Infrasound early warning model for debris flow in a typical drainage basin in Beijing mountainous area
-
摘要:
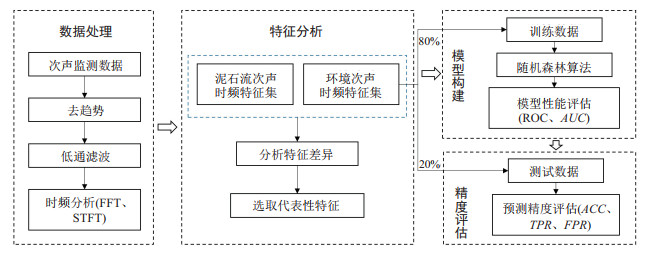
次声是泥石流监测预警的有效手段, 目前常用的阈值预警法仅考虑了个别次声时频特征, 容易造成误报和漏报。因此, 需综合考虑多种次声时频特征, 提升泥石流次声预警准确度。基于北京市草甸水村泥石流的次声监测数据, 分析了该流域泥石流次声和环境次声的时频特征差异, 并基于随机森林算法构建了泥石流次声识别模型。结果表明, 泥石流次声的有效声压为0.4~1.0 Pa, 环境次声的有效声压多低于0.1 Pa, 但噪音会引起声压上升至0.4 Pa以上; 噪音次声能量多集中在低于6 Hz的频段, 泥石流次声在6~15 Hz频段的能量明显高于噪音次声。因此, 泥石流次声的甄别需综合考虑时频域的多个特征, 重点是6~15 Hz频段对应的能量。基于随机森林算法, 以有效声压、6~15 Hz有效声压、短时过零率、主频、主频振幅为特征变量构建的泥石流次声识别模型
AUC 值为0.99, 对测试数据识别准确率为90.0%, 相比传统声压阈值法提升了15.0%。研究结果说明随机森林模型能够较为精准地甄别泥石流次声信号, 适用于北京山区的泥石流次声预警, 可为其他区域的泥石流次声预警研究提供参考。Abstract:Objective Infrasound is an effective approach for debris flow warning. Traditional threshold-based warning methods focus solely on individual infrasound characteristics, which can lead to false alarms or missed detections. Thus, incorporating multiple time-frequency characteristics is essential to improve warning accuracy.
Methods Infrasound data from Caodianshui Village, Beijing, were analyzed to differentiate the infrasound characteristics of debris flows from environmental background. A random forest algorithm was employed to establish an infrasound warning model for debris flows.
Results The effective pressure of debris flow infrasound ranges from 0.4 to 1.0 Pa, while environmental infrasound typical remains below 0.1 Pa, though noise can raise it above 0.4 Pa.Noise infrasound energy is primarily concentrated below 6 Hz, whereas debris flow infrasound exhibits significantly higher energy in the 6-15 Hz. Therefore, comprehensive time-frequency characteristics, especially the energy in the range of 6-15 Hz, should be considered when identifying debris flow infrasound. Using effective infrasound pressure, infrasound pressure within 6-15 Hz, zero crossing rate, dominant frequency, and its amplitude as characteristic variables, a debris flow warning model was constructed based on a random forest algorithm. The model achieved an
AUC of 0.99, with a 90% recognition accuracy for test data, a 15% improvement over threshold methods.Conclusion The random forest-based infrasound warning model substantially improves warning accuracy for debris flows and is applicable to typical basins in the Beijing mountainous areas. This approach offers a valuable reference for infrasound-based debris flow warning research in other areas.
-
表 1 次声传感器技术参数
Table 1. Technical parameters of the infrasound sensor
序号 参数类型 参数值 1 采样频率/Hz 50 2 频率响应范围/Hz 1~25 3 灵敏度/(mV·Pa-1) 50 4 动态上线范围/Pa 100 5 传感器本底噪声/dBa < 16 表 2 次声时频特征部分样本数据
Table 2. Partial sample data of infrasound time-frequency characteristics
样本序号 短时过零率/% 有效声压/Pa 6~15 Hz频段有效声压/Pa 主频/Hz 主频振幅/Pa 是否为泥石流次声 1 31.75 0.56 0.35 6.24 0.32 1(是) 2 39.68 0.48 0.25 5.46 0.16 1(是) 3 26.98 0.65 0.24 2.34 0.46 0(否) 4 36.51 0.11 0.07 1.56 0.06 0(否) 5 28.57 0.03 0.01 0.78 0.02 0(否) 表 3 随机森林算法和声压阈值法的混淆矩阵
Table 3. Confusion matrixes of random forest algorithm and pressure threshold method
随机森林算法 真实值 泥石流次声 非泥石流次声 预测值 泥石流次声 6 2 非泥石流次声 0 12 声压阈值法 真实值 泥石流次声 非泥石流次声 预测值 泥石流次声 6 5 非泥石流次声 0 9 注:表中数据为对应类别的样本数目 -
[1] 张楠, 方志伟, 韩笑, 等. 近年来我国泥石流灾害时空分布规律及成因分析[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(2): 299-308.ZHANG N, FANG Z W, HAN X, et al. The study on temporal and spatial distribution law and cause of debris flow disaster in China in recent years[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2018, 25(2): 299-308. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] JAKOB M, HUNGR O. Debris-flow hazards and related phenomena[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2005. [3] BADOUX A, GRAF C, RHYNER J, et al. A debris-flow alarm system for the Alpine Illgraben catchment: Design and performance[J]. Natural Hazards, 2009, 49(3): 517-539. doi: 10.1007/s11069-008-9303-x [4] KOGELNIG A, HVBL J, SURIÑACH E, et al. Infrasound produced by debris flow: Propagation and frequency content evolution[J]. Natural Hazards, 2014, 70(3): 1713-1733. doi: 10.1007/s11069-011-9741-8 [5] DOWLING C A, SANTI P M. Debris flows and their toll on human life: A global analysis of debris-flow fatalities from 1950 to 2011[J]. Natural Hazards, 2014, 71(1): 203-227. doi: 10.1007/s11069-013-0907-4 [6] HVBL J, ZHANG S C, KOGELNIG A. Infrasound measurements of debris flow[J]. WIT Transactions on Engineering Sciences, 2008: 3-12. [7] MARCHETTI E, WALTER F, BARFUCCI G, et al. Infrasound array analysis of debris flow activity and implication for early warning[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 2019, 124(2): 567-587. doi: 10.1029/2018JF004785 [8] LIU D L, LENG X P, WEI F Q, et al. Monitoring and recognition of debris flow infrasonic signals[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2015, 12(4): 797-815. doi: 10.1007/s11629-015-3471-4 [9] 章书成, 余南阳. 泥石流次声波警报器DFW-Ⅰ Ⅲ型简介[J]. 山地学报, 2008(4): 2.ZHANG S C, YU N Y. Mud-rock flow infrasonic alarm DFW-Ⅰ Ⅲ introduction[J]. Mountain Research, 2008(4): 2. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] CHOU H T, CHANG Y L, ZHANG S C, et al. Calibration of infrasound monitoring system and acoustic characteristics of debris-flow movement by field studies[C]//Anon. 4th International Conference on Debris-Flow Hazards Mitigation-Mechanics, Prediction and Assessment. [S. l. ]: [s. n. ], 2007: 571-580. [11] CHOU H T, CHANG Y L, ZHANG S C. Acoustic signals and geophone response of rainfall-induced debris flows[J]. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, 2013, 36(3): 335-347. doi: 10.1080/02533839.2012.730269 [12] 胡至华. 泥石流声波信号特征与类型识别[D]. 成都: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院水利部成都山地灾害与环境研究所), 2020.HU Z H. Characteristics and type identification of debris flow acoustic signal[D]. Chengdu: Institution of Mountain Hazards and Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) [13] 赵星, 李龙, 李禹霏, 等. 泥石流自动化监测预警技术的应用: 以贵州省望谟县望谟河泥石流为例[J]. 工程地质学报, 2014, 22(3): 443-449.ZHAO X, LI L, LI Y F, et al. Application of early warning technology to automatic monitoring of debris-flow: A case study of Wangmo River debris flow in Wangmo County, Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2014, 22(3): 443-449. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] 李朝安, 王良玮, 廖凯, 等. 山区铁路沿线泥石流灾害预警研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2014, 33(增刊2): 3810-3816.LI C A, WANG L W, LIAO K, et al. Study of early warning mechanism of debris flow along railway line in mountainous areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(S2): 3810-3816. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 周铭. 不同形态泥石流地声与次声特性比较研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2014.ZHOU M. Research on the characteristic of ground vibrations and infrasound produced by different types of debris flows[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] 胡雨豪, 袁路, 马东涛, 等. 泥石流次声警报研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2018, 33(6): 606-613.HU Y H, YUAN L, MA D T, et al. Research progress on debris flow infrasound warning[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2018, 33(6): 606-613. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] 黄发明, 李金凤, 王俊宇, 等. 考虑线状环境因子适宜性和不同机器学习模型的滑坡易发性预测建模规律[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(2): 44-59. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0010HUANG F M, LI J F, WANG J Y, et al. Modelling rules of landslide susceptibility prediction considering the suitability of linear environmental factors and different machine learning models[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 44-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0010 [18] 赵玉, 陈丽霞, 梁梦姣. 基于LSTM_TCN模型的降雨型滑坡时间概率预测及气象预警建模[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(2): 201-214. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220657ZHAO Y, CHEN L X, LIANG M J. Temporal probability prediction and meteorological early warning modeling of rainfall-induced landslide based on LSTM_TCN model[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(2): 201-214. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220657 [19] 邓日朗, 张庆华, 刘伟, 等. 基于改进两步法采样策略和卷积神经网络的崩塌易发性评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(2): 186-200. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220535DENG R L, ZHANG Q H, LIU W, et al. Collapse susceptibility evaluation based on an improved two-step sampling strategy and a convolutional neural network[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(2): 186-200. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220535 [20] 刘艳辉, 黄俊宝, 肖锐铧, 等. 基于随机森林的福建省区域滑坡灾害预警模型研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2022, 30(3): 944-955.LIU Y H, HUANG J B, XIAO R H, et al. Study on early warning model for regional landslides based on random forest in Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2022, 30(3): 944-955. (in Chinese with English abstract) [21] 翟淑花, 于家烁, 程素珍, 等. 北京山区暴雨泥石流预警模型研究[J]. 人民长江, 2021, 52(3): 16-20.ZHAI S H, YU J S, CHENG S Z, et al. Research on early warning of storm debris flow in Beijing mountain area[J]. Yangtze River, 2021, 52(3): 16-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) [22] 王颖, 李新森, 付钰涵, 等. 北京山区泥石流灾害预警模型及应用效果[J]. 国土资源信息化, 2021(5): 58-62.WANG Y, LI X S, FU Y H, et al. The key technology research of meteorological early warning for debris flow disaster in the mountainous areas in Beijing based on GIS[J]. Land and Resources Informatization, 2021(5): 58-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] 陈文鸿, 余斌, 柳清文, 等. 北京山区泥石流激发降雨特征及其临界值[J]. 人民长江, 2021, 52(4): 27-33.CHEN W H, YU B, LIU Q W, et al. Characteristics and threshold of rainfall triggering debris flow in Beijing mountainous area[J]. Yangtze River, 2021, 52(4): 27-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] HEIDEMAN M T, JOHNSON D H, BURRUS C S. Gauss and the history of the fast Fourier transform[J]. Archive for History of Exact Sciences, 1985, 34(3): 265-277. [25] SEJDI Ĉ E, DJUROVIĈ I, JIANG J. Time-frequency feature representation using energy concentration: An overview of recent advances[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2009, 19(1): 153-183. [26] BREIMAN L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1): 5-32. [27] SNOEK J, LAROCHELLE H, ADAMS R P. Practical Bayesian optimization of machine learning algorithms[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. [ S. l. ]: [s. n. ], 2012. -





 下载:
下载: