Hydrogeochemical characteristics and genesis of Jiusuo geothermal field in southwestern Hainan, China
-
摘要:
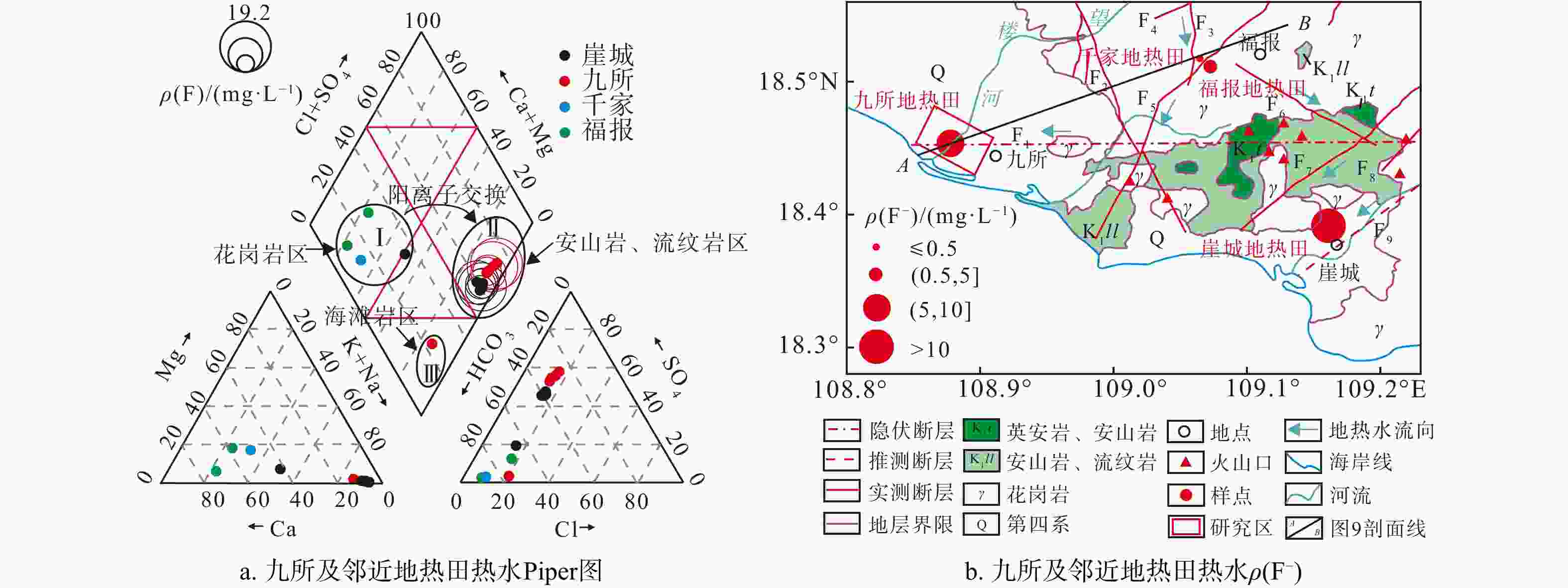
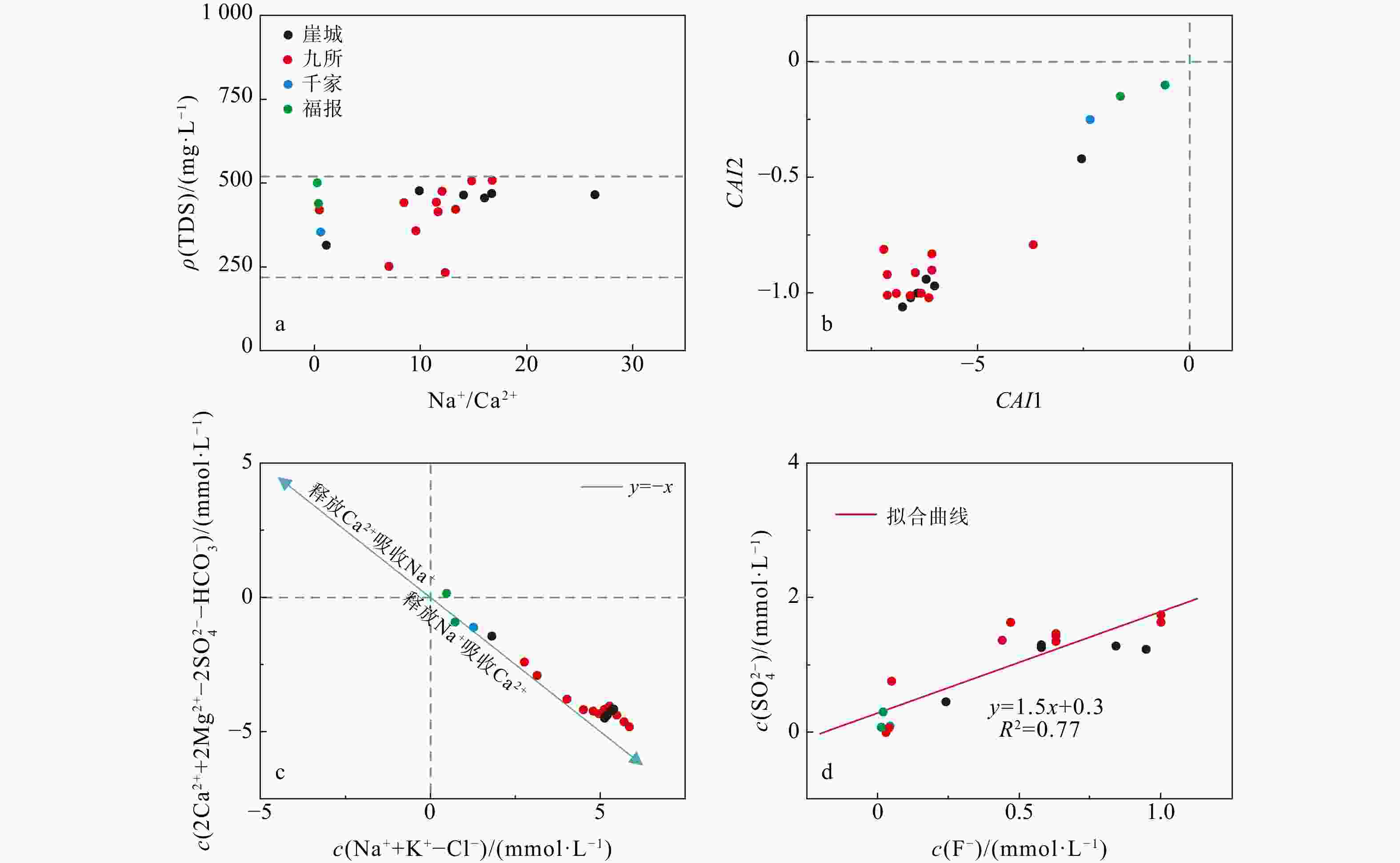
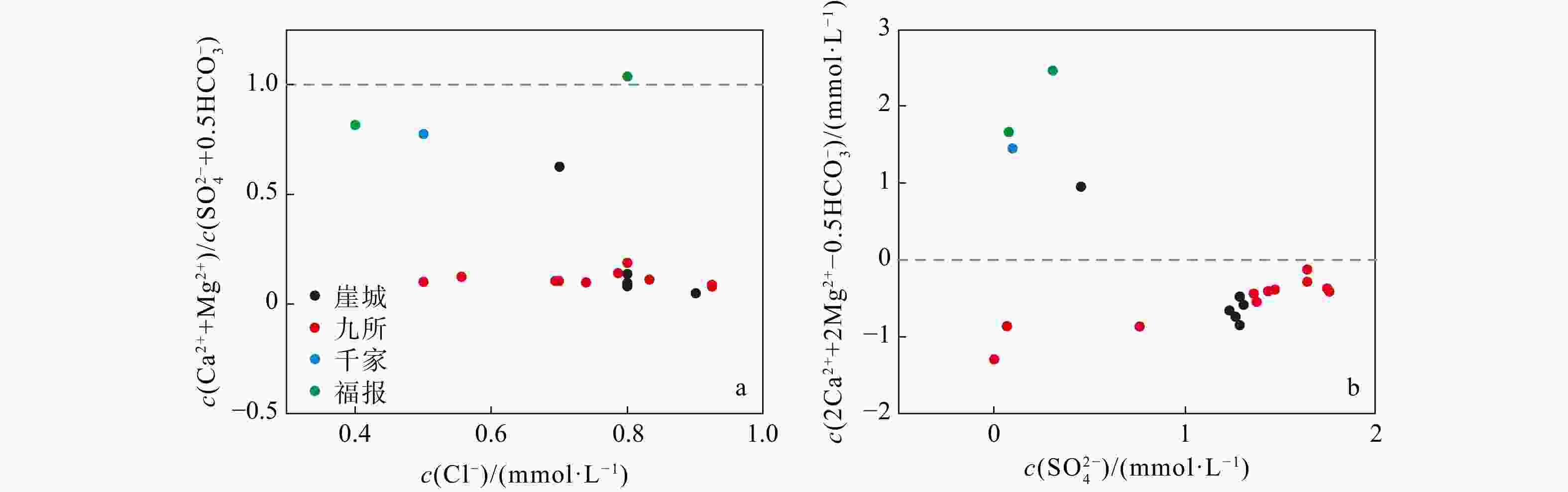
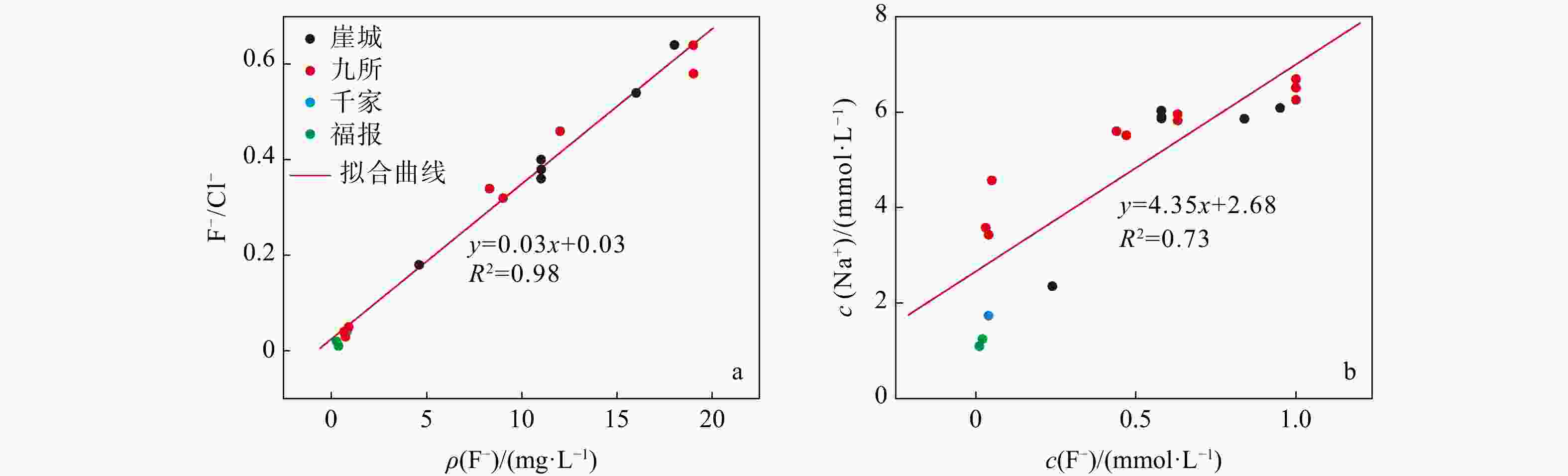
海南岛地热资源丰富,以往的地热勘查大多停留在生产层面,而对地热水化学成分的来源、水-岩作用、多方法评价热储温度和地热田成因机制等未深入研究。基于前人资料的深入分析,可以加深对成因机制的认识,为地热田开发提供参考。利用离子的比值及相关性、Piper图、F−浓度分布图、硅-焓图解与SiO2混合模型和硅-焓方程法,探讨了九所地热田热水化学组分的来源、阳离子交换、F−成因、热储温度和循环深度,提出了成因概念模型。结果显示:热水化学类型为SO4·HCO3-Na 型;SO42−主要源于安山岩、流纹岩区硫化物氧化;含F矿物溶解、离子交换是F−浓度的控制因素;热储温度99~169℃,冷水混合比例80%~93%,冷、热水混合前蒸汽损失的质量分数约10%;循环深度1.8~3.8 km。概念模型揭示:热水沿构造运移,从花岗岩区流向安山岩、流纹岩区,同时汲取热能,发生矿物溶滤和离子交换,导致F−、SO42−等组分浓度改变,引起水化学类型演化,在水力差和浮力差双重驱动下上升,于地下浅部与孔隙冷水混合存储于沉积盖层之下形成地热田。关于琼西南地热田的热源是否存在幔源热的问题目前没有充分证据,需进一步深入研究。
Abstract:Hainan Island harbors abundant geothermal resources. However, previous geothermal explorations have focused primarily on production, overlooking critical research areas such as the origins of geothermal water chemistry, water-rock interactions, methods for evaluating thermal reservoir temperatures, and mechanisms of geothermal field formation.
Objective This study leverages existing exploration data to deepen our understanding of the genetic mechanism of geothermal fields and to offer valuable insights for their development.
Methods We employed a range of analytical techniques, including major ion ratios and correlations, Piper diagrams, fluoride concentration maps, silicon-enthalpy and SiO2 mixing model graphs, silicon-enthalpy equations, and water
δ D andδ 18O values. Focusing on the geothermal water of Jiusuo, we investigated the sources of chemical components, the cation exchange processes, the origin of F− events, the most likely reservoir temperatures, and the circulation depths of geothermal water, ultimately proposing a conceptual model explaining the genesis of the field.Results The results indicate that the hydrochemistry of geothermal water is mainly characterized by SO4·HCO3-Na type, with Ca2+ and Mg2+ replacing Na+ and K+ in the rock. The primary source of SO42− is the sulfide oxidation of andesite and rhyolite. The fluoride concentration is regulated by the dissolution of minerals such as mica, amphibole, and fluorite, along with ion exchange and alkaline environments. The chemical composition is predominantly shaped by silicate mineral dissolution, ion exchange, and the degree of development of geological strata and structures. Most likely, when mixed with cold groundwater, the temperature range of geothermal water in this area falls to 99℃-169℃, with cold groundwater contributing 80% to 93% of the mix and approximately 10% steam loss prior to mixing. The circulation depth of geothermal water ranges from 1.8 to 3.8 km.
Conclusion The proposed conceptual model suggests that the geothermal water in the Jiusuo geothermal field originates from rainfall recharge and flows under the control of the Furongtian-Wangxia structural belt, Ledong-Xichang structural belt, and Jiusuo-Lingshui deep large fault belt. The water flows from the granite areas to the andesite and rhyolite areas, where it absorbs heat from both radioactive decay in granite and potential minor mantle-derived thermal energy. This process leads to silicate mineral dissolution, cation exchange, and sulfide oxidation, resulting in increased concentrations of fluoride ions (F−), sulfate ions (SO42−), and other chemical components in water. These processes cause an evolution in water chemical types. Owing to the increase in temperature, the density and viscosity of geothermal water decrease, and the pressure increases, generating buoyancy. Driven by both the hydraulic gradient and buoyancy gradient, geothermal water ascends along the Jiusuo-Lingshui deep large fault belt and rock fractures in the subsurface. It then mixes with cold groundwater near the surface before being embedded in the Quaternary and Tertiary sedimentary layers, ultimately forming a geothermal field. While mantle-derived thermal energy's presence in the deep region of geothermal fields in southwestern Hainan remains unconfirmed, it presents an intriguing scientific question meriting further investigation.
-
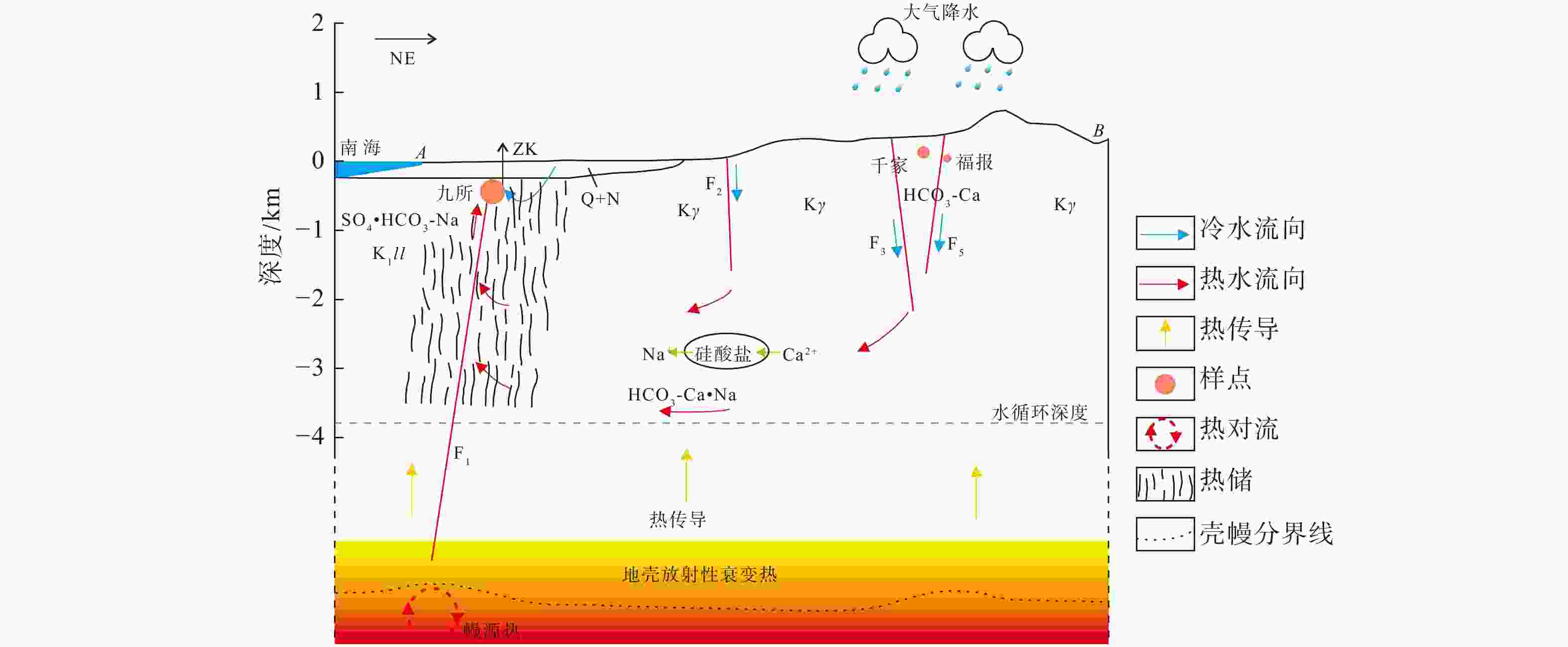
图 9 九所地热系统概念模型
剖面线A-B位置见图2b;ZK为钻孔;N+Q为新近系和第四系沉积地层;Kγ为白垩纪花岗岩;F1为九所-陵水断裂带;F2为石门山断裂带;F3为芙蓉田-王下构造带;F5为乐东-西昌断裂带;样点大小表示ρ(F−)大小。
Figure 9. A conceptual model of the Jiusuo geothermal system
表 1 九所及邻近地热田水化学参数表
Table 1. Hydrochemical parameters of geothermal fields in Jiusuo and neighboring areas
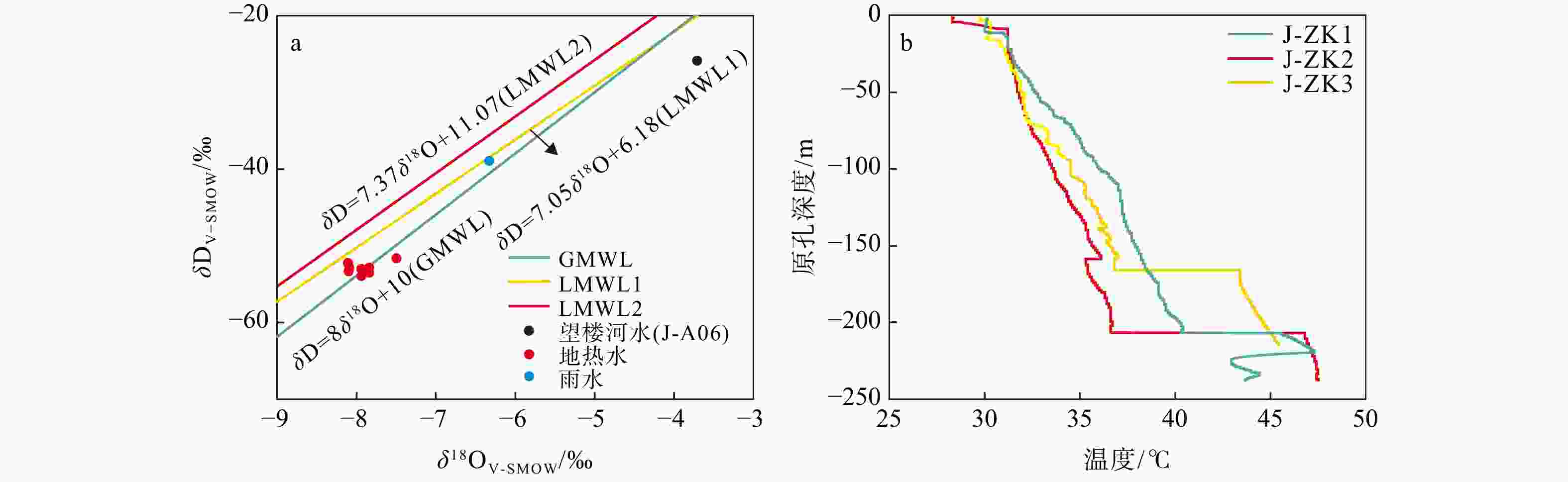
地热田 样品编号 K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO42− CO32− HCO3− NO3− F− ρB/(mg·L−1) 千家 Q-ZK1 3.2 40.1 57.3 11.8 19.4 8.9 0.0 290.0 4.8 0.8 福报 F-ZK2 2.9 25.4 75.4 4.0 15.9 7.3 0.0 296.0 <0.2 0.3 F-ZK4 1.1 28.8 63.4 12.1 28.7 29.3 16.0 207.0 5.0 0.4 崖城 Y-8 3.9 135.0 8.9 0.5 30.2 123.0 16.0 133.0 1.6 11.0 Y-1 3.4 136.0 7.4 0.3 27.2 121.0 11.0 138.0 1.4 11.0 Y-7 3.5 139.0 8.6 0.4 28.7 125.0 16.0 127.0 0.3 11.0 Y-ZK1 3.6 140.0 7.3 0.4 28.2 118.0 15.0 128.0 0.6 18.0 Y-ZK2 6.1 54.2 42.1 4.4 25.1 43.4 9.8 184.0 2.1 4.6 Y-ZK3 5.0 135.0 11.9 0.9 29.5 123.0 20.0 139.0 <0.2 16.0 九所 J-B03 2.9 79.1 9.8 0.9 26.6 6.2 15.0 173.0 2.1 0.7 J-B05 1.4 82.4 5.9 0.6 17.2 <0.2 5.0 198.0 2.7 0.7 J-A04 1.7 134.0 9.3 0.4 26.2 137.0 9.4 110.0 <0.2 12.0 J-ZK1a 1.8 129.0 9.6 0.5 24.6 132.0 14.0 129.0 1.4 8.3 J-ZK1b 2.0 134.0 9.0 0.4 26.2 141.0 19.0 105.0 6.3 12.0 J-ZK2a 2.5 104.0 9.5 0.9 19.7 73.2 14.0 172.0 8.6 0.9 J-ZK2b 2.0 137.0 8.4 0.6 26.2 130.0 19.0 110.0 4.4 12.0 J-ZK2c 3.0 154.0 9.0 0.5 32.8 166.0 14.0 110.0 3.3 19.0 J-ZK3a 2.9 127.0 13.0 0.7 27.9 157.0 9.4 101.0 5.0 9.0 J-ZK3b 2.1 144.0 10.5 0.4 29.5 157.0 14.0 101.0 3.3 19.0 J-ZK3c 3.4 150.0 7.7 0.4 32.8 167.0 14.0 96.7 5.4 19.0 地热田 样品编号 温度/°C pH TDS SiO2 修正SiO2 δ18OV-SMOW/‰ δDV-SMOW/‰ 水化学类型 ρB/(mg·L−1) 千家 Q-ZK1 42 8.21 354 — — — — HCO3-Ca·Na 福报[17] F-ZK2 47 7.56 502 — — — — HCO3-Ca F-ZK4 35 8.39 440 — — — — HCO3-Ca 崖城[7] Y-8 55 7.00 466 — — — — SO4·HCO3-Na Y-1 50 8.10 457 — — — — SO4·HCO3-Na Y-7 57 8.09 465 — — — — SO4·HCO3-Na Y-ZK1 58 8.46 470 — — — — SO4·HCO3-Na Y-ZK2 34 8.35 315 — — — — SO4·HCO3-Na Y-ZK3 46 8.14 477 — — — — SO4·HCO3-Na 九所 J-B03 35 8.43 252 21.6 — — — HCO3-Na J-B05 36 8.96 234 18.8 — — — HCO3-Na J-A04 44 8.72 420 34.2 29.7 −7.84 −53.5 SO4·HCO3-Na J-ZK1a 45 8.72 415 27.5 23.6 −7.84 −52.8 SO4·HCO3-Na J-ZK1b 45 8.81 444 35.7 29.9 −7.86 −53.2 SO4·HCO3-Na J-ZK2a 39 8.85 359 30.6 — −7.50 −51.6 HCO3·SO4-Na J-ZK2b 40 8.85 422 24.3 20.5 −7.94 −53.0 SO4·HCO3-Na J-ZK2c 41 8.73 507 49.3 43.1 −8.09 −52.8 SO4·HCO3-Na J-ZK3a 42 8.68 443 29.4 — −7.94 −53.9 SO4·HCO3-Na J-ZK3b 42 8.71 476 45.4 39.7 −8.10 −53.3 SO4·HCO3-Na J-ZK3c 38 8.75 509 57.5 50.5 −8.11 −52.2 SO4·HCO3-Na J-A06(望楼河) 28 7.01 131 45.2 — −3.71 −25.8 — 雨水 — — — — — −6.33 −38.9 — 注:J-ZK1a、J-ZK1b,J-ZK2a、J-ZK2b、J-ZK2c,J-ZK2c、J-ZK3a、J-ZK3b、J-ZK3c分别为钻孔ZK1、ZK2和ZK3不同深度水样 表 2 硅-焓图解与二氧化硅混合模型绘图数据
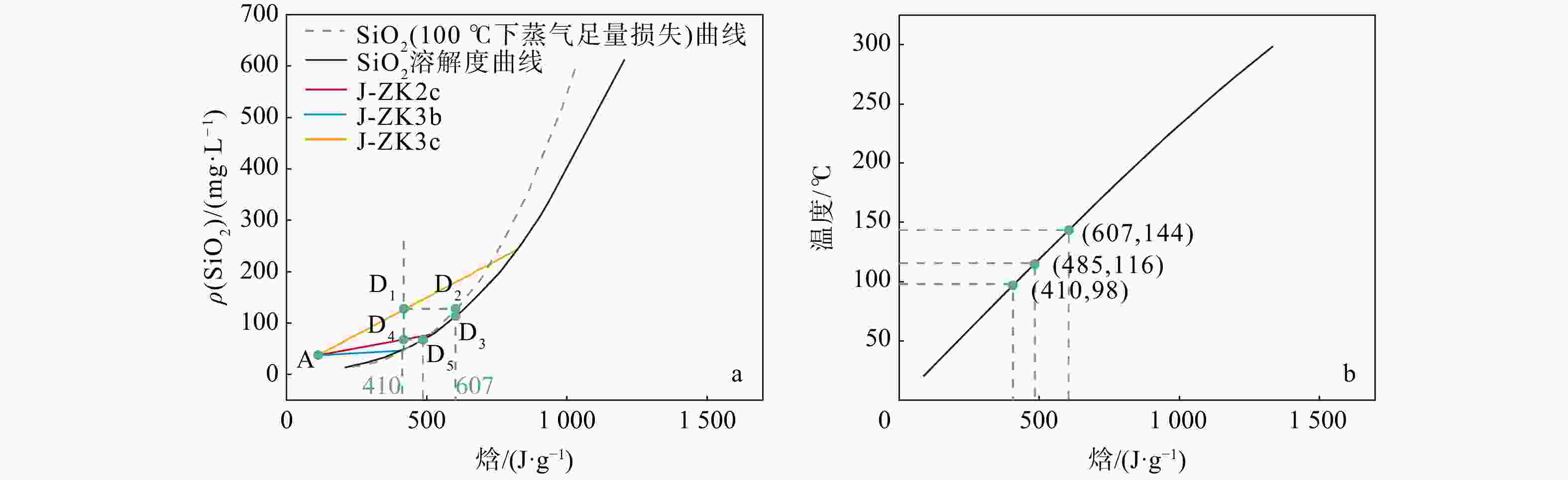
Table 2. Mapping data for silicon-enthalpy diagram with silica mixing model
ρ(SiO2)/
(mg·L−1)[37]焓/
(J·g−1)[37]T/°C 100°C下蒸气足量
损失的焓/(J·g−1)点编号 修正后焓/
(J·g−1)修正后ρ(SiO2)/
(mg·L−1)13.5 209.3 56.3 234.4 A 115.0 37.9 26.6 314.0 78.8 330.7 D1 419.0 127.5 48.0 419.1 100.9 423.3 D2 607.0 127.5 80.0 525.0 122.5 514.4 D3 607.0 115.0 125.0 632.2 143.5 604.3 D4 419.0 68.0 185.0 741.1 163.9 693.0 D5 485.0 68.0 265.0 852.4 184.4 780.9 — — — 365.0 966.7 204.3 870.4 — — — 486.0 1085.2 223.7 962.0 — — — 614.0 1210.0 240.7 1042.0 — — — 表 3 不同方法计算的热储温度
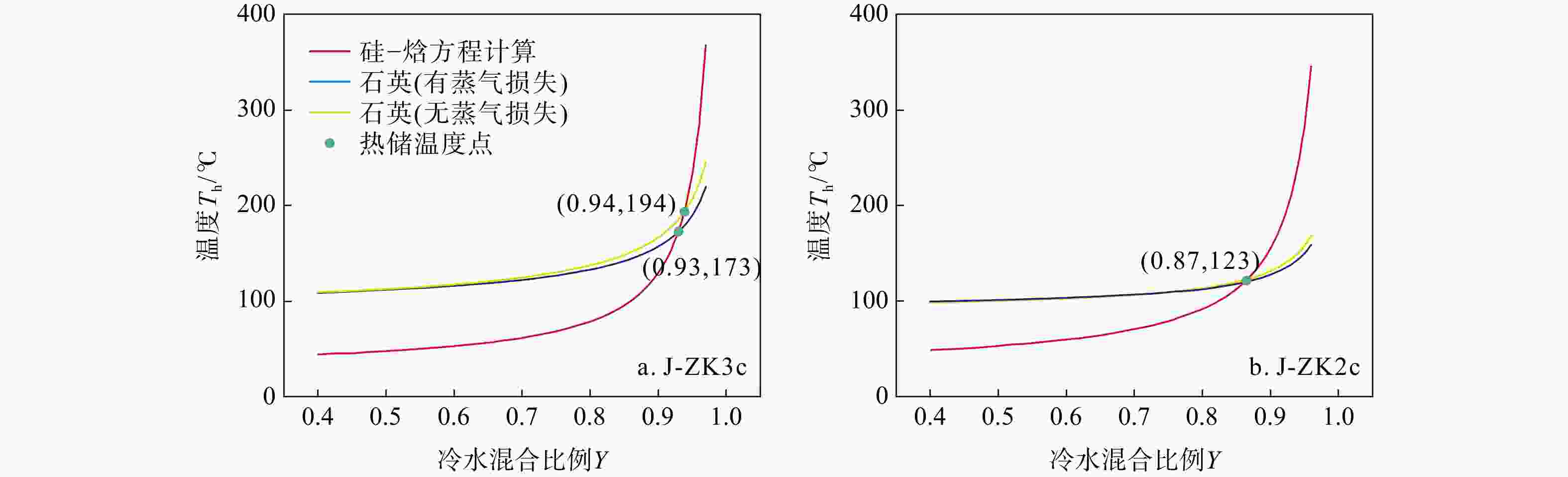
Table 3. Temperature of geothermal reservoir calculated by different methods
样品编号 硅-焓方程法热储
温度/℃冷水混入比例
(硅-焓方程)硅-焓图解与SiO2混合
模型热储温度/℃冷水混入比例
(混合模型)最可能的热储
温度均值/℃冷水混入
比例均值J-ZK2c 123 0.87 116 0.85 120 0.86 J-ZK3b 99 0.80 98 0.79 99 0.80 J-ZK3c 194 0.94 144 0.91 169 0.93 均值 139 0.87 119 0.85 129 0.86 -
[1] HU H Y,LU G P,LU Q Y,et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and geothermometry of hot springs in the tensile tectonic region Leizhou Peninsula and Hainan Island in South China[J]. Geofluids,2022(1):1-21. [2] 卫兴,师红杰,陈松,等. 水文地球化学方法在地热勘查中的应用:以湖北省应城市为例[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(3):68-80.WEI X,SHI H J,CHEN S,et al. Application of hydrogeo- chemical methods in geothermal resource exploration:A case study of Yingcheng City,Hubei Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(3):68-80. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] BA J J,SU C T,LI Y Q,et al. Characteristics of heat flow and geothermal fields in Ruidian,western Yunnan Province,China[J]. International Journal of Heat and Technology,2018,36(4):1203-1211. doi: 10.18280/ijht.360407 [4] 王云. 滇东南地热流体地球化学特征研究[D]. 北京:中国地震局地球物理研究所,2021.WANG Y. A research on geochemical characteristics of geothermal fluids in southeast Yunnan Province,China[D]. Beijing:Institute of Geophysics,China Earthquake Administration,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 路畅,周晓成,李营,等. 玛多Ms7.4地震地表破裂带与东昆仑断裂带温泉的水文地球化学特征[J]. 地震地质,2021,43(5):1101-1126.LU C,ZHOU X C,LI Y,et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater in the surface rupture zone of Madoi Ms7.4 earthquake and hot springs in the east Kunlun fault[J]. Seismology and Geology,2021,43(5):1101-1126. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] FOURIER R O,ROWE J J. Estimation of underground temperatures from the silica content of water from hot springs and wet-steam wells[J]. American Journal of Science,1966,264:685-697. [7] 王文梅,徐子东,欧阳正平,等. 海南省三亚市崖城地热田地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 工程勘察,2017(10):38-45.WANG W M,XU Z D,OUYANG Z P,et al. Analysis of geochemical characteristics and formation reasons of Yacheng geothermal field in Sanya of Hainan Province[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying,2017(10):38-45. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 徐单. 海南省龙沐湾地热田的水文地球化学研究[D]. 南昌:东华理工大学,2017.XU D. Hydrogeochemistry of geothermal field of Longmu Bay,Hainan Province[D]. Nanchang:East China University of Technology,2017. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 高芳蕾,杨小强,吴爱国,等. 海南岛温泉特征与地下热水成因[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2009,39(2):281-287.GAO F L,YANG X Q,WU A G,et al. Characteristics of thermal springs and genesis of thermal underground water Hainan Island[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2009,39(2):281-287. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 张颖. 海南岛温泉特征及成因研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2019.ZHANG Y. A study of the characteristics and formation of the hot springs in Hainan Island[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences(Beijing),2019. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 袁晓博,方念乔,董海龙. 海南岛高峰、保城地区花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 现代地质,2019,33(1):85-97.YUAN X B,FANG N J,DONG H L. Geochronology,geochemistry and tectonic significance of Gaofeng and Baocheng granite batholiths in Hainan Island[J]. Geoscience,2019,33(1):85-97. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 汪啸风,马大铨,蒋大海,等. 海南岛地质之三构造地质[M]. 北京:地质出版社,1991.WANG X F,MA D Q,JIANG D H,et al. The geology of Hainan Island(3):Tectonic geology [M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House,1991. (in Chinese) [13] 梁定勇,许国强,肖瑶,等. 海口江东新区新近纪-第四纪标准地层与组合分区[J]. 科学技术与工程,2021,21(26):11053-11063.LIANG D Y,XU G Q,XIAO Y,et al. Neogene-Quaternary stratigraphic standard and combined zoning of Haikou Jiangdong New District[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2021,21(26):11053-11063. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 陈哲培,钟盛中,何圣华,等. 海南省岩石地层[M]. 武汉:中国地质大学出版社,1997.CHEN Z P,ZHONG S Z,HE S H,et al. Petrostratigraphy in Hainan Province[M]. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences Press,1997. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 钱会,马致远,李培月. 水文地球化学[M]. 北京:地质出版社,2012.QIAN H,MA Z Y,LI P Y. Hydrogeochemistry[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House,2012. (in Chinese) [16] 王贵玲,蔺文静,张薇,等. 中国地热志(华南卷)[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2022.WANG G L,LIN W J,ZHANG W,et al. Geothermal atlas of China (South China)[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2022. (in Chinese) [17] 王江思,欧阳正平,徐子东,等. 基于水文地球化学信息和环境同位素的地下热水成因分析[J]. 地球与环境,2018,46(1):7-13.WANG J S,OUYANG Z P,XU Z D,et al. Geothermal water genesis analysis using hydrogeochemical information and environmental isotopes[J]. Earth and Environment,2018,46(1):7-13. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] HE P,ZHANG H R,LI S H,et al. Geological and hydrochemical controls on water chemistry and stable isotopes of hot springs in the Three Parallel Rivers region,southeast Tibetan Plateau:The genesis of geothermal waters[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2024,906(1):1-13. [19] 王晨光,郑绵平,张雪飞,等. 西藏南部古堆高温地热田水化学特征及其成因研究[J]. 地质学报,2024,98(2):558-578.WANG C G,ZHENG M P,ZHANG X F,et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and origin of geothermal fluids in the Gudui high-temperature geothermal system in Comei County,southern Tibet[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2024,98(2):558-578. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 陶兰初,朱星强,张七道,等. 滇东富源古敢水族乡热水塘锶-氟-硅-氡型理疗热矿水的地球化学特征及成因[J]. 地质评论,2023,69(3):959-972.TAO L C,ZHU X Q,ZHANG Q D,et al. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of Sr-F-Si-Rn physiotherapy hot mineral water of reshuitang in Gugan Shui Nationality Township,Fuyuan County,eastern Yunnan[J]. Geological Review,2023,69(3):959-972. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 祁士华. 地热地球化学勘查[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2021.QI S H. Geothermal geochemical exploration[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2021. (in Chinese) [22] 王贝贝,卢国平,胡晓农,等. 粤西深大断裂温热泉水化学分析[J]. 环境化学,2019,38(5):1150-1160.WANG B B,LU G P,HU X N,et al. Hydrochemical characterization of the thermal spring waters in the deep fault region in western Guangdong[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2019,38(5):1150-1160. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] LI D N,GAO X B,WANG Y X,et al. Diverse mechanisms drive fluoride enrichment in groundwater in two neighboring sites in northern China[J]. Environmental Pollution,2018,237:430-441. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.02.072 [24] 李明礼,多吉,王祝,等. 西藏日多温泉水化学特征及其物质来源[J]. 中国岩溶,2015,34(3):209-216.LI M L,DUO J,WANG Z,et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and material sources of the Riduo thermal spring in Tibet[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2015,34(3):209-216. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 章旭,郝红兵,刘康林,等. 西藏沃卡地堑地下水水文地球化学特征及其形成机制[J]. 中国地质,2020,47(6):1702-1714. doi: 10.12029/gc20200608ZHANG X,HAO H B,LIU K L,et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and genetic model of Oiga Graben geothermal waters system in Tibet[J]. Geology in China,2020,47(6):1702-1714. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12029/gc20200608 [26] 李义曼,罗霁,陈凯,等. 广东省丰良地热田高氟地热流体成因及热储温度评价[J]. 地质评论,2023,69(4):1337- 1348.LI Y M,LUO J,CHEN K,et al. Genesis of geothermal fluid with high fluorine content and reservoir temperature assessment in Fengliang geothermal field,eastern Guangdong[J]. Geological Review,2023,69(4):1337-1348. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 许金昭,刘桂建,司雯,等. 安徽涡河流域水化学与同位素特征及水体转化关系[J]. 环境科学,2024,45(6):3196- 3204.XU J Z,LIU G J,SI W,et al. Hydrochemical and stable isotopic characteristics and transformation relationship of water bodies in the Guohe River Basin,Anhui Province [J]. Environmental Science,2024,45(6):3196-3204. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] NDOYE S,FONTAIN C,GAYE C B,et al. Groundwater quality and suitability for different uses in the Saloum area of Senegal[J]. Water,2018,10:1-20. [29] LUO J,LI Y M,TIAN J,et al. Geochemistry of geothermal fluid with implications on circulation and evolution in Fengshun-Tangkeng geothermal field,South China[J]. Geothermics,2022,100:1-14. [30] 潘欢迎,邹常健,毕俊擘,等. 新疆阿克苏典型山前洪积扇内高氟地下水的化学特征及氟富集机制[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(3):194-203.PAN H Y,ZOU C J,BI J B,et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and fluoride enrichment mechanisms of high-fluoride groundwater in a typical piedmont proluvial fan in Aksu area,Xinjiang,China[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(3):194-203. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] 刘英俊,曹励明,李兆麟,等. 元素地球化学[M]. 北京:科学出版社,1984.LIU Y J,CAO L M,LI Z L,et al. Elementary geochemistry [M]. Beijing:Science Press,1984. (in Chinese) [32] 叶海龙,樊柄宏,白细民,等. 石城地热带水文地球化学特征与成因分析[J]. 地质学报,2023,97(1):238-249. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2023.01.016YE H L,FAN B H,BAI X M,et al. Analysis of hydrogeo-chemical characteristics and origin in the Shicheng geothermal belt[J]. Acta Geological Sinica,2023,97(1):238-249. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2023.01.016 [33] 梁礼革,朱明占,朱思萌,等. 桂东地区地热水中氟的分布及其富集过程研究[J]. 安全与环境工程,2015,22(1):1-6.LIANG L G,ZHU M Z,ZHU S M,et al. Spatial distribution and enrichment of fluoride in geothermal water from eastern Guangxi,China[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2015,22(1):1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] GIZAW B. The origin of high bicarbonate and fluoride concentration in waters of the Main Ethiopian Rift Valley,East African Rift System[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences,1996,22(4):391-402. doi: 10.1016/0899-5362(96)00029-2 [35] 郑西来,郭建青. 二氧化硅地热温标及其相关问题的处理方法[J]. 地下水,1993,18(2):85-88.ZHENG X L,GUO J Q. The treatment of silica geothermometer and its related problems[J]. Groundwater,1993,18(2):85-88. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] 汪集旸,熊亮萍,庞忠和. 中低温对流型地热系统[M]. 北京:科学出版社,1993.WANG J Y,XIONG L P,PANG Z H. Medium-low temperature convective geothermal system[M]. Beijing:Science Press,1993. (in Chinese) [37] 宋红利,杨宇,李海福,等. 基于硅-焓混合模型热储温度估算方法[J],天然气勘探与开发,2021,44(3):112-117.SONG H L,YANG Y,LI H F,et al. Methods to estimate the temperature in geothermal reservoirs based on the silicon-enthalpy hybrid model[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development,2021,44(3):112-117. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] 严家禄,余晓福,王永青. 水和水蒸气性质图表[M]. 北京:高等教育出版社,2004.YAN J L,XU X F,WANG Y Q. Thermodynamic property tables and diagram for water and steam[M]. Beijing:Higher Education Press,2004. (in Chinese) [39] 张彦鹏,黎清华,余绍文. 海南岛东海岸官塘地区地热水水化学学特征及其循环演化过程识别[J]. 地球科学,2024,49(3):952-964.ZHANG Y P,LI Q H,XU S W. Hydrochemical characteristics constraints on evolution of geothermal water in Guantang area on the east coast of Hainan Island[J]. Earth Science,2024,49(3):952-964. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] FOURNIER R O,TRUESDELLl A H,PARK M,et al. Geochemical indicators of subsurface temperature:Part 2. Estimate of temperature and fractions of hot water mixed with cold water[J]. Journal Research U. S. Geo. Survey,1974,2(3):263-270. [41] WANG X,LU G P,HU BILL X,et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics geothermometry application of thermal water in coastal Xinzhou and Shenzao geothermal fields,Guangdong,China[J]. Geofluids,2018(1):1-24. [42] CRAIG H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters[J]. Science,1961,133:1702-1703. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3465.1702 [43] 柳长柱,文健,薛桂澄,等. 海南岛地热资源研究[M]. 广州:广东旅游出版社,2022.LIU C Z,WEN J,XUE G C,et al. Study on geothermal resources in Hainan Island[M]. Guangzhou:Guangdong Travel & Tourism Press,2022. (in Chinese) [44] 雷栋,潘良云,陈强,等. 海南岛隆起山地型地热资源地质条件及潜力[J/OL]. 地质通报. (2023-9-7)[2024-5-8]. https://link.cnki. net/urlid/11.4648.P.20230906.2107.002.LEI D,PAN L Y,CHEN Q,et al. Geological conditions and potential of upland geothermal resources in Hainan Island [J/OL]. (2023-9-7)[2024-5-8]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.4648.P.20230906.2107.002. (in Chinese with English abstract [45] LI Y M,LUO J,TIAN J,et al. Formation of the hydrothermal system from granite reservoir for power generation in igneous rock areas of South China[J]. Geothermics,2023,110:1-15. [46] 史浙明,叶海龙,吕少杰,等. 断裂带水力特性研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(4):47-54.SHI Z M,YE H L,LÜ S J,et al. Advances in fault zone hydraulic properties[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(4):47-54. (in Chinese with English abstract [47] LU G P,WANG X,LI F S,et al. Deep geothermal processes acting on faults and solid tides in coastal Xinzhou geothermal field,Guangdong,China[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors,2017,264:76-88. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2016.12.004 [48] CHEN L,MA T,DU Y,et al. Hydrochemical and isotopic (2H,18O and 37Cl)constraints on evolution of geothermal water in coastal plain of southwestern Guangdong Province,China[J]. Journal of Volcanology Geothermal Research,2016,318:45-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2016.03.003 [49] 胡亚轩,郝明,秦姗兰,等. 海南岛现今三维地壳运动与断裂活动性研究[J]. 地球物理学报,2018,61(6):2310-2321. doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0274HU Y X,HAO M,QIN S L,et al. Present-day 3D crustal motion and fault activity in the Hainan Island[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2018,61(6):2310-2321. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0274 [50] 毛绪美,叶建桥,董亚群,等. 地热驱动力:广东阳江新洲地热田驱动地热水运移的一种额外非重力作用的分析方法[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(1):137-145.MAO X M,YE J Q,DONG Y Q,et al. Geothermal driving force:A new additional non-gravity action driving the migration of geothermal water in the Xinzhou geothermal field of Yangjiang,Guangdong[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(1):137-145. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: