Settlement and deformation monitoring and spatio-temporal data interpolation method for urban ultra long subway tunnels under soft soil foundation
-
摘要:
城市地铁隧道的沉降监测与收敛变形的精准监控对于保障运营安全及周边环境稳定性至关重要。传统的监测方式, 如人工巡检和固定传感器监测, 存在实时性差、数据有限等问题。以上海地铁2号线东延伸段(在软土地基下采用盾构技术建造的大型城市地下隧道工程)为例, 介绍了一种创新的无线传感网络(wireless sensor network, 简称WSN)监测技术, 针对无线传感网络监测数据可能存在缺失的问题, 提出了一种适用于无线传感网络特性的缺失值补全算法, 以填补长达8年的监测周期中可能出现的数据空白点。通过以上监测网络及算法获取了该隧道的完整监测数据及特征指标, 并揭示了软土地基盾构隧道横向收敛变形的部分影响因素。本研究在确保了监测数据的有效性和完整性的基础上, 为软土地基盾构隧道的施工安全和地铁运营安全提供了技术支持和数据保障。
Abstract:Objective Precise monitoring of settlement and convergence deformation in urban subway tunnels is crucial for ensuring operational safety and the stability of the surrounding environment. Traditional methods, such as manual inspections and fixed sensor monitoring, suffer from poor real-time performance and limited data availability.
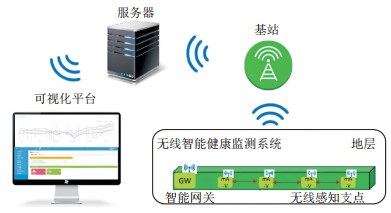
Methods To address the limitations of traditional approaches, an innovative wireless sensor network (WSN) monitoring system is introduced in this study by taking the East Extension Section of Shanghai Metro Line 2, a large-scale urban underground tunnel constructed using shield technology in soft soil as the example. Additionally, a missing value imputation algorithm tailored to WSN characteristics is proposed to address the potential data gaps in WSN monitoring which may arise in the following 8-year monitoring period.
Results The implementation of this monitoring network and algorithm provides full data and characteristic indicators for the tunnel monitoring, which aids in revealing the influencing factors of lateral convergence deformation in shield tunnels constructed in soft soil.
Conclusion By ensuring the effectiveness and completeness of the monitoring data, this research offers technical support and data assurance for the safety of shield tunnels in soft soil and the operational safety of subways.
-
表 1 横向收敛变形关键参数拟合值
Table 1. Fitting values for key parameters of lateral convergence deformation
环号 主振幅/mm 主周期/d 年均增长/mm 1690环 0.352 7 352 0.356 1840环 0.325 6 376 0.342 1940环 0.692 5 362 0.168 1990环 0.884 9 367 0.571 表 2 机器学习补全方法均方差
Table 2. Mean squared error of machine learning imputation methods
方法 均方差MSE/10-5 XGBoost 39.41 随机森林 77.56 MLP 33.74 融合模型 7.869 表 3 LSTM补全模型结构
Table 3. Structure of LSTM imputation model
层数 名称 单元数 1 LSTM层 100 2 LSTM层 150 3 LSTM层 200 4 LSTM层 100 5 全连接层 100 6 Leaky ReLU激活层 — 7 输出层 — -
[1] 黄震, 傅鹤林, 黄宏伟, 等. 一种运营地铁盾构隧道结构健康状况评价方法[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2018, 14(5): 1410-1418.HUANG Z, FU H L, HUANG H W, et al. A method for evaluating the health condition of operation metro shield tunnel structure[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2018, 14(5): 1410-1418. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] 张冬梅, 刘印, 黄宏伟. 软土盾构隧道渗流引起的地层和隧道沉降[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 41(8): 1185-1190. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-374x.2013.08.011ZHANG D M, LIU Y, HUANG H W. Leakage-induced settlement of ground and shield tunnel in soft clay[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2013, 41(8): 1185-1190. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-374x.2013.08.011 [3] 邵华, 黄宏伟, 王如路. 上海运营地铁盾构隧道收敛变形规律研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2020, 16(4): 1183-1191.SHAO H, HUANG H W, WANG R L. Analysis on convergence deformation law of shield tunnel in Shanghai metro[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2020, 16(4): 1183-1191. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] PROTOPAPADAKIS E, VOULODIMOS A, DOULAMIS A, et al. Automatic crack detection for tunnel inspection using deep learning and heuristic image post-processing[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2019, 49(7): 2793-2806. doi: 10.1007/s10489-018-01396-y [5] KIM B, CHO S. Image-based concrete crack assessment using mask and region-based convolutional neural network[J]. Structural Control and Health Monitoring, 2019: e2381. doi: 10.1002/stc.2381 [6] XU Y, WEI S Y, BAO Y Q, et al. Automatic seismic damage identification of reinforced concrete columns from images by a region-based deep convolutional neural network[J]. Structural Control and Health Monitoring, 2019, 26(3): e2313. doi: 10.1002/stc.2313 [7] 朱付广, 徐东升, 谭瑞山, 等. 武汉地铁小洪山段隧道变形智能监测与分析[J]. 土木工程与管理学报, 2022, 39(2): 148-156.ZHU F G, XU D S, TAN R S, et al. Analysis of intelligent monitoring on tunnel deformation in Wuhan metro of Xiaohongshan section[J]. Journal of Civil Engineering and Management, 2022, 39(2): 148-156. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 杨光华, 黄致兴, 李志云, 等. 考虑侧向变形的软土地基非线性沉降计算的简化法[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2017, 39(9): 1697-1704.YANG G H, HUANG Z X, LI Z Y, et al. Simplified method for nonlinear settlement calculation in soft soils considering lateral deformation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 39(9): 1697-1704. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] 王飞, 薛哲敏, 黄宏伟. 盾构隧道收敛变形倾角感知布设优化研究[J]. 天津大学学报(自然科学与工程技术版), 2019, 52(增刊1): 63-69.WANG F, XUE Z M, HUANG H W. Layout optimization of tilt sensors for convergence monitoring in shield tunnel[J]. Journal of Tianjin University (Science and Technology), 2019, 52(S1): 63-69. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] 李斯. 盾构隧道下穿高铁路基沉降监测与预警[J]. 铁道建筑, 2023, 63(11): 127-130.LI S. Monitoring and early warning of subgrade settlement for high speed railway undercrossed by shield tunnel[J]. Railway Engineering, 2023, 63(11): 127-130. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] 宋新海. 盾构隧道施工地表沉降监测与Peck公式变形预测分析[J]. 铁道建筑技术, 2021(6): 11-16.SONG X H. Ground surface settlement monitoring and analysis on the deformation prediction by Peck formula in shield tunnel construction[J]. Railway Construction Technology, 2021(6): 11-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] 刘威, 朱鸿鹄, 王涛, 等. 基于分布式声波传感的大地探测技术研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 29-41. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0228LIU W, ZHU H H, WANG T, et al. Research progress of earth exploration technologies based on distributed acoustic sensing[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 29-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0228 [13] 吴迪, 梁泰铭, 吴静, 等. 基于MEMS传感器的滑坡监测算法设计与试验[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(6): 39-50. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20240214WU D, LIANG T M, WU J, et al. Design and experiment of landslide monitoring algorithm based on MEMS sensor[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(6): 39-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20240214 [14] 曾鹏, 张志强, 李天斌, 等. 隧道围岩收敛变形预测模型动态选择与变形量概率预测[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(6): 15-25. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20240187ZENG P, ZHANG Z Q, LI T B, et al. Dynamic selection of optimal tunnel convergence prediction model for a probabilistic deformation prediction[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(6): 15-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20240187 [15] 常乐. 城市地铁隧道基坑变形监测与分析[J]. 价值工程, 2023, 42(25): 156-158.CHANG L. Monitoring and analysis of foundation pit deformation of urban subway tunnel[J]. Value Engineering, 2023, 42(25): 156-158. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] 李纳. 上海越江公路隧道沉降及收敛变形监测研究[J]. 工程建设与设计, 2019(10): 107-108.LI N. Monitoring study on settlement and convergence deformation of river-crossing highway tunnel in Shanghai[J]. Construction & Design for Engineering, 2019(10): 107-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] 陈恺. 软土盾构隧道非达西渗流引起的沉降解析研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2023, 19(5): 1454-1461.CHEN K. Analytical solution for non-darcy flow induced settlement of shield tunnel in soft soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2023, 19(5): 1454-1461. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] 薛哲敏, 盾构隧道结构横向变形的无线感知方法及养护策略[D]. 上海: 同济大学, 2017XUE Z M. Wireless sensing method and maintenance strategy for lateral deformation of shield tunnel structure[D]. Shanghai: Tongji University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] LIN S S, ZHOU A N, SHEN S L. Multi-status Bayesian network for analyzing collapse risk of excavation construction[J]. Automation in Construction, 2024, 158: 105193. [20] LEE J, LEE Y, PARK S, et al. Implementing a digital twin of an underground utility tunnel for geospatial feature extraction using a multimodal image sensor[J]. Applied Sciences, 2023, 13(16): 9137. [21] HUANG H W, CHENG W, ZHOU M L, et al. Towards automated 3D inspection of water leakages in shield tunnel linings using mobile laser scanning data[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(22): 6669. [22] PAN R Y, DAN D H, YAN X F. Interval uncertainty identification and application of strain modes in bridge structures based on monitoring big data[J]. International Journal of Structural Stability and Dynamics, 2024: 2450277. [23] 张东明, 黄宏伟, 王飞, 等. 盾构隧道结构安全智慧感知技术研究[C]//中国土木工程学会. 中国土木工程学会2016年学术年会论文集. [出版地不详]: [出版社不详], 2016.ZHANG D M, HUANG H W, WANG F, et al. Research on smart sensing technology for safety of shield tunnel structures[C]//China Civil Engineering Society. Proceedings of the China Civil Engineering Society Annual Conference. [S. l. ]: [s. n. ], 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) -





 下载:
下载: