Bayesian methods for geostatistical variogram model selection and comparative study
-
摘要:
变异函数量化了空间2点地质属性的变异性,对地质统计分析至关重要。当地质数据随空间坐标呈现趋势变化时,正确选择和估计变异函数十分困难。为实现变异函数的模型选择和参数估计,提出了基于贝叶斯理论的变异函数选择方法,采用拉普拉斯近似方法将后验概率分布近似为高斯分布。首先计算出参数的后验概率分布,随后分别计算每个备选变异函数的贝叶斯模型证据,以确定最优模型。探讨了2种模型选择方法在变异函数选择中的适用性,包括贝叶斯模型证据(BME)、Akaike information criterion(AIC)识别准则和Bayesian information criterion(BIC)识别准则。通过实测静力触探试验的锥端阻力数据,说明了该方法,并从模型拟合度和复杂度罚值2个方面比较3种方法在变异函数模型选择中的差异性。研究表明,给定试验数据条件下,BME能够合理地考虑变异函数的拟合度和复杂性;而AIC和BIC识别准则在模型参数个数相同时,仅能反映不同变异函数的拟合度差异,因此,在这种情况下推荐采用BME选择变异函数。本研究方法能够在考虑趋势项参数条件下合理地选择地质统计学变异函数,所选最优变异函数与试验变异函数较一致,为地质统计学分析提供了有效的参考。
Abstract:Objective The variogram quantifies the variability of geological attributes between two spatial points and is of crucial significance for geostatistical analysis. When geological data exhibit a trend variation along spatial coordinates, the accurate selection and estimation of the variogram become exceptionally difficult.
Methods To realize the model selection and parameter estimation of the variogram, this paper presents a variogram selection approach based on Bayesian theory, employing the Laplace approximation method to approximate the posterior probability distribution as a Gaussian one. Firstly, the posterior probability distribution of the parameters is computed, and subsequently, the Bayesian model evidence (BME) of each alternative variogram is calculated respectively to determine the optimal model. This study investigates the applicability of two model selection methods in the selection of variograms, encompassing Bayesian model evidence (BME), Akaike information criterion (AIC), and Bayesian information criterion (BIC).
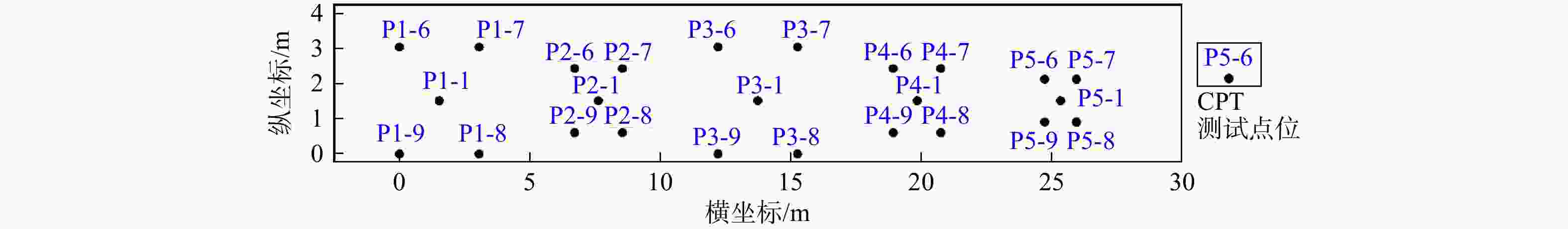
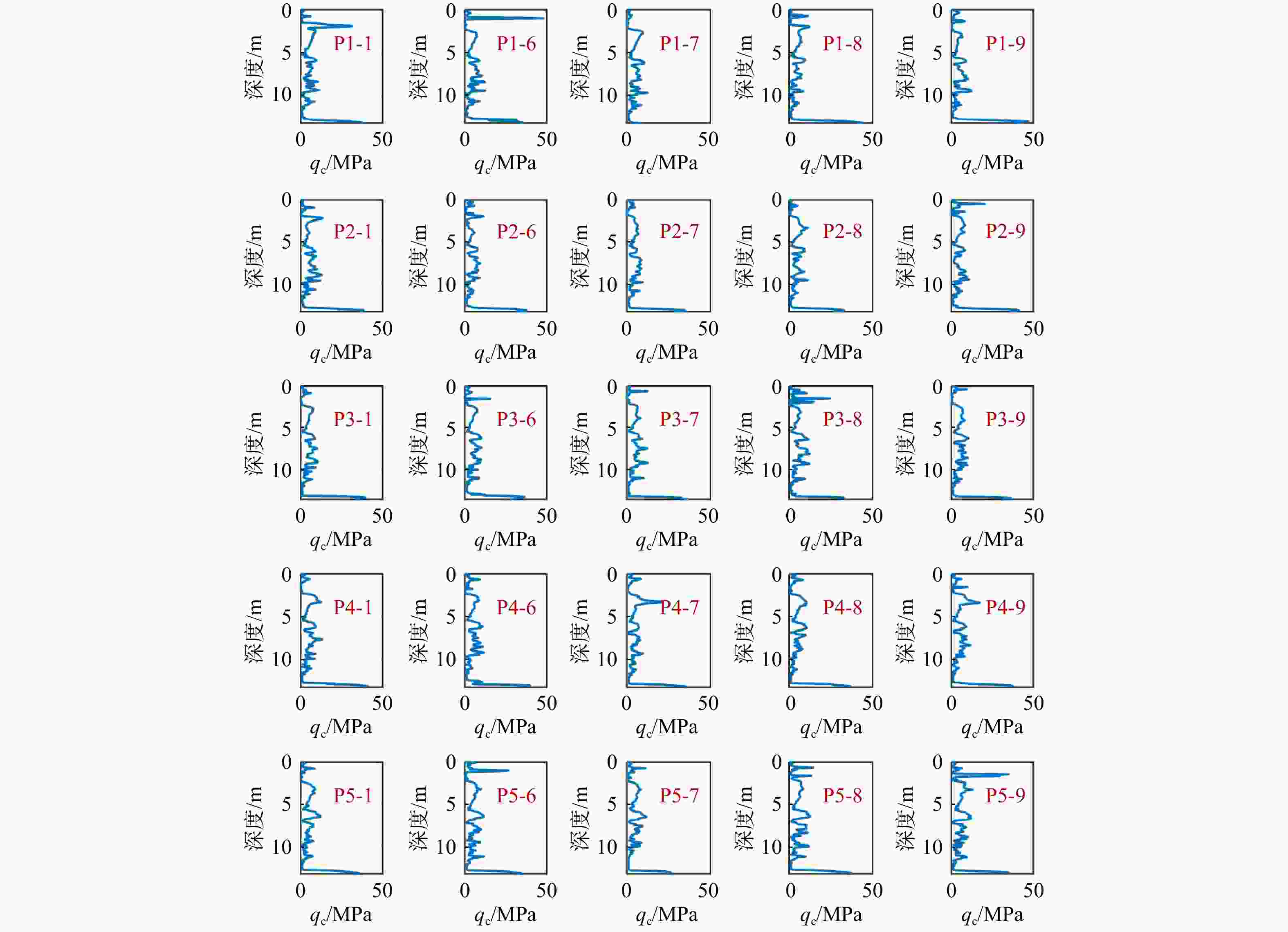
Results The proposed method is elucidated through the measured cone tip resistance data from static cone penetration tests, and the disparities among the three methods in the selection of variogram models are compared from the perspectives of model fitting and complexity penalty.
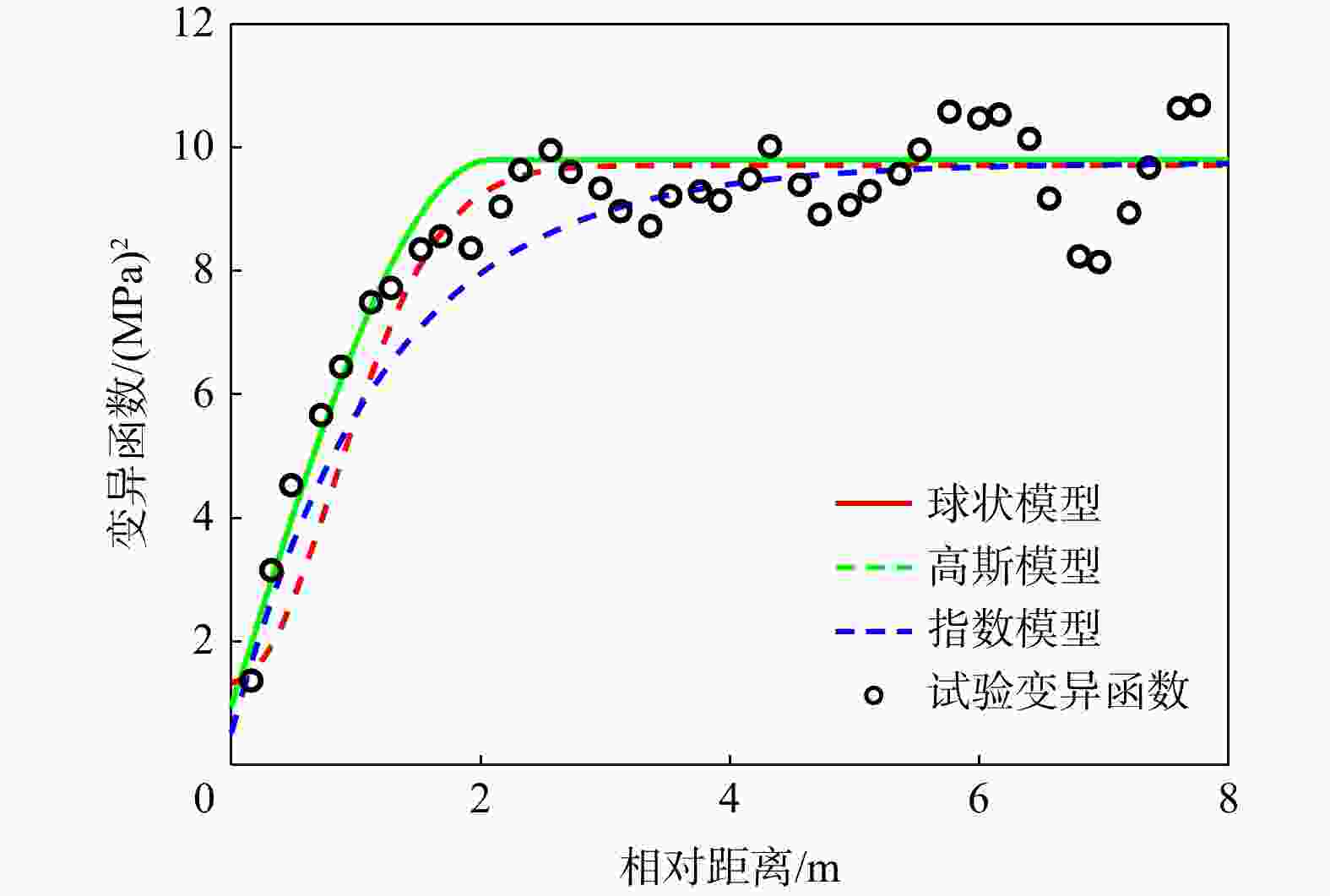
Conclusion The research reveals that, under the given experimental data conditions, BME can rationally take into account the fitting degree and complexity of the variogram; while the AIC and BIC identification criteria can merely reflect the fitting degree differences of different variograms when the number of model parameters is the same. Consequently, in such circumstances, BME is recommended for the selection of variograms. The method proposed in this study is capable of reasonably selecting the geostatistical variogram considering the trend term parameters, and the selected optimal variogram is relatively consistent with the experimental variogram, providing an effective reference for geostatistical analysis.
-
Key words:
- cone penetration test /
- Bayesian theory /
- Laplace approximation /
- variogram /
- model selection /
- BME /
- geostatistic
-
表 1 常用理论变异函数模型及其协方差函数公式
Table 1. Commonly used theoretical variance function model and its covariance function formula
模型 变异函数$ \gamma \left( h \right) $ 协方差函数$C(h)$ 指数
模型$ \left\{ {\begin{aligned} &{{c_0} + {c_1}(1 - \exp ( - h/a)){\text{ }},h > 0} \\ &{0 \qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\;\; ,h = 0} \end{aligned}} \right. $ $\left\{ {\begin{aligned} &{{c_1}\exp ( - h/a){\text{ }},h > 0} \\ &{{c_0} + {c_1}\quad\quad\;\;,h = 0} \end{aligned}} \right.$ 高斯
模型$\left\{ {\begin{aligned} &{{c_0} + {c_1}(1 - \exp ( - {h^2}/{a^2})){\text{ }},h > 0} \\ &{0 \qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\quad\;,h = 0} \end{aligned}} \right.$ $\left\{ {\begin{aligned} &{{c_1}\exp ( - {h^2}/{a^2}){\text{ }},h > 0} \\ &{{c_0} + {c_1}\quad\quad\quad\;\;,h = 0} \end{aligned}} \right.$ 球状
模型$ \left\{ \begin{aligned} &{c_0} + {c_1}\qquad\qquad\qquad\;{\text{ , }}h > a \\ &{{c_0} + {c_1}\left( {1.5\frac{h}{a} - 0.5\frac{{{h^3}}}{{{a^3}}}} \right){\text{ }},0 < h \leqslant a} \\ &{0\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\;{\text{ , }}h = 0} \\ \end{aligned} \right. $ $\left\{ {\begin{aligned} &{0 \qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad,h > a} \\ &{{c_1}\left(1 - 1.5\frac{h}{a} + 0.5\frac{{{h^3}}}{{{a^3}}}\right){\text{ }},h \leqslant a} \\ &{{c_0} + {c_1}\qquad\qquad\qquad,h = 0} \end{aligned}} \right.$ 注:$ {c_0} $为块金值;$ {c_1} $为偏基台值;$ {c_0} + {c_1}{\text{ }} $为基台值;$a$为变差距离或相关长度;$h$为空间2点的距离;下同 表 2 3种模型比选准则
Table 2. Three model selection criteria
模型比选 拟合度 罚值 BME $ \ln \left( {{P} \left( {{\cambriabifont\text{z}}|{{\boldsymbol{\theta }}^*},{C_i}} \right)} \right) $ $ - \ln \left( {{\mathrm{P}}_{\mathrm{r}} \left( {{{\mathbf{\theta }}^*}|{C_i}} \right)} \right) - \dfrac{{{d}}}{2}\ln \left( {2\pi } \right) + \dfrac{1}{2}\ln \left( {\left| \boldsymbol{H} \right|} \right) $ AIC $ 2\ln {P} {\left( {{\cambriabifont\text{z}}|{\boldsymbol{\theta }},{C_i}} \right)_{\max }} $ $ 2d $ BIC $ 2\ln {P} {\left( {{\cambriabifont\text{z}}|{\boldsymbol{\theta }},{C_i}} \right)_{\max }} $ $ d\ln \left( {{N_m}} \right) $ 注:表中代号含义详见正文 表 3 模型参数的先验分布
Table 3. Prior distribution of model parameters
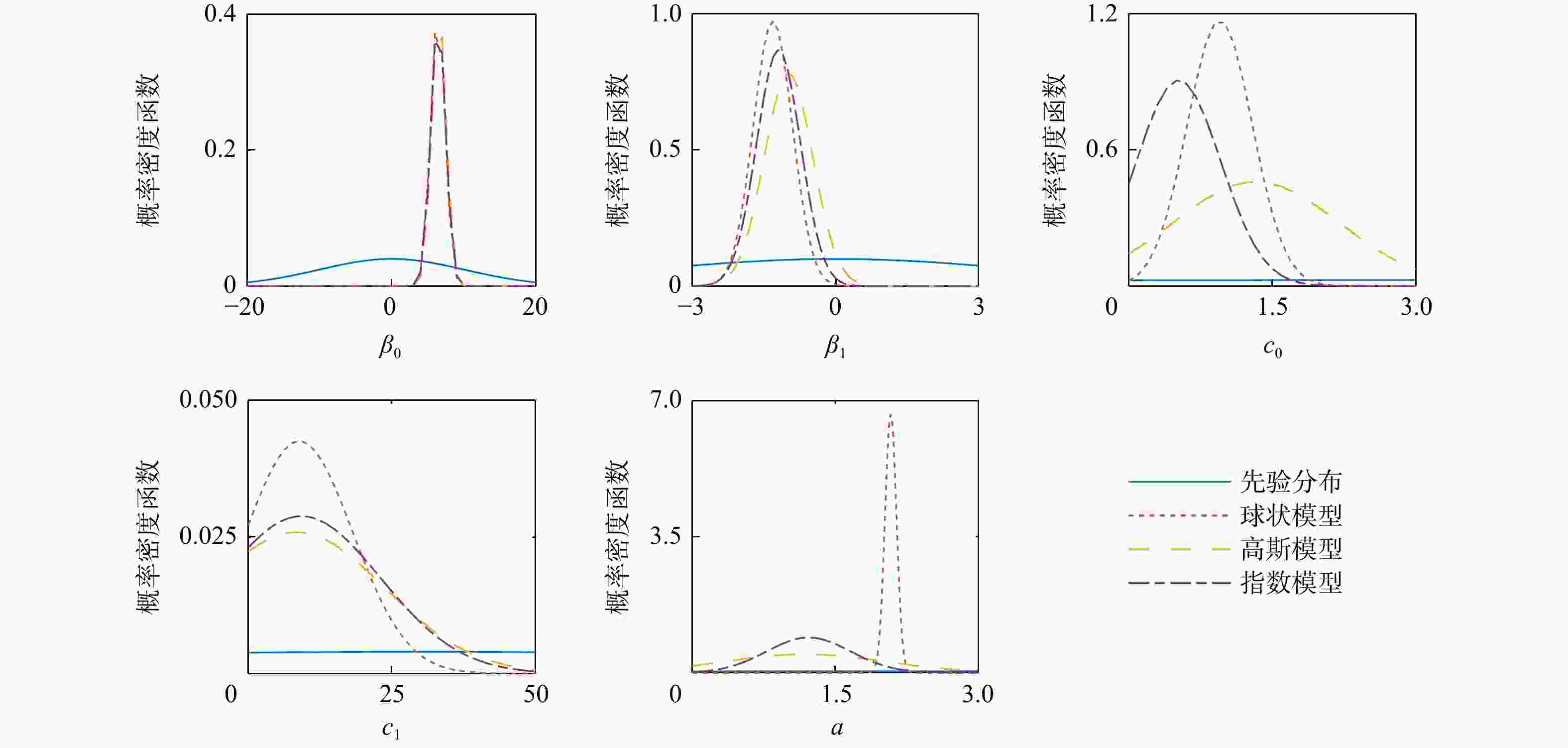
模型参数 ${\beta _0}$ ${\beta _1}$ ${c_0}( \geqslant 0)$ ${c_1}\left( { \geqslant 0} \right)$ $a\left( { \geqslant 0} \right)$ 平均值 0 0 5 30 5 标准差 10 10 100 200 10 注:β0. 常数项参数;β1.一次项参数;下同 表 4 P1-6点位CPT测试数据下3种模型的计算结果
Table 4. Calculation results of three models under P1-6 data
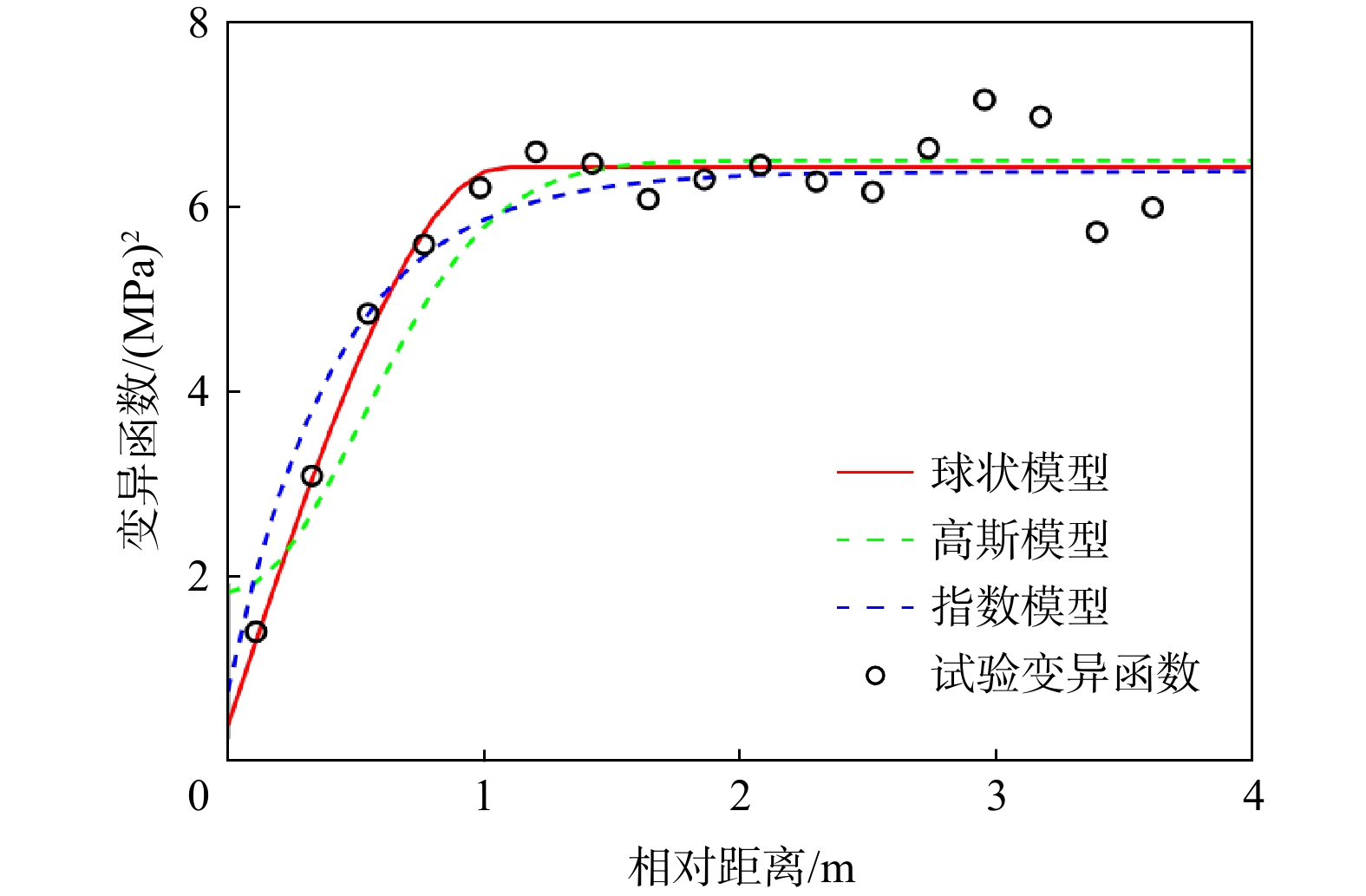
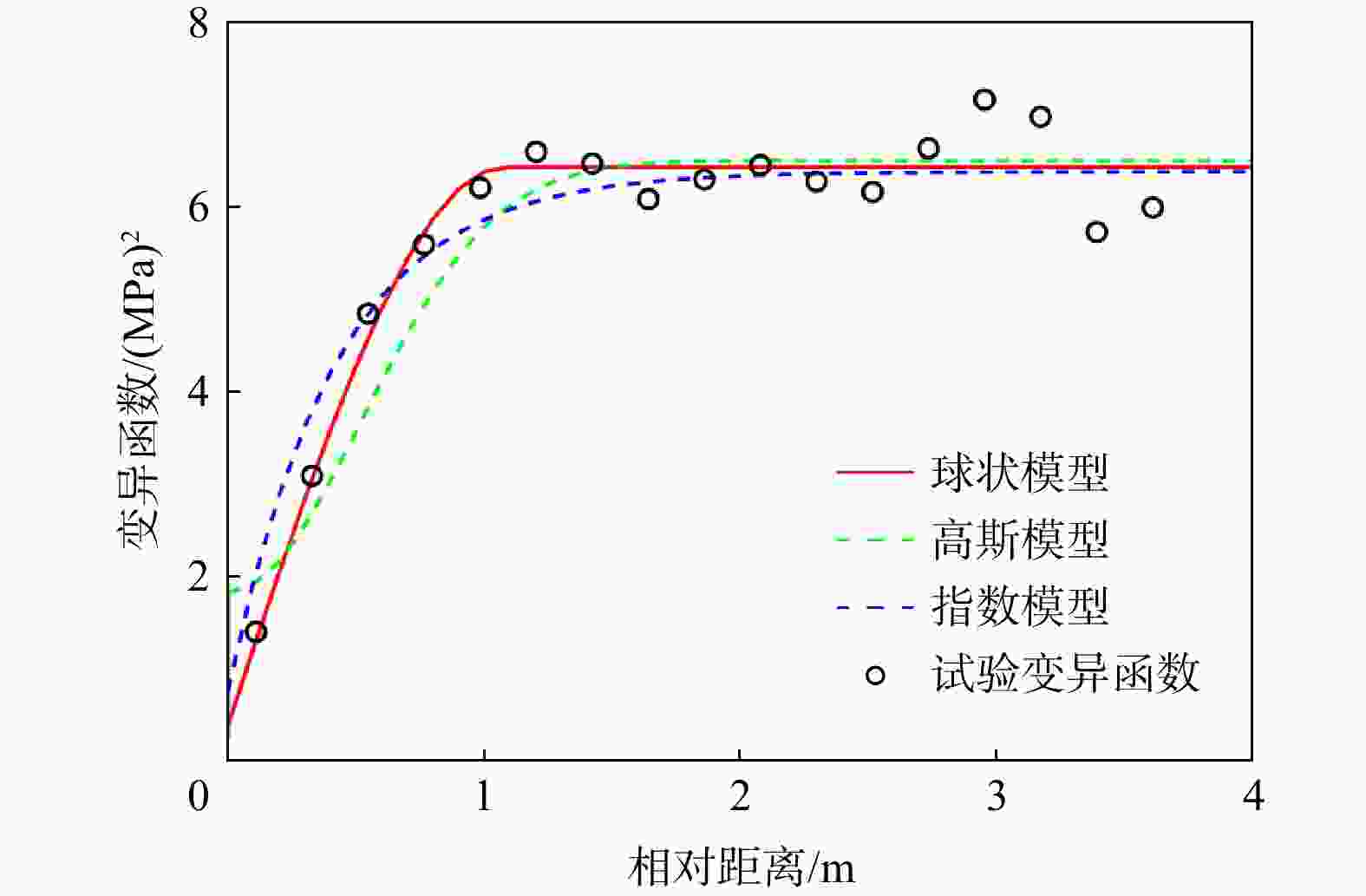
模型 后验均值 后验标准差 模型证据 模型选择概率 ${\beta _0}$ ${\beta _1}$ ${c_0}$ ${c_1}$ $a$ ${\beta _0}$ ${\beta _1}$ ${c_0}$ ${c_1}$ $a$ 球状模型 6.39 −1.31 0.95 8.85 2.08 0.99 0.41 0.34 9.39 0.06 −122.43 0.6814 高斯模型 6.57 −0.98 1.33 8.38 1.18 0.99 0.51 0.87 15.42 0.84 −150.81 0 指数模型 6.45 −1.19 0.52 9.23 1.22 1.00 0.46 0.44 13.85 0.44 −123.19 0.3186 表 5 基于P1-6点值测试数据变异函数模型选择结果对比
Table 5. Comparison of selection results based on variation function model of P1-6 data
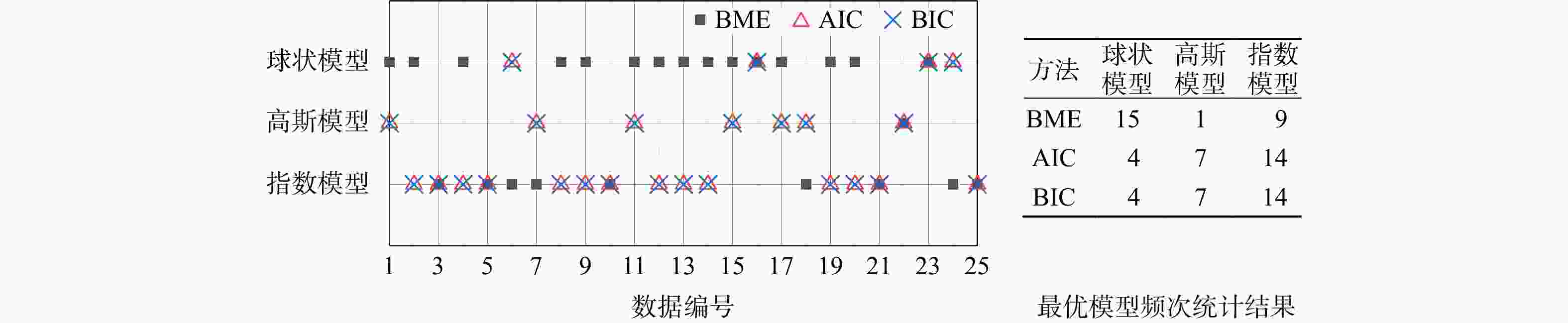
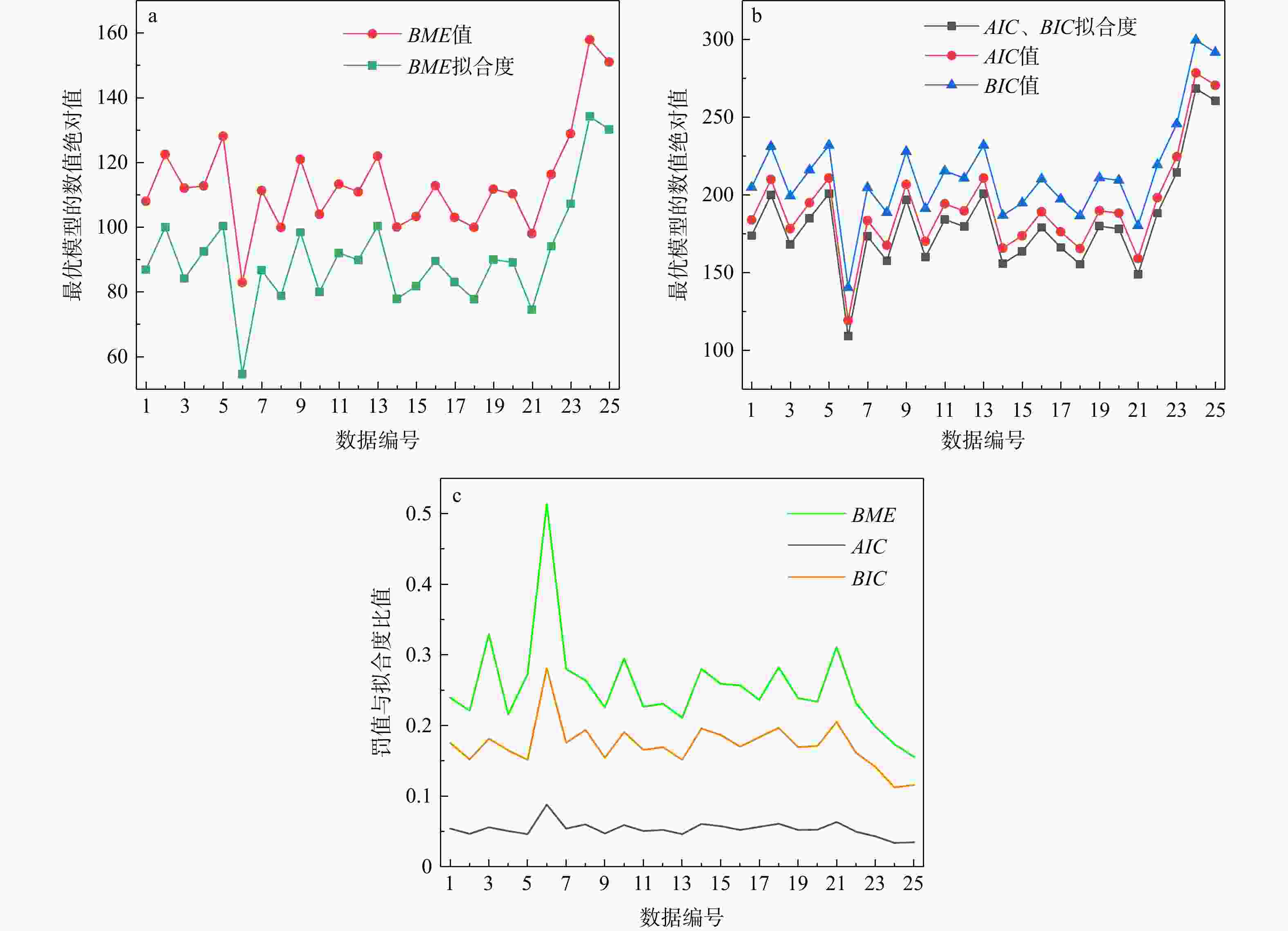
模型 BME AIC识别准则 BIC识别准则 BME值 拟合度 罚值 AIC值 拟合度 罚值 BIC值 拟合度 罚值 球状 −122.43 −110.01 −12.42 230.02 220.02 10 251.09 220.02 31.07 高斯 −150.81 −137.80 −13.01 285.60 275.60 10 306.67 275.60 31.07 指数 −123.19 −109.69 −13.50 229.38 219.38 10 250.45 219.38 31.07 -
[1] CHEN Q S,WANG C F,JUANG C H. Probabilistic and spatial assessment of liquefaction-induced settlements through multiscale random field models[J]. Engineering Geology,2016,211:135-149. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.07.002 [2] LI X Y,ZHANG L M,LI J H. Using conditioned random field to characterize the variability of geologic profiles[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2016,142(4):04015096. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001428 [3] LUO N,ARWADE S R,DEGROOT D J. Probabilistic analysis of offshore geotechnical site investigation in a homogeneous stiff clay deposit[J]. Journal of Physics (Conference Series),2020,1452(1):012037. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1452/1/012037 [4] 揭鸿鹄,蒋水华,常志璐,等. 融合多源信息的降雨入渗边坡概率反分析及可靠度预测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2024,35(1):28-36.JIE H H,JIANG S H,CHANG Z L,et al. Probabilistic inverse-analysis and reliability prediction of rainfall-induced landslides for slope with multi-source information[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2024,35(1):28-36. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 汪泉娟,孙敬锋,杨英杰,等. 克里金方法与深度学习方法用于浅层地下水位估计的对比研究:以深汕特别合作区为例[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(4):291-301.WANG Q J,SUN J F,YANG Y J,et al. A comparative study of Kriging and deep learning methods for shallow groundwater level estimation:A case study of the Shenzhen-Shanwei Special Cooperation Zone[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(4):291-301. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] BAECHER G,CHRISTIAN J. Reliability and statistics in geotechnical engineering[M]. [S. 1.]: Wiley,2003. [7] CHRISTIAN J T,LADD C C,BAECHER G B. Reliability applied to slope stability analysis[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,1994,120(12):2180-2207. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1994)120:12(2180) [8] 杨文礼,白光顺,孙滨,等. 云南哀牢山地区地质灾害因子敏感性和易发性评价:以新平县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2024,35(6):145-152.YANG W L,BAI G S,SUN B,et al. Sensitivity and susceptibility assessment of geological hazard factors:A case study of Xinping County in the Ailao Mountain area of Yunnan Province,China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2024,35(6):145-152. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 花卫华,宿紫莹,朱玉华,等. 大范围地质体分块建模方法[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(6):257-265.HUA W H,SU Z Y,ZHU Y H,et al. Large-range geological block modeling method[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(6):257-265. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] PHOON K K,KULHAWY F H. Characterization of geotechnical variability[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1999,36(4):612-624. doi: 10.1139/t99-038 [11] 夏侯云山,张抒,唐辉明,等. 考虑参数空间变异结构的结构化交叉约束随机场模拟方法研究[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(12):4935-4945.XIAHOU Y S,ZHANG S,TANG H M,et al. Study of structural cross-constraint random field simulation method considering spatial variation structure of parameters[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2019,40(12):4935-4945. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] CAO Z J,WANG Y. Bayesian model comparison and selection of spatial correlation functions for soil parameters[J]. Structural Safety,2014,49:10-17. doi: 10.1016/j.strusafe.2013.06.003 [13] 田密,李典庆,曹子君,等. 基于贝叶斯理论的土性参数空间变异性量化方法[J]. 岩土力学,2017,38(11):3355-3362.TIAN M,LI D Q,CAO Z J,et al. Quantification of spatial variability of soil parameters using Bayesian approaches[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2017,38(11):3355-3362. (in Chinese) [14] ZHAO T Y,SONG C,LU S F,et al. Prediction of uniaxial compressive strength using fully Bayesian Gaussian process regression (FB-GPR) with model class selection[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2022,55(10):6301-6319. doi: 10.1007/s00603-022-02964-y [15] 黄宇,杨荣森,韩晓东,等. 基于定向半变异函数的裂隙网络空间变异性分析[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(2):186-193.HUANG Y,YANG R S,HAN X D,et al. Analysis of the spatial variability on a fracture network based on an oriented semivariogram[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(2):186-193. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 林军,蔡国军,邹海峰,等. 基于随机场理论的江苏海相黏土空间变异性评价研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2015,37(7):1278-1287. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201507014LIN J,CAI G J,ZOU H F,et al. Assessment of spatial variability of Jiangsu marine clay based on random field theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2015,37(7):1278-1287. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11779/CJGE201507014 [17] 宋超,赵腾远,许领. 基于贝叶斯高斯过程回归与模型选择的岩石单轴抗压强度估计方法[J]. 岩土工程学报,2023,45(8):1664-1673. doi: 10.11779/CJGE20220734SONG C,ZHAO T Y,XU L. Estimation of uniaxial compressive strength based on fully Bayesian Gaussian process regression and model selection[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2023,45(8):1664-1673. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11779/CJGE20220734 [18] 王继玲,周维博,孙梨梨,等. 石川河富平地下水库渗透系数空间变异性研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(3):34-43.WANG J L,ZHOU W B,SUN L L,et al. Study on the spatial vriability of hydraulic conductivity of underground reservoir in Fuping section of Shichuan River[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(3):34-43. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] STUEDLEIN A W,KRAMER S L,ARDUINO P,et al. Geotechnical characterization and random field modeling of desiccated clay[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2012,138(11):1301-1313. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000723 [20] UZIELLI M,MAYNE P W. Probabilistic assignment of effective friction angles of sands and silty sands FROM CPT using quantile regression[J]. Georisk (Assessment and Management of Risk for Engineered Systems and Geohazards),2019,13(4):271-275. doi: 10.1080/17499518.2019.1663388 [21] PHOON K K,QUEK S T,AN P. Identification of statistically homogeneous soil layers using modified Bartlett statistics[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2003,129(7):649-659. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2003)129:7(649) [22] 张国萍,王林,曹子君,等. 考虑不确定性的土水特征曲线模型确定方法比较研究[J]. 自然灾害学报,2018,27(4):151-158.ZHANG G P,WANG L,CAO Z J,et al. Comparative study of different methods for determining the soil water characteristic curve model considering uncertainty[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2018,27(4):151-158. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] XU J B,ZHANG L L,LI J H,et al. Probabilistic estimation of variogram parameters of geotechnical properties with a trend based on Bayesian inference using Markov chain Monte Carlo simulation[J]. Georisk (Assessment and Management of Risk for Engineered Systems and Geohazards),2021,15(2):83-97. doi: 10.1080/17499518.2020.1757720 [24] YUEN K V. Recent developments of Bayesian model class selection and applications in civil engineering[J]. Structural Safety,2010,32(5):338-346. doi: 10.1016/j.strusafe.2010.03.011 [25] 左自波,张璐璐,程演,等. 基于MCMC法的非饱和土渗流参数随机反分析[J]. 岩土力学,2013,34(8):2393-2400.ZUO Z B,ZHANG L L,CHENG Y,et al. Probabilistic back analysis of unsaturated soil seepage parameters based on Markov chain Monte Carlo method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2013,34(8):2393-2400. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] CAO Z J,WANG Y. Bayesian model comparison and characterization of undrained shear strength[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2014,140(6):04014018. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001108 [27] 郭秋麟,任洪佳,于京都,等. 基于贝叶斯网络的油气勘探风险预测方法:以准噶尔盆地腹部侏罗系三工河组为例[J]. 中国石油勘探,2023,28(1):108-119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2023.01.010GUO Q L,REN H J,YU J D,et al. Prediction method of petroleum exploration risks based on Bayesian network:A case study of the Jurassic Sangonghe Formation in the hinterland of Junggar Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration,2023,28(1):108-119. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2023.01.010 [28] 李建文,赵文,吴振坤,等. 煤矿采空区覆岩“三带” 智能识别方法[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2024,52(4):164-171. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.08.0460LI J W,ZHAO W,WU Z K,et al. Intelligent identification method for overburden three zones of a goaf[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2024,52(4):164-171. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.08.0460 [29] CAO Z J,WANG Y,LI D Q. Quantification of prior knowledge in geotechnical site characterization[J]. Engineering Geology,2016,203:107-116. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.08.018 [30] 钟世英,刘长飞,时文浩. MATLAB工具箱自动识别探地雷达空洞图像技术[J]. 计算机辅助工程,2024,33(4):8-14.ZHONG S Y,LIU C F,SHI W H. MATLAB toolbox automatic recognition of GPR cavity image technology[J]. Computer Aided Engineering,2024,33(4):8-14. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] 张闻宇,张智刚,颜小挺,等. AI大模型在MATLAB课程教学中的应用[J]. 现代信息科技,2024,8(24):195-198.ZHANG W Y,ZHANG Z G,YAN X T,et al. Application of AI big model in MATLAB course teaching[J]. Modern Information Technology,2024,8(24):195-198. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] 邹鹤民. 基于贝叶斯网络的公路隧道围岩失稳风险评估及系统开发[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(6):89-101.ZOU H M. Risk assessment and system development of surrounding rock instability in highway tunnel based on Bayesian network[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(6):89-101. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 朱悦,彭荣华,胡祥云,等. 基于变维度贝叶斯反演的地热黏土盖层音频大地电磁探测能力研究[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(3):341-350.ZHU Y,PENG R H,HU X Y,et al. Research on audio-frequency magnetotelluric detection capability of geothermal clay cap based on trans-dimensional Bayesian inversion[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(3):341-350. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] 杨灿,刘磊磊,张遗立,等. 基于贝叶斯优化机器学习超参数的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(2):228-238.YANG C,LIU L L,ZHANG Y L,et al. Machine learning based on landslide susceptibility assessment with Bayesian optimized the hyperparameters[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(2):228-238. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: