.0 35.0 14 83.0 93.609 Ⅰ Ⅰ Ⅰ Ⅰ Ⅰ 样本6 57 5.0 29.0 20 74.0 84.605 Ⅱ Ⅱ Ⅱ Ⅱ Ⅱ 样本7 44 4.0 23.0 24 74.0 78.266 Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ 样本8 43 1.4 16.0 44 56.0 63.306 Ⅳ Ⅳ Ⅳ Ⅳ Ⅳ 样本9 42 3.3 21.0 44 53.0 67.826 Ⅳ Ⅳ Ⅳ Ⅳ Ⅳ 样本10 47 5.0 27.0 37 59.0 75.982 Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ 样本11 44 4.5 38.0 14 88.0 87.719 Ⅱ Ⅱ Ⅰ Ⅰ Ⅰ 样本12 55 6.0 38.0 14.7 88.0 91.452 Ⅰ Ⅰ Ⅰ Ⅰ Ⅰ 样本13 63 8.0 42.0 10 84.0 98.477 Ⅰ Ⅰ Ⅰ Ⅰ Ⅰ 样本14 53 4.2 18.5 40 41.5 70.662 Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅳ 样本15 41 0.65 13.0 44 51.0 60.559 Ⅳ Ⅳ Ⅳ Ⅳ Ⅳ 注:Ⅰ,Ⅱ,Ⅲ,Ⅳ分别表示膨胀土胀缩等级为极高、高、中、低,下同 表 8 膨胀土胀缩等级计算结果与实际结果对比分析
Table 8. Comparison and analysis of the calculated results of the swelling-shrinking grades of expansive soil with the actual results
-
[1] 崔晓宁, 王起才, 张戎令, 等. 基于主成分分析法的膨胀土膨胀力预测[J]. 水利水电技术, 2018, 49(7): 181-186.CUI X N, WANG Q C, ZHANG R L, et al. Principal component analysis-based prediction of swelling force of expansive soil[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2018, 49(7): 181-186. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] 谭罗荣, 张梅英, 邵梧敏, 等. 风干含水量W65用作膨胀土判别分类指标的可行性研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 1994, 2(1): 15-26.TAN L R, ZHANG M Y, SHAO W M, et al. The practicability research on use of air-dry moisture content W65 as identification index of the swelling soil[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 1994, 2(1): 15-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) [3] 刘特洪. 工程建设中的膨胀土问题[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 1997.LIU T H. Expansive soil problem in engineering construction[M]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 1997. (in Chinese) [4] 高卫东. 基于Logistic回归模型的膨胀土判别与分类[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2020, 37(6): 153-155.GAO W D. Discrimination and classification of expansive soil based on Logistic regression model[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2020, 37(6): 153-155. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] WANG M W, CHEN G Y. A novel coupling model for risk analysis of swell and shrinkage of expansive soils[J]. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 2011, 62(7): 2854-2861. (in Chinese with English abstract)) [6] 汪明武, 赵奎元, 张立彪. 基于联系期望的膨胀土和改良土胀缩性评价模型[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2014, 36(8): 1553-1557.WANG M W, ZHAO K Y, ZHANG L B. A novel evaluation model based on connectional expectation for swelling-shrinkage grade of untreated and treated expansive clay[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(8): 1553-1557. (in Chinese with English abstract) [7] 高岭, 李建朋, 李雪校. 基于燕尾突变模型和标准吸湿含水率的膨胀土分类方法[J]. 武汉大学学报(工学版), 2021, 54(4): 325-331.GAO L, LI J P, LI X X. Classification method for expansive soil based on swallowtail catastrophe model and standard moisture absorption rate[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2021, 54(4): 325-331. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 高树增, 张雁. 基于熵权直觉模糊集的改良膨胀土胀缩性等级评价[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 39(3): 131-138.GAO S Z, ZHANG Y. Evaluation of expansion and shrinkage grade of improved expansive soil based on entropy weight intuitionistic fuzzy set[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University(Natural Science), 2020, 39(3): 131-138. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] 高树增, 安改红, 张雁. 基于熵权正态云模型的改良膨胀土胀缩性评价[J]. 电子世界, 2019(13): 9-11.GAO S Z, AN G H, ZHANG Y. Evaluation of expansion and shrinkage of improved expansive soil based on entropy weight normal cloud model[J]. Electronic World, 2019(13): 9-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] 汪明武, 李健, 徐鹏, 等. 膨胀土与石灰改良膨胀土胀缩性的云模型评价[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 44(2): 396-400.WANG M W, LI J, XU P, et al. Cloud model for shrinkage-swelling property classification of untreated and lime-treated expansive clays[J]. Journal of Southeast University(Natural Science Edition), 2014, 44(2): 396-400. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] 丁加明, 王永和, 丁力行. 基于粗糙集的膨胀土分级指标重要性分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2006, 27(9): 1514-1518.DING J M, WANG Y H, DING L X. Significance of expansive soil classification indexes analysed by rough sets[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2006, 27(9): 1514-1518. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] 史秀志, 胡海燕, 周健. 基于信息熵-未确知测度理论的膨胀土胀缩分级评价[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2010, 30(4): 144-149.SHI X Z, HU H Y, ZHOU J. The classification of the grade of shrink and expansion for the expansive soils based on information entropy and uncertainty measurement theory[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2010, 30(4): 144-149. (in Chinese with English abstract) [13] 徐诗然. 基于功效系数法的水上运输业企业绩效评价[J]. 物流工程与管理, 2021, 43(1): 163-165.XU S R. Performance evaluation of water transportation enterprises based on efficiency coefficient method[J]. Logistics Engineering and Management, 2021, 43(1): 163-165. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] 黄冠文. 基于功效系数法的格力电器企业绩效评价[J]. 中国农业会计, 2022(11): 91-94.HUANG G W. Corporate performance evaluation of Gree Electric Appliances based on efficiency coefficient method[J]. Chinese Agricultural Accounting, 2022(11): 91-94. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 崔娇娇. 基于功效系数法的家电行业企业绩效评价[J]. 经营与管理, 2024(3): 55-61.CUI J J. Enterprise performance evaluation of home appliance industry based on efficiency coefficient method[J]. Business and Management, 2024(3): 55-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] 张琳, 果春山, 王春阳, 等. 基于功效系数法的山东省国家高新区创新能力评价[J]. 科学与管理, 2022, 42(6): 85-92.ZHANG L, GUO C S, WANG C Y, et al. Research on evaluation of innovation ability of national high-tech zones in Shandong Province based on efficacy coefficient method[J]. Science and Management, 2022, 42(6): 85-92. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] 胡倡瑞, 王平, 郑先伟, 等. 基于功效系数法的地表变形破坏预警研究[J]. 人民长江, 2022, 53(6): 146-152.HU C R, WANG P, ZHENG X W, et al. Study on early warning of surface deformation and failure based on efficacy coefficient method[J]. Yangtze River, 2022, 53(6): 146-152. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] 李海东, 张少阳. 功效系数法在企业财务风险预警中的应用: 以A零部件制造企业为例[J]. 财务与会计, 2018(11): 44-45.LI H D, ZANG S Y. Application of efficiency coefficient method in enterprise financial risk warning: A case study of A Parts Manufacturing Enterprise[J]. Finance andAccounting, 2018(11): 44-45. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] 王迎超, 尚岳全, 孙红月, 等. 基于功效系数法的岩爆烈度分级预测研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2010, 31(2): 529-534.WANG Y C, SHANG Y Q, SUN H Y, et al. Study of prediction of rockburst intensity based on efficacy coefficient method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2010, 31(2): 529-534. (in Chinese with English abstract) [20] 徐佳, 张勤, 吴继敏. 功效系数法在确定岩体优势结构面中的应用[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2008, 30(4): 617-620.XU J, ZHANG Q, WU J M. Application of efficacy coefficient method to determination of rock preferred structrual plane[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2008, 30(4): 617-620. (in Chinese with English abstract) [21] 胡志. 软科学直观预测技术: 特尔菲方法[J]. 医学与哲学, 1989(10): 26-29.HU Z. Intuitive prediction technique of soft science: Delphi method[J]. Medicine & Philosophy, 1989(10): 26-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) [22] 孙亮, 潘懋, 陈建平, 等. 五台-吕梁地区沉积变质型铁矿证据权重法成矿预测[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(5): 118-125.SUN L, PAN M, CHEN J P, et al. Metallogenic prediction of the sedimentary metamorphic iron deposits with application of evidence weight method in Wutai-Lüliang area, Shanxi Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(5): 118-125. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] 陈新民, 李生林. 膨胀土判别与分类的灰关联分析法[J]. 岩土力学, 1996, 17(4): 30-34.CHEN X M, LI S L. A new approach for identification and classification of expansive soils with grey correlation analysis[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 1996, 17(4): 30-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] 马鸿发, 刘清秉, 李靖. 掺砂率与干密度对膨润土收缩特性影响[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(6): 76-85. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220099MA H F, LIU Q B, LI J. Effect of shrinkage characteristics of bentonite with different sand mixing rates and dry densities[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(6): 76-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220099 [25] 王广月, 马华月, 刘健. 路基膨胀土胀缩等级的物元可拓识别模型[J]. 公路交通科技, 2005, 22(11): 30-33.WANG G Y, MA H Y, LIU J. Matter-element extension model of expansive soils' expansive scale in embankments[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2005, 22(11): 30-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) [26] 张慧颖, 曾建民. 物元可拓模型的改进及其在膨胀土分类中的应用[J]. 岩土力学, 2008, 29(6): 1681-1684.ZHANG H Y, ZENG J M. Improvement of matter-element extension model and its application to classification of expansive soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008, 29(6): 1681-1684. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] 夏连学, 张慧颖. 变权靶心贴近度在膨胀土分类中的应用[J]. 长安大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 28(4): 32-34.XIA L X, ZHANG H Y. Application of target approaching in variable weight to expansive soil classification[J]. Journal of Chang'an University(Natural Science Edition), 2008, 28(4): 32-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) [28] 曹净, 欧孝夺, 周东, 等. 南宁膨胀土胀缩性模糊评判分析[J]. 中南公路工程, 2004, 29(3): 15-18.CAO J, OU X D, ZHOU D, et al. Fuzzy evaluation on swell-shrink characteristics of Nanning swelling soil[J]. Central South Highway Engineering, 2004, 29(3): 15-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) -





 下载:
下载: