-
摘要:
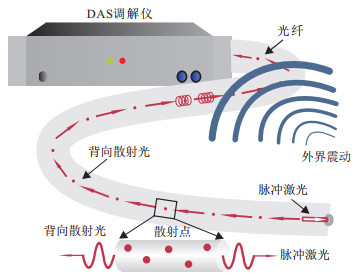
煤矿采空区覆岩破裂信号作为开采沉陷的前兆特征, 对其开展监测有助于预警采空区塌陷事件。但现有手段难以实现大范围、全方位、分布式的监测。以我国宁东矿区羊场湾煤矿为研究区域, 引入分布式声波传感技术(distributed acoustic sensing, 简称DAS)对采空区覆岩破裂信号开展连续监测。针对DAS数据信噪较低的问题, 对比试验了5种去噪方法。对预处理后的信号开展时频分析, 提取覆岩破裂信号; 进一步将DAS信号转换为递归图以构建数据集, 训练基于卷积神经网络的覆岩破裂信号智能识别模型。结果表明, 同步压缩小波变换能够很好地压制DAS数据的噪声。覆岩破裂信号与非覆岩破裂信号的递归图之间具有明显区别, 训练得到的VGG-16模型在分类二者的任务上实现了85%的准确率。因此, 利用DAS技术监测覆岩破裂具有可行性, 本研究所提出的基于递归图和卷积神经网络VGG-16的深度学习方法可实现对覆岩破裂信号的智能识别。研究成果为后续开发基于DAS系统的开采沉陷智能预警系统提供了一定技术支撑。
Abstract:Objective As socioeconomic development advances, challenges associated with coal mining beneath structures such as buildings, water bodies, and railways have intensified markedly. It is increasingly imperative to extract underground minerals within acceptable boundaries while diligently monitoring the environmental impacts of such activities. Previous research showed that mining-induced subsidence was a primary contributor to environmental geological disasters in mining areas, particularly when the integrity of the overlying strata is breached. Therefore, it is crucial to develop methodologies for the early detection of surface subsidence, which requires in-depth research into monitoring the fracture signals from overburden rock. Existing methods, including acoustic emission and microseismic monitoring systems, face significant challenges in achieving widespread, comprehensive, and distributed monitoring. In response to these limitations, distributed acoustic sensing (DAS), a state-of-the-art optoelectronic sensing technique, has recently gained prominence and been extensively employed across geophysical exploration fields such as oil and gas exploration and seismic monitoring. We explore applying DAS technology to enhance the monitoring and identification of fracture signals in the overburden of mined-out areas, aiming to improve both safety and sustainability in mining operations.
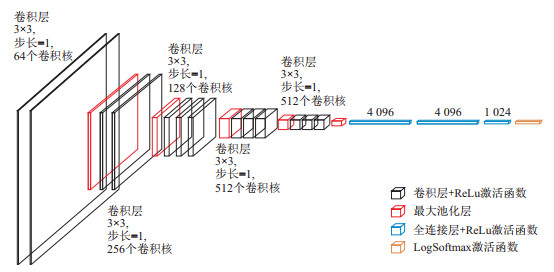
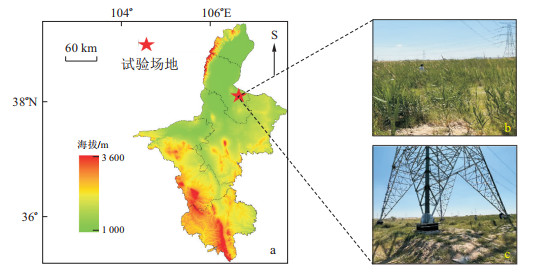
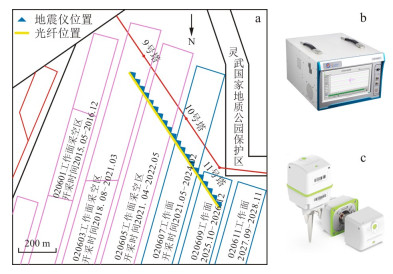
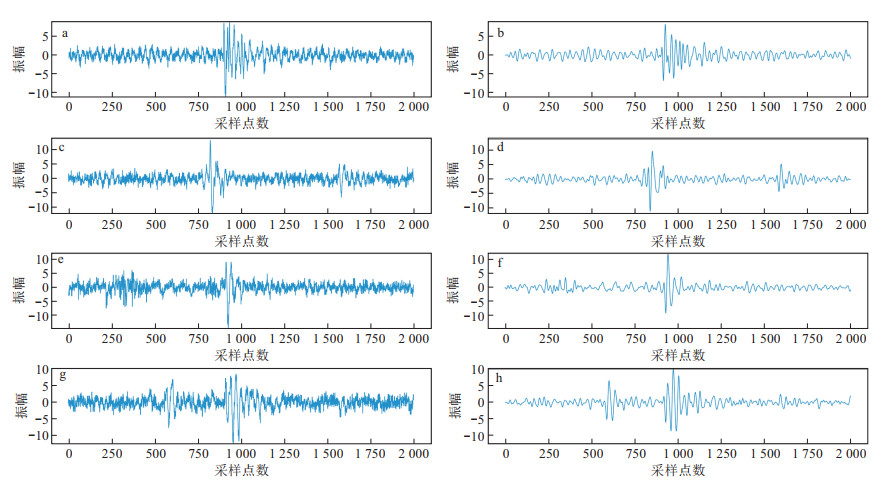
Methods This research selects a coal mine in Ningdong town, Lingwu city, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. DAS technology is used to continuously monitor the fracture signals of the overburden in underground voids. A fibre optic cable was installed at the bottom of a trench stretching parallel to the coal mining face with dimensions of approximately 1 km in length, 15 cm in width, and 30 cm in depth. Additionally, several triaxial node seismometers were deployed along the route for comparison validation. Given the low signal-to-noise ratio of DAS data, comparative experiments were conducted using five denoising techniques: high-pass filtering, empirical mode decomposition, Fourier transform, F-X deconvolution, and synchronous compression wavelet transform. The DAS signals were preprocessed through detrending, mean removal, and denoising, followed by time-frequency analysis to extract overburden fracture signals. The event signals collected by the DAS system which formed a dataset were converted into recurrence plots. This dataset was used to train an intelligent recognition model for overburden fracture signals based on the convolutional neural network VGG-16.
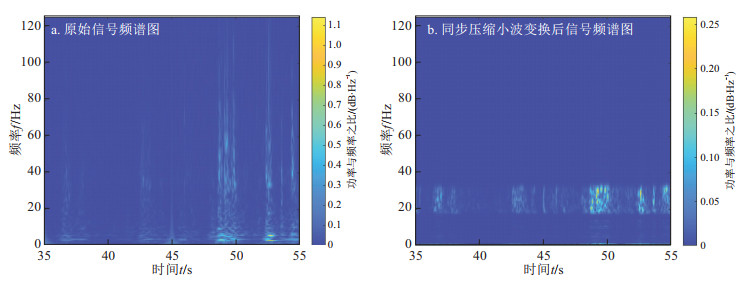
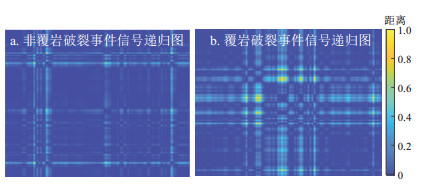
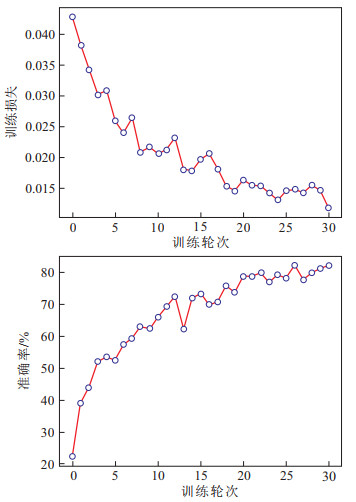
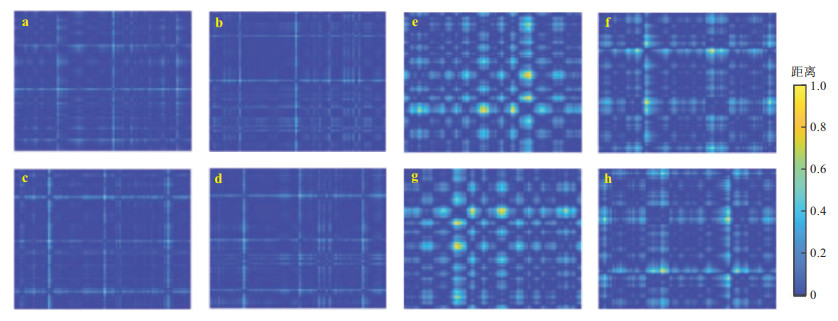
Results The results demonstrate that synchronous compression wavelet transform effectively eliminates noise from DAS data. The overburden fracture signals detected by DAS were consistent with those by seismometers. Recurrence plots of DAS-collected fracture signals differed from nonfracture signals, which can be distinguished by the trained VGG-16 model with an accuracy of 85%.
Conclusions Monitoring overburden fractures via DAS technology is feasible. The proposed deep learning approach, based on recurrence plots and the VGG-16 convolutional neural network, can effectively recognize fracture signals. This research provides significant technical support for developing an intelligent early warning system for mining subsidence based on DAS.
-
所有作者声明不存在利益冲突。
-
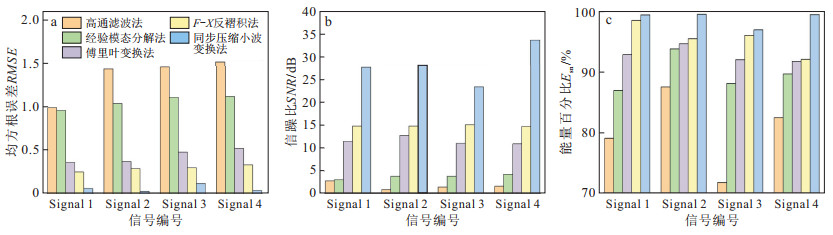
表 1 不同降噪方法降噪效果对比
Table 1. Comparison of denoising effects of different denoising methods
去噪处理方法 评价指标 信号编号 Signal 1 Signal 2 Signal 3 Signal 4 高通滤波法 RMSE 0.99 1.44 1.46 1.52 SNR/dB 2.73 0.83 1.34 1.49 Esn/% 79.03 87.51 71.78 82.46 经验模态分解法 RMSE 0.96 1.04 1.11 1.12 SNR/dB 3.00 3.70 3.74 4.17 Esn/% 86.94 93.77 88.09 89.63 傅里叶变换法 RMSE 0.36 0.37 0.48 0.52 SNR/dB 11.44 12.69 10.98 10.83 Esn/% 92.83 94.61 92.01 91.74 F-X反褶积法 RMSE 0.25 0.29 0.30 0.33 SNR/dB 14.79 14.73 15.06 14.69 Esn/% 98.47 95.46 96.01 92.06 同步压缩小波变换法 RMSE 0.06 0.03 0.12 0.04 SNR/dB 27.69 33.92 23.36 33.63 Esn/% 99.37 99.46 96.91 99.43 注:RMSE为均方根误差;SNR为信躁比;Esn为能量百分比; 下同 表 2 VGG-16模型具体参数
Table 2. Specific parameters of the VGG-16 model
序号 类别 核参数 步长 1 Input Iayer — — 2 Conv 1 3×3×64 1 3 Conv 2 3×3×64 1 4 Max Pool 1 2×2 2 5 Conv 3 3×3×128 1 6 Conv 4 3×3×128 1 7 Max Pool 2 2×2 2 8 Conv 5 3×3×256 1 9 Conv 6 3×3×256 1 10 Conv 7 3×3×256 1 11 Max Pool 3 2×2 2 12 Conv 8 3×3×512 1 13 Conv 9 3×3×512 1 14 Conv 10 3×3×512 1 15 Max Pool 4 2×2 2 16 Conv 11 3×3×512 1 17 Conv 12 3×3×512 1 18 Conv 13 3×3×512 1 19 Max Pool 5 2×2 2 20 Fully nected 1 4 096 — 21 Fully nected 2 4 096 — 22 Fully nected 3 1 024 — 23 LogSoftmax — — -
[1] 姜岳, R.MISA, 李鹏宇, 等. 矿山开采沉陷理论发展历程综述[J]. 金属矿山, 2019(10): 1-7.JIANG Y, MISA R, LI P Y, et al. Summary and development of mining subsidence theory[J]. Metal Mine, 2019(10): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] 郭广礼, 王悦汉, 马占国. 煤矿开采沉陷有效控制的新途径[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2004, 33(2): 150-153.GUO G L, WANG Y H, MA Z G. A new method for ground subsidence control in coal mining[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2004, 33(2): 150-153. (in Chinese with English abstract) [3] 李效甫. 刘天泉院士与特殊开采技术[J]. 中国煤炭, 1997, 23(4): 57-58.LI X F. Academician Liu Tianquan and special mining technology[J]. China Coal, 1997, 23(4): 57-58. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] 纪洪广, 王宏伟, 曹善忠, 等. 花岗岩单轴受压条件下声发射信号频率特征试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 31(增刊1): 2900-2905.JI H G, WANG H W, CAO S Z, et al. Experimental research on frequency characteristics of acoustic emission signals under uniaxial compression of granite[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 31(S1): 2900-2905. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] 王晓南, 陆菜平, 薛俊华, 等. 煤岩组合体冲击破坏的声发射及微震效应规律试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2013, 34(9): 2569-2575.WANG X N, LU C P, XUE J H, et al. Experimental research on rules of acoustic emission and microseismic effects of burst failure of compound coal-rock samples[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(9): 2569-2575. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] SALVONI M, DIGHT P M. Rock damage assessment in a large unstable slope from microseismic monitoring-MMG Century mine (Queensland, Australia) case study[J]. Engineering Geology, 2016, 210: 45-56. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.06.002 [7] 戴峰, 李彪, 徐奴文, 等. 白鹤滩水电站地下厂房开挖过程微震特征分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2016, 35(4): 692-703.DAI F, LI B, XU N W, et al. Microseismic characteristic analysis of underground powerhouse at Baihetan hydropower station subjected to excavation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(4): 692-703. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] GHOSH G K, SIVAKUMAR C. Application of underground microseismic monitoring for ground failure and secure longwall coal mining operation: A case study in an Indian Mine[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2018, 150: 21-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2018.01.004 [9] 刘威, 朱鸿鹄, 王涛, 等. 基于分布式声波传感的大地探测技术研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 29-41. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0228LIU W, ZHU H H, WANG T, et al. Research progress of earth exploration technologies based on distributed acoustic sensing[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 29-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0228 [10] 朱鸿鹄. 工程地质界面: 从多元表征到演化机理[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 1-19. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220661ZHU H H. Engineering geological interface: From multivariate characterization to evolution mechanism[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 1-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220661 [11] 蔡海文, 叶青, 王照勇, 等. 分布式光纤声波传感技术研究进展[J]. 应用科学学报, 2018, 36(1): 41-58.CAI H W, YE Q, WANG Z Y, et al. Progress in research of distributed fiber acoustic sensing techniques[J]. Journal of Applied Sciences, 2018, 36(1): 41-58. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] LI Z F, SHEN Z C, YANG Y, et al. Rapid response to the 2019 Ridgecrest earthquake with distributed acoustic sensing[J]. AGU Advances, 2021, 2(2): e2021AV000395. doi: 10.1029/2021AV000395 [13] MOLENAAR M M, HILL D, WEBSTER P, et al. First downhole application of distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) for hydraulic fracturing monitoring and diagnostics[C]//Anon. SPE Hydraulic Fracturing Technology Conference and Exhibition. Richardson: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2011. [14] DALEY T M, FREIFELD B M, AJO-FRANKLIN J, et al. Field testing of fiber-optic distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) for subsurface seismic monitoring[J]. The Leading Edge, 2013, 32(6): 699-706. doi: 10.1190/tle32060699.1 [15] LIOR I, SLADEN A, RIVET D, et al. On the detection capabilities of underwater distributed acoustic sensing[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (Solid Earth), 2021, 126(3): e2020JB020925. doi: 10.1029/2020JB020925 [16] FANG G, LI Y E, ZHAO Y M, et al. Urban near-surface seismic monitoring using distributed acoustic sensing[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47(6): e86115. [17] MARTIN E R, HUOT F, MA Y B, et al. A seismic shift in scalable acquisition demands new processing: Fiber-optic seismic signal retrieval in urban areas with unsupervised learning for coherent noise removal[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2018, 35(2): 31-40. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2017.2783381 [18] DALEY T M, MILLER D E, DODDS K, et al. Field testing of modular borehole monitoring with simultaneous distributed acoustic sensing and geophone vertical seismic profiles at Citronelle, Alabama[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2016, 64(5): 1318-1334. doi: 10.1111/1365-2478.12324 [19] WANG J, ZHU H H, MEI G X, et al. Field monitoring of bearing capacity efficiency of permeable pipe pile in clayey soil: A comparative study[J]. Measurement, 2021, 186: 110151. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.110151 [20] MOUSAVI S M, LANGSTON C A, HORTON S P. Automatic microseismic denoising and onset detection using the synchrosqueezed continuous wavelet transform[J]. Geophysics, 2016, 81(4): 341-355. doi: 10.1190/geo2015-0598.1 [21] OZKOK F O, CELIK M. Convolutional neural network analysis of recurrence plots for high resolution melting classification[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2021, 207: 106139. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106139 [22] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]//Anon. International Conference on Learning Representations(ICLR). [S. l. ]: [s. n. ], 2015: 1-14. [23] 朱鸿鹄, 施斌, 严珺凡, 等. 基于分布式光纤应变感测的边坡模型试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2013, 32(4): 821-828.ZHU H H, SHI B, YAN J F, et al. Physical model testing of slope stability based on distributed fiber-optic strain sensing technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2013, 32(4): 821-828. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] 程刚, 施斌, 朱鸿鹄, 等. 光纤和砂土界面耦合性能的分布式感测试验研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 2019, 25(4): 487-494.CHENG G, SHI B, ZHU H H, et al. Experimental study on coupling performance of fiber and sand interface based on distributed sensing[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2019, 25(4): 487-494. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25] 张诚成, 施斌, 刘苏平, 等. 钻孔回填料与直埋式应变传感光缆耦合性研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2018, 40(11): 1959-1967.ZHANG C C, SHI B, LIU S P, et al. Mechanical coupling between borehole backfill and fiber-optic strain-sensing cable[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 40(11): 1959-1967. (in Chinese with English abstract)) ZHANG C C, SHI B, LIU S P, et al. Mechanical coupling between borehole backfill and fiber-optic strain-sensing cable[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 40(11): 1959-1967. (in Chinese with English abstract) 期刊类型引用(11)
1. 汪宗欣 ,曾雄伟 ,苗凤彬 ,陈荣 ,刘浩 . 湖北宜昌早寒武世岩家河组-水井沱组界线元素地球化学特征及其地质意义. 华南地质. 2023(02): 320-332 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 白洋,谢宏,王孟斋,卢正浩. 贵州铜仁坝黄牛蹄塘组黑色岩系有机质富集机理. 地质科技通报. 2023(05): 115-127 .  本站查看
本站查看3. 郑锋利,平瑞,宋慧波,胡斌,刘顺喜. 华北西部地区太原组不同古氧相遗迹化石组合特征. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版). 2022(05): 58-67 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 饶耕玮,刘晓东,刘平辉,戴朝成,黄光辉. 二连盆地川井坳陷白垩系地层元素地球化学特征及地质意义. 科学技术与工程. 2021(08): 3023-3031 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 罗胜元,陈孝红,倪方杰. 自然伽马能谱测井在富有机质页岩评价和地质导向中的应用. 测井技术. 2021(03): 297-304 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 危凯,陈孝红,王传尚,刘安,曾雄伟,李志宏. 湘鄂西地区晚埃迪卡拉世-早寒武世硅质岩成因及其页岩气地质意义. 地质科技通报. 2020(02): 20-30 .  本站查看
本站查看7. 盛贤才,肖传桃,梁西文,刘漪,甘玉青. 鄂西地区寒武系底部层状硅质岩成因及其地质意义. 长江大学学报(自然科学版). 2020(04): 1-8+121 .  百度学术
百度学术8. 刘国恒,翟刚毅,邹才能,黄志龙,夏响华,石砥石,周志,陈榕,张聪,于抒放. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组泥页岩硅质来源与油气富集. 石油实验地质. 2019(01): 45-55+67 .  百度学术
百度学术9. 陈孝红,危凯,张保民,李培军,李海,刘安,罗胜元. 湖北宜昌寒武系水井沱组页岩气藏主控地质因素和富集模式. 中国地质. 2018(02): 207-226 .  百度学术
百度学术10. 陈孝红,张保民,陈林,张国涛,李培军,张淼. 鄂西宜昌地区晚奥陶世—早志留世页岩气藏的主控地质因素与富集模式. 地球学报. 2018(03): 257-268 .  百度学术
百度学术11. 郭俊锋,强亚琴,宋祖晨,郑亚娟,姚肖永,肖良,李相传. 寒武纪早期岩家河生物群:研究进展和展望. 古生物学报. 2017(04): 461-475 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(7)
-





 下载:
下载:

 百度学术
百度学术


