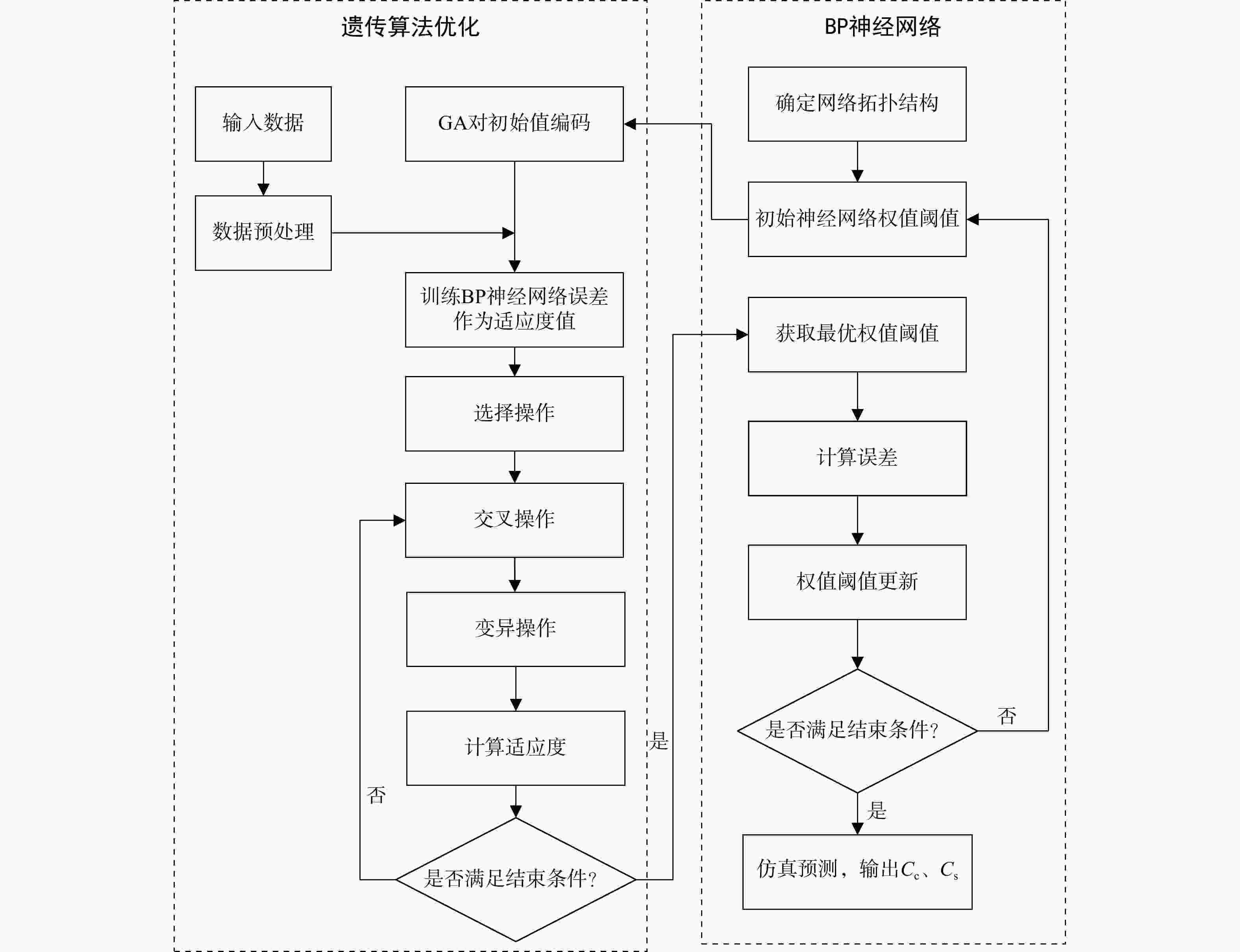
Prediction of the compression index and swell index of soft soils via an optimized multiple-output neural network
-
摘要:
软弱土的压缩指数$ {C_{\mathrm{c}}} $和回弹指数$ {C_{\mathrm{s}}} $是计算土体沉降和回弹的重要参数,采用机器学习算法可高效预测$ {C_{\mathrm{c}}} $和$ {C_{\mathrm{s}}} $,减少室内试验周期和费用。引入孔压静力触探(CPTU)原位测试数据,利用土类指数${I_{\mathrm{c}}}$量化土层信息,融合室内试验和原位测试数据,改进遗传算法优化的BP神经网络(GA-BPNN),实现多输出功能,同时预测$ {C_{\mathrm{c}}} $和$ {C_{\mathrm{s}}} $。通过相关性分析,确定多输出GA-BPNN模型输入参数,利用TC 304标准场地数据库,将预测结果与多输出BPNN模型、单输出GA-BPNN模型比较,进而验证多输出GA-BPNN模型能效,并获得预训练模型参数。在南京有限场地数据条件下,进一步讨论多输出GA-BPNN模型的优越性,分析预训练、原位测试数据对模型效果的影响,最后进行敏感性分析。结果表明,利用标准场地数据获得预训练多输出GA-BPNN模型,在有限数据条件下,可有效预测$ {C_{\mathrm{c}}} $和$ {C_{\mathrm{s}}} $;加入原位测试数据的的GA-BPNN模型预测$ {C_{\mathrm{c}}} $(${R^2} = 0.96$)和$ {C_{\mathrm{s}}} $(${R^2} = 0.97$)精确度较高,预测结果更加接近实测值,预测结果相关性与已有研究保持一致。通过预训练的多输出GA-BPNN模型,可在有限场地数据条件下,快速准确预测软弱土的$ {C_{\mathrm{c}}} $和$ {C_{\mathrm{s}}} $,对工程实践中的多元参数预测具有良好的应用前景。
Abstract:Objective The compression index
C c and swell indexC s of soil are critical parameters for calculating soil settlement and swelling. Utilizing machine learning algorithms to predict these indices quickly and efficiently can significantly reduce testing duration and costs.Methods In this study, we introduce Piezocone Penetration Test (CPTU) in-situ data and quantify soil layer information using the Soil Behaviour Type (SBT) index
I c. We then combine laboratory data with CPTU data to develop a multi-output genetic algorithm-optimized backpropagation neural network (GA-BPNN) model. The input parameters for the multi-output GA-BPNN model were determined through correlation analysis. Using the TC304 standard site database, the prediction results from the multi-output GA-BPNN model were compared with those from the multi-output BPNN model and the single-output GA-BPNN model, verifying the effectiveness of the multi-output GA-BPNN model and obtaining pre-trained model parameters. For sites with limited data in Nanjing, the superiority of the multi-output BPNN model was further evaluated by analyzing the impact of pre-training and in-situ test data on model performance. A sensitivity analysis was also conducted to assess the robustness of the model.Results The results demonstrate that the pre-trained multi-output GA-BPNN model, derived from standard site data, can effectively predict the compression and swell indices under limited data conditions. When combined with in-situ test data, the multi-output GA-BPNN model exhibits high prediction accuracy for these indices, with predicted values closely matching measured data. The consistency of the predicted results aligns well with existing studies.
Conclusion The pre-trained multi-output GA-BPNN model can efficiently predict the compression and swell indices of soft soil under limited data conditions. The proposed method shows significant potential for multi-parameter prediction in engineering practice, enhancing the efficiency and reliability of geotechnical engineering assessments.
-
Key words:
- compression index /
- swell index /
- multiple-output /
- optimized neural network /
- GA-BPNN model /
- soft soil
-
表 1 经验预测公式总结
Table 1. Summary of the empirical prediction formulas
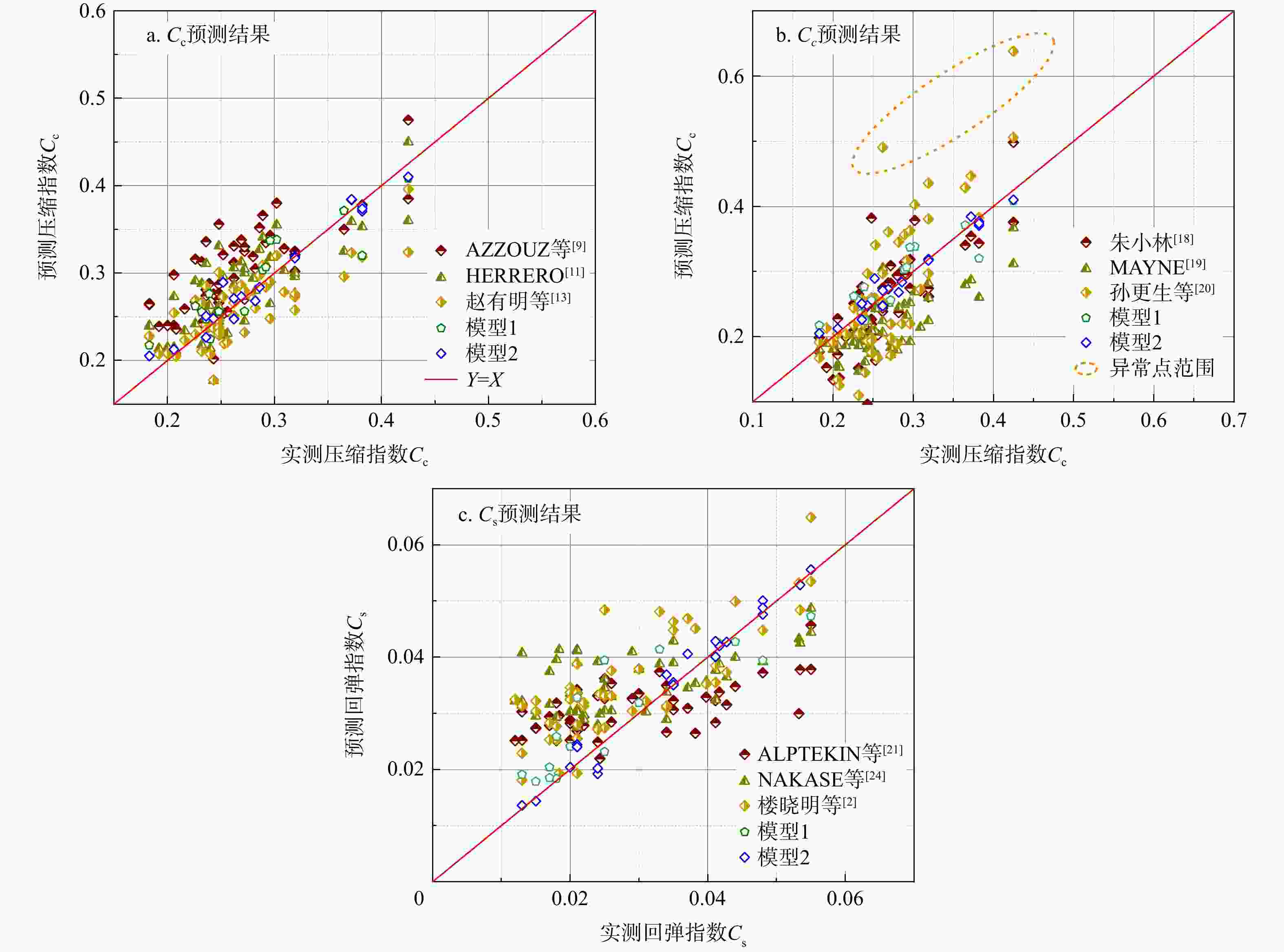
压缩性指数 参数 相关性 适用土类 参考文献 ${C_{\mathrm{c}}}$ $ {{{w}}_{\text{n}}} $ $ {C_{\mathrm{c}}} = 0.01{{{w}}_{\text{n}}} - 0.05 $ 所有土 AZZOUZ等[9] $ {C_{\mathrm{c}}} = 0.01{{{w}}_{\text{n}}} $ 黏土 KOPPULA等[10] $ {C_{\mathrm{c}}} = 0.01{{{w}}_{\text{n}}}-{0}{\text{.075}} $ 黏土 HERRERO[11] $ {C_{\mathrm{c}}} = 0.013{{{w}}_{\text{n}}} - 0.115 $ 黏土 PARK等[12] $ {C_{\mathrm{c}}} = 0.008{{{w}}_{\text{n}}} + 0.063 $ 淤泥 赵有明等[13] $ {C_{\mathrm{c}}} = 0.008{{{w}}_{\text{n}}} - 0.024 $ 淤泥 顾小芸[14] $ {C}_{{\mathrm{c}}}=1.843(0.01{{w}}_{\text{n}}-0.222) $ 淤泥质土 魏道垛等[15] e ${C_{\mathrm{c}}} = 0.54{{e - 0}}{\text{.19}}$ 黏土 NISHIDA[16] ${C_{\mathrm{c}}} = 0.43{{e - 0}}{\text{.11}}$ 黏土 COZZOLINO[17] ${C_{\mathrm{c}}} = 0.49{{e - 0}}{\text{.11}}$ 黏土 PARK等[12] ${C_{\mathrm{c}}} = 0.521{{e - 0}}{\text{.2874}}$ 黏土 朱小林[18] ${{{w}}_{\text{L}}}$ ${C_{\mathrm{c}}} = 0.006{{{w}}_{\mathrm{L}}}{{ - 0}}{\text{.054}}$ 黏土 AZZOUZ等[9] ${C_{\mathrm{c}}} = \dfrac{{({{{w}}_{\mathrm{L}}}{{ - 13)}}}}{{109}}$ 黏土 MAYNE[19] ${C_{\mathrm{c}}} = 0.014{{{w}}_{\mathrm{L}}}{{ - 0}}{\text{.168}}$ 黏土 PARK等[12] ${C_{\mathrm{c}}} = 0.022{{{w}}_{\mathrm{L}}}{- {0}}{\text{.528}}$ 淤泥质土 孙更生等[20] $ {{w}}_{\text{n}},{{w}}_{\text{L}} $ ${C_{\mathrm{c}}} = 0.009{{{w}}_{\text{n}}} + 0.005{{{w}}_{\text{L}}}$ 黏土 KOPPULA等[10] ${C_{\mathrm{c}}} = 0.009{{{w}}_{\text{n}}} + 0.002{{{w}}_{\text{L}}} - 0.001$ 黏土 AZZOUZ等[9] $ {{w}}_{\text{n}},{e} $ ${C_{\mathrm{c}}} = 0.4{{e + 0}}{\text{.000\ 4}}{{{w}}_{\text{n}}}{{ - 0}}{\text{.01}}$ 黏土 AZZOUZ等[9] ${C_{\text{s}}}$ ${{{w}}_{\text{n}}}$ ${C_{\mathrm{s}}} = 0.000\ 87{{{w}}_{\text{n}}}$ 海相黏土 ALPTEKIN等[21] $ {C_{\mathrm{s}}} = 0.013\ 3{{\text{e}}^{0.036{{{w}}_{\text{n}}}}} $(式中e为自然底数) 淤泥质土 IŞIK[22] ${{{w}}_{\text{L}}}$ $ {C_{\mathrm{s}}} = 0.021\ 4 + 0.001\ 3{{{w}}_{\text{L}}} $ 海相黏土 ALPTEKIN等[21] $ {{w}}_{\text{L}},{{G}}_{\text{s}} $ ${C_{\mathrm{s}}} = 0.000\ 463{{{w}}_{\text{L}}} \cdot {{{G}}_{\text{s}}}$ 所有土 NAGARAJ等[23] ${{{w}}_{\text{P}}}$ ${C_{\mathrm{s}}} = 0.001\ 94({{{w}}_{\text{P}}}{{ - 4}}{\text{.6)}}$ 黏土 NAKASE等[24] ${I_{\text{p}}}$ ${C_{\mathrm{s}}} = 0.003{I_{\text{p}}} - 0.005$ 粉质黏土 楼晓明等[2] ${{e}}$ ${C_{\mathrm{s}}} = 0.0121{{{{\mathrm{e}}}}^{1.313\ 1{{e}}}}$(底数中e为自然底数) 淤泥质土 IŞIK[22] $ {e},\rho ,{{w}}_{\text{L}} $ ${C_{\mathrm{s}}} = - 0.05 + 0.075e + 0.015\rho + 0.000\ 3{{{w}}_{\text{L}}}$ 海相黏土 ALPTEKIN等[21] 注:wn. 含水率;e. 孔隙比;wL. 液限指数;wP. 塑限指数;IP. 塑性指数;Gs. 相对密度;ρ. 密度;下同 表 2 室内试验数据统计分析
Table 2. Statistical analysis of laboratory data
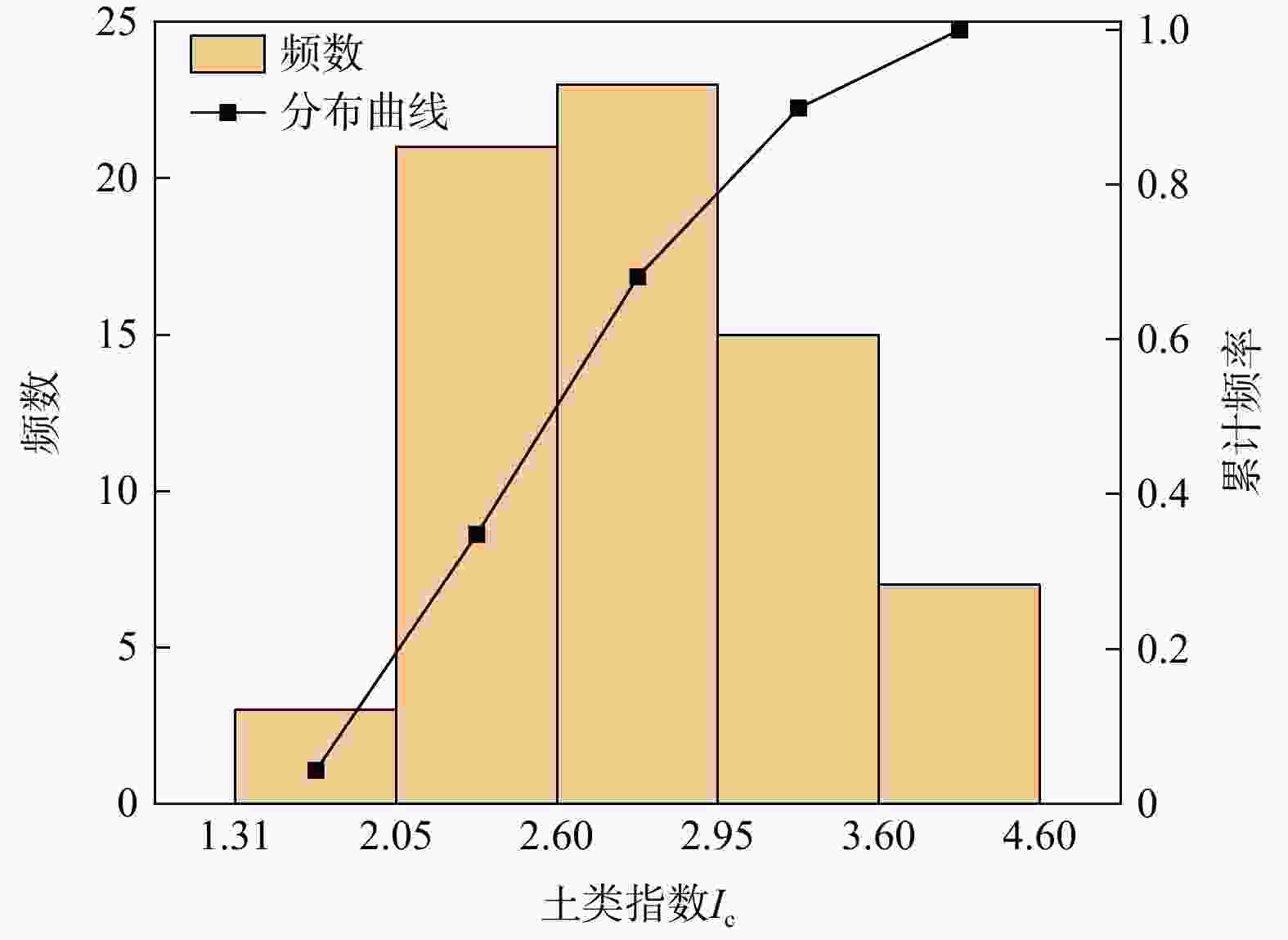
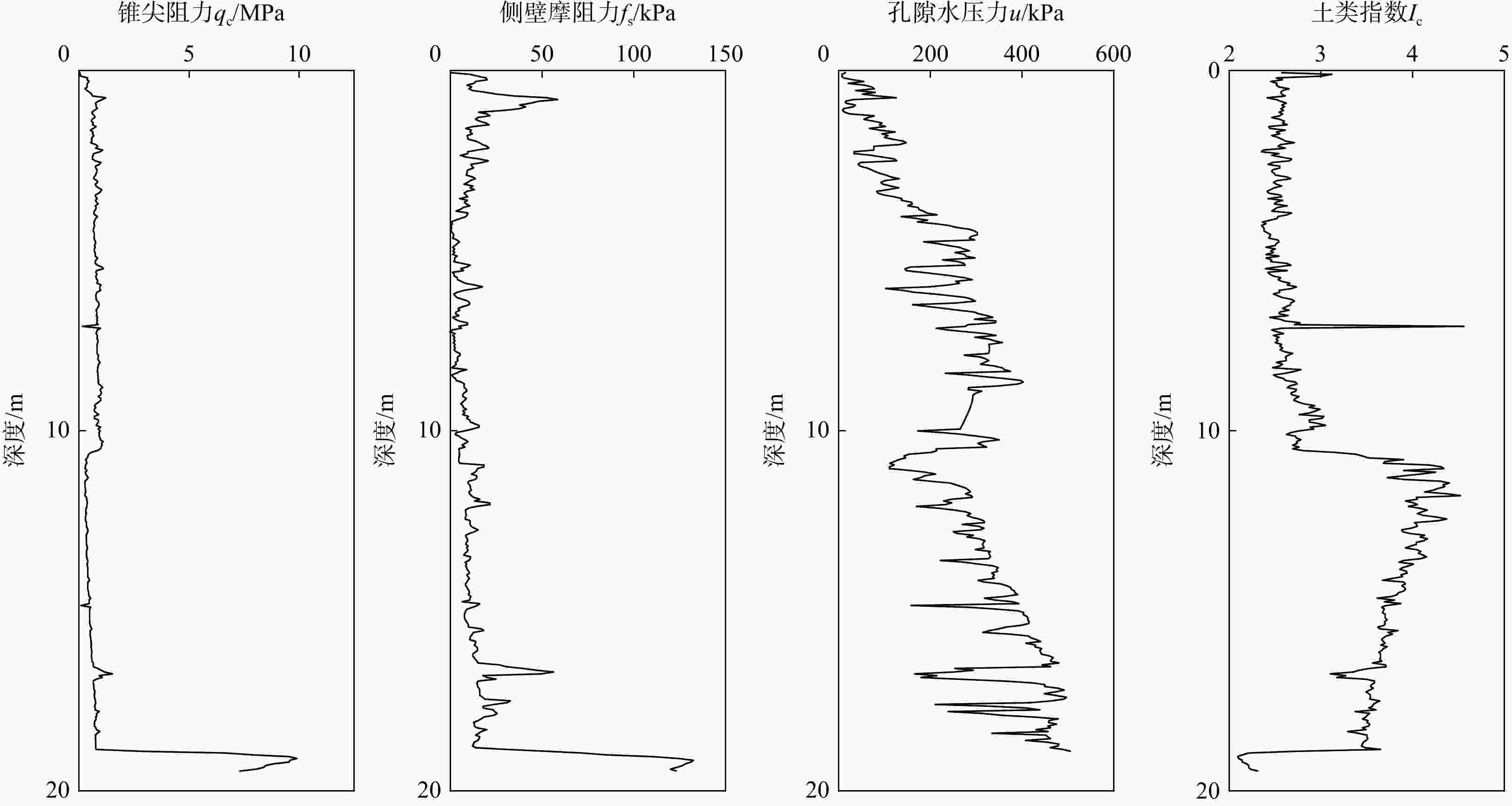
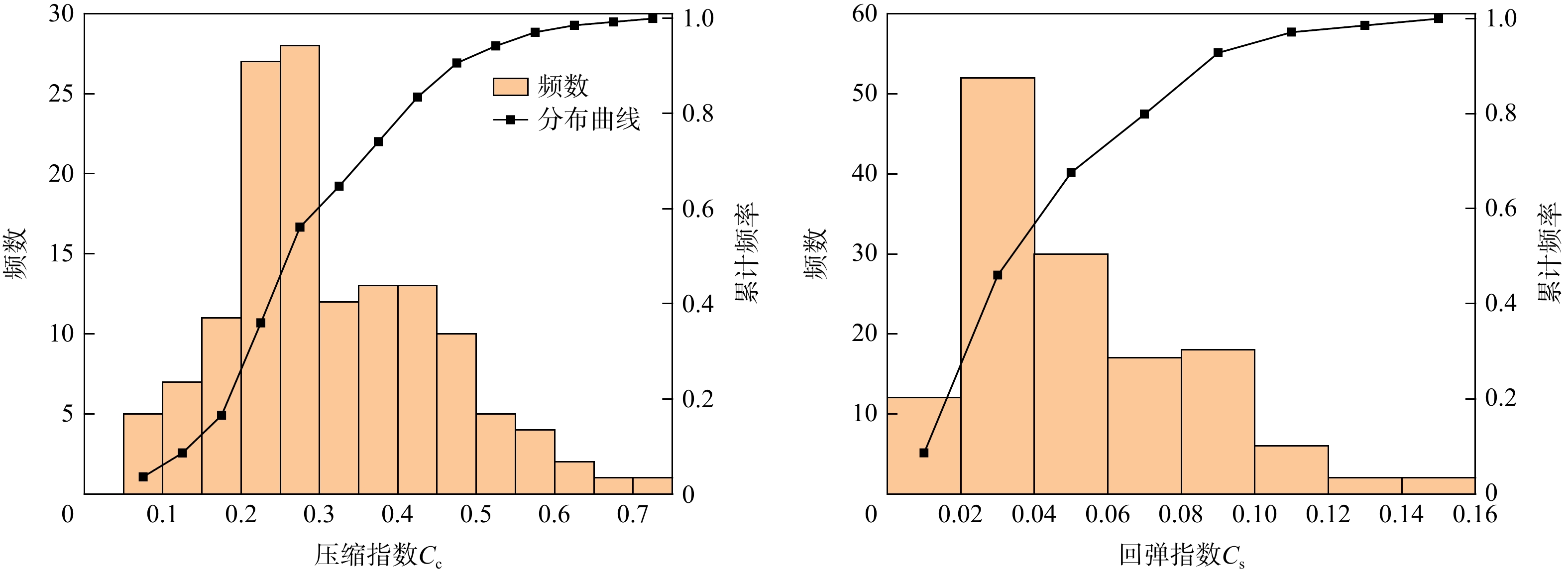
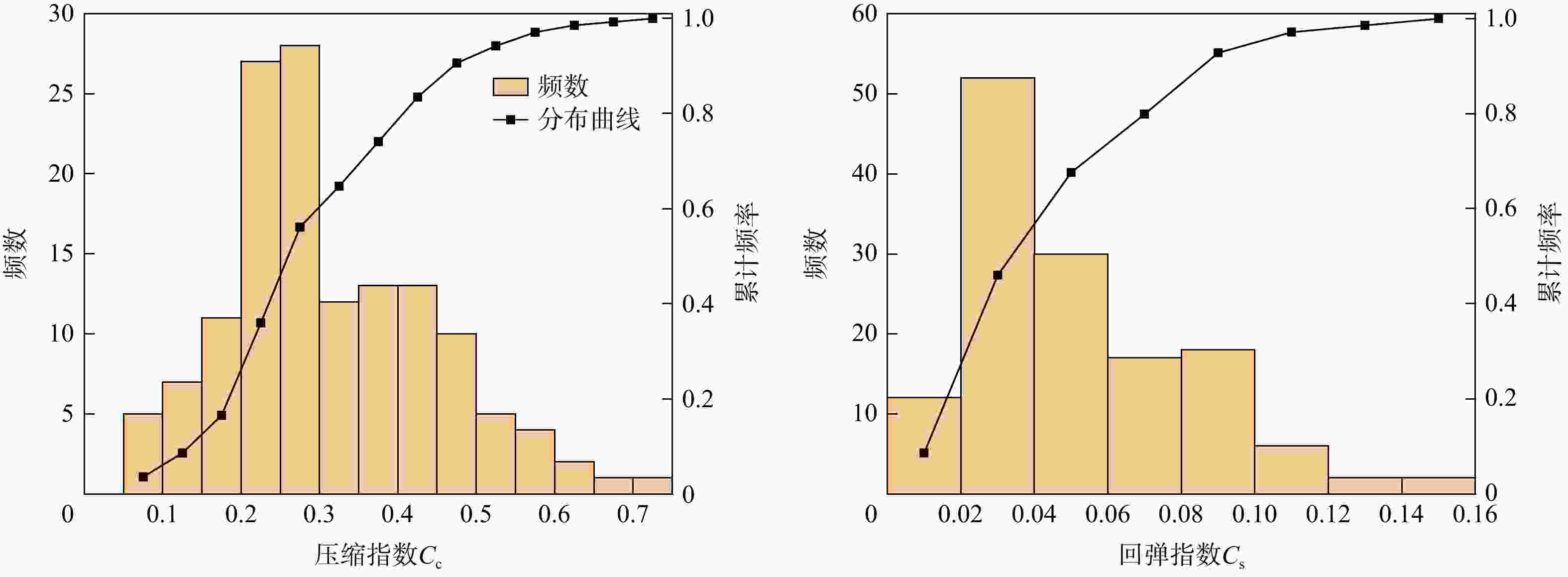
参数 H/m wn/% γ/(KN·m−3) e wL/% wp/% Ip IL $\sigma {'_{\mathrm{v}}}$/kPa ${C_{\mathrm{c}}}$ ${C_{\mathrm{s}}}$ 平均值 7.153 43.352 17.59 1.198 44.922 23.504 21.419 1.249 65.476 0.315 0.05 最小值 0.3 23 14.98 0.520 19 12 1 0.150 4 0.052 0.012 最大值 20.1 74.9 20.6 2.360 94 39 60.6 6.183 213.82 0.700 0.15 标准误差 0.463 0.958 0.083 0.025 1.452 0.332 1.216 0.085 4.594 0.011 0.003 注:参数含义见正文 表 3 土类指数${I_{\mathrm{c}}}$分类表[47]
Table 3. Soil behaviour type index ${I_{\mathrm{c}}}$ chart
土类 ${I_{\mathrm{c}}}$ 砾砂−砂 ${I_{\mathrm{c}}} < 1.31$ 砂土:纯净砂−粉质砂土 $1.31 < {I_{\mathrm{c}}} < 2.05$ 砂土混合物:粉质砂土−砂质粉土 $2.05 < {I_{\mathrm{c}}} < 2.60$ 粉土混合物:黏质粉土−粉质黏土 $2.60 < {I_{\mathrm{c}}} < 2.95$ 黏土:黏土−粉质黏土 $2.95 < {I_{\mathrm{c}}} < 3.60$ 有机质土−泥炭 ${I_{\mathrm{c}}} > 3.60$ 表 4 多模型输入数据相关性分析
Table 4. Model input data correlation analysis
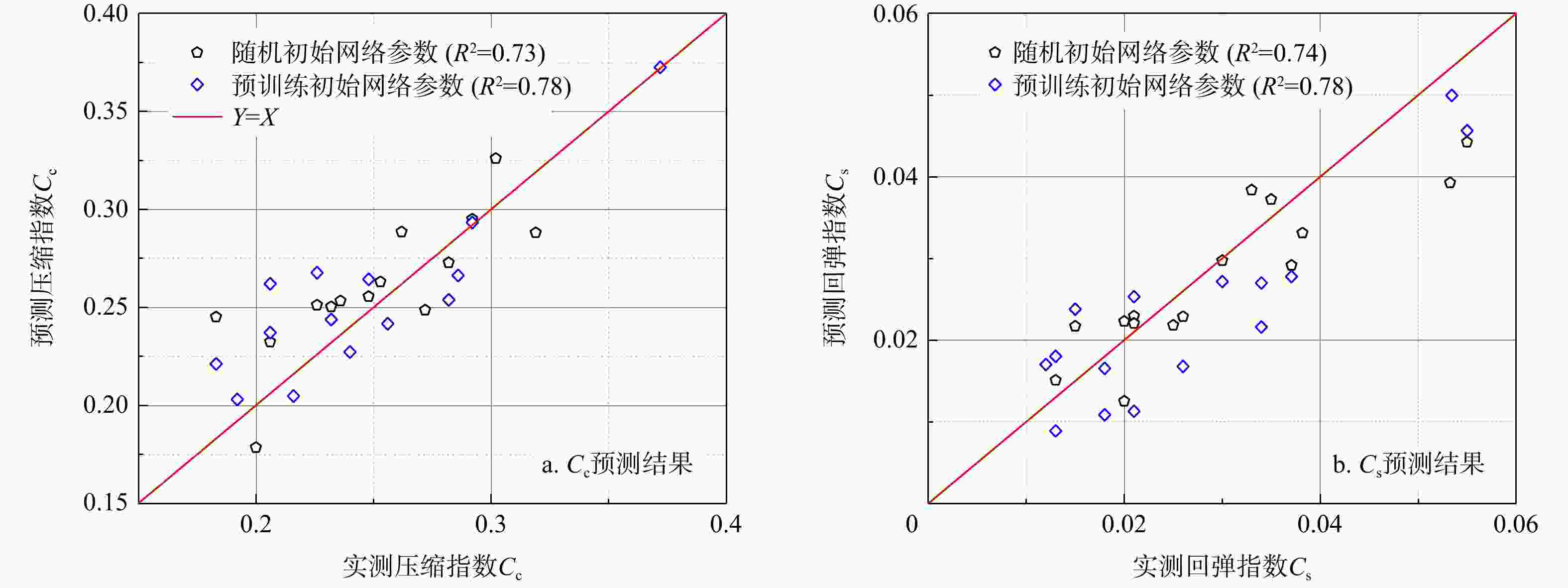
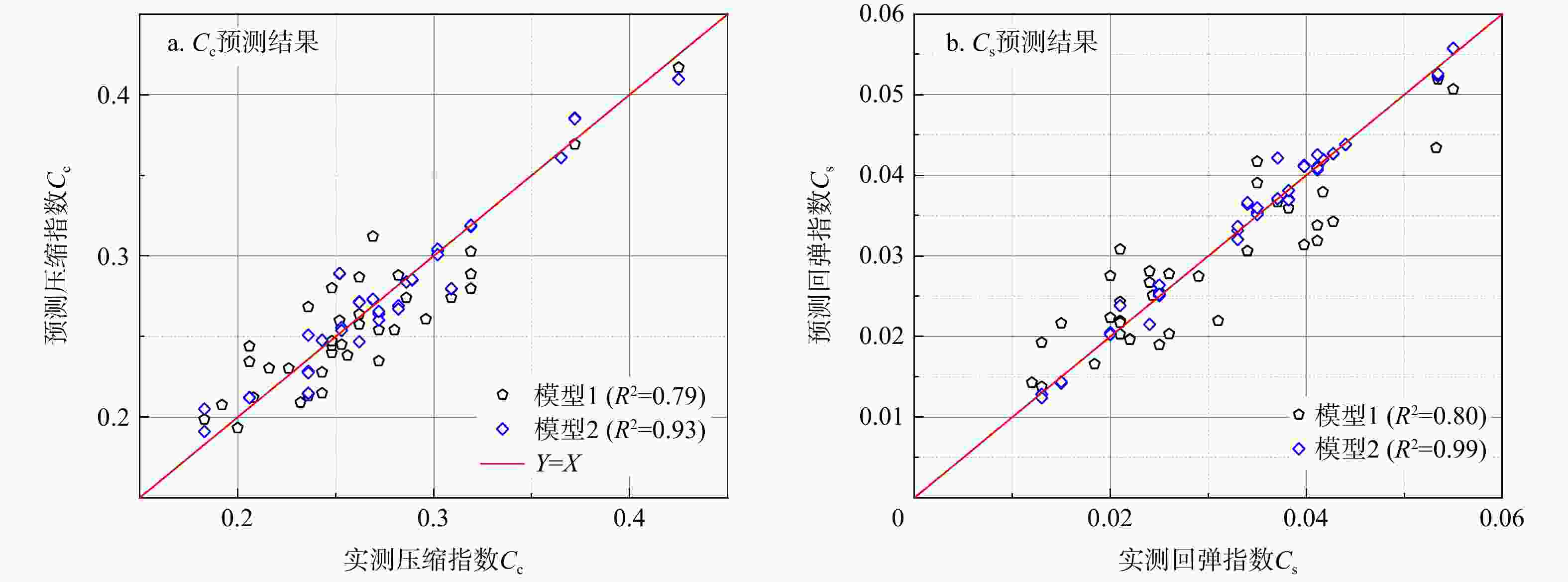
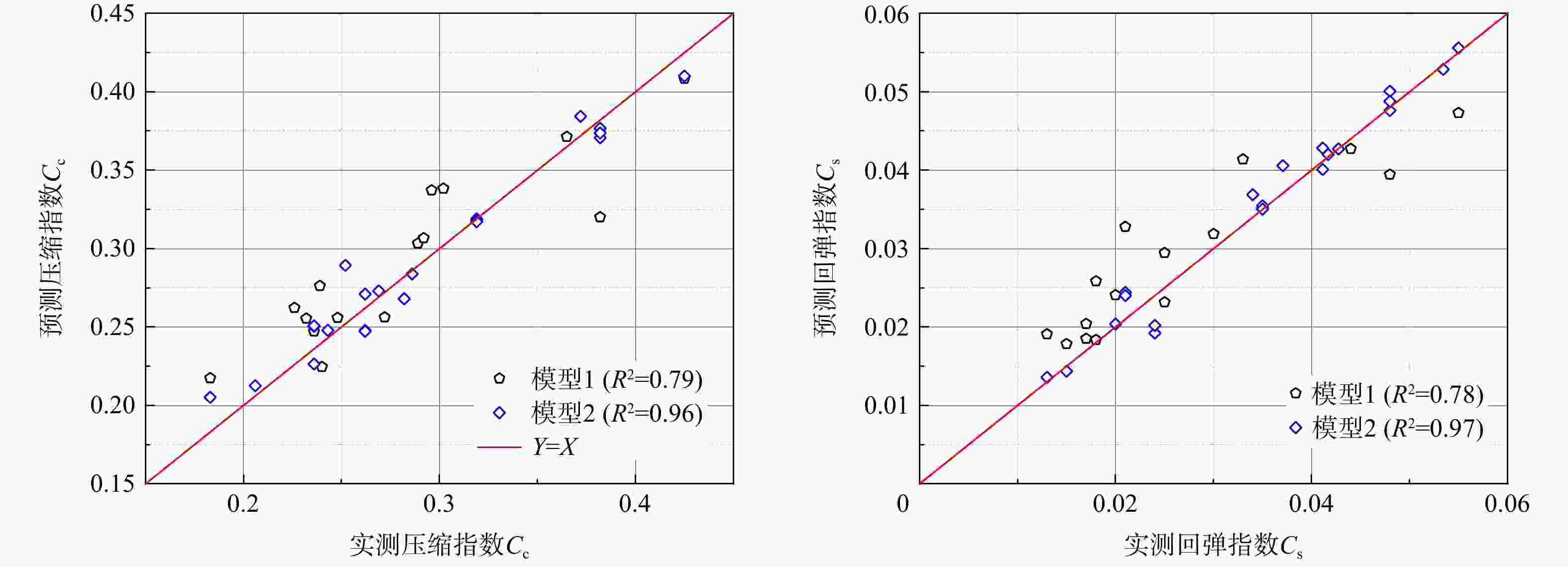
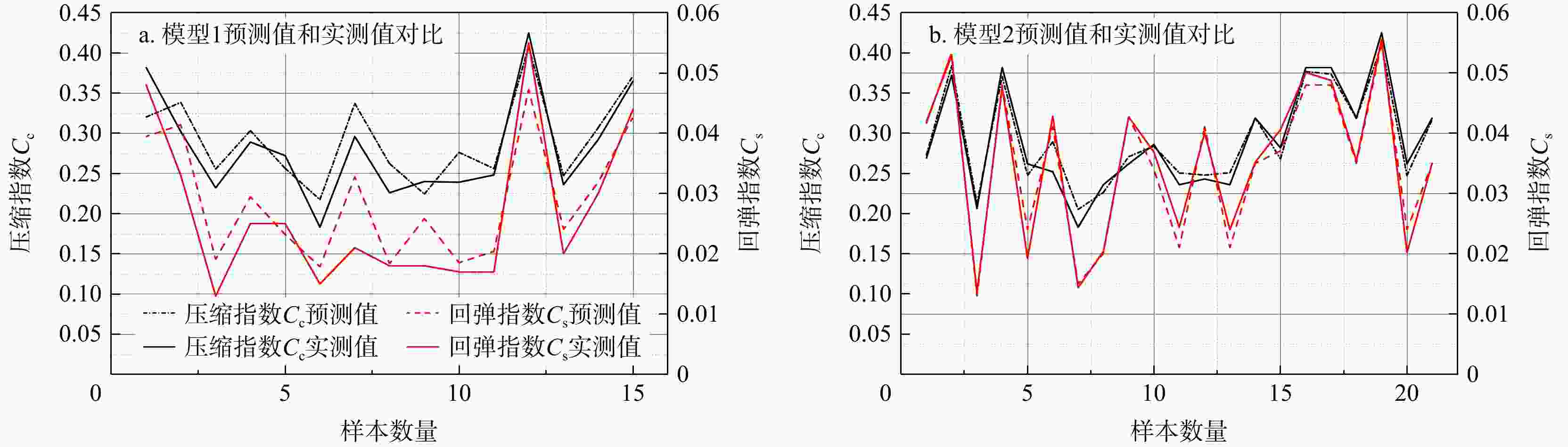
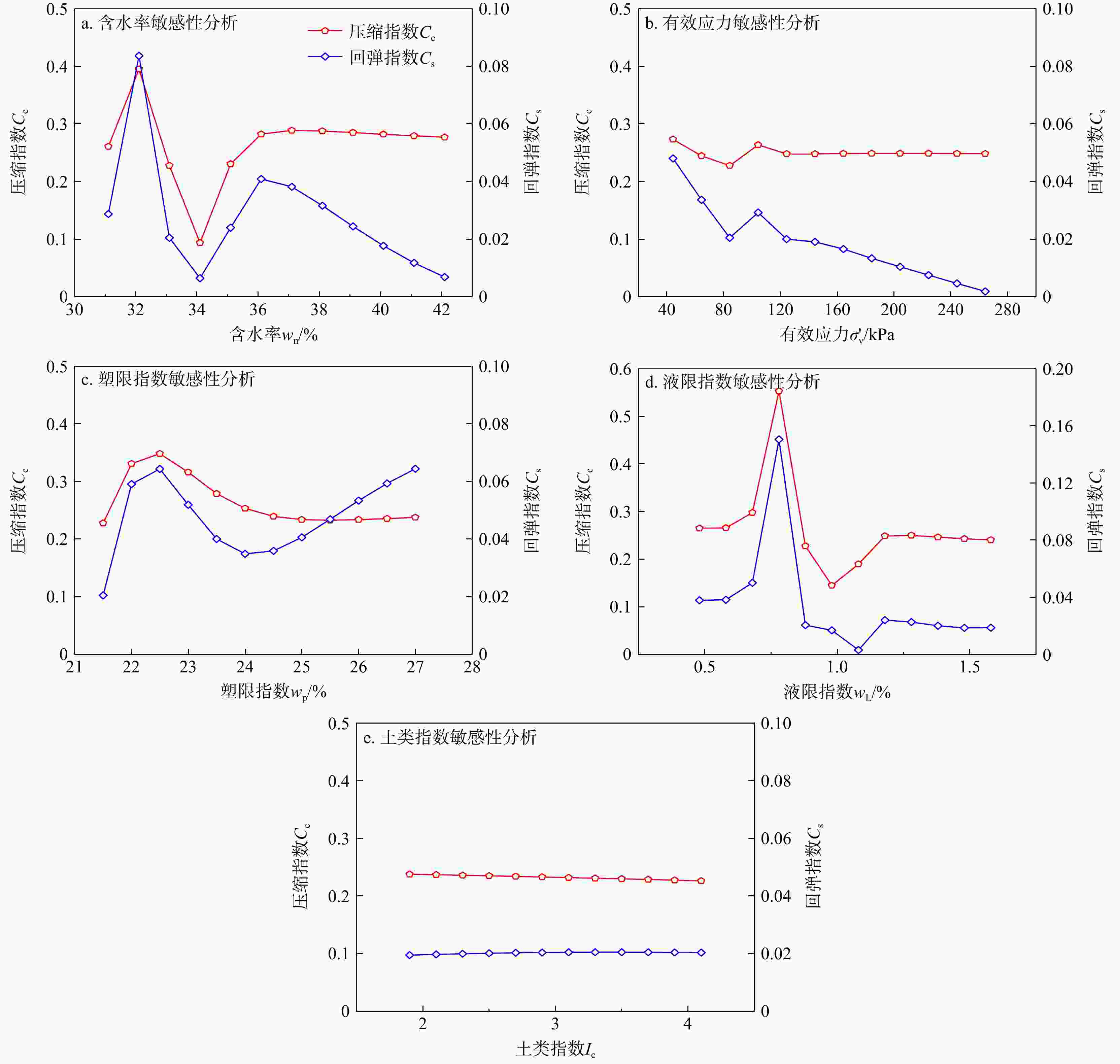
参数 e wn/% wL/% wp/% $\gamma $/(kN·m−3) $ \sigma {'_v} $/kPa H/m Ip IL Ic e 1 0.93 0.49 0.42 0.76 0.37 0.22 0.47 0.07 0.26 wn/% 1 0.44 0.34 0.70 0.48 0.32 0.44 0.16 0.31 wL/% 1 0.77 0.47 0.51 0.48 0.99 0.51 0.09 wp/% 1 0.40 0.27 0.25 0.64 0.39 0.44 $\gamma $/(kN·m−3) 1 0.21 0.14 0.46 0.18 0.23 $ \sigma {'_v} $/kPa 1 0.94 0.54 0.07 0.05 H/m 1 0.50 0.17 0.04 Ip 1 0.50 0.15 IL 1 0.27 Ic 1 注:参数含义见正文 表 5 南京场地不同GA-BPNN模型检验结果
Table 5. Different GA-BPNN model test results at the Nanjing site
模型 数据集 输出参数 ${R^2}$ 均方根误差
RMSE平均绝对偏差
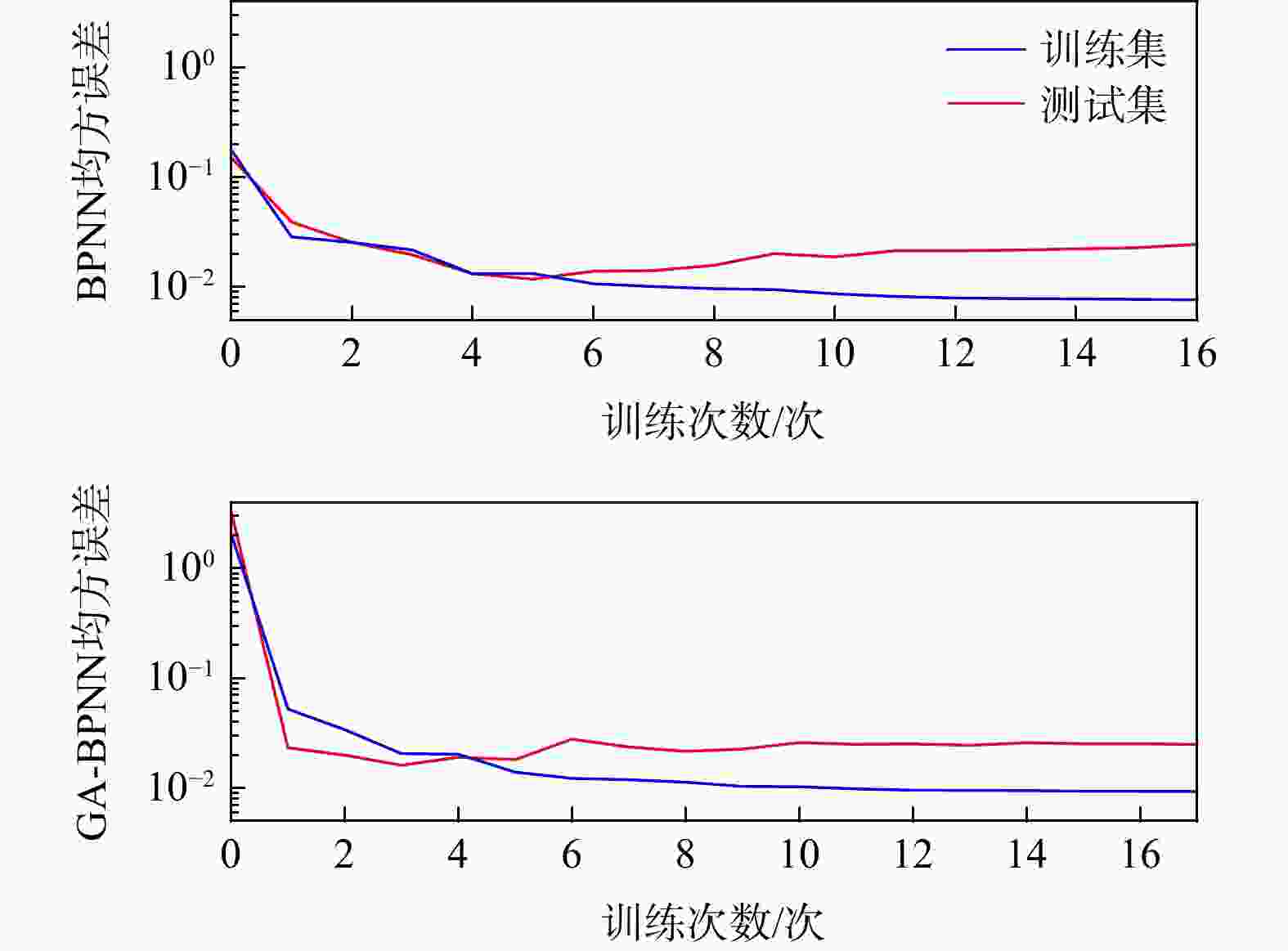
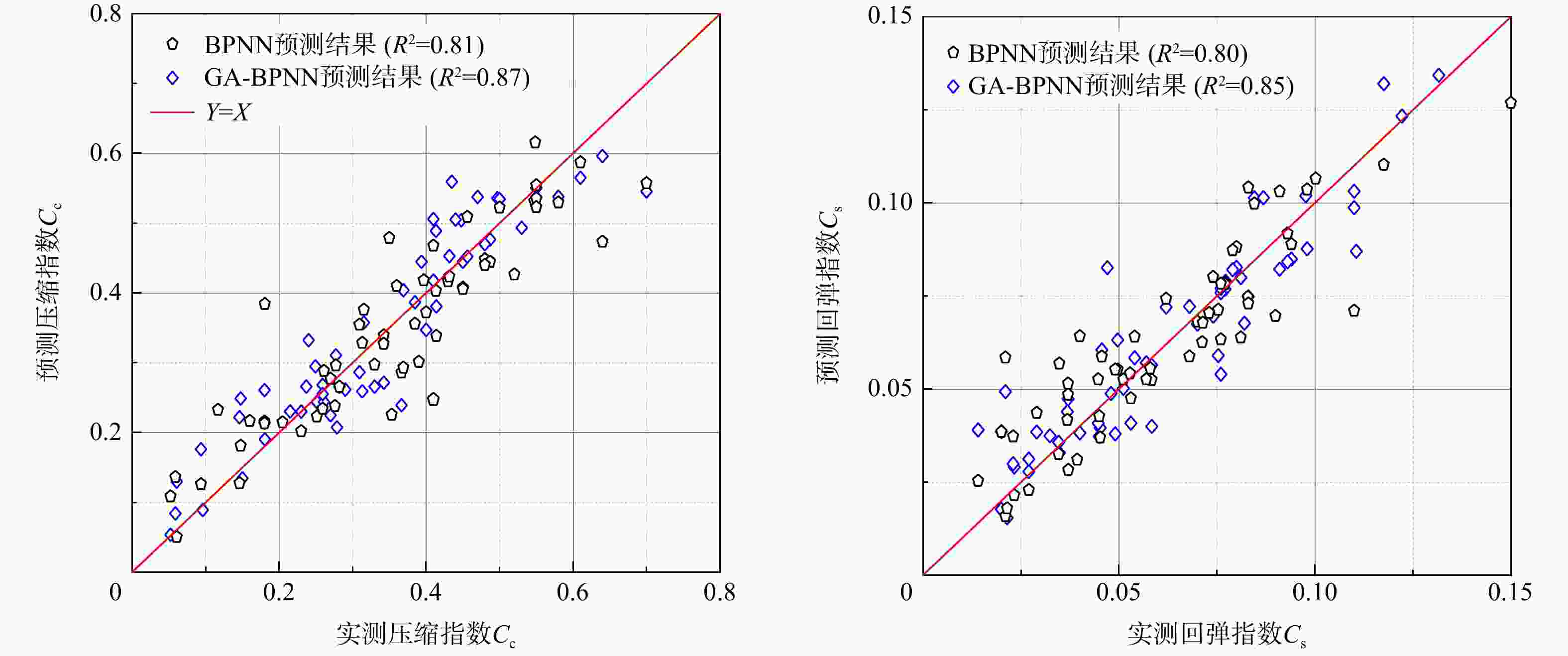
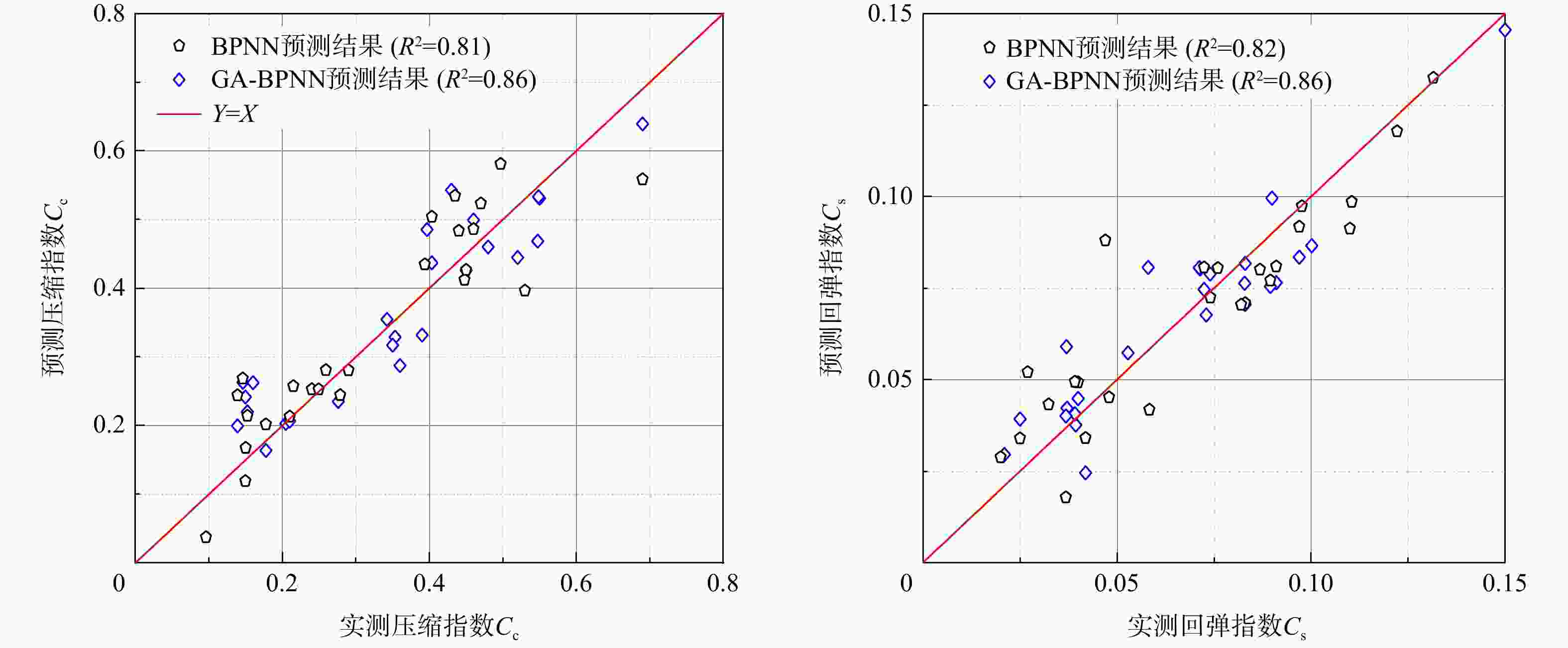
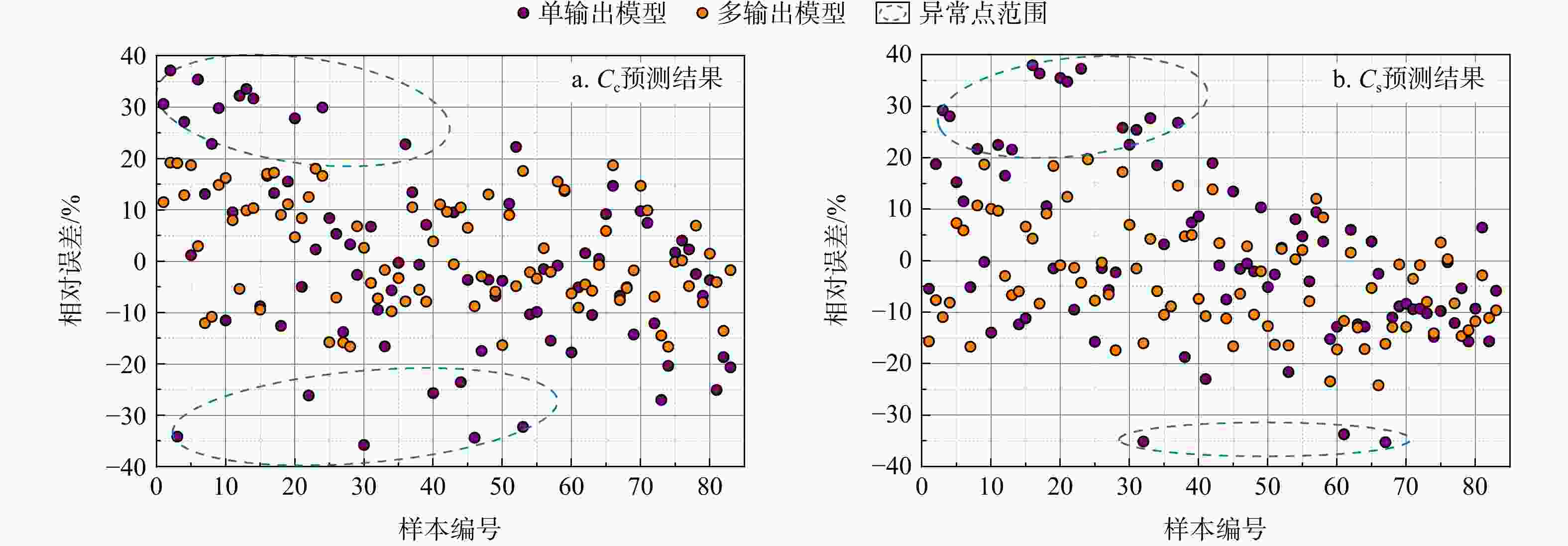
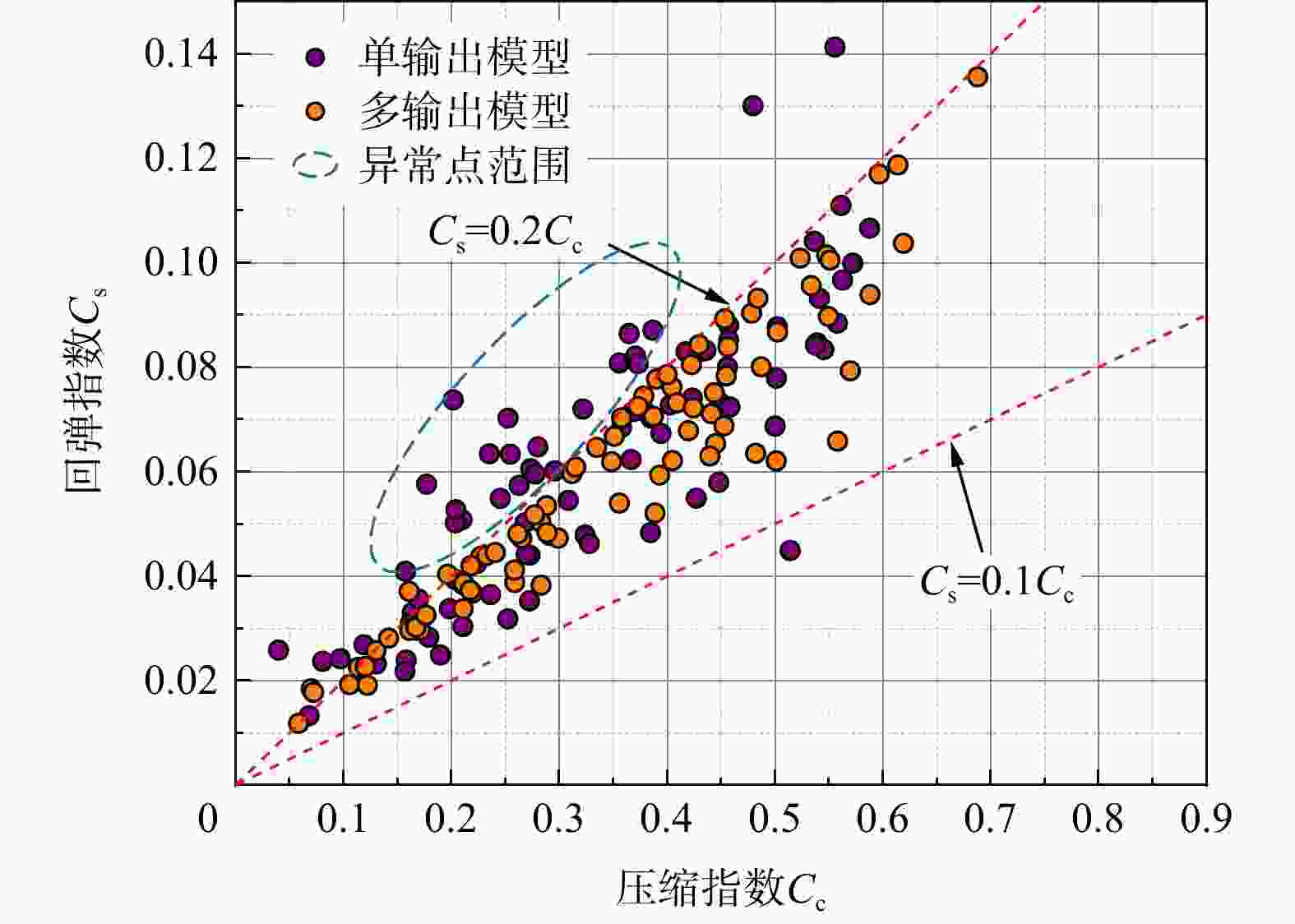
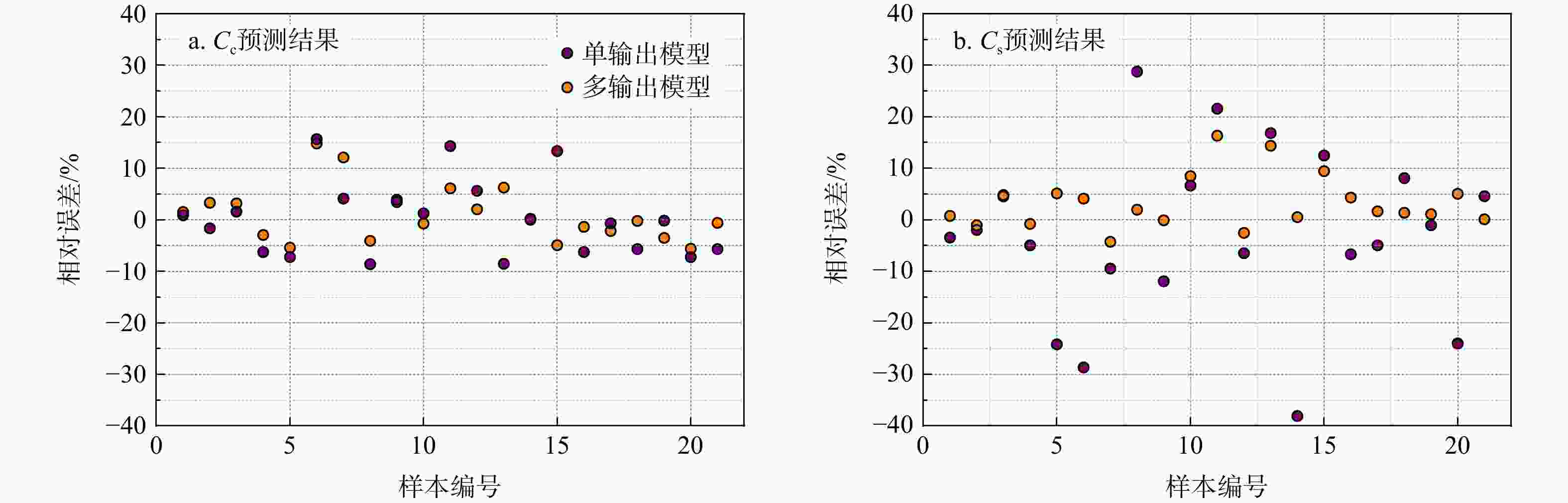
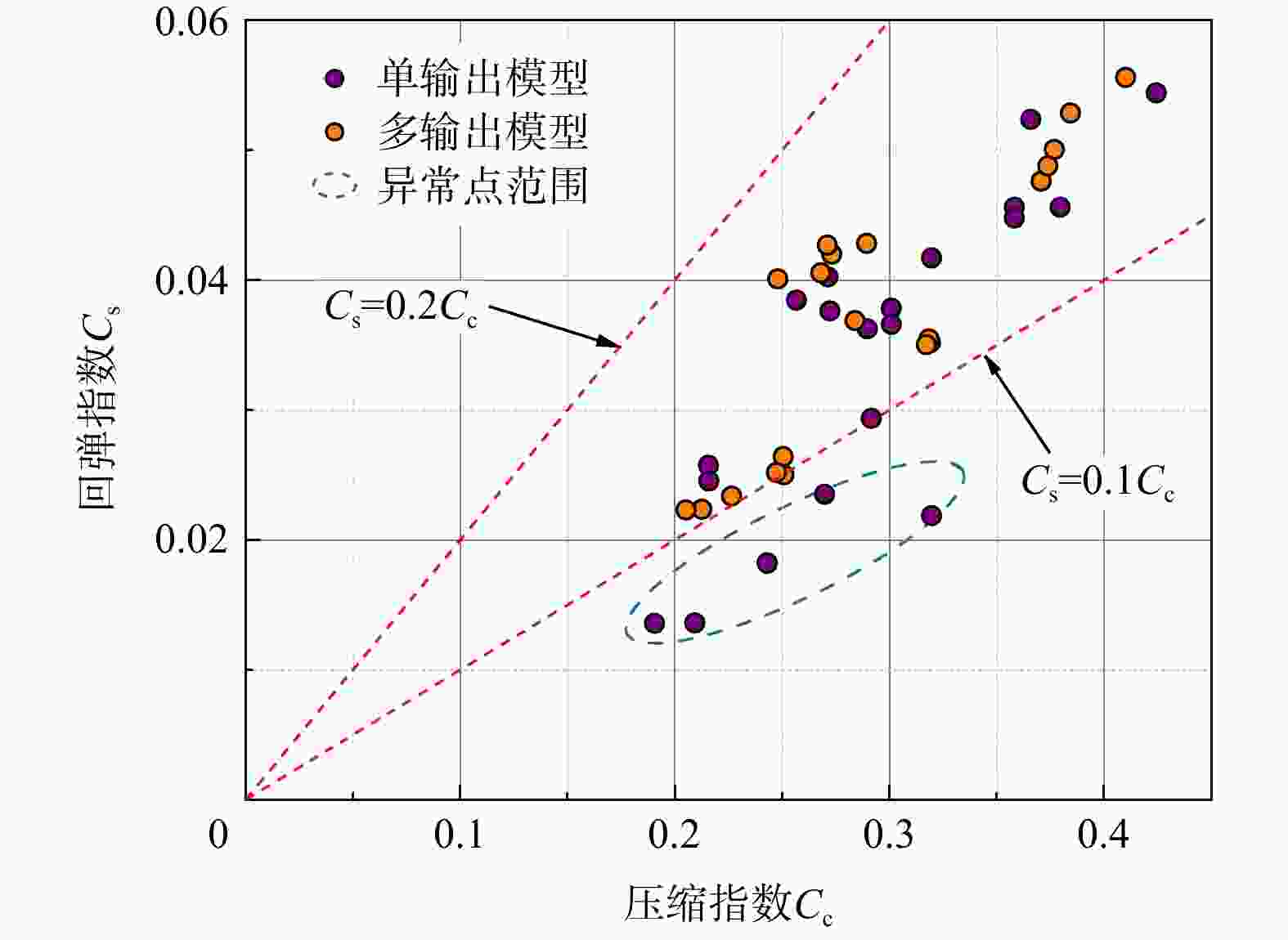
MAE模型1 训练集 $ {C_{\mathrm{c}}} $ 0.79 2.2×10−2 1.9×10−2 $ {C_{\text{s}}} $ 0.81 5.0×10−3 4.0×10−3 测试集 $ {C_{\mathrm{c}}} $ 0.82 2.9×10−2 2.5×10−2 $ {C_{\text{s}}} $ 0.84 6.0×10−3 5.0×10−3 模型2 训练集 $ {C_{\mathrm{c}}} $ 0.93 1.4×10−2 1.0×10−2 $ {C_{\text{s}}} $ 0.99 1.0×10−3 1.0×10−3 测试集 $ {C_{\mathrm{c}}} $ 0.96 1.3×10−2 1.1×10−2 $ {C_{\text{s}}} $ 0.97 2.0×10−3 1.0×10−3 -
[1] TIWARI B,AJMERA B. Consolidation and swelling behavior of major clay minerals and their mixtures[J]. Applied Clay Science,2011,54(3/4):264-273. [2] 楼晓明,李德宁,杨敏. 上海地区基坑底部粉质黏土回弹变形参数分析[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版),2012,40(4):535-540.LOU X M,LI D N,YANG M. Statistical analysis for rebound deformation parameters of silty clay at bottom of deep excavation in Shanghai[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science),2012,40(4):535-540. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 何平,王卫东,徐中华. 上海黏土压缩指数和回弹指数经验关系[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(10):3773-3782.HE P,WANG W D,XU Z H. Empirical correlations of compression index and swelling index for Shanghai clay[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2018,39(10):3773-3782. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 陈波,孙德安,吕海波. 海相软土压缩特性的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2013,34(2):381-388.CHEN B,SUN D A,LÜ H B. Experimental study of compression behavior of marine soft clays[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2013,34(2):381-388. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 周葆春,张彦钧,汤致松,等. 不同压实度荆门弱膨胀土的一维膨胀−压缩特性[J]. 岩土力学,2014,35(5):1275-1283.ZHOU B C,ZHANG Y J,TANG Z S,et al. One-dimensional swelling-compression characteristics of Jingmen weak expansive soil under different compactnesses[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2014,35(5):1275-1283. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 张帆舸,黄昌富,姚铁军,等. 泥炭土压缩及回弹变形规律试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2021,43(增刊2):259-262.ZHANG F G,HUANG C F,YAO T J,et al. Experimental study on laws of compression and rebound deformation of peaty soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2021,43(S2):259-262. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] MESRI G,VARDHANABHUTI B. Compression of granular materials[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2009,46(4):369-392. doi: 10.1139/T08-123 [8] 高彦斌,张松波,葛潇楠. 我国沿海地区软黏土压缩指数统计及与国外其他地区对比[J]. 岩土力学,2017,38(9):2713-2720.GAO Y B,ZHANG S B,GE X N. Comparisons of compression index of Chinese coastal soft clay and soils from foreign regions[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2017,38(9):2713-2720. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] AZZOUZ A S,KRIZEK R J,COROTIS R B. Regression analysis of soil compressibility[J]. Soils and Foundations,1976,16(2):19-29. doi: 10.3208/sandf1972.16.2_19 [10] KOPPULA S D. Statistical estimation of compression index[J]. Geotechnical Testing Journal,1981,4(2):68-73. doi: 10.1520/GTJ10768J [11] RENDON-HERRERO O. Universal compression index equation[J]. Journal of the Geotechnical Engineering Division,1980,106(11):1179-1200. doi: 10.1061/AJGEB6.0001058 [12] PARK H I,LEE S R. Evaluation of the compression index of soils using an artificial neural network[J]. Computers and Geotechnics,2011,38(4):472-481. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2011.02.011 [13] 赵有明,江辉煌,张惠明. 深圳地区软黏土变形参数研究[J]. 中国铁道科学,2004,25(3):40-43. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2004.03.009ZHAO Y M,JIANG H H,ZHANG H M. Deformation parameters of Shenzhen soft clay[J]. China Railway Science,2004,25(3):40-43. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2004.03.009 [14] 顾小芸. 应用数理统计方法确定海洋土的工程特性[C]//佚名. 中国土木工程学会第四届土力学及基础工程学术会议论文集. 武汉:[出版社不详],1983:422-428.GU X Y. Through the method of mathematical statistics to determine the engineering properties of marine soil[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the fourth academic conference on soil mechanics and foundation engineering of China Civil Engineering Society. Wuhan:[S. n. ],1983:422-428. (in Chinese) [15] 魏道垛,胡中雄. 上海浅层地基土的前期固结压力及有关压缩性参数的试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,1980,2(4):13-22. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1980.04.002WEI D D,HU Z X. Experimental study of preconsolidation pressure and compressibility parameters of Shanghai subsoil[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,1980,2(4):13-22. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1980.04.002 [16] NISHIDA Y. A brief note on compression index of soil[J]. Journal of the Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division,1956,82(3):1027-1-1027-14. [17] COZZOLINO V M. Statistical forecasting of compression index[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the 5th international conference on soil mechanics and foundation engineering. Paris:[S. n. ],1961,1:51-53. [18] 朱小林. 软土压缩性参数的估算方法[J]. 勘察科学技术,1987(4):20-22.ZHU X L. The estimation method of compressibility parameters of soft soil[J]. Site Investigation Science and Technology,1987(4):20-22. (in Chinese) [19] MAYNE P W. Cam-clay predications of undrained strength[J]. Journal of the Geotechnical Engineering Division,1980,106(11):1219-1242. doi: 10.1061/AJGEB6.0001060 [20] 孙更生,郑大同. 软土地基与地下工程[M]. 北京:中国建筑工业出版社,1984.SUN G S,ZHENG D T. Soft soil foundation and underground engineering[M]. Beijing:China Architecture & Building Press,1984. (in Chinese) [21] ALPTEKIN A,TAGA H. Prediction of compression and swelling index parameters of quaternary sediments from index tests at Mersin district[J]. Open Geosciences,2019,11(1):482-491. doi: 10.1515/geo-2019-0038 [22] IŞIK N. Estimation of swell index of fine grained soils using regression equations and artificial neural networks[J]. Scientific Research and Essays,2009,4:1047-1056. [23] NAGARAJ T S,SRINIVASA MURTHY B R. A critical reappraisal of compression index equations[J]. Géotechnique,1986,36(1):27-32. [24] NAKASE A,KAMEI T,KUSAKABE O. Constitutive parameters estimated by plasticity index[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,1988,114(7):844-858. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1988)114:7(844) [25] ZHANG J,HU J Z,LI X,et al. Bayesian network based machine learning for design of pile foundations[J]. Automation in Construction,2020,118:103295. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103295 [26] ZHANG D M,ZHANG J Z,HUANG H W,et al. Machine learning-based prediction of soil compression modulus with application of 1D settlement[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University(Science A),2020,21(6):430-444. doi: 10.1631/jzus.A1900515 [27] AHMAD M,AL-MANSOB R A,RAMLI A B B,et al. Unconfined compressive strength prediction of stabilized expansive clay soil using machine learning techniques[J]. Multiscale and Multidisciplinary Modeling,Experiments and Design,2024,7(1):217-231. doi: 10.1007/s41939-023-00203-7 [28] 黄发明,陈彬,毛达雄,等. 基于自筛选深度学习的滑坡易发性预测建模及其可解释性[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(5):1696-1710.HUANG F M,CHEN B,MAO D X,et al. Landslide susceptibility prediction modeling and interpretability based on self-screening deep learning model[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(5):1696-1710. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 蒋水华,刘源,章浩龙,等. 先验概率分布及似然函数模型的选择对边坡可靠度评价影响的定量评估[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(9):3087-3097.JIANG S H,LIU Y,ZHANG H L,et al. Quantitatively evaluating the effects of prior probability distribution and likelihood function models on slope reliability assessment[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2020,41(9):3087-3097. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 赵玉,陈丽霞,梁梦姣. 基于LSTM_TCN模型的降雨型滑坡时间概率预测及气象预警建模[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(2):201-214.ZHAO Y,CHEN L X,LIANG M J. Temporal probability prediction and meteorological early warning modeling of rainfall-induced landslide based on LSTM_TCN model[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(2):201-214. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] YAN D D,ZHAO T Y,XU L,et al. Statistical modeling of multivariate loess properties in Taiyuan using regular vine copula with optimized tree structure[J]. Transportation Geotechnics,2023,41:101025. doi: 10.1016/j.trgeo.2023.101025 [32] 黄发明,李金凤,王俊宇,等. 考虑线状环境因子适宜性和不同机器学习模型的滑坡易发性预测建模规律[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(2):44-59.HUANG F M,LI J F,WANG J Y,et al. Modelling rules of landslide susceptibility prediction considering the suitability of linear environmental factors and different machine learning models[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(2):44-59. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 李可飞,许领,赵腾远,等. 基于Johnson分布体系黄土滑坡影响范围的概率预测[J]. 工程地质学报,2023,31(2):493-501.LI K F,XU L,ZHAO T Y,et al. Probabilistic prediction of loess landslide impact range using Johnson's system[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2023,31(2):493-501. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] 张驰,潘懋,胡水清,等. 融合储层纵向信息的机器学习岩性识别方法[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(3):289-299.ZHANG C,PAN M,HU S Q,et al. A machine learning lithologic identification method combined with vertical reservoir information[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(3):289-299. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] 王才进,武猛,杨洋,等. 基于生物地理优化的人工神经网络模型预测软土的固结系数[J]. 岩土力学,2023,44(10):3022-3030.WANG C J,WU M,YANG Y,et al. Prediction of consolidation coefficient of soft soil using an artificial neural network models with biogeography-based optimization[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2023,44(10):3022-3030. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] 王长虹,吴昭欣,王昆,等. CPTU数据校准上海深层软土参数的随机力学−贝叶斯方法[J]. 岩土工程学报,2023,45(1):75-84. doi: 10.11779/CJGE20211494WANG C H,WU Z X,WANG K,et al. Stochastic mechanics-based Bayesian method for calibrating geotechnical parameters of Shanghai deep soft clay using CPTU data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2023,45(1):75-84. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11779/CJGE20211494 [37] 段伟,蔡国军,刘松玉,等. 基于多功能CPTU测试的无黏性土状态参数评价研究[J]. 中国公路学报,2022,35(1):200-209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2022.01.018DUAN W,CAI G J,LIU S Y,et al. Evaluation of state parameter of cohesion less soils based on multifunctional CPTU data[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport,2022,35(1):200-209. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2022.01.018 [38] ZHAO Z N,CONGRESS S S C,CAI G J,et al. Bayesian probabilistic characterization of consolidation behavior of clays using CPTU data[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2022,17(3):931-948. doi: 10.1007/s11440-021-01277-8 [39] WU M,CAI G J,WANG C J,et al. Mapping constrained modulus differences in a highway widening project based on CPTU data and two-dimensional anisotropic geostatistics[J]. Transportation Geotechnics,2022,32:100686. doi: 10.1016/j.trgeo.2021.100686 [40] TANKIEWICZ M,BAGgIŃSKA I. Assessment and verification of correlations in CPTu testing on the example of soil from the Wroclaw surroundings (Poland)[J]. Archives of Mining Sciences,2021,66(2):313-327. [41] KOSTER K,DE LANGE G,HARTING R,et al. Characterizing void ratio and compressibility of Holocene peat with CPT for assessing coastal-deltaic subsidence[J]. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology and Hydrogeology,2018,51(2):210-218. doi: 10.1144/qjegh2017-120 [42] NGHIA-NGUYEN T,KIKUMOTO M,NGUYEN-XUAN H,et al. Optimization of artificial neutral networks architecture for predicting compression parameters using piezocone penetration test[J]. Expert Systems with Applications,2023,223:119832. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.119832 [43] KIRTS S,PANAGOPOULOS O P,XANTHOPOULOS P,et al. Soil-compressibility prediction models using machine learning[J]. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering,2018,32(1):04017067. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CP.1943-5487.0000713 [44] ZHANG P,YIN Z Y,JIN Y F. Bayesian neural network-based uncertainty modelling:Application to soil compressibility and undrained shear strength prediction[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2022,59(4):546-557. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2020-0751 [45] 高大钊. 土力学与基础工程[M]. 北京:中国建筑工业出版社,1998.GAO D Z. Soil mechanics and foundation engineering[M]. Beijing:China Architecture & Building Press,1998. (in Chinese) [46] OZER M,ISIK N S,ORHAN M. Statistical and neural network assessment of the compression index of clay-bearing soils[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2008,67(4):537-545. doi: 10.1007/s10064-008-0168-8 [47] ROBERTSON P K,WRIDE C F. Evaluating cyclic liquefaction potential using the cone penetration test[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1998,35(3):442-459. doi: 10.1139/t98-017 [48] DING S F,SU C Y,YU J Z. An optimizing BP neural network algorithm based on genetic algorithm[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review,2011,36(2):153-162. doi: 10.1007/s10462-011-9208-z [49] 旷杜敏,龙志林,周益春,等. 基于BP神经网络的岩土胶结材料速率敏感效应预测研究[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(增刊1):390-399.KUANG D M,LONG Z L,ZHOU Y C,et al. Prediction of rate-dependent behaviors of cemented geo-materials based on BP neural network[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2019,40(S1):390-399. (in Chinese with English abstract [50] 周喻,吴顺川,焦建津,等. 基于BP神经网络的岩土体细观力学参数研究[J]. 岩土力学,2011,32(12):3821-3826. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2011.12.045ZHOU Y,WU S C,JIAO J J,et al. Research on mesomechanical parameters of rock and soil mass based on BP neural network[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2011,32(12):3821-3826. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2011.12.045 [51] 薛新华,张我华,刘红军. 基于遗传算法和模糊神经网络的边坡稳定性评价[J]. 岩土力学,2007,28(12):2643-2648. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.12.031XUE X H,ZHANG W H,LIU H J. Evaluation of slope stability based on genetic algorithm and fuzzy neural network[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2007,28(12):2643-2648. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.12.031 [52] VIGNAUX G A,MICHALEWICZ Z. A genetic algorithm for the linear transportation problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems,Man,and Cybernetics,1991,21(2):445-452. doi: 10.1109/21.87092 [53] HE Z G,NGUYEN H,VU T H,et al. Novel integrated approaches for predicting the compressibility of clay using cascade forward neural networks optimized by swarm- and evolution-based algorithms[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2022,17(4):1257-1272. doi: 10.1007/s11440-021-01358-8 -




 下载:
下载: