Deformation history analysis and movement process simulation of glacier debris flow in Sanggu Valley in southern Tibet
-
摘要:
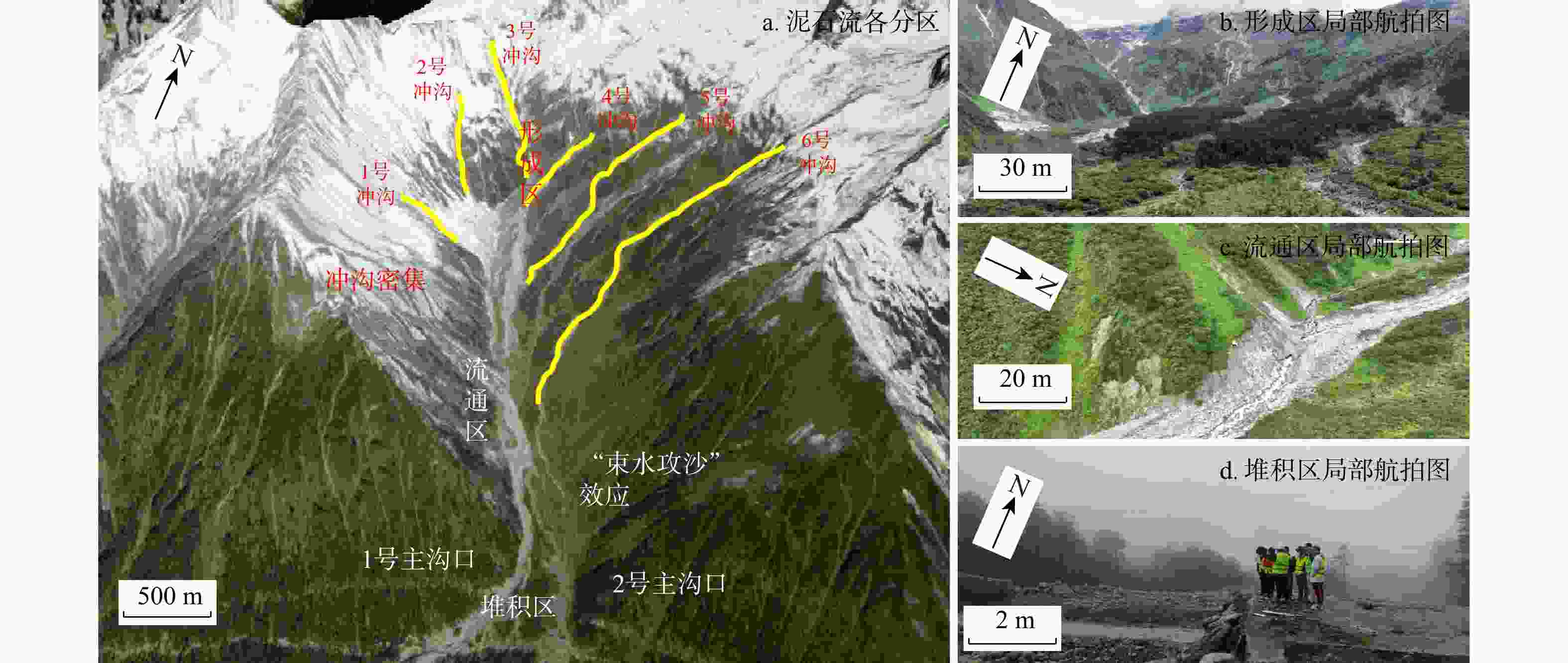
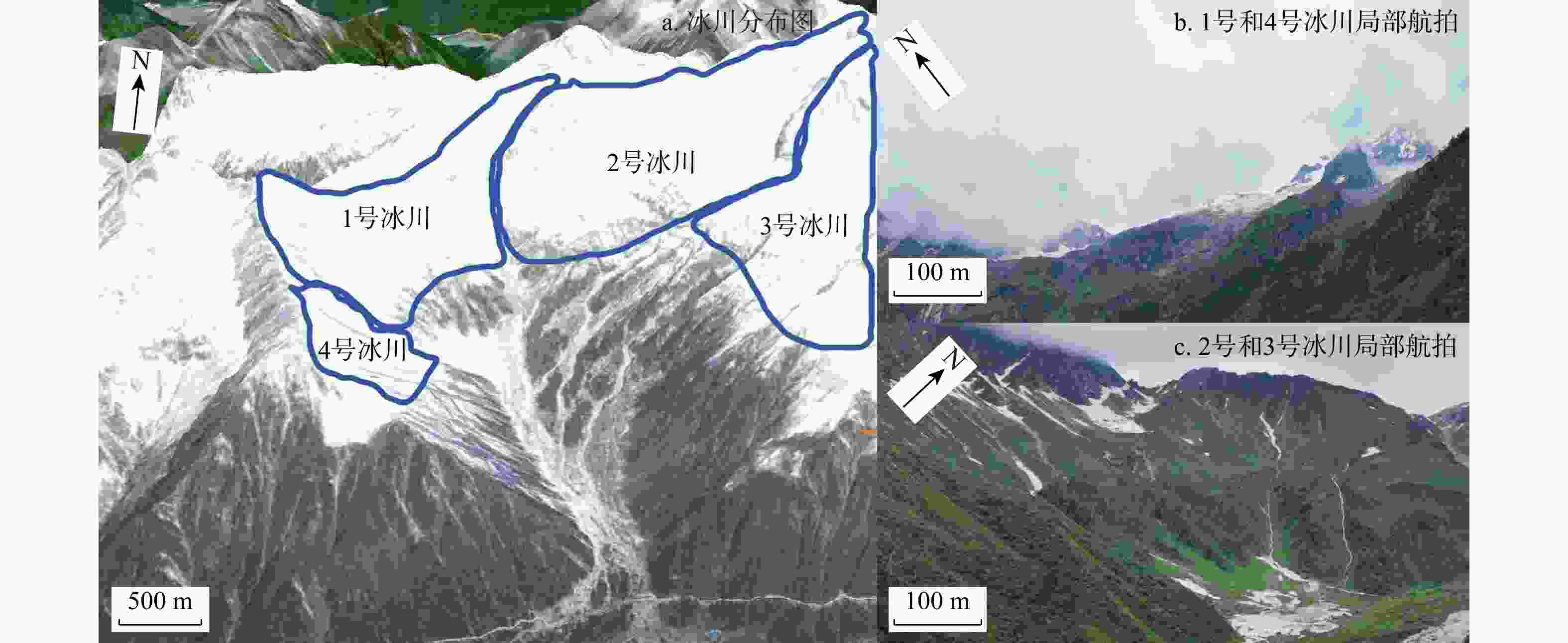
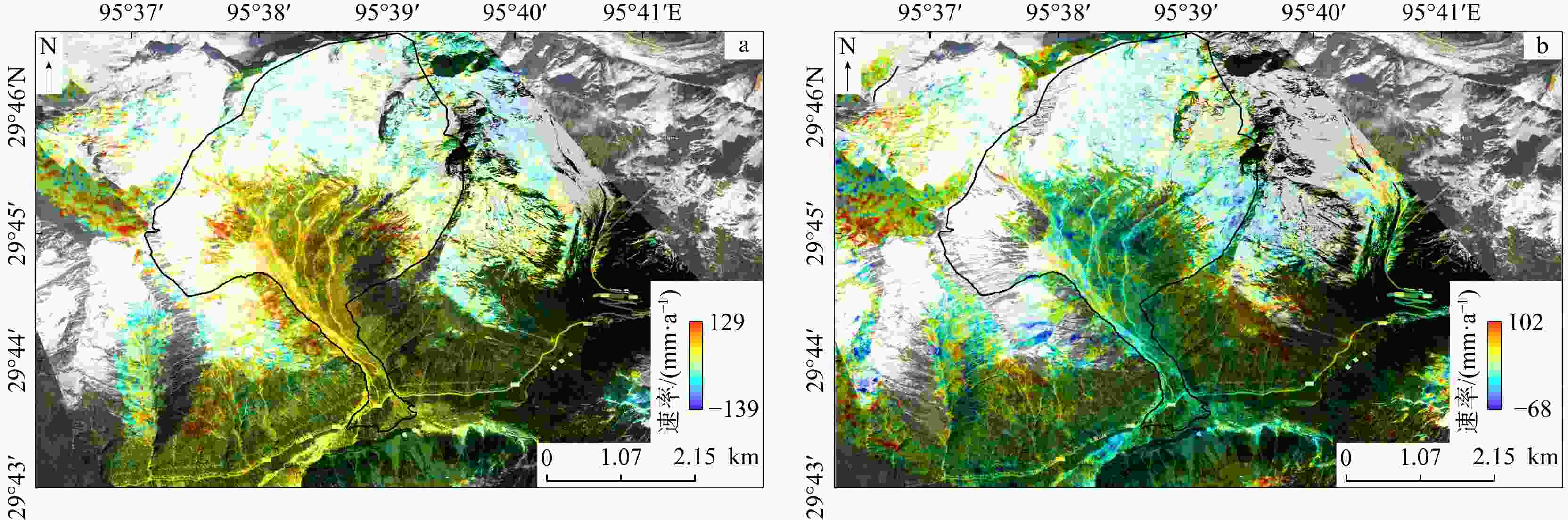
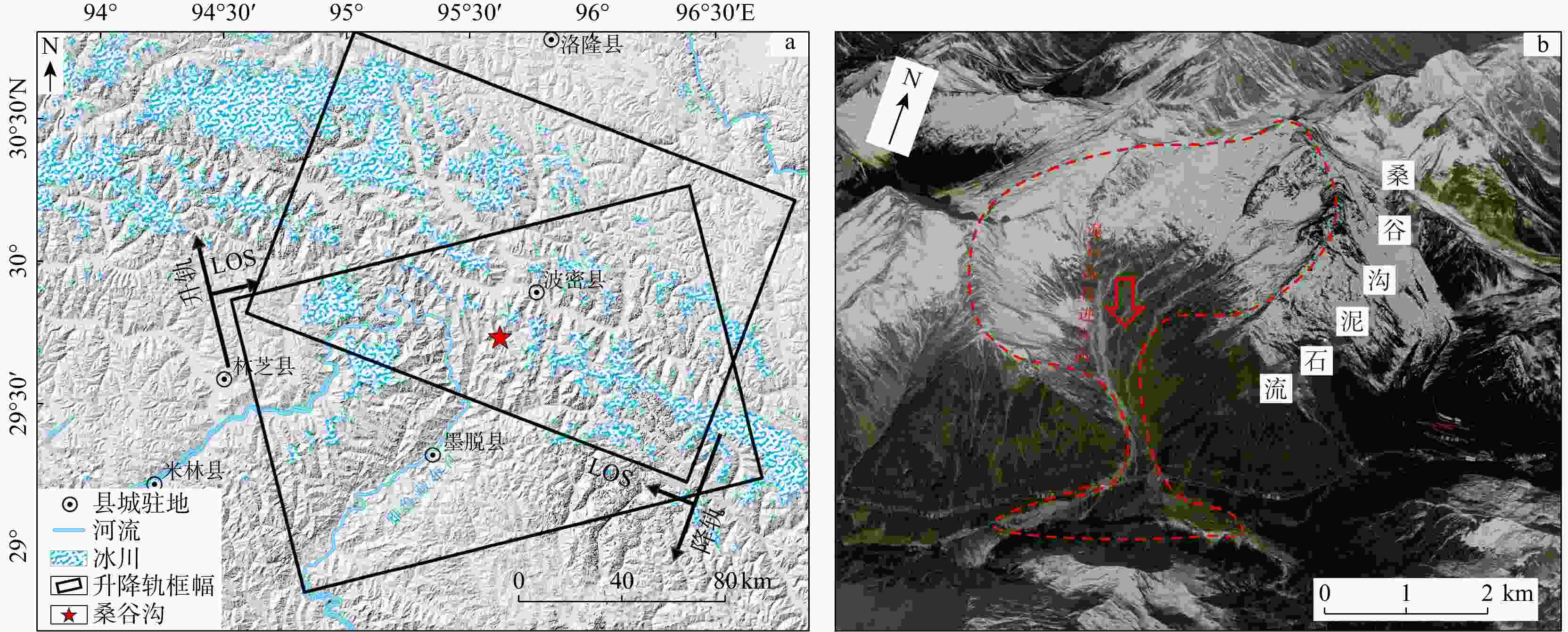
藏东南雅鲁藏布江流域冰川型泥石流规模大、持续时间长、冲击力强,由于传统方法难以定量描述大尺度泥石流形成机理问题,根据桑谷沟流域泥石流现场实地调研、无人机航拍、卫星影像信息以及地质气象数据,揭示桑谷沟泥石流的暴发与物源、降雨量等因素之间关系,提出了一种联合InSAR与RAMMS技术全面分析泥石流爆发前物源形变过程与爆发期间泥石流运动特征的方法。基于SBAS-InSAR技术,针对桑谷沟泥石流2次爆发期间的形变进行分析,结合卫星影像图、无人机影像以及现场勘察,实现了桑谷沟泥石流灾害爆发前形变过程反演和灾变趋势预测;采用RAMMS泥石流数值模拟软件对桑谷沟泥石流爆发期间运动过程进行了模拟。研究表明:①通过InSAR技术解算桑谷沟泥石流LOS向形变,坡体长期处于蠕滑状态;物源区内最大形变速率为139 mm/a,流通区内速率最大为46 mm/a,堆积区速率最大为20 mm/a;降雨作用为泥石流发育提供了大量的松散来源。②根据不同步时状态下泥石流堆积深度和流速状态,将研究区演进过程划分为初始运动、加速运动、减速−最终3个阶段。该方法联合冰川泥石流形变历史分析和运动过程模拟,对泥石流发展趋势及预测提供科学依据,并为工程防治设计提供参考。
Abstract:Glacial debris flows in the Yarlung Zangbo River basin of southeastern Tibet are characterized by their large scale, prolonged duration, and significant societal and environmental impacts. Investigating the deformation characteristics and influencing factors of Sanggu Valley debris flow offers critical scientific insights for predicting, early warning, and mitigating glacial debris flow disasters in this region. Traditional methods often fall short in quantitatively describing the formation mechanisms of large-scale debris flows. To address this limitation, this study integrates field investigations, unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) aerial photography, satellite imagery, and geological and meteorological data.
Objective This study aims to elucidate the relationship between debris flow outbreaks in Sanggu Valley and key influencing factors, including material sources and rainfall patterns.
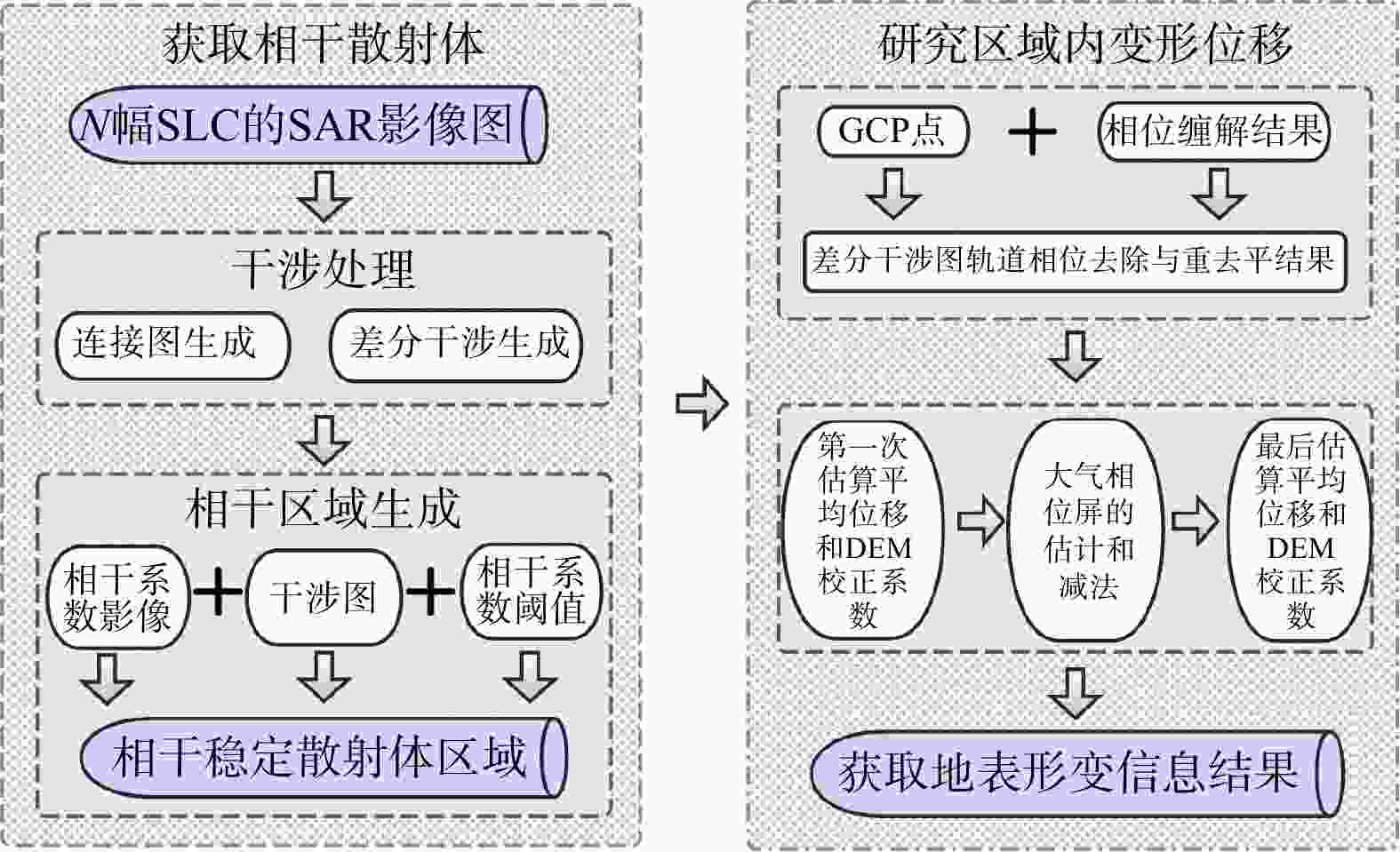
Methods A novel method combining interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) and random-access mass spectrometry (RAMMS) techniques is developed to analyze the deformation process of debris flows before and during their initiation. SBAS-InSAR technology is employed to quantify the deformation of Sanggu Valley debris flow during two outbreaks, complemented by satellite images, UAV images, and field investigations. This approach enables the inversion of deformation processes and the prediction of disaster trends prior to the Sanggu Valley debris flow event. Additionally, RAMMS debris flow numerical simulation software is utilized to model the movement dynamics of the Sanggu Valley debris flow during its eruption.
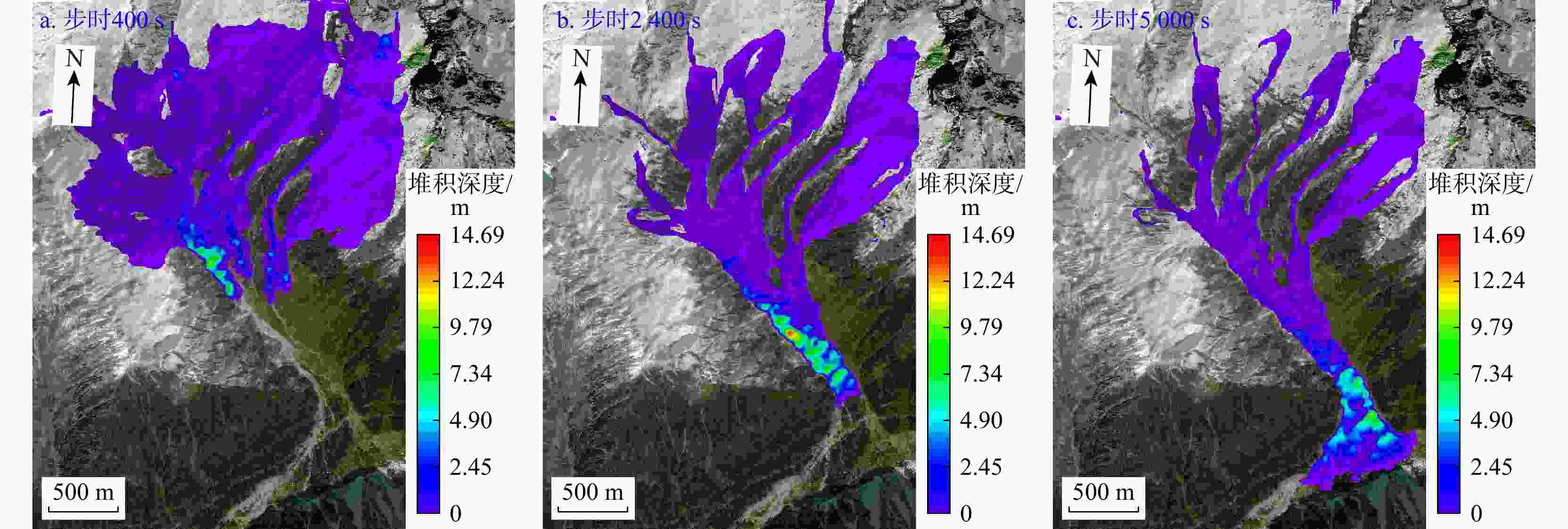
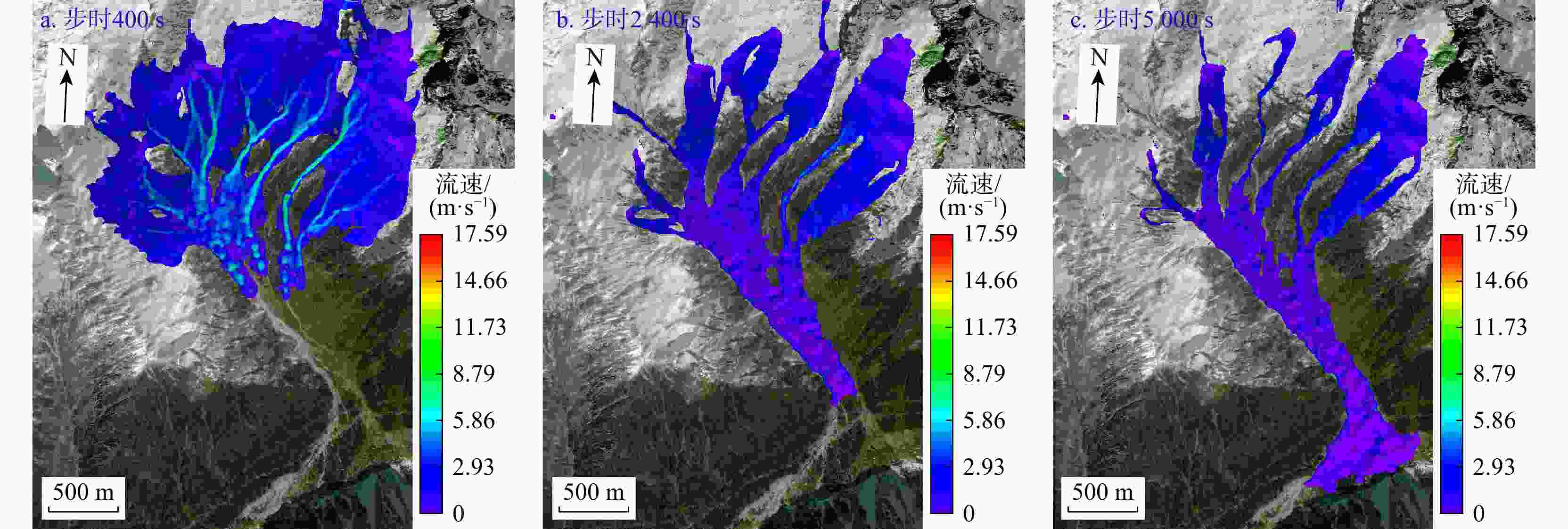
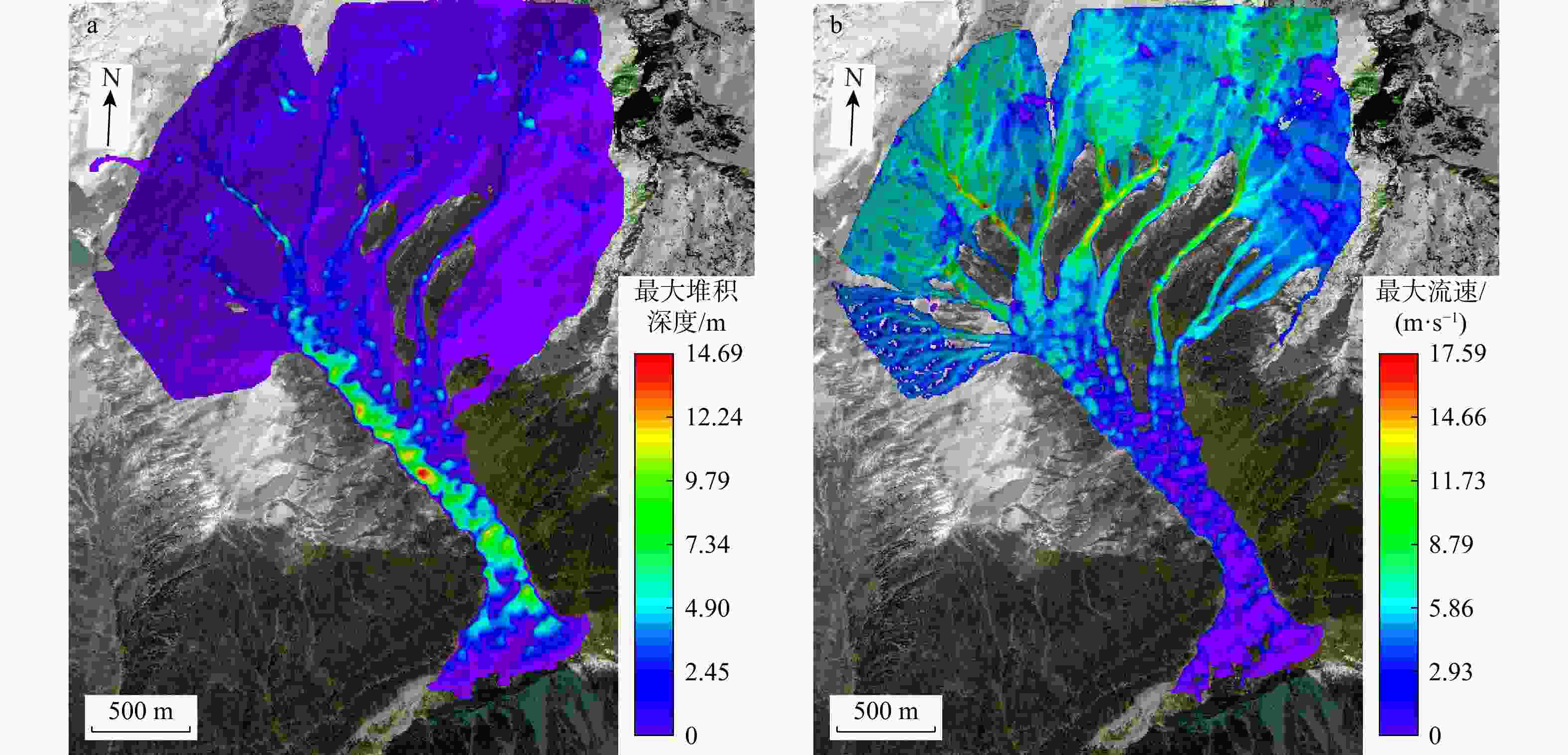
Results This study yields the following key findings: ① InSAR-derived LOS deformation analysis of the Sanggu Valley debris flow reveals the prolonged slope creep, with maximum deformation rates of 139 mm/a in the source area, 46 mm/a in the flow area, and 20 mm/a in the accumulation area. Rainfall is identified as a critical factor in supplying loose materials for debris flow development. ②The evolution process of the debris flow is categorized into three stages: initial motion, accelerated motion, and deceleration.
Conclusion The proposed methodology, which integrates historical deformation analysis and numerical simulation of glacial debris flow dynamics, provides a scientific foundation for predicting debris flow development trends and designing effective engineering control measures.
-
Key words:
- glacier debris flow /
- SBAS-InSAR /
- RAMMS /
- drone aerial photography /
- causes of debris flow /
- Sanggu Valley /
- southern Tibet
-
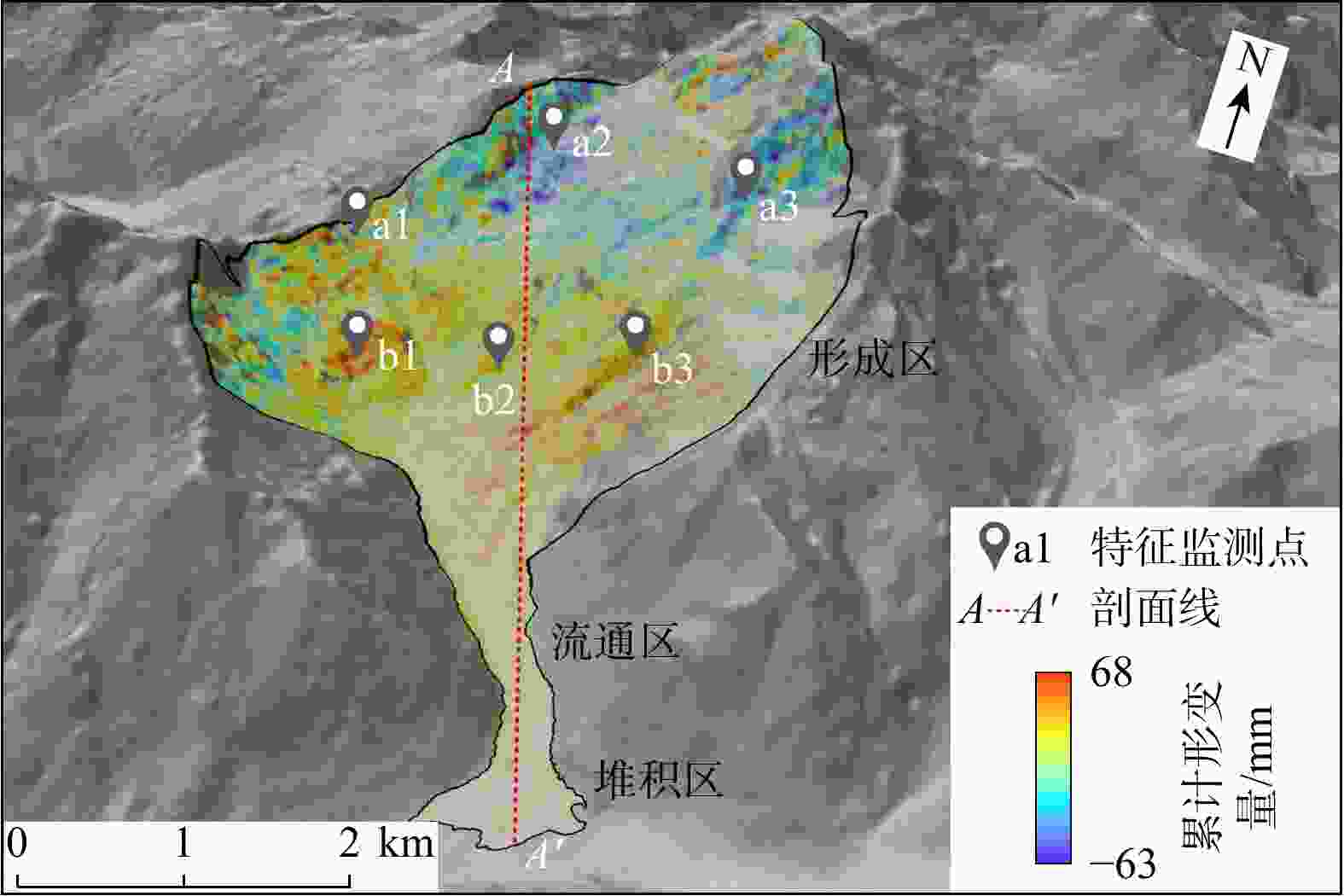
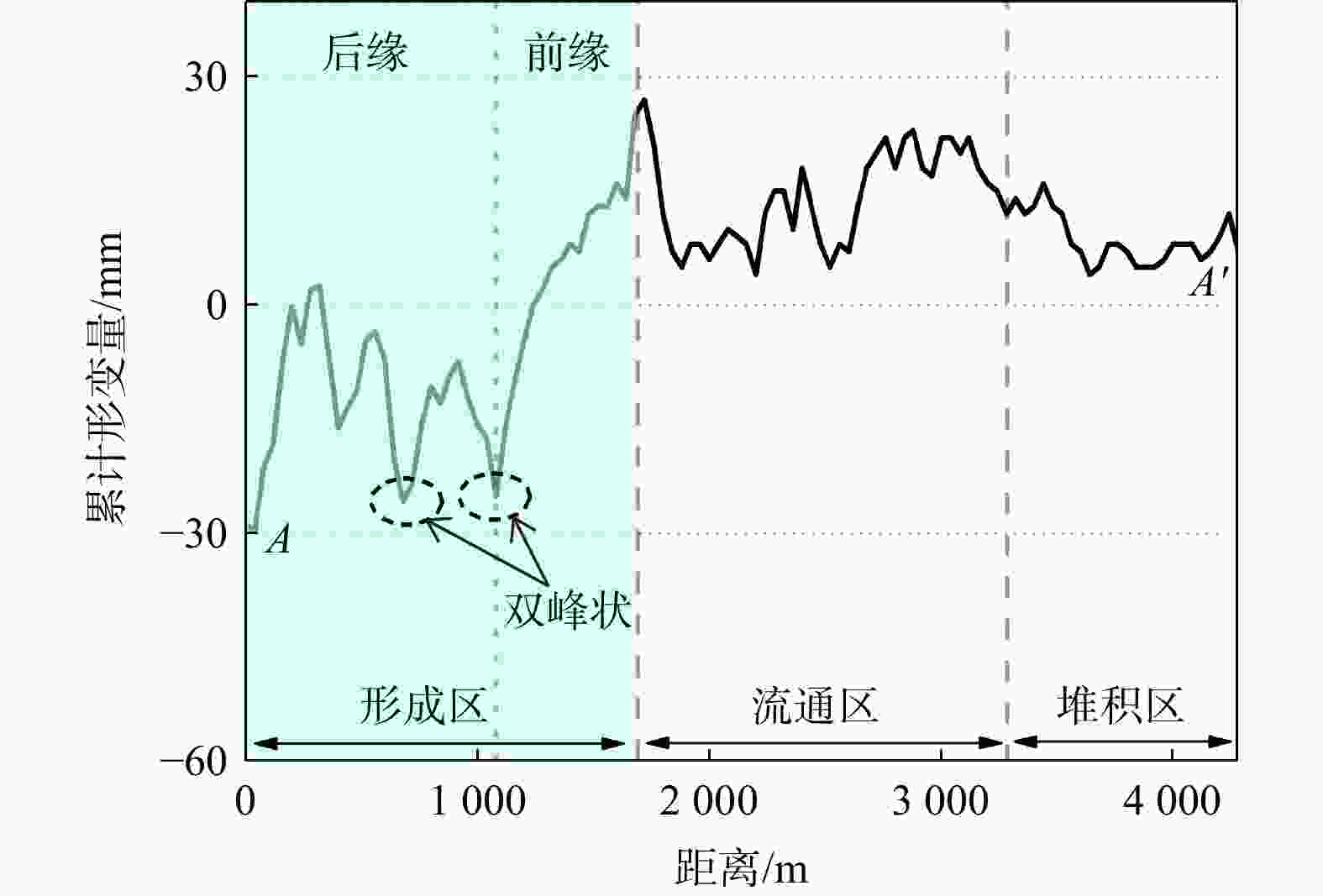
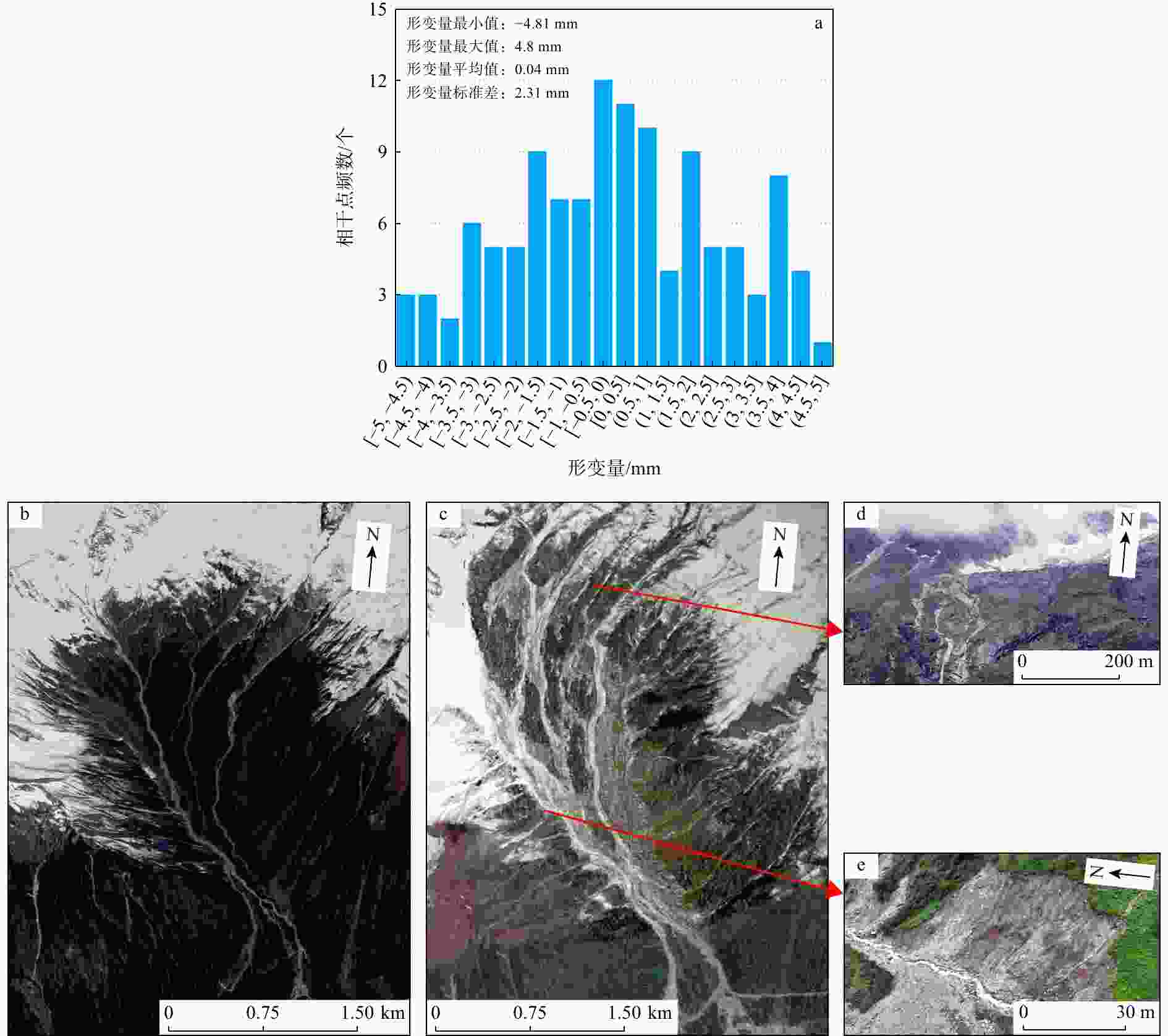
图 8 2020/10−2021/06坡体累计形变剖面(剖面A−A'位置见图7)
Figure 8. Slope cumulative deformation profile from October 2020 to June 2021
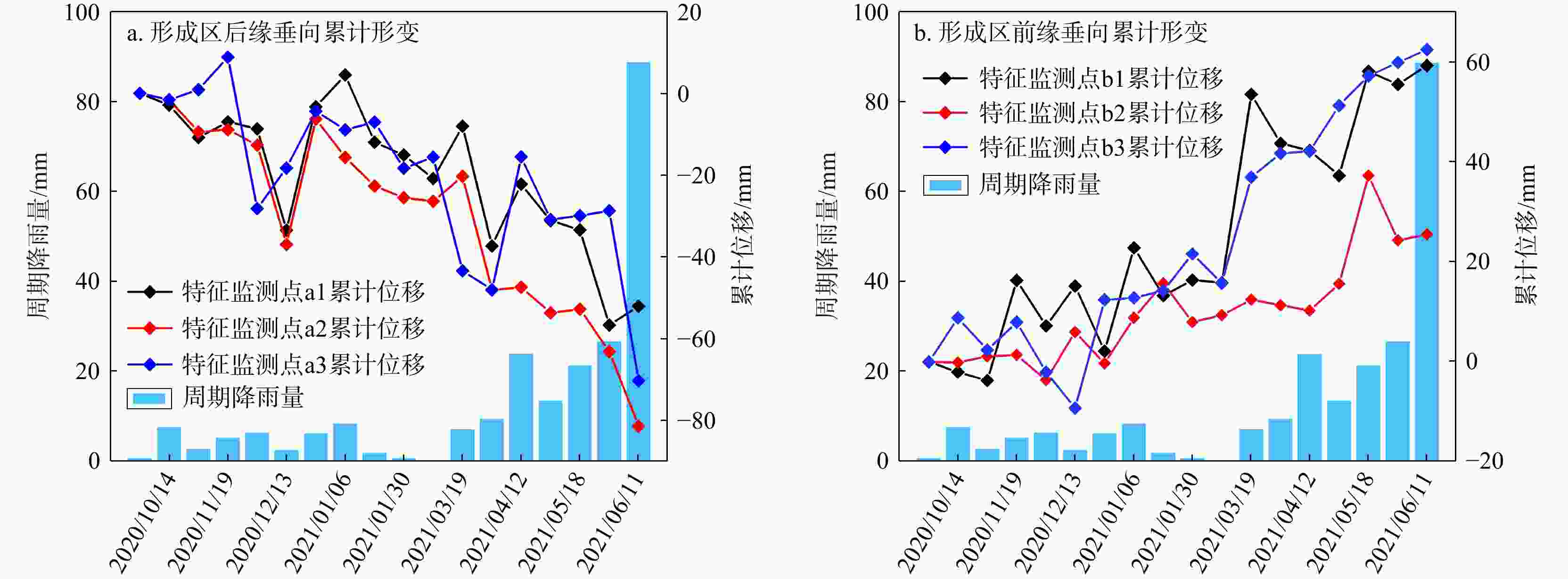
图 9 泥石流形成区时序形变与降雨数据相关性对比(降雨量数据来源于美国国家海洋和大气管理局,源格式为csv;特征监测点位置见图7)
Figure 9. Formation zone time-series deformation of debris flow in relation rainfall data
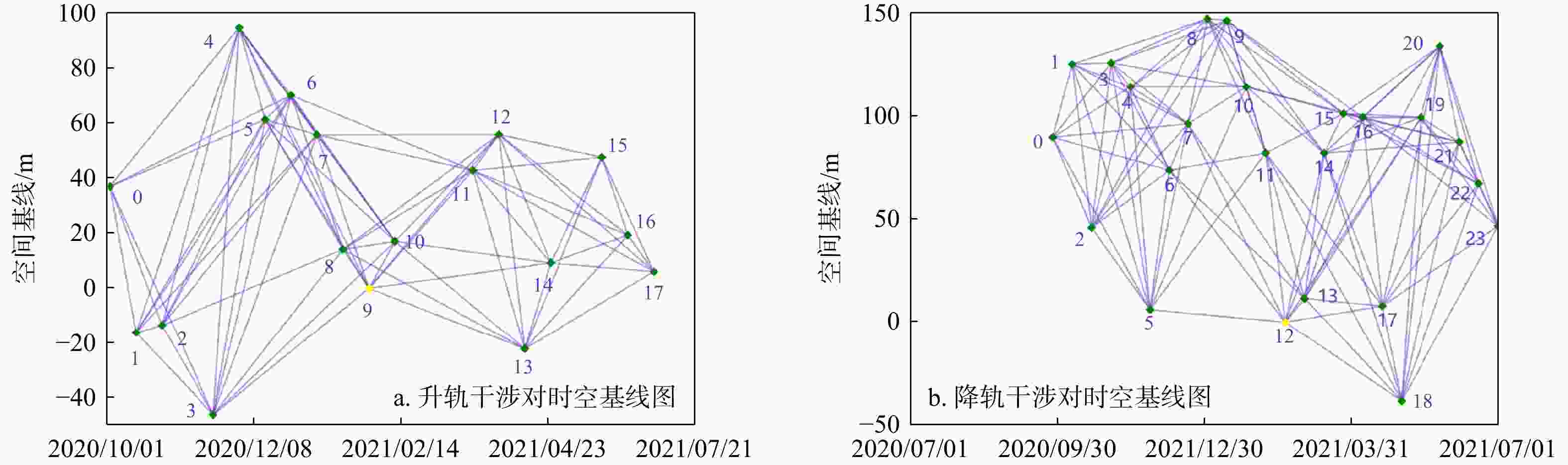
表 1 Sentinel-1A升降轨SAR影像参数
Table 1. Sentinel-1A ascending and descending orbit SAR image parameters
参数类别 SAR传感器Sentinel-1A 轨道方向 升轨 降轨 空间分辨率/m 5×20 5×20 重访周期/d 12 12 入射角/(°) 40.92 37.03 飞行角/(°) 347.30 192.70 影像数量/个 18 24 监测时间 2020-10-02−2021-06-11 2020-09-27−2021-06-30 -
[1] 徐雨晴,何吉成. 1951−1996年中国铁路泥石流灾害的时空特征[J]. 水土保持通报,2016,36(1):337-342.XU Y Q,HE J C. Spatial and temporal characteristics of debris flow of China railways in 1951-1996[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2016,36(1):337-342. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 黄润秋. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2007,26(3):433-454.HUANG R Q. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in China since the 20th Century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2007,26(3):433-454. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 龙飞,龚诚,黄海,等. 藏东南直白沟冰崩型泥石流孕灾条件与动力特征[J]. 水土保持通报,2022,42(6):31-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-288X.2022.6.stbctb202206004LONG F,GONG C,HUANG H,et al. Formation conditions and dynamic characteristics of debris flow triggered by an ice avalanche at Zhibai gully in Southeast Tibet[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2022,42(6):31-38. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-288X.2022.6.stbctb202206004 [4] 侯伟鹏,余国安,岳蓬胜. 典型高山峡谷泥石流堆积扇发育过程及特征:以藏东南帕隆藏布流域天摩沟为例[J]. 山地学报,2023,41(4):532-544.HOU W P,YU G A,YUE P S. Development and geomorphic characteristics of a typical debris flow fan in alpine valley:A case study of the Tianmo gully in the Parlung Tsangpo basin,Southeast Tibet,China[J]. Mountain Research,2023,41(4):532-544. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] ARMIJO R,TAPPONNIER P,MERCIER J L,et al. Quaternary extension in southern Tibet:Field observations and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (Solid Earth),1986,91(B14):13803-13872. doi: 10.1029/JB091iB14p13803 [6] REN L Y,DUAN K Q,XIN R. Impact of future loss of glaciers on precipitation pattern:A case study from south-eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Atmospheric Research,2020,242:104984. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2020.104984 [7] STOCK J,DIETRICH W E. Valley incision by debris flows:Evidence of a topographic signature[J]. Water Resources Research,2003,39(4):2001WR001057. doi: 10.1029/2001WR001057 [8] 李尧,崔一飞,李振洪,等. 川藏交通廊道林波段冰川泥石流发育动态演化分析及监测预警方案[J]. 地球科学,2022,47(6):1969-1984. doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2022.6.dqkx202206006LI Y,CUI Y F,LI Z H,et al. Evolution of glacier debris flow and its monitoring system along Sichuan-Tibet traffic corridor[J]. Earth Science,2022,47(6):1969-1984. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2022.6.dqkx202206006 [9] 翟毅飞. 藏东南地区冰川泥石流分布规律与规模频率特征研究[D]. 拉萨:西藏大学,2022.ZHAI Y F. The distribution and scale and outbreak frequency characteristics of glacial debris flow in Southeast Tibet[D]. Lhasa:Tibet University,2022. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 张菊. 冰川泥石流易发性评价方法及应用研究[D]. 四川绵阳:西南科技大学,2021.ZHANG J. Research on evaluation method and application of the susceptibility of glacial debris flow[D]. Mianyang Sichuan:Southwest University of Science and Technology,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] DE HAAS T,NIJLAND W,DE JONG S M,et al. How memory effects,check dams,and channel geometry control erosion and deposition by debris flows[J]. Scientific Reports,2020,10(1):14024. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71016-8 [12] 崔鹏,陈容,向灵芝,等. 气候变暖背景下青藏高原山地灾害及其风险分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展,2014,10(2):103-109.CUI P,CHEN R,XIANG L Z,et al. Risk analysis of mountain hazards in Tibetan Plateau under global warming[J]. Progressus Inquisitiones DE Mutatione Climatis,2014,10(2):103-109. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 杨俊,徐智,兰立军,等. 黄土高原典型小流域降水变化特征研究[J]. 中国水土保持,2022(8):25-28.YANG J,XU Z,LAN L J,et al. The characteristics of precipitation change in the typical small watershed of Loess Plateau[J]. Soil and Water Conservation in China,2022(8):25-28. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] LIU S,HU K H,ZHANG S J,et al. Comprehensive evaluation of satellite-based precipitation at sub-daily time scales over a high-profile watershed with complex terrain[J]. Earth and Space Science,2019,6(12):2347-2361. doi: 10.1029/2019EA000855 [15] 詹聪聪. 古乡沟泥石流特征及预警分析研究[D]. 拉萨:西藏大学,2022.ZHAN Z Z. Study on the characteristics and early warning analysis of the Guxiangou mudslide[D]. Lhasa:Tibet University,2022(in Chinese with English abstract [16] 张宇欣,李育,朱耿睿. 青藏高原海拔要素对温度、降水和气候型分布格局的影响[J]. 冰川冻土,2019,41(3):505-515.ZHANG Y X,LI Y,ZHU G R. The effects of altitude on temperature,precipitation and climatic zone in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2019,41(3):505-515. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] CHEN Y,DONG J L,GUO F,et al. Review of landslide susceptibility assessment based on knowledge mapping[J]. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment,2022,36(9):2399-2417. doi: 10.1007/s00477-021-02165-z [18] 杨春宇,文艺,潘星,等. 基于SBAS-InSAR的山体滑坡形变监测分析[J]. 测绘通报,2023(11):12-17.YANG C Y,WEN Y,PAN X,et al. Monitoring and analysis of landslide deformation based on SBAS-InSAR[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping,2023(11):12-17. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 葛大庆,戴可人,郭兆成,等. 重大地质灾害隐患早期识别中综合遥感应用的思考与建议[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):949-956.GE D Q,DAI K R,GUO Z C,et al. Early identification of serious geological hazards with integrated remote sensing technologies:Thoughts and recommendations[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):949-956. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 弓永峰,王辉,吴学华,等. 基于时序InSAR的宁夏西吉县滑坡灾害隐患识别[J]. 安全与环境工程,2022,29(6):114-121.GONG Y F,WANG H,WU X H,et al. Identification of potential landslide hazards using time-series InSAR in Xiji County of Ningxia[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2022,29(6):114-121. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 张晓东. 基于遥感和GIS的宁夏盐池县地质灾害风险评价研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2018.ZHANG X D. Study on geological disaster risk assessment based on RS and GIS in Yanchi County,Ningxia[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences(Beijing),2018. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 耿丹,涂宽,谌华,等. SBAS-InSAR和高分辨率光学遥感相结合的矿区地表形变时空演化特征研究[J]. 自然灾害学报,2022,31(1):251-264.GENG D,TU K,SHEN H,et al. Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of surface deformation in mining area based on SBAS-InSAR and high resolution optical remote sensing[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2022,31(1):251-264. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 武德宏,郝利娜,严丽华,等. 金沙江滑坡群InSAR探测与形变因素分析[J]. 自然资源遥感,2024,36(3):259-266.WU D H,HAO L N,YAN L H,et al. InSAR-based detection and deformation factor analysis of landslide clusters in the Jinsha River[J]. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources,2024,36(3):259-266. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 李晓恩,周亮,苏奋振,等. InSAR技术在滑坡灾害中的应用研究进展[J]. 遥感学报,2021,25(2):614-629. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20209297LI X E,ZHOU L,SU F Z,et al. Application of InSAR technology in landslide hazard:Progress and prospects[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin,2021,25(2):614-629. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11834/jrs.20209297 [25] 李振洪,宋闯,余琛,等. 卫星雷达遥感在滑坡灾害探测和监测中的应用:挑战与对策[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):967-979.LI Z H,SONG C,YU C,et al. Application of satellite radar remote sensing to landslide detection and monitoring:Challenges and solutions[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):967-979. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 张璇钰,刘桂卫,孙琪皓,等. 综合遥感技术在山区铁路泥石流勘察中的应用[J]. 铁道勘察,2024,50(1):16-22.ZHANG X Y,LIU G W,SUN Q H,et al. Application of comprehensive remote sensing technology in mountain railway debris flow survey[J]. Railway Investigation and Surveying,2024,50(1):16-22. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 刘桂卫,李国和,陈则连,等. 多源遥感技术在艰险山区铁路地质勘察中应用[J]. 铁道工程学报,2019,36(8):4-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2019.08.002LIU G W,LI G H,CHEN Z L,et al. Application of remote sensing technology for geological investigation in mountain railways[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society,2019,36(8):4-8. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2019.08.002 [28] 石固林,徐浪,张璇钰,等. 西山村滑坡时序形变的SBAS-InSAR监测[J]. 测绘科学,2021,46(2):93-98.SHI G L,XU L,ZHANG X Y,et al. Monitoring time series deformation of Xishancun landslide with SBAS-InSAR[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping,2021,46(2):93-98. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 樊贵盛,贾宏骥,李海燕. 影响冻融土壤水分入渗特性主要因素的试验研究[J]. 农业工程学报,1999,15(4):88-94. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.1999.04.018FAN G S,JIA H J,LI H Y. Experimental study on main factors influencing water infiltration features of freezing and thawing soils[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,1999,15(4):88-94. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.1999.04.018 [30] 陈庭轩,李素敏,袁利伟. InSAR在云南德钦县一中河泥石流物源汇集及失稳模式中的探究[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,2022,42(2):158-164.CHEN T X,LI S M,YUAN L W. InSAR study on substance source collection and instability mode of Yizhong River debris flow in Deqin,Yunnan Province[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,2022,42(2):158-164. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] ZEITLER P K,MELTZER A S,BROWN L,et al. Tectonics and topographic evolution of Namche Barwa and the easternmost Lhasa Block,Tibet[M]. New York,USA:Geological Society of America,2014. [32] 杨宗佶,付校龙,游勇. 气候变化条件下降雨−融水型泥石流流量预测方法[J]. 人民长江,2021,52(12):34-39.YANG Z J,FU X L,YOU Y. Discharge prediction method for rainfall-melting water triggered glacial debris flows under climate change scenarios[J]. Yangtze River,2021,52(12):34-39. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 屈永平,肖进,潘义为. 藏东南地区冰川泥石流形成条件初步分析:以天摩沟冰川泥石流为例[J]. 水利水电技术,2018,49(12):177-184.QU Y P,XIAO J,PAN Y W. Preliminary analysis on formation conditions of glacier debris flow in Southeast Tibet:A case of glacial debris flow in Tianmo gully[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,2018,49(12):177-184. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] FERRETTI A,PRATI C,ROCCA F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2000,38(5):2202-2212. doi: 10.1109/36.868878 [35] BERARDINO P,FORNARO G,LANARI R,et al. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2002,40(11):2375-2383. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.803792 [36] 杨沛璋,崔圣华,裴向军,等. 基于SBAS-InSAR和光学遥感影像的大型倾倒变形体变形演化[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(6):63-75.YANG P Z,CUI S H,PEI X J,et al. Deformation and evolution of large dumping bodies based on SBAS-InSAR and optical remote sensing images[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(6):63-75. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] 李凡,李素敏,杨渊,等. 基于时序InSAR的沙湾大沟滑坡型泥石流发育特征研究[J]. 地球物理学进展,2023,38(2):532-541.LI F,LI S M,YANG Y,et al. Research on the development characteristics of landslide-type debris flow in Shawandagou based on MT-InSAR[J]. Progress in Geophysics,2023,38(2):532-541. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] 中华人民共和国国土资源部. 泥石流灾害防治工程勘查规范:DZ/T0220-2006[S]. 北京:地质出版社,2006.Ministry of Land and Resources,People's Republic of China. Specification of geological investigation for debris flow stabilization:DZ/T0220-2006[S]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House,2006. (in Chinese) [39] 陈兰,范宣梅,熊俊麟,等. 藏东南多依弄巴流域冰湖溃决危险性评价[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(2):258-266.CHEN L,FAN X M,XIONG J L,et al. Hazard assessment of glacial lake outbursts in the Doyinongba basin,southeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(2):258-266. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 庞海松,谢骏锦,张小明,等. 基于RAMMS数值模拟的短时强降雨型泥石流危险性评价[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(2):215-225.PANG H S,XIE J J,ZHANG X M,et al. Hazard assessment of debris flow induced by short-time heavy rainfall based on RAMMS numerical simulation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(2):215-225. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: