Fiber optic nerve sensing system for landslide monitoring: Technology and application
-
摘要:
滑坡灾害在我国分布广泛, 实施有效的监测预警和风险管理措施是该领域防灾减灾的关键。近几十年来, 分布式光纤传感技术(distributed fiber optic sensing, 简称DFOS)在滑坡监测领域取得了显著进展, 相较于常规监测方法具有分布式、长距离、大量程和多参量监测的优势。首先介绍了几种有代表性的光纤传感技术, 提出滑坡光纤神经感测系统的概念, 并详细阐述了各类光纤传感器的工作原理及其布设工法。在此基础上, 介绍了2个利用超弱反射光纤布拉格光栅(ultra-weak fiber Bragg grating, 简称UWFBG)监测技术的典型滑坡案例, 并进一步讨论了当前存在的技术瓶颈。案例分析结果表明, 光纤神经感测系统能实现远程、实时、高精度的地下多参量数据采集, 可准确探测潜在滑面及其他关键界面位置, 界面处的多物理量变化为揭示滑坡地下演化过程提供了重要的数据支持, 为滑坡预测预警提供了新的思路。
Abstract:Significance Landslide disasters are widely distributed in China. Effective monitoring, early warning, and risk management measures are key to disaster prevention and mitigation.
Progress Compared with conventional techniques, distributed fiber optic sensing (DFOS) technology has made significant progress in landslide monitoring in recent decades, owing to its strengths in distributed, long-distance, large-range, and multiparameter monitoring. This paper first introduces several representative fiber optic sensing technologies, then proposes the concept of a fiber optic neural sensing system for landslides, and last elaborates the working principles of various fiber optic sensors and their deployment methods. Two typical landslide monitoring cases using ultra-weak fiber Bragg grating (UWFBG) monitoring technology are introduced, and the current technical bottlenecks are discussed.
Conclusions and Prospects The case studies show that the fiber optic neural sensing system can achieve remote, real-time, high-precision underground multiparameter data acquisition, accurately detect potential slip surfaces and other key interfaces. Additionally, multiphysical changes at these interfaces provide important data support for understanding the underground evolution of landslides, which offers new insights into landslide prediction and early warning.
-
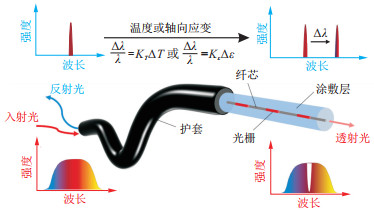
图 1 FBG传感原理图[19]
KT.温度比例系数;Kε.应变比例系数; λ.波长; Δλ.波长变化量; ΔT.温度变化量; Δε.光纤轴向应变量
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of FBG sensing principle
图 2 UWFBG分布式测量原理图[18]
t.同一入射光下的反射时间差;λ1, λ2, …, λn-1, λn.不同光栅的位置
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of UWFBG sensing principle
图 3 BOTDR/A传感原理[27]
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of BOTDR/A sensing principle
图 4 边坡与管道相互作用模型光纤分布图[30]
t.刚性加载板厚度, mm; B.刚性加载板宽度, mm; b.临坡距, mm; P.强度;H.管道上覆土层厚度,mm; D.管道外径, mm;H1,H2,H3.xoz平面S型布设的3层横向光缆的水平高度; θ边坡坡脚角度, (°)
Figure 4. Schematic diagram of fiber distribution in the slope-pipe interaction model
图 5 离心机边坡模型光纤分布图[32]
Figure 5. Schematic diagram of fiber distribution in centrifuge slope model
图 6 基于光纤传感器的高速公路边坡监测系统[34]
Figure 6. Highway slope monitoring system based on fiber optic sensors
图 7 表征水库滑坡热-水-力学行为的光纤神经感测系统[18]
Figure 7. Fiber-optic nerve system for characterizing thermo-hydro-mechanical behavior of reservoir landslides
图 8 新铺滑坡及测点布置平面图[19]
Figure 8. Plan view of the Xinpu landslide with in-situ instrumentation
图 9 集成多物理监测系统[19]
Figure 9. Integrated multi-physical monitoring system
图 10 深部钻孔测斜(a)和应变监测(b)结果以及降雨、库水位数据(c)[19]
Figure 10. Subsurface inclination(a) and strain profiles(b), as well as rainfall and reservoir water level data(c)
表 1 光纤神经感测系统中典型的传感器及感测光缆
Table 1. Typical fiber optic sensors and sensing cables in a fiber optic nerve system
传感器名称 监测变量 适用场合 实物图 光纤光栅位移计 位移 滑坡不同深度处的变形监测,地表裂缝监测 
光纤光栅渗压计 孔隙水压力 地下多孔介质的孔隙水压力、渗透压力监测 
光纤光栅土压力计 土压力 滑坡与结构体界面处的土压力监测 
光纤光栅土体含水率计 温度、含水率 滑坡不同深度处的土体含水率监测 
非金属加强温度感测光缆 温度 恶劣工况如强电场、强磁场干扰的地下钻孔温度监测 
铜网内加热水分感测光缆 温度、含水率、渗流速率 地下水分场和渗流场监测 
外定点应变感测光缆 应变 滑坡深部变形、地表裂缝监测 
-
[1] 彭建兵, 王启耀, 门玉明, 等. 黄土高原滑坡灾害[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019.PENG J B, WANG Q Y, MEN Y M, et al. Landslide disaster in Loess Plateau[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019. (in Chinese) [2] 董文文, 朱鸿鹄, 孙义杰, 等. 边坡变形监测技术现状及新进展[J]. 工程地质学报, 2016, 24(6): 1088-1095.DONG W W, ZHU H H, SUN Y J, et al. Current status and new progress on slope deformation monitoring technologies[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2016, 24(6): 1088-1095. (in Chinese with English abstract) [3] 程刚, 王振雪, 李刚强, 等. 我国滑坡监测文献计量研究的可视化分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(7): 172-179.CHENG G, WANG Z X, LI G Q, et al. Visual analysis of bibliometric research on landslide monitoring in China[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(7): 172-179. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] 许强. 对滑坡监测预警相关问题的认识与思考[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(2): 360-374.XU Q. Understanding the landslide monitoring and early warning: Consideration to practical issues[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(2): 360-374. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] FAN X M, XU Q, SCARINGI G, et al. Failure mechanism and kinematics of the deadly June 24th 2017 Xinmo landslide, Maoxian, Sichuan, China[J]. Landslides, 2017, 14(6): 2129-2146. doi: 10.1007/s10346-017-0907-7 [6] 唐辉明. 重大滑坡预测预报研究进展与展望[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(6): 1-13. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0203TANG H M. Advance and prospects of major landslides prediction and forecasting[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(6): 1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0203 [7] MACCIOTTA R, HENDRY M T. Remote sensing applications for landslide monitoring and investigation in western Canada[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(3): 366. doi: 10.3390/rs13030366 [8] ASLAN G, FOUMELIS M, RAUCOULES D, et al. Landslide mapping and monitoring using persistent scatterer interferometry (PSI) technique in the French Alps[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(8): 1305. doi: 10.3390/rs12081305 [9] ZHANG Y, LI Y X, MENG X M, et al. Automatic mapping of potential landslides using satellite multitemporal interferometry[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(20): 4951. doi: 10.3390/rs15204951 [10] ZHANG L, CUI Y F, ZHU H H, et al. Shear deformation calculation of landslide using distributed strain sensing technology considering the coupling effect[J]. Landslides, 2023, 20(8): 1583-1597. doi: 10.1007/s10346-023-02051-5 [11] 施斌, 张丹, 朱鸿鹄. 地质与岩土工程分布式光纤监测技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019.SHI B, ZHANG D, ZHU H H. Distributed fiber optic sensing for geoengineering monitoring[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019. (in Chinese) [12] SUN Y J, ZHANG D, SHI B, et al. Distributed acquisition, characterization and process analysis of multi-field information in slopes[J]. Engineering Geology, 2014, 182: 49-62. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.08.025 [13] MA J X, PEI H F, ZHU H H, et al. A review of previous studies on the applications of fiber optic sensing technologies in geotechnical monitoring[J]. Rock Mechanics Bulletin, 2023, 2(1): 100021. doi: 10.1016/j.rockmb.2022.100021 [14] ZHANG C C, ZHU H H, LIU S P, et al. A kinematic method for calculating shear displacements of landslides using distributed fiber optic strain measurements[J]. Engineering Geology, 2018, 234: 83-96. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.01.002 [15] WANG D Y, ZHU H H, WANG J, et al. Characterization of sliding surface deformation and stability evaluation of landslides with fiber-optic strain sensing nerves[J]. Engineering Geology, 2023, 314: 107011. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2023.107011 [16] KOGURE T, OKUDA Y. Monitoring the vertical distribution of rainfall-induced strain changes in a landslide measured by distributed fiber optic sensing with Rayleigh backscattering[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(9): 4033-4040. doi: 10.1029/2018GL077607 [17] ZENI L, PICARELLI L, AVOLIO B, et al. Brillouin optical time-domain analysis for geotechnical monitoring[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 7(4): 458-462. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2015.01.008 [18] YE X, ZHU H H, WANG J, et al. Subsurface multi-physical monitoring of a reservoir landslide with the fiber-optic nerve system[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2022, 49(11): e98211. [19] ZHU H H, YE X, PEI H F, et al. Probing multi-physical process and deformation mechanism of a large-scale landslide using integrated dual-source monitoring[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2024, 15(2): 101773. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2023.101773 [20] LIU S P, SHI B, GU K, et al. Fiber-optic wireless sensor network using ultra-weak fiber Bragg gratings for vertical subsurface deformation monitoring[J]. Natural Hazards, 2021, 109(3): 2557-2573. doi: 10.1007/s11069-021-04932-1 [21] YE X, ZHU H H, CHENG G, et al. Thermo-hydro-poro-mechanical responses of a reservoir-induced landslide tracked by high-resolution fiber optic sensing nerves[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2024, 16(3): 1018-1032. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.04.004 [22] GAO Y X, ZHU H H, QIAO L, et al. Feasibility study on sinkhole monitoring with fiber optic strain sensing nerves[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2023, 15(11): 3059-3070. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2022.12.026 [23] WANG D Y, ZHU H H, WU B, et al. Performance evaluation of underground pipelines subjected to landslide thrust with fiber optic strain sensing nervess[J]. Acta Geotechnica, 2024, 19: 6993-7009. doi: 10.1007/s11440-024-02311-1 [24] LI H J, ZHU H H, LI Y H, et al. Fiber Bragg grating-based flume test to study the initiation of landslide-debris flows induced by concentrated runoff[J]. Geotechnical Testing Journal, 2021, 44(4): 986-999. doi: 10.1520/GTJ20190290 [25] KOO K P, TVETEN A B, VOHRA S T. Dense wavelength division multiplexing of fibre Bragg grating sensors using CDMA[J]. Electronics Letters, 1999, 35(2): 165. doi: 10.1049/el:19990135 [26] BAO X Y, CHEN L. Recent progress in Brillouin scattering based fiber sensors[J]. Sensors, 2011, 11(4): 4152-4187. doi: 10.3390/s110404152 [27] WANG D Y, ZHU H H, HUANG J W, et al. Fiber optic sensing and performance evaluation of a water conveyance tunnel with composite linings under super-high internal pressures[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2023, 15(8): 1997-2012. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.02.026 [28] HORIGUCHI T, TATEDA M. BOTDA-nondestructive measurement of single-mode optical fiber attenuation characteristics using Brillouin interaction: Theory[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 1989, 7(8): 1170-1176. doi: 10.1109/50.32378 [29] 姚俊成, 刘洁, 王金路, 等. 基于主动加热型分布式温度感测光缆的土体导热系数测量方法[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2023, 50(1): 179-188.YAO J C, LIU J, WANG J L, et al. A study of soil thermal conductivity measurement based on the actively heated distributed temperature sensing cable[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(1): 179-188. (in Chinese with English abstract) [30] 喻文昭, 朱鸿鹄, 王德洋, 等. 荷载作用下砂土边坡-管道相互作用试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2024, 45(5): 1309-1320.YU W Z, ZHU H H, WANG D Y, et al. Experimental study of sandy slope-pipe interaction under loading[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2024, 45(5): 1309-1320. (in Chinese with English abstract) [31] ZHU H H, SHI B, ZHANG C C. FBG-based monitoring of geohazards: Current status and trends[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(3): 452. doi: 10.3390/s17030452 [32] ZHANG L, SHI B, ZENI L, et al. An fiber Bragg grating-based monitoring system for slope deformation studies in geotechnical centrifuges[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(7): 1591. doi: 10.3390/s19071591 [33] SANG H W, ZHANG D, GAO Y L, et al. Strain distribution based geometric models for characterizing the deformation of a sliding zone[J]. Engineering Geology, 2019, 263: 105300. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105300 [34] ZHU H H, HO A N L, YIN J H, et al. An optical fibre monitoring system for evaluating the performance of a soil nailed slope[J]. Smart Structures and Systems, 2012, 9(5): 393-410. doi: 10.12989/sss.2012.9.5.393 [35] 武生辉, 仝德富, 苏爱军, 等. 新铺下二台滑坡变形机制及中长期预报模型[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(6): 35-44. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0235WU S H, TONG D F, SU A J, et al. Deformation mechanism and medium- and long-term landslide prediction model of Xinpu Xia'ertai landslide[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(6): 35-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0235 [36] 俞良晨. 暂时性承压水作用下南京某山前缓坡滑动过程模拟分析[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2021.YU L C. Simulation analysis of the sliding process of a piedmontgentle slope under the action of the temporary groundwater in the confined aquifer in Nanjing[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) [37] CHEN M L, YANG X G, ZHOU J W. Spatial distribution and failure mechanism of water-induced landslides in the reservoir areas of Southwest China[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2023, 15(2): 442-456. [38] YANG B B, LIU Z Q, LACASSE S, et al. Spatiotemporal deformation characteristics of Outang landslide and identification of triggering factors using data mining[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2024, 16(10): 4088-4104. -





 下载:
下载: