Identification and genetic mechanism of recharge sources in groundwater-rich area of Changxiao karst water system in Jinan City
-
摘要:
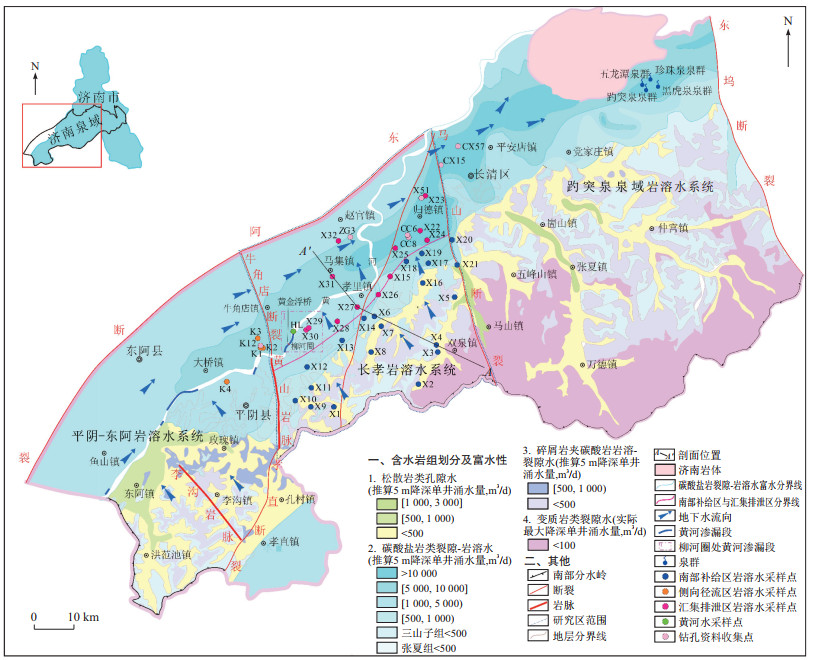
为识别济南长孝岩溶水系统岩溶地下水富集区补给源并揭示其富水机制, 利用水化学方法和自组织神经网络(SOM-KM)耦合法揭示研究区岩溶地下水补给源和空间分布规律, 利用端元混合模型定量计算富水区岩溶地下水的补给源贡献比; 并结合地形地貌、地质构造、地层岩性及汇水条件探究岩溶地下水富集机制。结果表明, 汇集排泄区岩溶地下水与南部补给区、侧向径流区岩溶地下水和黄河水水化学特征皆具相似性, 水力联系密切, 指示汇集排泄区岩溶地下水接受南部山区、侧向径流岩溶地下水和黄河水三源补给, 枯水期三者补给贡献率分别为75.09%、21.02%、3.89%。汇集排泄区碳酸盐岩分布广泛且裂隙岩溶发育, 尤其在马集-孝里-归德一带, 加之该地区岩溶地下水补给源丰富, 且在岩溶地下水自东南向西北径流过程中, 在北部受砂岩泥岩阻水地层的阻滞, 地下水汇聚于可溶岩与非可溶岩接触带, 形成地层阻滞型岩溶地下水富水构造。通过揭示长孝岩溶水系统岩溶地下水富集机制, 可为后续准确计算可采资源量、济南市保泉供水提供科学支撑。
Abstract:Objective and methods In this study, the hydrochemical method and self-organized neural network (SOM-KM) coupling method were employed to identify recharge sources and reveal the water-rich mechanism in the karst groundwater-rich area of the Changxiao karst water system in Jinan City. The contribution ratio of karst groundwater recharge sources in the karst groundwater-rich area was quantitatively calculated using the end-element mixed model. The enrichment mechanism of karst groundwater is explored by combining with topography, geological structure, stratigraphic lithology, and catchment conditions.
Results The results showed that the karst groundwater in the catchment drainage area had similar water chemistry to that in the southern recharge area, the karst groundwater in the lateral runoff area, and the Yellow River, indicating a close hydraulic connection. This implies that the karst groundwater in the catchment drainage area is recharged by three sources: The southern mountain area, the karst groundwater in the lateral runoff area, and the Yellow River. The contribution ratios of the three components are 75.09%, 21.02%, and 3.89%, respectively. Carbonate rocks are widely distributed, and fissured karst is well developed in the accumulation and discharge areas, especially in the Maji-Xiaoli-Guide area. Moreover, there are abundant karst groundwater recharge sources in this area. During the runoff process of karst groundwater from southeast to northwest, it is impeded by sandstone and mudstone in the north. As a result, it accumulates in the contact zone between soluble rock and insoluble rock, thus forming impeded-type karst groundwater-rich structures.
Conclusion Revealing the enrichment mechanism of karst groundwater in the Changxiao karst water system can provide scientific support for accurate calculations of recoverable resources and the protection of the springs in Jinan.
-
图 5 黄河水位岩溶地下水监测井-柳河圈村X30水位动态曲线对比图(位置见图 1)
Figure 5. Comparison of dynamic water level curves between Yellow River water level and karst groundwater monitoring well X30 in Liuhe Quan Village
图 10 钻孔涌水量与距断裂(或接触带)距离幂函数关系曲线图(钻孔位置见图 1)
Figure 10. Power function relationship curve between borehole water inflow and the distances boreholes and fracture/contact zone
图 11 水文地质钻孔裂隙岩溶发育段与涌水量统计图(钻孔位置见图 1)
Q.第四系;O1t.土峪组; O2b.北庵庄组; O2d.东黄山组; O2w.王阳山组; ∈4O1s.三山子组; ∈.寒武系; Ar3γ.新太古界; N.新近系;下同
Figure 11. Statistics of fissure/karst development section in hydrogeological borehole and water inflow
图 12 阻滞型富水构造形成机理图(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 12. Formation mechanism of the impeded water-rich structure
表 1 岩溶地下水及黄河水水化学指标
Table 1. Hydrochemical indices of karst groundwater and Yellow River water
样品区 TDS Ca2+ Mg2+ Na+ K+ Cl- SO42- HCO3- NO3- 水化学类型 ρB/(mg·L-1) 南部补给区 最大值 825.13 183.00 43.20 26.50 8.76 81.20 210.00 377.00 154.00 HCO3·SO4-Ca 最小值 482.58 92.90 9.64 11.10 0.10 23.50 88.00 274.00 19.50 平均值 630.33 156.13 27.78 15.32 0.70 50.34 135.13 316.00 77.92 标准差 105.56 28.33 9.86 5.70 0.44 22.71 33.67 33.65 40.42 变异系数 0.17 0.18 0.35 0.37 0.63 0.45 0.25 0.11 0.52 侧向径流区 最大值 842.38 189.00 40.70 44.50 1.04 119.00 142.00 444.00 63.30 HCO3-Ca·Mg 最小值 361.00 71.10 23.12 22.50 0.40 28.00 33.80 278.00 11.50 平均值 502.68 108.50 28.77 30.50 0.75 54.43 66.63 345.81 24.78 标准差 60.96 6.99 6.08 10.67 0.20 4.39 3.66 90.91 22.24 变异系数 0.12 0.06 0.21 0.35 0.27 0.08 0.05 0.26 0.90 汇集排泄区 最大值 1179.36 270.00 47.90 57.70 7.26 124.00 228.00 487.00 272.00 HCO3-Ca
HCO3·SO4-Ca最小值 343.56 78.80 15.00 11.30 0.063 23.30 13.20 213.00 4.85 平均值 634.42 156.14 25.98 23.88 1.03 66.00 105.05 322.49 104.08 标准差 246.78 64.34 10.00 13.51 1.54 33.00 62.58 77.13 86.88 变异系数 0.39 0.41 0.38 0.57 1.50 0.50 0.60 0.24 0.83 黄河 586.00 57.70 26.70 96.90 4.13 103.00 188.00 176.00 13.6 SO4·Cl·HCO3-Na·Ca 表 2 补给源计算参数及补给源贡献率计算结果
Table 2. Calculation parameters of recharge sources and calculation results of contribution ratios from recharge sources
样品区 ρ(TDS)/(mg·L-1) ρ(Ca2+)/(mg·L-1) 补给源贡献率/% 汇集排泄区岩溶地下水富集区 505.03 120.50 — 南部补给区 533.19 134.63 75.09 侧向径流区 389.44 81.66 21.02 黄河水 586.00 57.70 3.89 表 3 钻孔涌水量与距断裂(或接触带)距离(钻孔位置见图 1)
Table 3. Borehole water inflow and the distances from boreholes and fractured/contact zone
钻孔编号 钻孔位置 距断裂(或接触带)距离/m 含水层代号 单井涌水量/(m3·d-1) 降深/m CC6 曹楼水厂 1 500 ∈4O1sa+∈4O1sb 12 240 2.58 CX57 长孝水源地 1 460 O2b 14 432 3.41 CX15 长孝水源地 390 O2b 14 040 1.77 X51 薛庄水厂 2 500 O2b 8 928 0.95 ZG3 赵官镇葛庄西150 m 4 669 O2b+O2g 6 000 16.00 X31 马集镇齐庄社区 5 000 O2w 7 018 2.71 X27 孝里镇孝里三村 10 000 O2b 6 960 1.53 X4 双泉镇段店村 10 800 ∈3z 6 171 1.74 注:∈4O1sa+∈4O1sb.山子山a段+b段;O2b.北庵庄组;O2g.阁庄组;O2w.王阳山组;∈3z.张夏组 -
[1] STEVANOVIĈ Z. Karst waters in potable water supply: A global scale overview[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2019, 78(23): 662. doi: 10.1007/s12665-019-8670-9 [2] GOLDSCHEIDER N, CHEN Z, AULER A S, et al. Global distribution of carbonate rocks and karst water resources[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2020, 28(5): 1661-1677. doi: 10.1007/s10040-020-02139-5 [3] STEVANOVIĈ Z. Global distribution and use of water from karst aquifers[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2018, 466(1): 217-236. doi: 10.1144/SP466.17 [4] 侯新文, 邢立亭, 孙蓓蓓, 等. 济南市岩溶水系统分级及市区与东西郊的水力联系[J]. 济南大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 28(4): 300-305.HOU X W, XING L T, SUN B B, et al. Karst watersystem classification in Jinan and the hydraulic connection between downtown and east and west suburbs[J]. Journal of University of Jinan (Science and Technology), 2014, 28(4): 300-305. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] AYADI Y, MOKADEM N, BESSER H, et al. Hydrochemistry and stable isotopes (δ18O and δ2H) tools applied to the study of karst aquifers in southern Mediterranean Basin (Teboursouk area, NW Tunisia)[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2018, 137: 208-217. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2017.10.018 [6] BAUER-GOTTWEIN P, GONDWE B R N, CHARVET G, et al. Review: The Yucatán Peninsula karst aquifer, Mexico[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2011, 19(3): 507-524. doi: 10.1007/s10040-010-0699-5 [7] MINER W J, ADAMSON J K, ROCHAT P Y. Reconnaissance of the Diquini and Mariani springs and insights regarding the Massif de la Selle karst aquifer of Haiti[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2022, 30(5): 1349-1366. doi: 10.1007/s10040-022-02487-4 [8] 郭高轩, 刘文臣, 辛宝东, 等. 北京岩溶水勘查开发的现状与思考[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2011, 9(2): 33-36.GUO G X, LIU W C, XIN B D, et al. Current situations and discussions on karst groundwater resources exploration in Beijing[J]. South-to-North Water Diversion and Water Science & Technology, 2011, 9(2): 33-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] WANG J L, JIN M G, LU G P, et al. Investigation of discharge-area groundwaters for recharge source characterization on different scales: The case of Jinan in northern China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2016, 24(7): 1723-1737. doi: 10.1007/s10040-016-1428-5 [10] 梁永平, 王维泰. 中国北方岩溶水系统划分与系统特征[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(6): 860-868.LIANG Y P, WANG W T. The division and characteristics of karst water systems in northern China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2010, 31(6): 860-868. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] 梁永平, 赵春红. 中国北方岩溶水功能[J]. 中国矿业, 2018, 27(增刊2): 297-299.LIANG Y P, ZHAO C H. Karst water function in northern China[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2018, 27(S2): 297-299. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] SU H, KANG W D, XU Y J, et al. Evaluation of groundwater quality and health risks from contamination in the north edge of the Loess Plateau, Yulin City, Northwest China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2017, 76(13): 467. doi: 10.1007/s12665-017-6781-8 [13] SUN L, ZHANG Y B, SI H Y, et al. Simulation and prediction of shallow groundwater depth in the North China Plain based on regional periodic characteristics[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2021, 80(18): 635. doi: 10.1007/s12665-021-09933-8 [14] 杨会峰, 曹文庚, 支传顺, 等. 近40年来华北平原地下水位演变研究及其超采治理建议[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(4): 1142-1155.YANG H F, CAO W G, ZHI C S, et al. Evolution of groundwater level in the North China Plain in the past 40 years and suggestions on its overexploitation treatment[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(4): 1142-1155. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] ZHU H H, XING L T, MENG Q H, et al. Water recharge of Jinan karst springs, Shandong, China[J]. Water, 2020, 12(3): 694. doi: 10.3390/w12030694 [16] 康凤新, 郑婷婷, 冯亚伟, 等. 北方岩溶区降水入渗补给系数及补给机制: 以羊庄岩溶水系统为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(2): 268-282. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220477KANG F X, ZHENG T T, FENG Y W, et al. Recharge coefficients and recharge mechanisms of precipitation to groundwater in karst areas of North China: A case study of Yangzhuang karst water system[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(2): 268-282. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220477 [17] 徐军祥, 邢立亭, 佟光玉, 等. 济南泉域地下水环境演化与保护[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2004, 31(6): 69-73.XU J X, XING L T, TONG G Y, et al. Groundwater environment evolution and its conservation in Jinan spring catchment[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2004, 31(6): 69-73. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] QI S Z, HENG F X, JI L N. Landscape change of land use in the karst Region of Jinan City, North China[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering and Landscape Management, 2023, 31(1): 1-8. doi: 10.3846/jeelm.2023.18063 [19] 汪家权, 吴义锋, 钱家忠, 等. 济南泉域保泉与供水的地下水开采方案研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2004, 23(6): 1228-1231.WANG J Q, WU Y F, QIAN J Z, et al. Scheme of groundwater exploited to keep springs spurting and water supply in Jinan springs zone[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2004, 23(6): 1228-1231. (in Chinese with English abstract) [20] ZHANG N, SHEN J S, ZHOU A N, et al. Tunneling induced geohazards in mylonitic rock faults with rich groundwater: A case study in Guangzhou[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2018, 74: 262-272. [21] 刘春燕, 于开宁, 张英, 等. 西宁市浅层地下水化学特征及形成机制[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(6): 3228-3236.LIU C Y, YU K N, ZHANG Y, et al. Characteristics and driving mechanisms of shallow groundwater chemistry in Xining City[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(6): 3228-3236. (in Chinese with English abstract) [22] 於昊天, 马腾, 邓娅敏, 等. 江汉平原东部地区浅层地下水水化学特征[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(5): 685-692.YU H T, MA T, DENG Y M, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater in eastern Jianghan Plain[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(5): 685-692. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] TANG C L, ZHENG X Q, LIANG Y P. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation causes of ground karst water systems in the Longzici spring catchment[J]. Huan Jing Ke Xue, 2020, 41(5): 2087-2095. [24] 付舒, 毛龙富, 刘宏, 等. 阿子营黄龙泉域地下水化学特征及演化[J]. 地球与环境, 2023, 51(2): 153-163.FU S, MAO L F, LIU H, et al. Chemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in Huanglong spring catchment of Aziying[J]. Earth and Environment, 2023, 51(2): 153-163. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25] SÁNCHEZ D, BARBERÁ J A, MUDARRA M, et al. Hydrogeochemical tools applied to the study of carbonate aquifers: Examples from some karst systems of southern Spain[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 74(1): 199-215. [26] LIU J, WANG H, JIN D W, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution processes of karst groundwater in Carboniferous Taiyuan Formation in the Pingdingshan Coalfield[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2020, 79(6): 151. [27] ZHANG Y, SU C L, MA Y H, et al. Indicators of groundwater evolution processes based on hydrochemistry and environmental isotopes: A case study of the Dongyuan drinking water source area in Jinan City[J]. Huan Jing Ke Xue, 2019, 40(6): 2667-2674. [28] 贾超, 王丛, 刘森, 等. 济南西部冲积平原地下水水文地球化学特征研究[J]. 水利水电技术(中英文), 2022, 53(3): 49-60.JIA C, WANG C, LIU S, et al. Study on hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater in the alluvial plain of western Jinan[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2022, 53(3): 49-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) [29] 王珺瑜, 王家乐, 靳孟贵. 济南泉域岩溶水水化学特征及其成因[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(5): 821-831.WANG J Y, WANG J L, JIN M G. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation causes of karst water in Jinan spring catchment[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(5): 821-831. (in Chinese with English abstract) [30] 殷秀兰, 王庆兵, 凤蔚. 济南岩溶泉域泉群区水化学与环境同位素研究[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 91(7): 1651-1660.YIN X L, WANG Q B, FENG W. Hydro-chemical and isotopic study of the karst spring catchment in Jinan[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2017, 91(7): 1651-1660. (in Chinese with English abstract) [31] 高宗军, 徐军祥, 王世臣, 等. 济南岩溶水微量元素分布特征及其水文地质意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(4): 135-146.GAO Z J, XU J X, WANG S C, et al. The distribution characteristics and hydrogeological significance of trace elements in karst water, Jinan, China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2014, 21(4): 135-146. (in Chinese with English abstract) [32] 高帅, 李常锁, 贾超, 等. 济南趵突泉泉域岩溶水化学特征时空差异性研究[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(增刊1): 61-70.GAO S, LI C S, JIA C, et al. Spatiotemporal difference study of karst hydrochemical characteristics in the Baotu spring area of Jinan[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(S1): 61-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) [33] 李常锁, 武显仓, 孙斌, 等. 济南北部地热水水化学特征及其形成机理[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(增刊1): 313-325.LI C S, WU X C, SUN B, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of geothermal water in northern Jinan[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(S1): 313-325. (in Chinese with English abstract) [34] 徐军祥. 济南泉水及其保护[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2020.XU J X. Jinan spring water and its protection[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2020. (in Chinese) [35] 雷璐宁, 石为人, 范敏. 基于改进的SOM神经网络在水质评价分析中的应用[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2009, 30(11): 2379-2383.LEI L N, SHI W R, FAN M. Water quality evaluation analysis based on improved SOM neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2009, 30(11): 2379-2383. (in Chinese with English abstract) [36] QIAO X J, LI G M, LI M, et al. Influence of coal mining on regional karst groundwater system: A case study in West Mountain area of Taiyuan City, northern China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2011, 64(6): 1525-1535. [37] 高旭波, 向绚丽, 侯保俊, 等. 水化学-稳定同位素技术在岩溶水文地质研究中的应用[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(5): 629-636.GAO X B, XIANG X L, HOU B J, et al. Application of hydrochemistry coupled with stable isotopes in the study of karst water hydrogeology[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(5): 629-636. (in Chinese with English abstract) [38] 周长松, 邹胜章, 冯启言, 等. 岩溶关键带水文地球化学研究进展[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(3): 37-50.ZHOU C S, ZOU S Z, FENG Q Y, et al. Progress in hydrogeochemical study of karst critical zone: A critical review[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2022, 29(3): 37-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) [39] 施龙青, 史雅迪, 邱梅, 等. 基于Piper图、灰色关联度和三维高密度电法的断层水源判别[J]. 中国科技论文, 2022, 17(1): 1-8.SHI L Q, SHI Y D, QIU M, et al. Identification of fault water source based on Piper diagram, grey correlation degree and 3D high density electric method[J]. China Sciencepaper, 2022, 17(1): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) [40] GIBBS R J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry[J]. Science, 1970, 170(3962): 1088-1090. [41] FETH J H, GIBBS R J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry: Evaporation-crystallization process[J]. Science, 1971, 172(3985): 870-872. [42] HOOPER R P, CHRISTOPHERSEN N, PETERS N E. Modelling streamwater chemistry as a mixture of soilwater end-members: An application to the Panola Mountain catchment, Georgia, U.S.A. [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1990, 116(1/4): 321-343. [43] 邢立亭, 周娟, 宋广增, 等. 济南四大泉群泉水补给来源混合比探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(3): 260-272.XING L T, ZHOU J, SONG G Z, et al. Mixing ratios of recharging water sources for the four largest spring groups in Jinan[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2018, 25(3): 260-272. (in Chinese with English abstract) [44] 王宇, 王梓溦. 岩溶地下水富集的地貌组合形态[J]. 中国岩溶, 2015, 34(4): 314-324.WANG Y, WANG Z W. Patterns of karst geomorphologic combinations in areas with rich groundwater[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2015, 34(4): 314-324. (in Chinese with English abstract) [45] 周宁, 刘波. 鄂西南岩溶地区表层岩溶带发育强度变化规律研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2009, 28(1): 1-6.ZHOU N, LIU B. Varying regulation of epikarst developing intensity in Southwest Hubei karst area[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2009, 28(1): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) [46] 胡海涛, 许贵森. 论构造体系与地下水网络[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1980(3): 1-7.HU H T, XU G S. On tectonic system and groundwater network[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 1980(3): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) [47] 李峰峰, 叶禹, 余义常, 等. 碳酸盐岩成岩作用研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 170-190. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0209LI F F, YE Y, YU Y C, et al. Research progress of carbonate rock diagenesis[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 170-190. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0209 [48] VERESS M. Karst types and their karstification[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2020, 31(3): 621-634. [49] 党学亚, 张茂省, 喻胜虎. 陕西渭北东部寒武纪-奥陶纪岩相古地理与岩溶水赋存关系[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(11): 1103-1108.DANG X Y, ZHANG M S, YU S H. Relations between Cambrian-Ordovician lithofacies-paleogeography and occurrence of karst groundwater in eastern Weibei, Shaanxi Province[J]. Regional Geology of China, 2004, 23(11): 1103-1108. (in Chinese with English abstract) -





 下载:
下载: