The geochemistry and genesis of hydrothermal barite deposits within interlaminar fracture zone, Yuqing County, Guizhou Province
-
摘要:
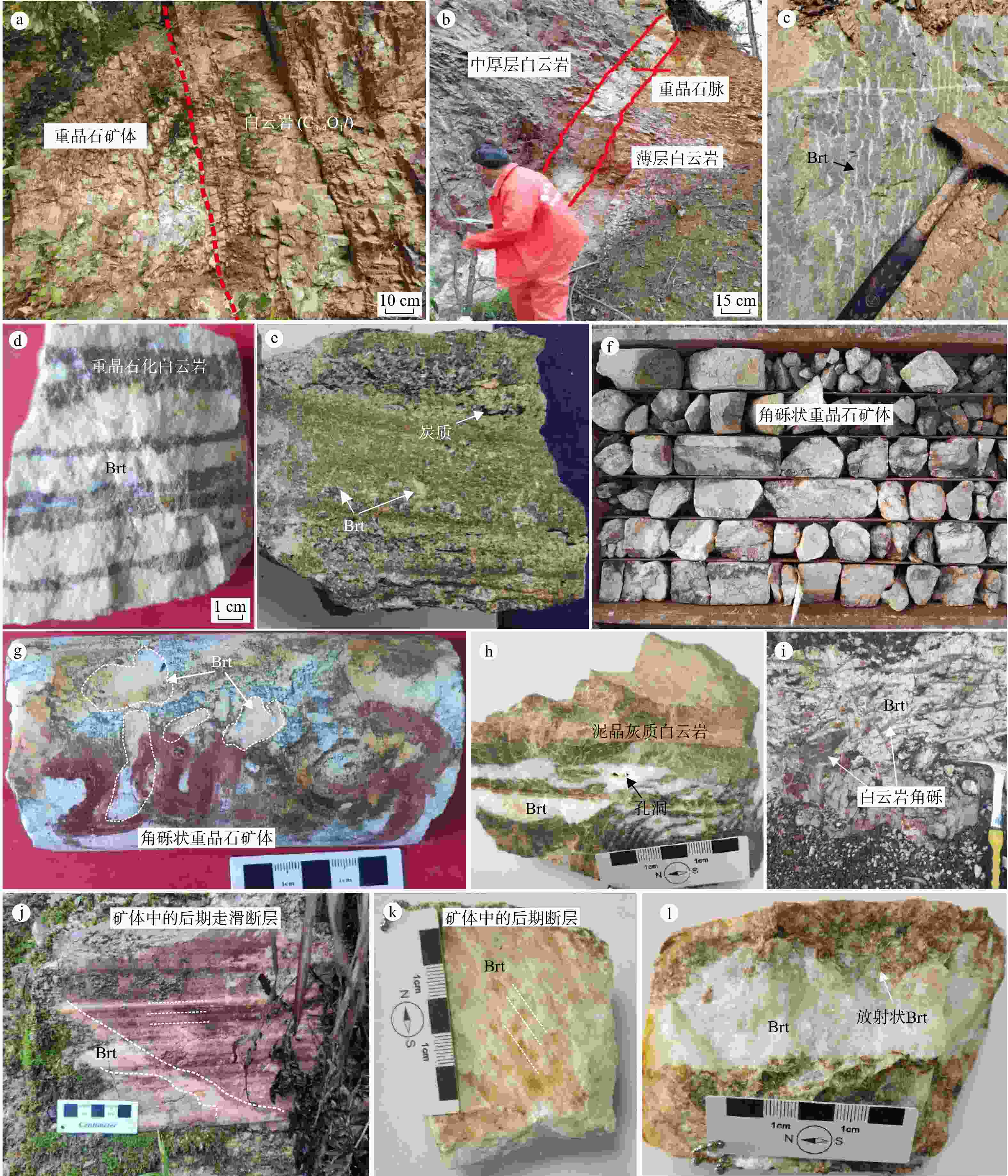
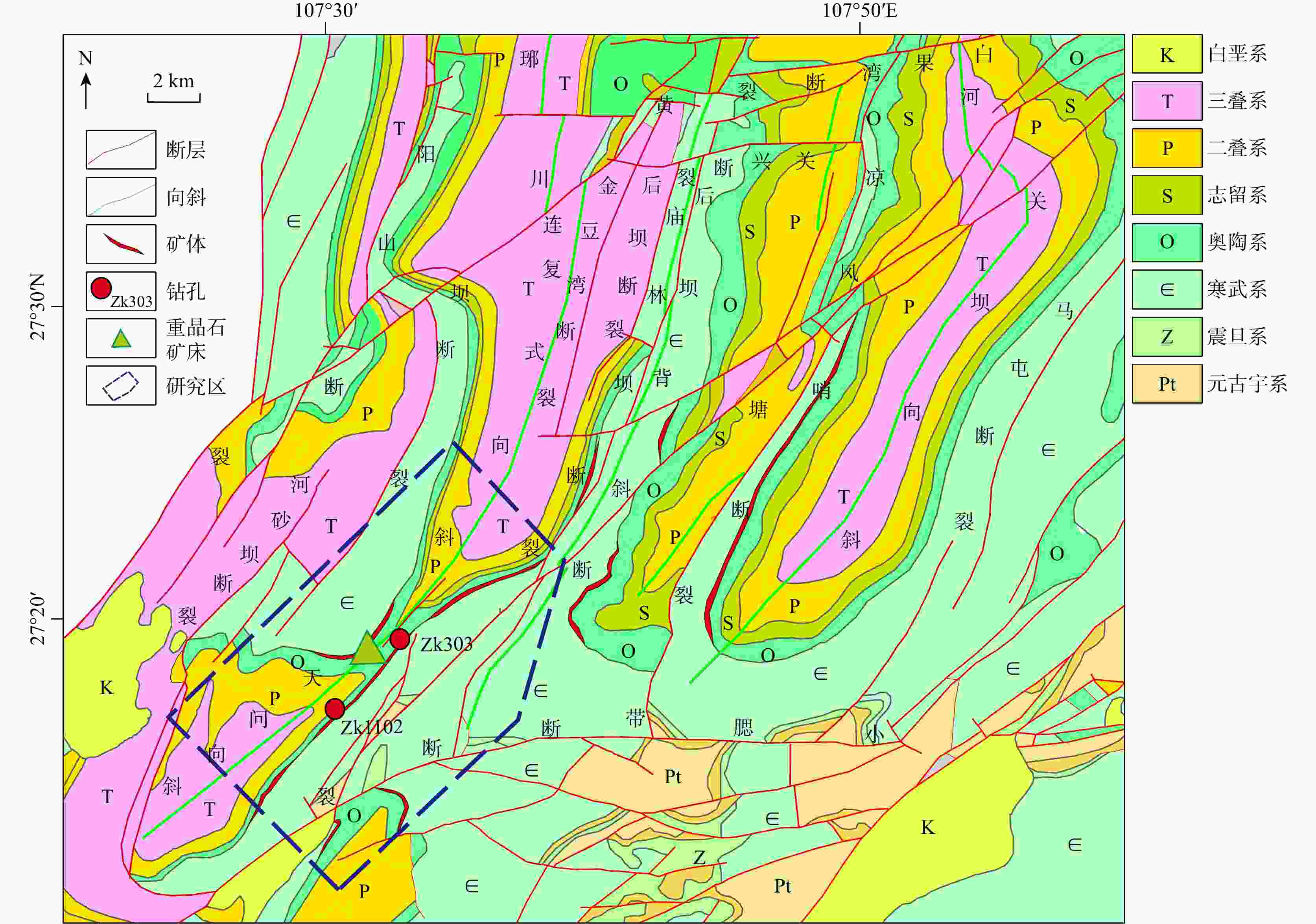
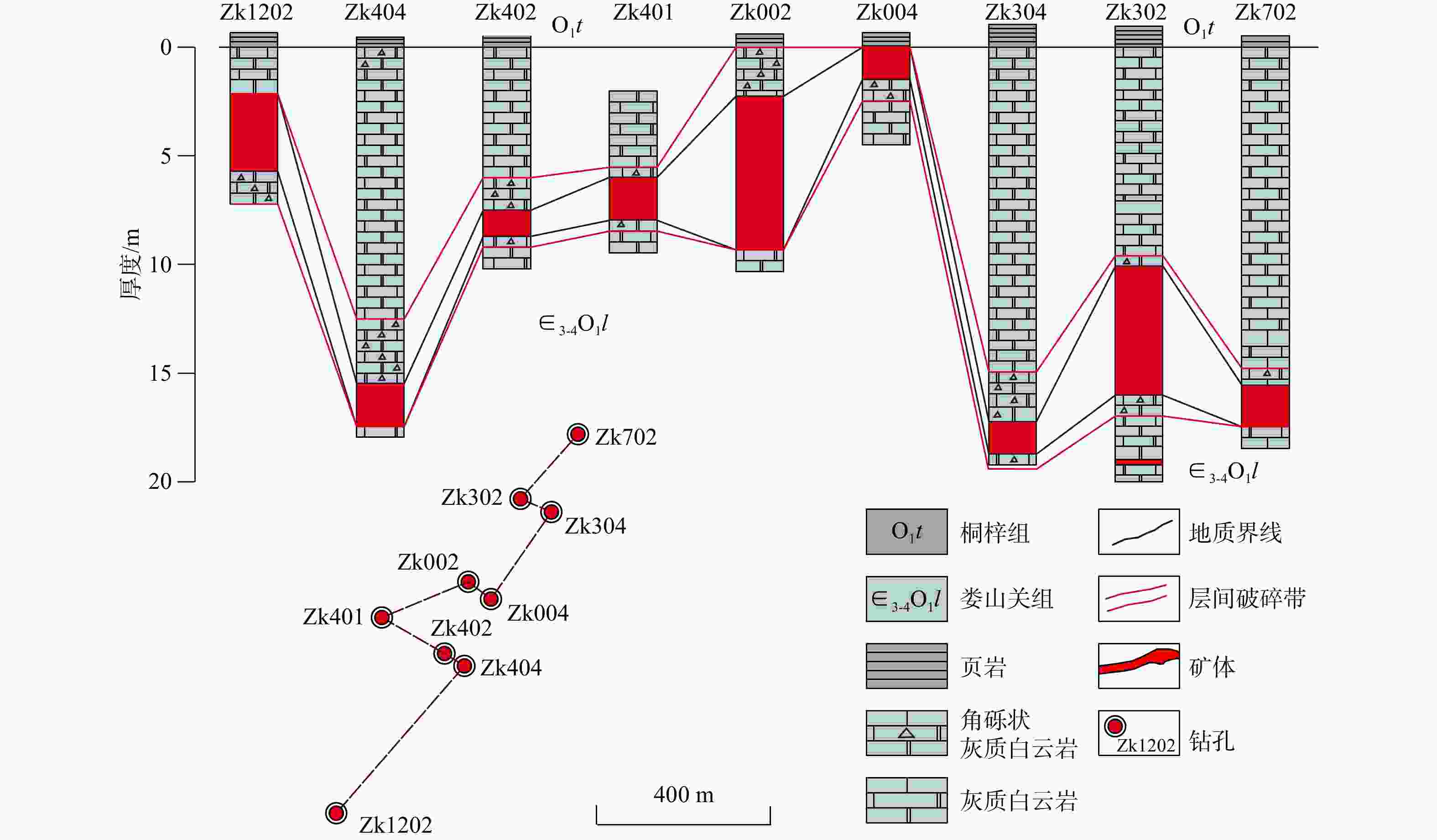
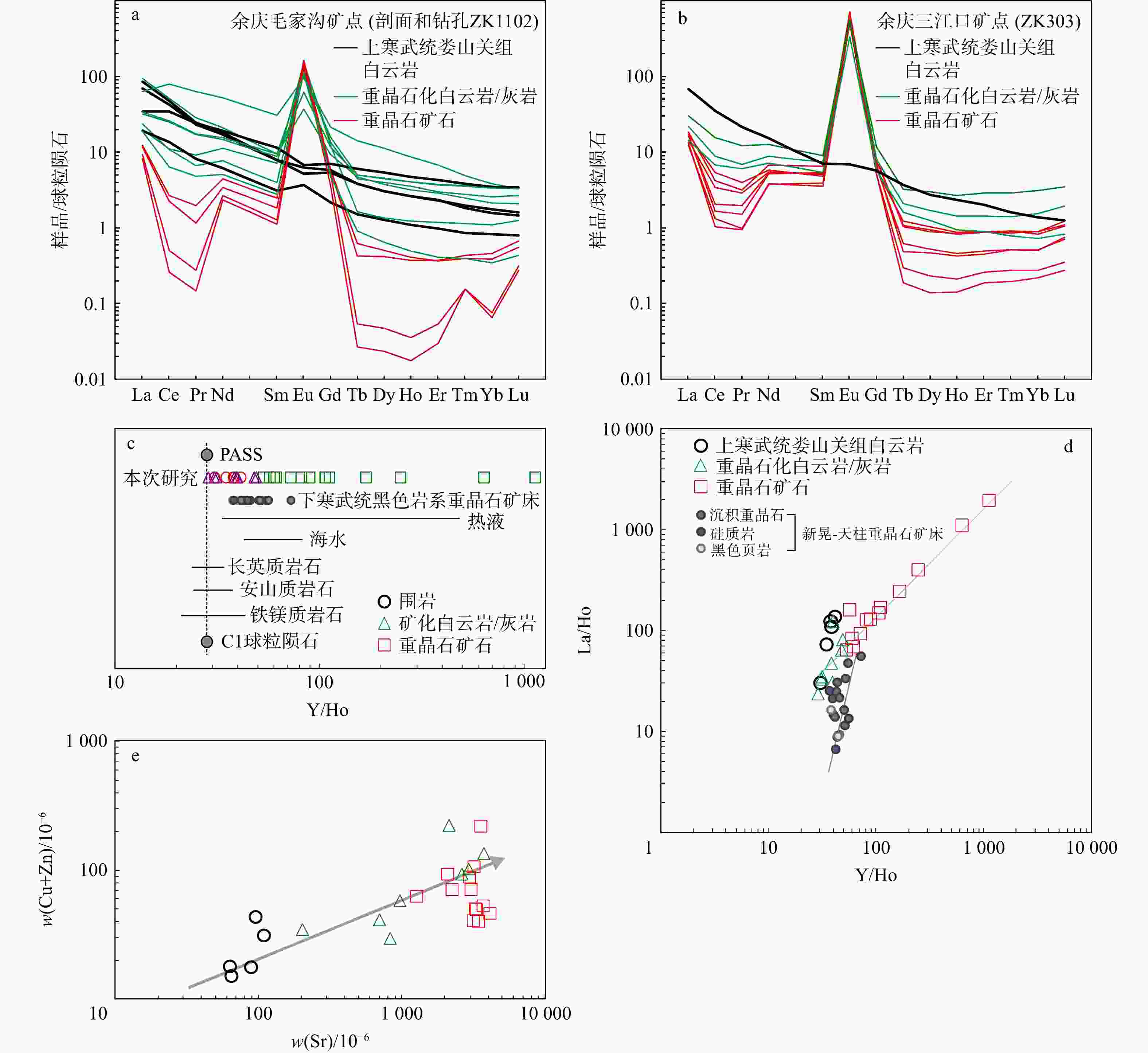
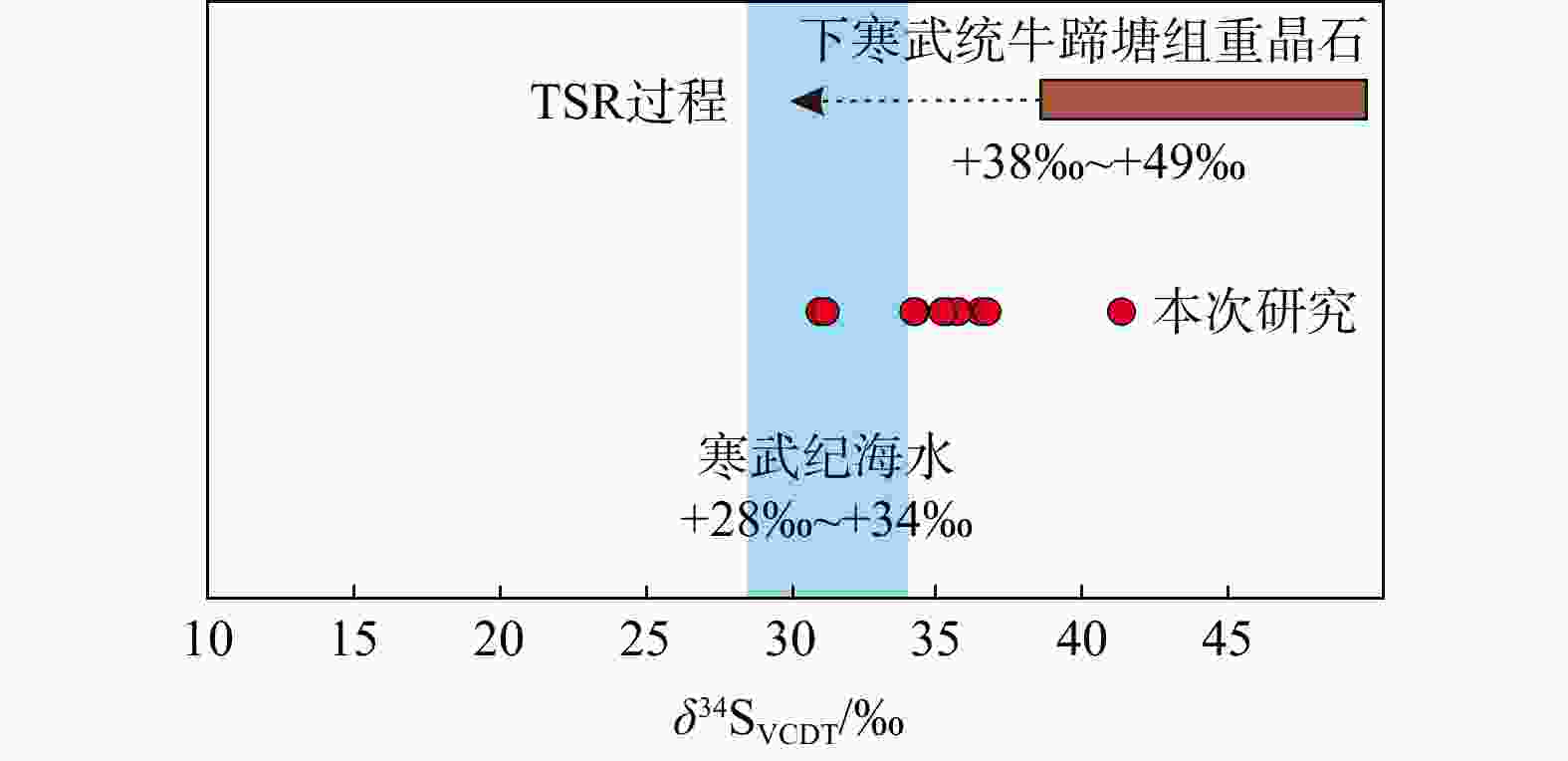
热液型重晶石因其高品质而成为近些年的重点勘查对象。位于扬子克拉通中部的武陵-苗岭一带是我国主要的热液重晶石成矿区,已成为重要钡资源基地。近些年,在贵州黔北新发现了受上寒武统娄山关组白云岩与下奥陶统桐梓组底部页岩接触部位控制的重晶石矿体,矿体延伸稳定,具有较大的成矿潜力,但其特殊热液成矿机制尚未开展系统研究,制约了进一步的勘查部署工作。以余庆地区热液型重晶石为研究对象,开展了系统的岩相学、主微量元素地球化学和硫同位素组成分析研究。野外地质调查表明,硅(碎屑岩)−钙(白云岩)界面产生的层间破碎带及张性裂隙是该区重晶石的主要控矿构造。元素地球化学分析表明,围岩白云岩样品δCe呈现无异常特征(平均1.06),而重晶石样品呈明显的δCe负异常(平均0.66),揭示重晶石在氧化条件下形成。Sr与Cu+Zn元素协变关系和Y/Ho比值指示成矿物质可能来自寒武系富Ba的碳酸盐岩(含膏岩)地层。同样重晶石硫同位素组成(δ34SVCDT:30.94‰~ 41.27‰)也指示硫主要来自寒武系海相蒸发岩。综合前人研究认为,构造运动驱使盆地流体发生运移,并萃取富Ba蒸发岩地层,在层间断层(硅−钙界面)与大气降水混合,形成重晶石矿床。
Abstract:Objective Hydrothermal barite deposits are the main exploration targets for barium. The Wuling-Miaoling area, located in the middle part of the Yangtze craton, contains abundant hydrothermal barite deposits. In recent years, some barite orebodies have been discovered within interlaminar fracture zone between the Upper Cambrian Loushanguan Formation and the in the Lower Ordovician Tongzi Formation in the region. The orebodies with stable extension are of great metallogenic potential. However, the genesis of the barite deposits in the Yuqing area are poorly understood, leading to ambiguity about the further ore exploration.
Methods In this contribution, we investigate the barite deposits in the Yuqing area, presenting a metallogenic model based on detailed petrographic observations and major/trace elements and sulfur isotopic analyses.
Results Our results show that the interlayer fracture zone and tensile fracture generated by silica-calcium interface are the main ore-controlling structures of barite in this area. The geochemistry of barite shows that the δCe of wall rocks (dolomite) has no abnormalities. In contrast, the negative δCe anomaly (mean 0.66) of barite samples indicates that barite is formed under oxidation conditions. The Sr vs. (Cu Zn), Y/Ho ratios and sulfur isotopes suggest that ore-forming material (S and Ba) soured from marine evaporite in the Cambrian strata.
Conclusion Based on previous studies, we propose that the Yanshanian tectonic event drove the migration of the basinal fluids that extracted the Ba-rich evaporite strata. The mixing with meteorite caused the precipitation of barite along the interlayer faults (silica-calcium interfaces).
-
Key words:
- major and trace elements /
- sulfur isotope /
- hydrothermal barite deposits /
- Yuqing area
-
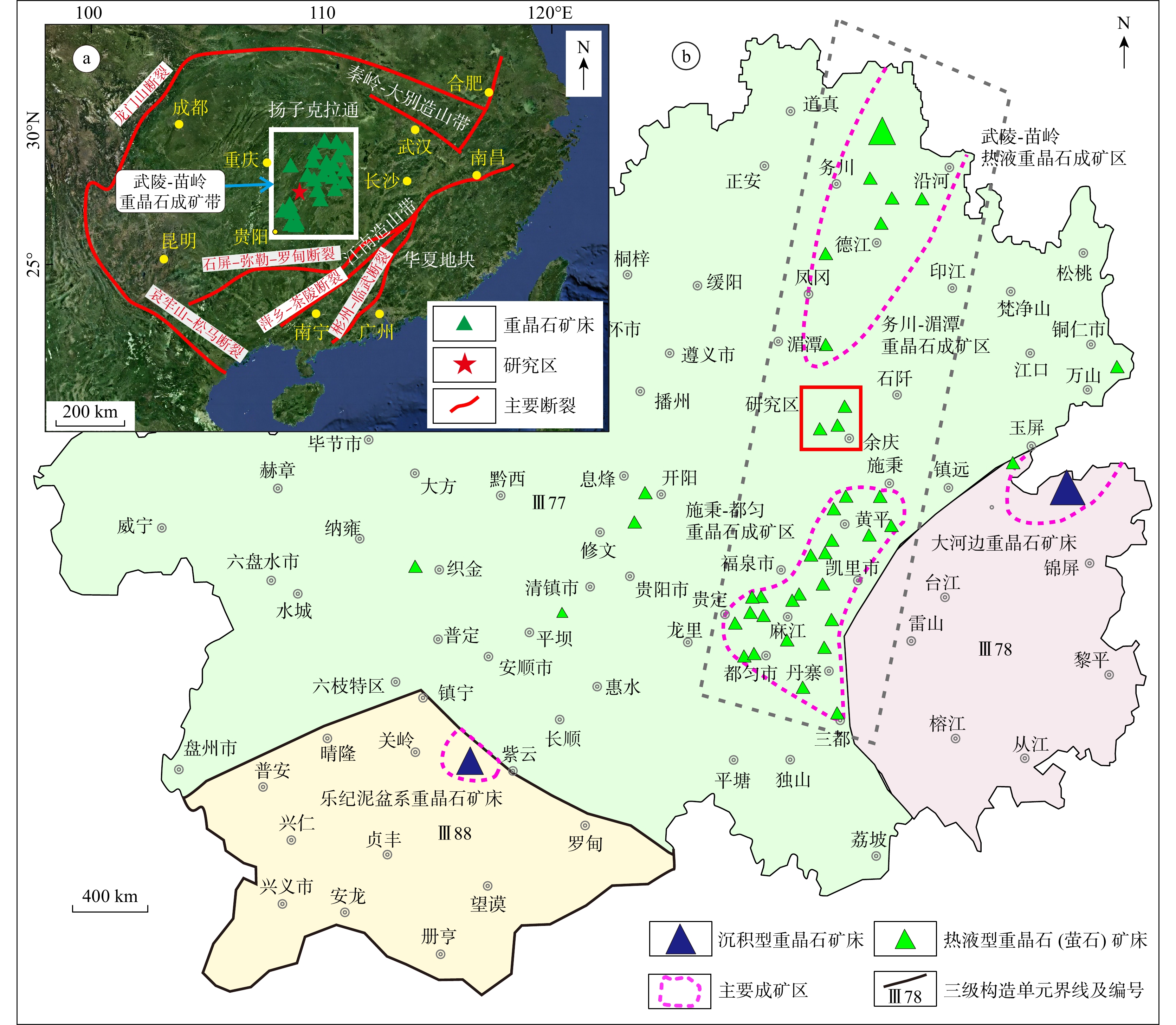
图 1 研究区大地构造位置(a)及贵州重晶石矿床分(沉积型和热液型)(b)图(据文献[6]修改)
Figure 1. Geotectonic location in the study area and distribution of barite deposits in Guizhou Province
表 1 贵州余庆地区重晶石矿石的主量元素组成
Table 1. The main element composition of barite ore in Yuqing area, Guizhou
wB/% 样品编号 岩性简述 SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 MgO CaO Na2O K2O MnO P2O5 TiO2 BaO SO3 SrO LOI SUM ZK303-Y1 角砾状矿石 35.51 1.88 1.06 0.50 0.00 0.44 0.73 0.000 0.000 0.101 34.18 16.78 0.82 7.91 99.90 ZK303-Y2 块状矿石 8.48 0.98 0.55 0.39 0.00 0.64 0.27 0.000 0.000 0.052 54.37 26.72 1.13 6.35 99.93 ZK303-Y3 块状矿石 8.18 0.74 0.55 0.41 0.00 0.53 0.30 0.023 0.000 0.049 54.74 26.97 1.22 6.21 99.92 ZK303-Y4 角砾状矿石 11.94 1.04 0.71 0.41 0.00 1.18 0.47 0.000 0.000 0.076 50.17 25.41 1.47 6.97 99.84 ZK303-Y5 重晶石白云质灰岩 58.09 3.45 2.77 1.03 0.00 0.32 1.82 0.022 0.035 0.188 15.05 9.26 0.50 7.40 99.94 ZK303-Y6 角砾状矿石 11.58 1.59 1.07 6.65 6.25 0.42 0.84 0.014 0.000 0.098 36.64 17.12 1.20 16.46 99.93 ZK303-Y7 块状矿石 6.34 0.58 0.27 0.39 0.00 0.89 0.32 0.000 0.000 0.047 64.50 19.23 1.85 5.49 99.90 ZK303-Y8 角砾状矿石 36.00 5.39 2.50 3.18 2.83 0.28 2.73 0.046 0.000 0.324 19.07 11.78 0.56 15.21 99.89 ZK303-Y9 角砾状矿石 18.39 1.34 1.21 0.48 0.00 0.45 0.75 0.000 0.110 0.093 42.95 21.38 1.38 11.21 99.75 ZK303-Y10 纹层状含萤石白云岩 9.48 0.38 0.22 19.53 29.11 0.00 0.13 0.038 0.000 0.036 0.13 0.05 0.00 40.80 99.90 BT02-Y1 块状矿石 2.32 0.13 0.15 0.34 0.00 0.63 0.05 0.000 0.000 0.000 61.94 30.07 1.99 2.35 99.97 表 2 贵州余庆地区重晶石矿石微量元素组成
Table 2. Composition of trace elements of barite ore in Yuqing area, Guizhou
wB/10−6 矿点 样品编号 岩性简述 Cu Zn Rb Sr La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Y 毛家沟
矿点BAR-1 脉状矿石 18.8 202.00 3.57 2149 5.59 6.57 0.63 3.58 0.60 8.87 2.56 0.06 0.34 0.07 0.20 0.03 0.19 0.03 3.36 BAR-2 网脉状矿石 21.6 113.00 10.5 3715 4.70 6.70 0.86 5.21 1.10 8.70 2.77 0.17 1.01 0.20 0.50 0.07 0.44 0.07 5.71 BAR-3 浸染状矿石 21.1 72.1 4.76 2097 2.75 1.37 0.11 1.60 0.279 7.58 1.18 0.016 0.106 0.021 0.062 0.011 0.078 0.017 1.86 BAR-4 角砾状状矿石 20.4 198 4.91 3540 2.95 1.64 0.187 2.07 0.376 9.41 1.21 0.023 0.128 0.023 0.061 0.01 0.066 0.014 1.87 MJG-3② 纹层状矿石 6.97 27.9 4.60 202 22.1 31.4 2.72 9.81 1.44 2.14 1.92 0.18 0.95 0.18 0.47 0.06 0.36 0.05 7.12 MJG-7 块状矿石 20.0 50.5 0.102 2244 2.19 0.307 0.026 1.25 0.195 9.32 1.08 0.002 0.012 0.002 0.009 0.004 0.013 0.008 1.26 SB-1 块状矿石 18.6 43.9 0.183 1276 1.93 0.16 0.014 1.09 0.171 8.28 0.743 0.001 0.006 0.001 0.005 0.004 0.011 0.007 1.12 SB-2 粗脉状矿石 15.5 34.0 2.95 3296 4.48 3.89 0.453 2.38 0.423 6.41 0.981 0.034 0.164 0.028 0.068 0.01 0.059 0.011 1.60 ZK1102-1 细脉状矿石 15.1 42.6 13.8 969 8.03 15.7 1.64 7.28 1.44 5.83 3.28 0.19 1.16 0.23 0.62 0.09 0.58 0.09 7.24 ZK1102-4 纹层状矿石 9.36 20.4 0.56 832 14.9 48.3 5.93 24.2 4.66 5.55 4.43 0.53 2.85 0.49 1.12 0.13 0.64 0.08 19.0 ZK1102-5 细脉状矿石 9.30 31.9 12.6 697 7.51 15.3 1.61 6.79 1.34 3.61 2.42 0.19 1.12 0.23 0.61 0.09 0.57 0.08 6.99 三江口
矿点ZK303-Y1 角砾状矿石 18.1 88.3 9.66 3199 4.40 2.58 0.299 3.15 0.991 40.0 1.59 0.04 0.24 0.047 0.144 0.022 0.15 0.028 3.37 ZK303-Y2 块状矿石 12.4 58.3 3.72 3051 3.88 1.25 0.186 2.46 0.799 38.5 1.31 0.023 0.132 0.026 0.082 0.013 0.085 0.019 2.76 ZK303-Y3 块状矿石 12.9 74.9 4.04 2960 4.08 1.02 0.143 2.42 0.819 40.9 1.41 0.018 0.119 0.024 0.075 0.013 0.087 0.018 2.66 ZK303-Y4 角砾状白云岩 10.3 42.5 4.62 3687 3.40 2.09 0.271 2.56 0.778 30.0 1.18 0.046 0.263 0.049 0.146 0.023 0.151 0.031 3.01 ZK303-Y5 重晶石白云质灰岩 16.70 77.00 20.70 2617 5.18 5.42 0.66 4.08 1.13 32.2 1.63 0.08 0.43 0.08 0.24 0.04 0.26 0.05 3.86 ZK303-Y6 角砾状矿石 10.9 39.2 6.81 3289 4.02 3.26 0.374 2.72 0.732 28.7 1.69 0.039 0.228 0.048 0.144 0.023 0.141 0.027 2.88 ZK303-Y7 块状矿石 9.33 31.1 2.46 3141 2.95 0.816 0.092 1.77 0.544 30.0 1.05 0.011 0.059 0.012 0.043 0.007 0.047 0.009 2 ZK303-Y8 角砾状矿石 19.90 81.90 31.50 2927 7.12 9.53 1.15 5.90 1.36 31.2 2.42 0.12 0.76 0.15 0.48 0.07 0.53 0.09 5.73 ZK303-Y9 角砾状矿石 7.26 39.1 5.82 4092 3.42 4.11 0.577 3.34 0.829 19.3 1.17 0.06 0.315 0.053 0.146 0.02 0.123 0.021 2.83 BT02-Y1 块状矿石 9.39 30.8 0.791 3420 3.19 0.636 0.089 1.74 0.591 31.9 1.04 0.007 0.035 0.008 0.031 0.005 0.037 0.007 1.98 表 3 贵州余庆地区重晶石矿石硫同位素组成
Table 3. Sulfur isotopic composition of barite ore in Yuqing area, Guizhou
wB/‰ 样品号 特征 d34S/32S δ34SVCDT BAR-1 脉状矿石 36.561 36.459116 BAR-2 网脉状矿石 34.438 34.217228 BAR-3 浸染状矿石 35.489 35.327084 BAR-4 角砾状状矿石 36.747 36.655532 MJG-7 块状矿石 34.371 34.146476 SB-1 块状矿石 35.821 35.677676 SB-2 粗脉状矿石 35.319 35.147564 ZK1102-1 细脉状矿石 31.339 30.944684 ZK1102-4-1 纹层状矿石 41.114 41.267084 ZK1102-5 脉状矿石 31.496 31.110476 -
[1] 胡瑞忠,陈伟,毕献武,等. 扬子克拉通前寒武纪基底对中生代大面积低温成矿的制约[J]. 地学前缘,2020,27(2):137-150.HU R Z,CHEN W,BI X W,et al. Control of the Precambrian basement on the formation of the Mesozoic largescale low-temperature mineralization in the Yangtze Craton[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2020,27(2):137-150. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 涂光炽. 我国西南地区两个别具一格的成矿带(域)[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,2002,21(1):1-2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2002.01.001TU G C. Two unique mineralization areas in Southwest China[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy Petrology and Geochemistry,2002,21(1):1-2. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2002.01.001 [3] HU R Z,FU S L,HUANG Y,et al. The giant South China Mesozoic low-temperature metallogenic domain:Reviews and a new geodynamic model[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2017,137:9-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.10.016 [4] CHEN J,HUANG Z L,YANG R D,et al. Gold and antimony metallogenic relations and ore-forming process of Qinglong Sb(Au) deposit in Youjiang Basin,SW China:Sulfide trace elements and sulfur isotopes[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2021,12(2):605-623. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2020.08.010 [5] WU T,HUANG Z L,YE L,et al. Origin of the carbonate-hosted danaopo Zn-Pb deposit in western Hunan Province,China:Geology and in situ mineral S-Pb isotope constraints[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2021,129:103941. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103941 [6] 陶平,陈建书,陈启飞,等. 关于贵州省成矿区带的划分方案[J]. 贵州地质,2018,35(3):171-180. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2018.03.002TAO P,CHEN J S,CHEN Q F,et al. Division scheme about the metallogenic zones of Guizhou Province[J]. Guizhou Geology,2018,35(3):171-180. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2018.03.002 [7] 潘忠华,范德廉. 川东南脉状萤石-重晶石矿床同位素地球化学[J]. 岩石学报,1996,12(1):127-136. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1996.01.011PAN Z H,FAN D L. Isotope geochemistry of vein fluorite and barite deposits in Southeast Sichuan[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,1996,12(1):127-136. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1996.01.011 [8] ZOU H,ZHANG S T,CHEN A Q,et al. Hydrothermal fluid sources of the Fengjia barite-fluorite deposit in Southeast Sichuan,China:Evidence from fluid inclusions and hydrogen and oxygen isotopes[J]. Resource Geology,2016,66(1):24-36. doi: 10.1111/rge.12084 [9] 陈云明,刘志臣,郭宇,等. 贵州务川地区热液型重晶石矿床地质特征与控矿因素研究[J]. 矿物学报,2023,43(6):813-823.CHEN Y M,LIU Z C,GUO Y,et al. A study on geological characteristics and ore-controlling factors of hydrothermal barite deposits in the Wuchuan area,Guizhou Province[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,2023,43(6):813-823. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 张怡婷,钟怡江,王春连,等. 中国重晶石矿床分布特征、成因类型、资源应用现状及其展望[J/OL]. 中国地质:1-30[2024-02-27]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20240226.1646.004.html.ZHANG Y T,ZHONG Y J,WANG C L,et al. Distribution characteristics,genesis types,current status of resource application of barite deposits in China and its prospects[J/OL]. Geology in China:1-30[2024-02-27]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20240226.1646.004.html.(in Chinese with English abstract [11] 杨瑞东,李鑫正,莫洪成,等. 湘西黔东寒武纪重晶石矿成矿规律与成矿模式[J]. 矿物学报,2023,43(2):173-184.YANG R D,LI X Z,MO H C,et al. Metallogenic regularity and model of Cambrian barite deposits in the western Hunan and eastern Guizhou[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,2023,43(2):173-184. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 邹灏,徐旃章,张寿庭,等. 重庆彭水火石垭重晶石−萤石矿床控矿因素与成因[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2013,40(1):89-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2013.01.012ZOU H,XU Z Z,ZHANG S T,et al. Ore-control factors and genesis of Huoshiya barite-fluorite deposit in Pengshui,Chongqing,China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition),2013,40(1):89-96. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2013.01.012 [13] LIANG Q,JING H,GREGOIRE D C. Determination of trace elements in granites by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Talanta,2000,51(3):507-513. doi: 10.1016/S0039-9140(99)00318-5 [14] DULSKI P. Interferences of oxide,hydroxide and chloride analyte species in the determination of rare earth elements in geological samples by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Fresenius' Journal of Analytical Chemistry,1994,350(4):194-203. [15] SHIELDS G,STILLE P. Diagenetic constraints on the use of cerium anomalies as Palaeoseawater redox proxies:An isotopic and REE study of Cambrian phosphorites[J]. Chemical Geology,2001,175(1/2):29-48. [16] 孙泽航,胡凯,韩善楚,等. 湘黔新晃−天柱重晶石矿床微量稀土元素和硫同位素研究[J]. 高校地质学报,2015,21(4):701-710.SUN Z H,HU K,HAN S C,et al. Trace and rare earth elements and sulfur isotope analysis of barite deposits in West Hunan and East Guizhou[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2015,21(4):701-710. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] CLAYPOOL G E,HOLSER W T,KAPLAN I R,et al. The age curves of sulfur and oxygen isotopes in marine sulfate and their mutual interpretation[J]. Chemical Geology,1980,28:199-260. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(80)90047-9 [18] RONCHI L H,TOURAY J C,MICHARD A,et al. The ribeira fluorite district,southern Brazil[J]. Mineralium Deposita,1993,28(4):240-252. doi: 10.1007/BF02421574 [19] SUN S S,MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society,London,Special Publications,1989,42(1):313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19 [20] BAU M,DULSKI P. Comparative study of yttrium and rare-earth element behaviours in fluorine-rich hydrothermal fluids[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,1995,119(2):213-223. [21] SASMAZ A,KRYUCHENKO N,ZHOVINSKY E,et al. Major,trace and rare earth element (REE) geochemistry of different colored fluorites in the Bobrynets region,Ukraine[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2018,102:338-350. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.09.014 [22] CASTORINA F,MASI U,PADALINO G,et al. Trace-element and Sr-Nd isotopic evidence for the origin of the Sardinian fluorite mineralization (Italy)[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2008,23(10):2906-2921. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.04.005 [23] MICHARD A. Rare earth element systematics in hydrothermal fluids[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1989,53(3):745-750. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(89)90017-3 [24] KESLER S E,JONES L M. Sulfur- and strontium-isotopic geochemistry of celestite,barite and gypsum from the Mesozoic basins of northeastern Mexico[J]. Chemical Geology,1981,31:211-224. [25] WHITFORD D J,KORSCH M J,SOLOMON M. Strontium isotope studies of barites; implications for the origin of base metal mineralization in Tasmania[J]. Economic Geology,1992,87(3):953-959. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.87.3.953 [26] 邹灏. 川东南地区重晶石−萤石矿成矿规律与找矿方向[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2013.ZOU H. Metallogenic regularity and prospecting direction of barite-fluorite deposit in southeast Sichuan[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences(Beijing),2013. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 李堃,刘飞,赵武强,等. 湘西−黔东地区碳酸盐岩容矿铅锌矿床成矿模式[J]. 地球科学,2021,46(4):1151-1172.LI K,LIU F,ZHAO W Q,et al. Metallogenic model of carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn deposits in West Hunan and East Guizhou Provinces,South China[J]. Earth Science,2021,46(4):1151-1172. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] 潘忠华. 川东南脉状萤石−重晶石矿矿床地质地球化学与成因研究[D]. 北京:中科院地质研究所,1993.PAN Z H. Geology,Geochemistry and genesis of vein-like fluorite-barite deposits in Southeast Sichuan[D]. Beijing:Institute of Geology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,1993. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] BAU M,DULSKI P. Distribution of yttrium and rare-earth elements in the Penge and Kuruman iron-formations,Transvaal Supergroup,South Africa[J]. Precambrian Research,1996,79(1/2):37-55. [30] 曹华文,张寿庭,高永璋,等. 内蒙古林西萤石矿床稀土元素地球化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 地球化学,2014,43(2):131-140.CAO H W,ZHANG S T,GAO Y Z,et al. REE geochemistry of fluorite from Linxi fluorite deposit and its geological implications,Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region[J]. Geochimica,2014,43(2):131-140. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] 罗华,郭盼,刘力,等. 湖北来凤革勒车地区铅锌−萤石矿流体包裹体与C-H-O-S-Pb同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(1):39-50.LUO H,GUO P,LIU L,et al. Fluid inclusion and C-H-O-S-Pb isotope characteristics and geological significance of lead-zinc-fluorite deposits in the Geleche area,Laifeng,Hubei Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(1):39-50. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] 徐书奎. 豫西寺家沟金矿床氢氧硫同位素特征及地质意义[J]. 地质科技情报,2017,36(5):143-147.XU S K. Hydrogen,oxygen and sulfur isotopic characteristics and geological significance of Sijiagou gold deposit,western Henan[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2017,36(5):143-147. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 郎兴海,邓煜霖,王旭辉,等. 西藏雄村矿区Ⅲ号矿体硫、铅同位素特征及成矿物质来源[J]. 地质科技情报,2018,37(4):1-9.LANG X H,DENG Y L,WANG X H,et al. Geochemical characteristics of sulfur and lead isotope compositions and implications for the sources of metals from No. Ⅲ ore body in Xiongcun mining area,Tibet[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2018,37(4):1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] 张海坤,胡鹏,曹亮,等. 印度尼西亚戴里Sedex型铅锌矿集区成矿流体特征及成矿物质来源:流体包裹体及同位素地球化学证据[J]. 地质科技通报,2020,39(3):170-177.ZHANG H K,HU P,CAO L,et al. Characteristics of mineralization fluids and mineralization material sources of the Sedex-type Dairi Pb-Zn ore concentration area in Indonesia:Evidence from fluid inclusions and isotopic geochemistry[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2020,39(3):170-177. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] 于皓丞,邱昆峰,孙志佳,等. 新疆阿合奇地区色帕巴衣铅矿床成因:地质、地球化学研究的启示[J]. 地质科技情报,2017,36(2):20-28.YU H C,QIU K F,SUN Z J,et al. Metallogenic model for the Sepabayi lead deposit in Akqi area,Xinjiang:Constraints from geology and geochemistry[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2017,36(2):20-28. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] 林秋伶,李小虎,孟兴伟,等. 现代海底热液区重晶石的地球化学特征及其影响因素[J]. 地质科学,2023,58(3):1091-1117. doi: 10.12017/dzkx.2023.059LIN Q L,LI X H,MENG X W,et al. Geochemical characterization of barite from modern submarine hydrothermal field and its affecting factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology (Scientia Geologica Sinica),2023,58(3):1091-1117. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12017/dzkx.2023.059 [37] 李文炎,余洪云. 中国重晶石矿床[M]. 北京:地质出版社,1991.LI W Y,YU H Y. Barite deposits in China[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House,1991. (in Chinese). [38] 潘忠华,范德廉. 川东南脉状萤石−重晶石矿床流体包裹体研究[J]. 矿物岩石,1994,14(4):9-16.PAN Z H,FAN D L. Fluid inclusion study of vein fluorite and barite ore in southeast Sichuan[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology,1994,14(4):9-16. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 邹灏,张寿庭,徐旃章,等. 川东南地区重晶石−萤石矿的稀土元素地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿物学报,2013,33(增刊2):191-192.ZOU H,ZHANG S T,XU Z Z,et al. Geochemical characteristics of rare earth elements in barite-fluorite deposits in southeastern Sichuan and their geological significance[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,2013,33(S2):191-192. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 张星垣. 川东南重晶石、萤石层控矿床的地质构造特征[J]. 中国区域地质,1988,7(4):81-85.ZHANG X Y. Barite and fluorite stratabound deposits in southeastern Sichuan and ore-controlling geological conditions[J]. Regional Geology of China,1988,7(4):81-85. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: