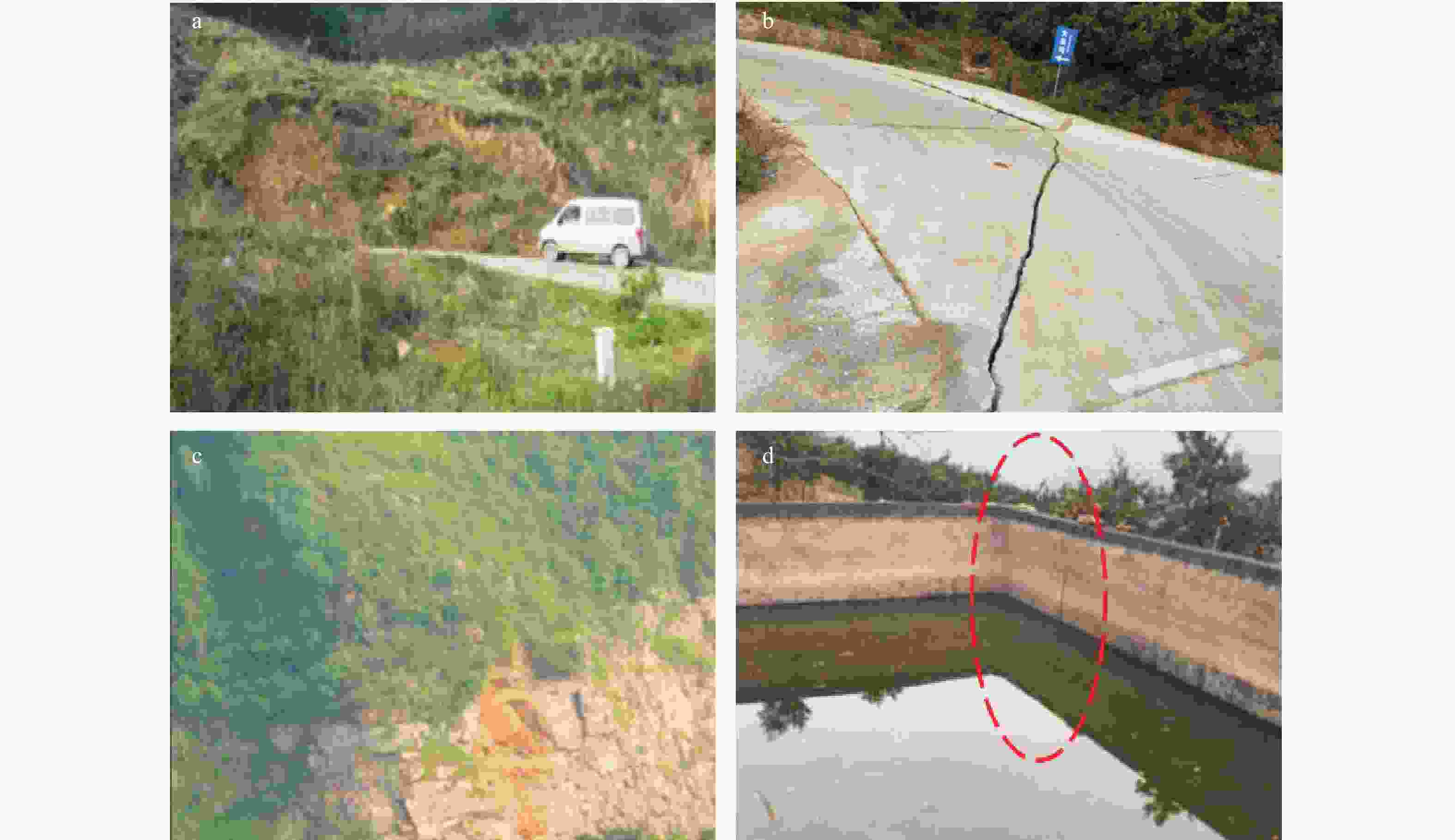
Analysis of spatio-temporal deformation characteristics of the Muyubao landslide via time series InSAR technology
-
摘要:
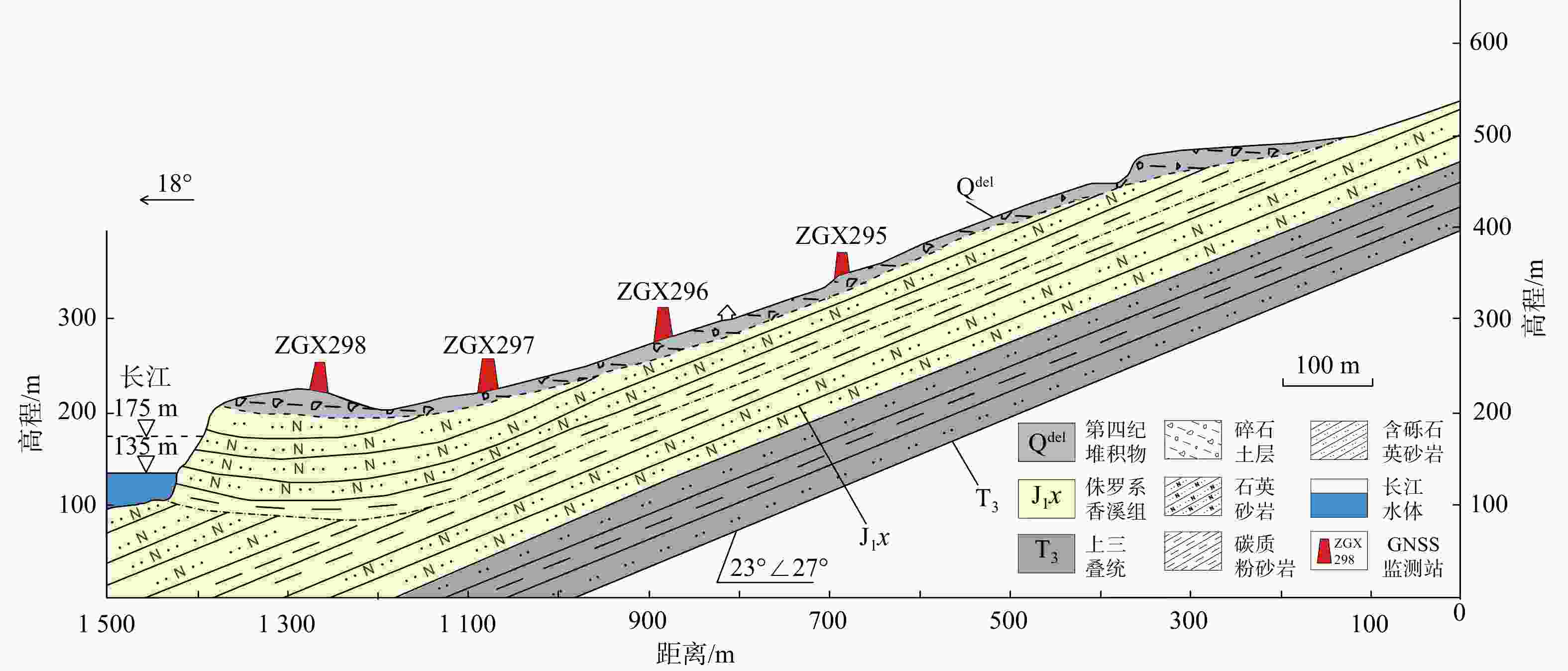
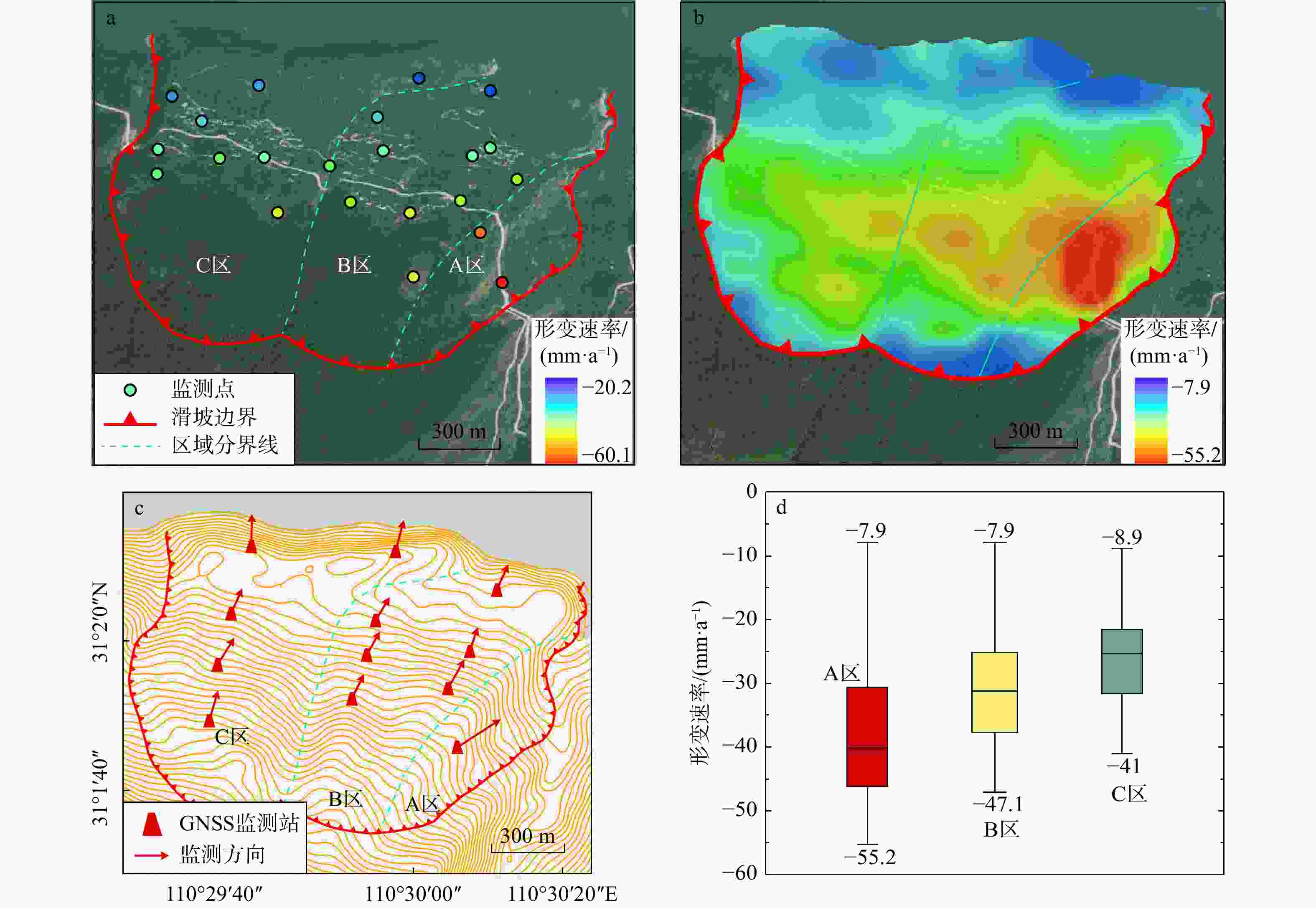
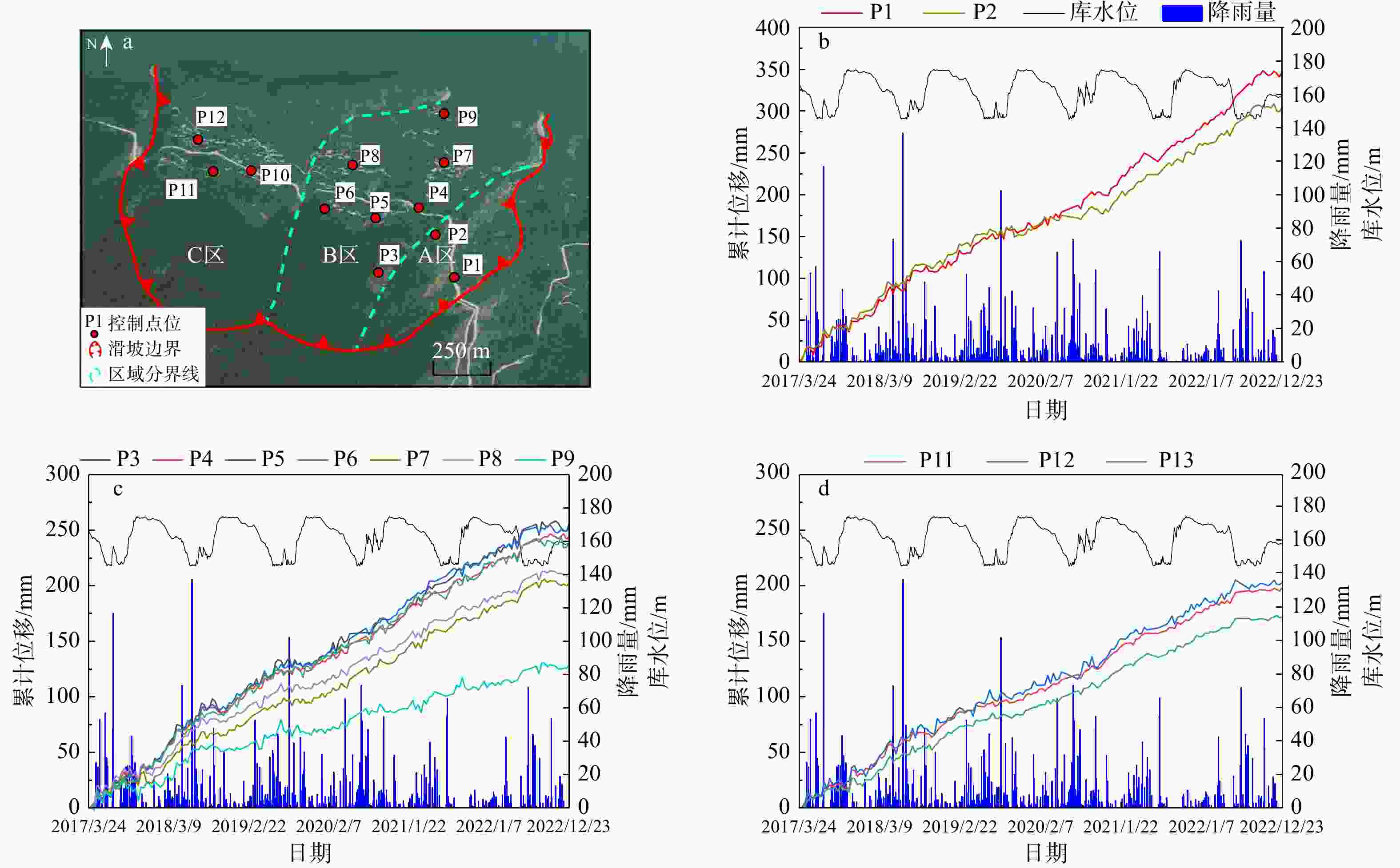
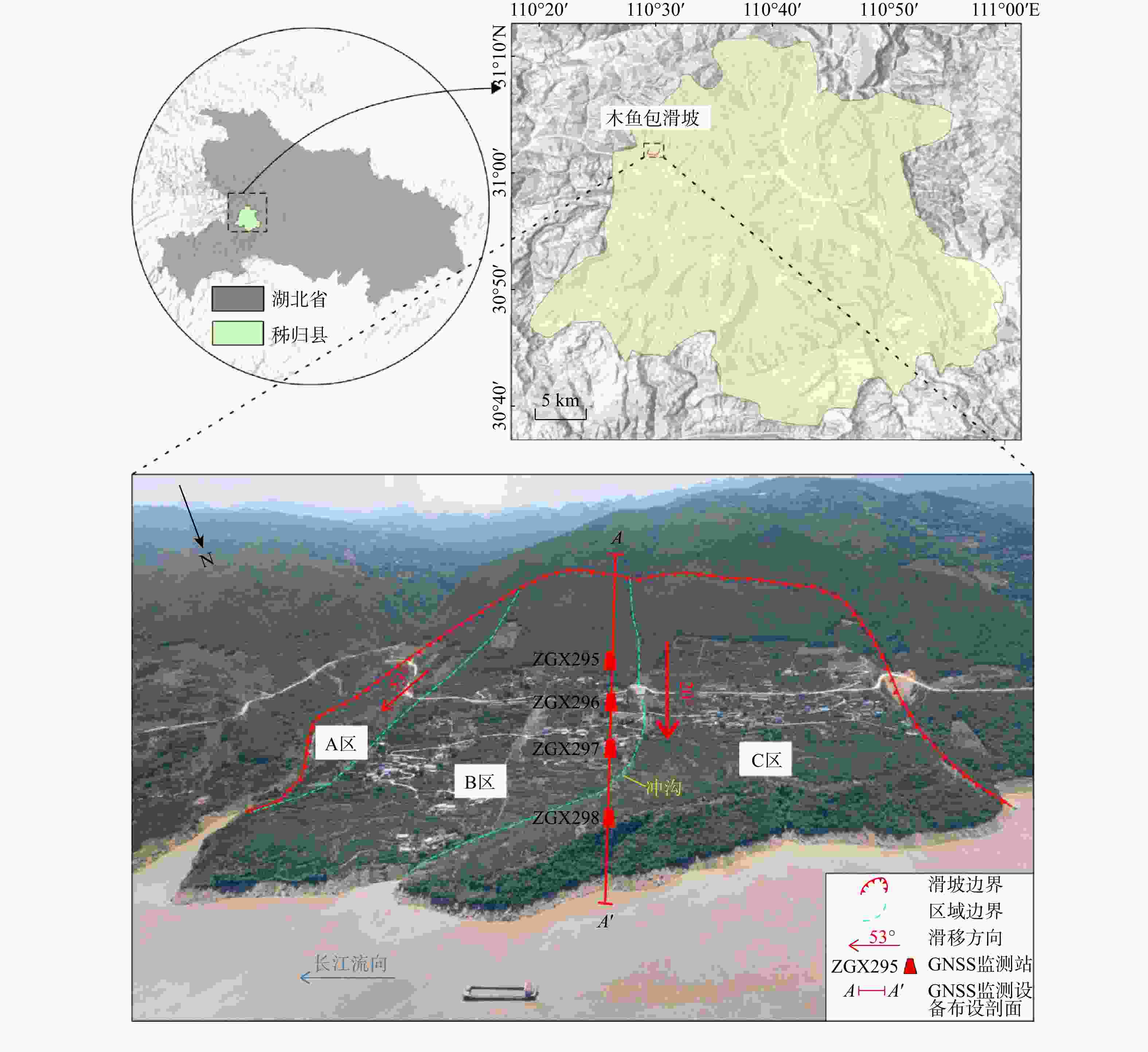
自2003年三峡库区蓄水以来,木鱼包滑坡持续变形,严重威胁长江航运和库区人民生命财产安全。为全面精准地分析滑坡地表变形信息,采用斯坦福永久散射体−多时相InSAR(StaMPS-MTI)技术和短基线集时序InSAR(SBAS-InSAR)技术结合哨兵一号数据反演木鱼包滑坡2017−2022年的地表形变,并与全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)监测数据进行对比分析,结合2种技术的优点,点面结合对滑坡的时空变形特征进行了分区研究。研究结果表明:InSAR技术得到的形变信息可靠,2种时序InSAR技术各有优劣;对比各个分区的形变速率区间值,滑坡东侧坡面(−30.6~−46.2 mm/a)>主滑面东侧(−25.2~−37.8 mm/a)>主滑面西侧(−21.5~−31.5 mm/a)。在InSAR形变结果和前人研究基础上,对木鱼包滑坡变形模式进行了总结:木鱼包滑坡变形受降雨和库水影响,分为整体变形和局部变形2种。在高水位运行期,滑坡受浮托减重作用发生整体变形,库水阈值约为168 m。强降雨入渗岩体使地下水位升高,促使整体变形的同时,影响浅层土体和破碎岩体导致局部变形。在库水位下降期,滑坡受浮托减重和动水压力共同影响,其中浮托减重作用占主导地位,动水压力存在约36 d的滞后时间。在低水位运行期和库水位上升期,整体变形停止,强降雨使局部变形区发生变形。研究结果证明时序InSAR技术可以有效识别和监测滑坡,可以为地质灾害防治、风险评价提供技术支撑。
-
关键词:
- 木鱼包滑坡 /
- 形变监测 /
- SBAS-InSAR /
- StaMPS-MTI /
- 三峡库区 /
- 库水位 /
- 降雨
Abstract:Since the impoundment of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area in 2003, the Muyubao landslide has continuously deformed, posing significant risks to Yangtze River navigation and the safety of people's lives and property in the reservoir area.
Objective To more comprehensively and accurately analyze the surface deformation information of the landslide,
Methods this study employs the Stanford method for persistent scatterers-multi-temporal InSAR (StaMPS-MTI) and small baseline subset InSAR (SBAS-InSAR) technology, combined with Sentinel-1 data, to invert the deformation information of the Muyubao landslide from 2017 to 2022. The deformation information is compared with GNSS monitoring data, and a regional analysis of the spatio-temporal deformation characteristics of the landslide is conducted by integrating the advantages of both technologies through a combination of point and surface measurements.
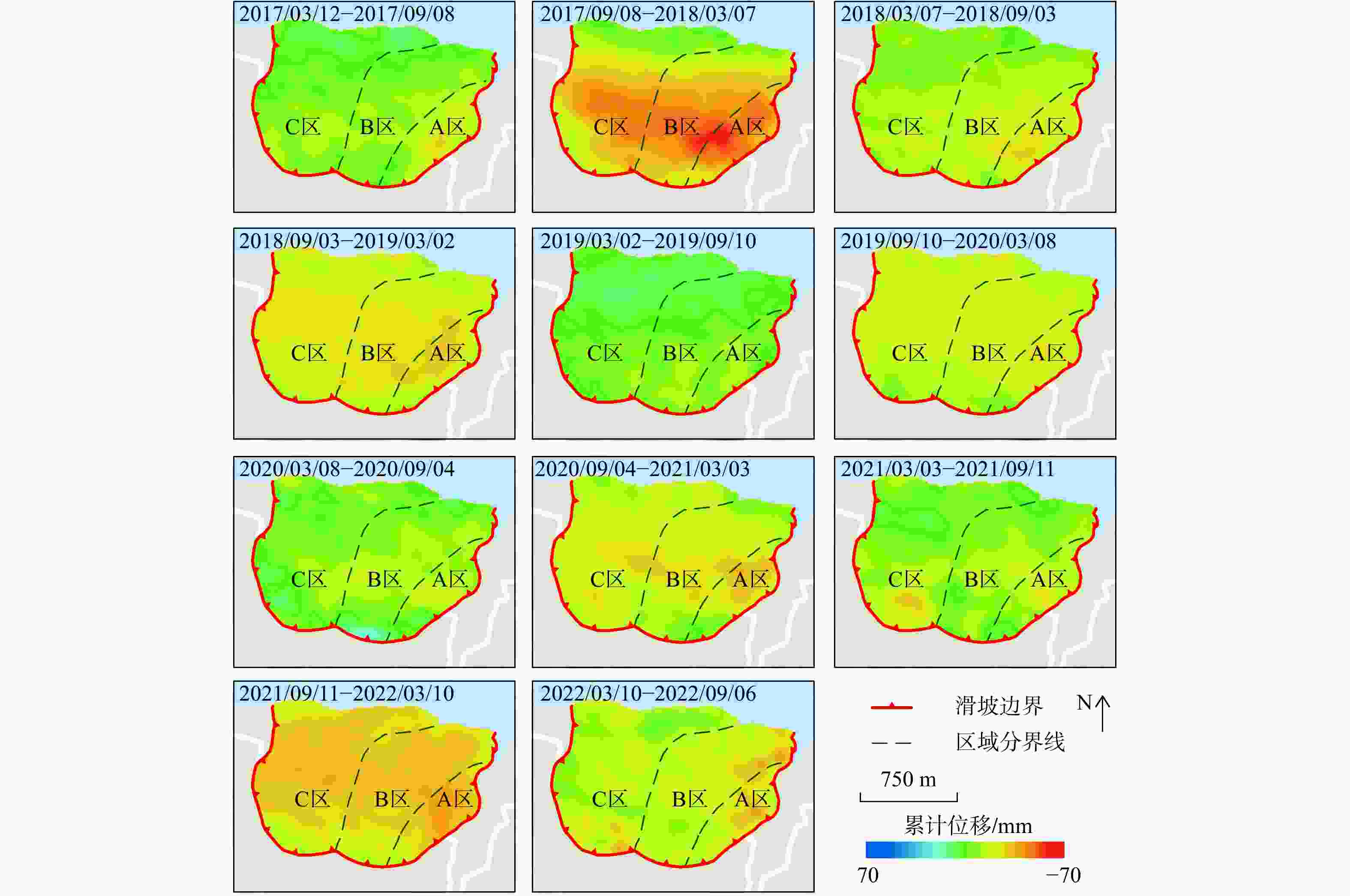
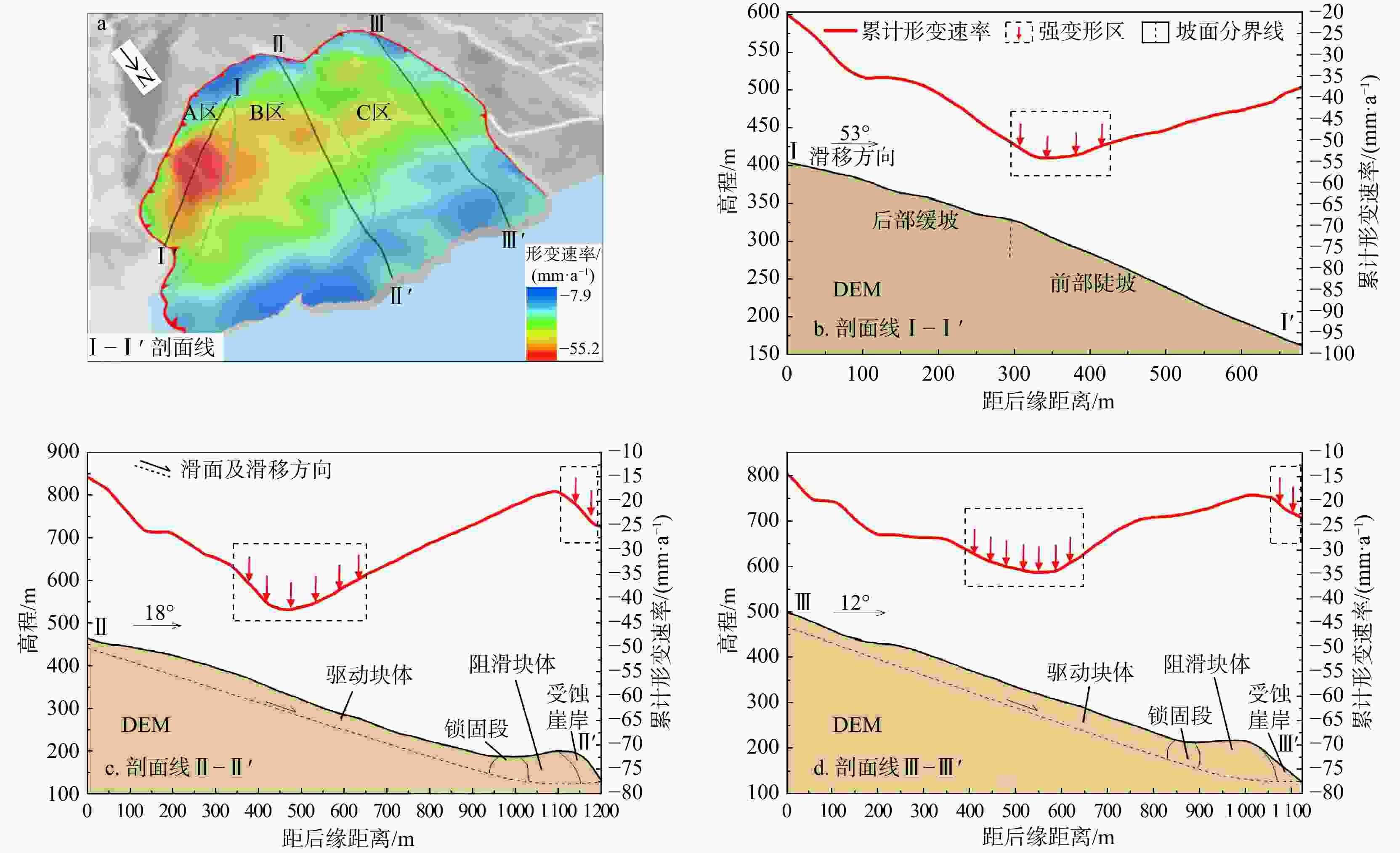
Results The results confirm that the deformation information obtained by InSAR technology is reliable, and each time-series InSAR technology has its own strengths and limitations. Specifically, the deformation rate intervals are as follows: the eastern slope of the landslide (−30.6 to −46.2 mm/year) > the eastern side of the major slipping plane (−25.2 to −37.8 mm/year) > the western side of the major slipping plane (−21.5 to −31.5 mm/year).
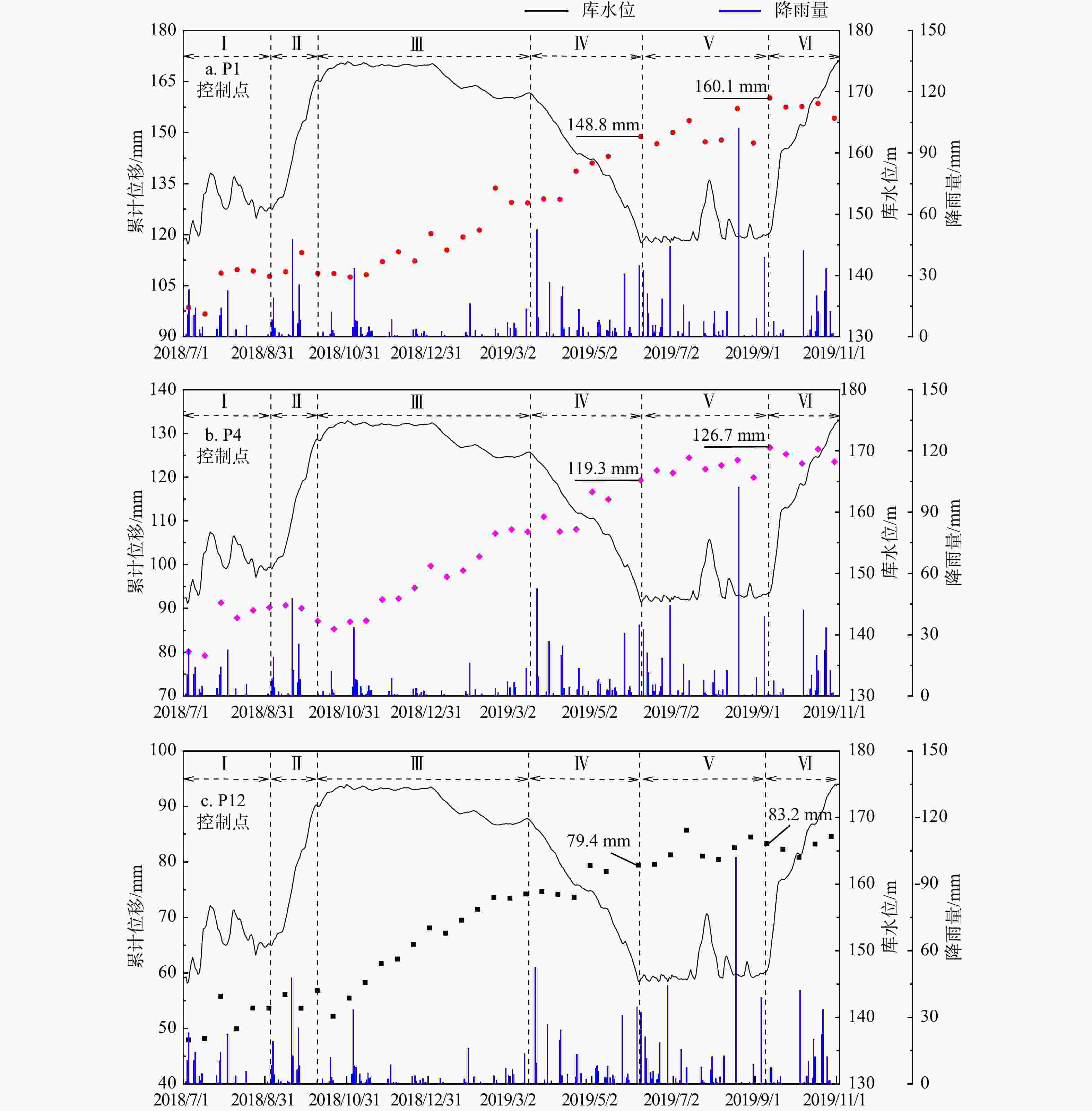
Conclusion Based on the InSAR deformation results and previous studies, the deformation mode of the Muyubao landslide can be summarized as follows: the landslide undergoes overall and local deformation influenced by rainfall and reservoir water levels. During high water level periods, buoyancy-induced weight loss causes overall deformation, with a critical water level threshold of approximately 168 m. Heavy rainfall infiltrates the rock mass, raising the groundwater level, which promotes overall deformation and triggers local deformation in shallow soil and fractured rock masses. During the reservoir water decline period, the landslide is influenced by both buoyancy-induced weight loss and hydrodynamic pressure, with buoyancy effects being dominant; the hydrodynamic pressure effect lags by about 36 days. During low water level and rising water periods, overall deformation ceases, and heavy rainfall primarily causes localized deformation. The results indicate that time-series InSAR technology can effectively identify and monitor landslides, providing technical support for geological disaster prevention and risk assessment.
-
Key words:
- Muyubao landslide /
- deformation monitoring /
- SBAS-InSAR /
- StaMPS-MTI /
- Three Gorges Reservoir area /
- reservoir water level /
- rainfall
-
表 1 木鱼包滑坡时序曲线结果对比表
Table 1. Time series curve results comparison table of the Muyubao landslide
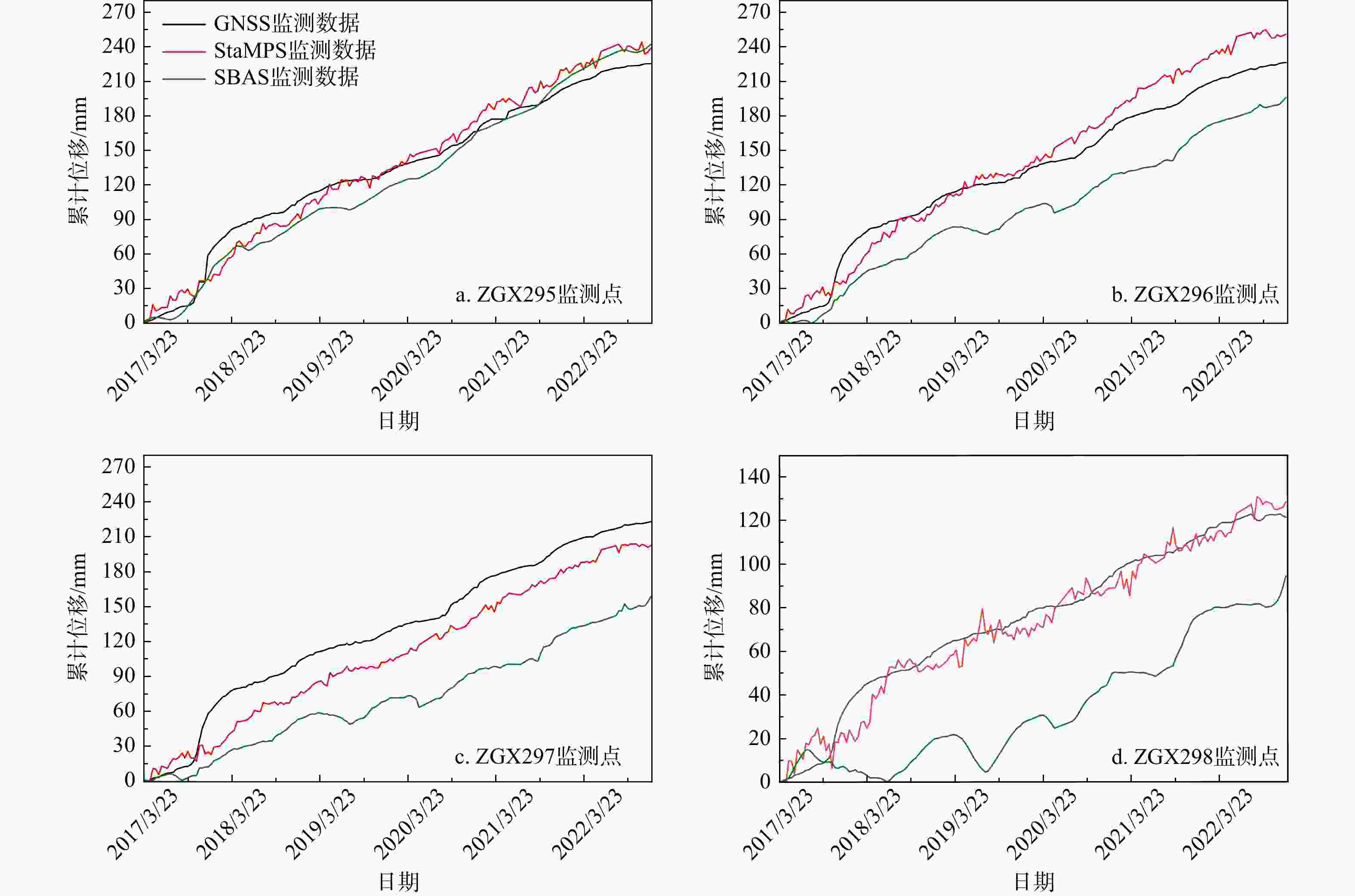
监测站点 RMSE/mm MAE/mm 余弦相似度 累计位移差/mm StaMPS SBAS StaMPS SBAS StaMPS SBAS StaMPS SBAS ZGX295 11.9315 14.6127 10.0547 12.2512 0.9973 0.9947 13.2312 16.4967 ZGX296 16.0125 34.8575 13.2624 33.243 0.9973 0.9951 24.7207 30.2178 ZGX297 23.0645 60.3476 21.7981 56.6074 0.9959 0.9886 20.3274 64.2438 ZGX298 7.3346 43.1930 5.8499 40.2692 0.9960 0.9318 7.0869 26.9161 表 2 StaMPS曲线与GNSS曲线拟合优度表
Table 2. Goodness of fit table of StaMPS curve and GNSS curve
监测站点 ZGX295 ZGX296 ZGX297 ZGX298 拟合优度R2 0.9644 0.9360 0.8666 0.9558 表 3 整体变形阶段统计表
Table 3. Statistical table of overall deformation stage
时段序号 时间 中高水位
(≥165 m)
累计天数/d高水位
(≥170 m)
累计天数/d月峰值
降雨量/
mm平均累计
位移增量/
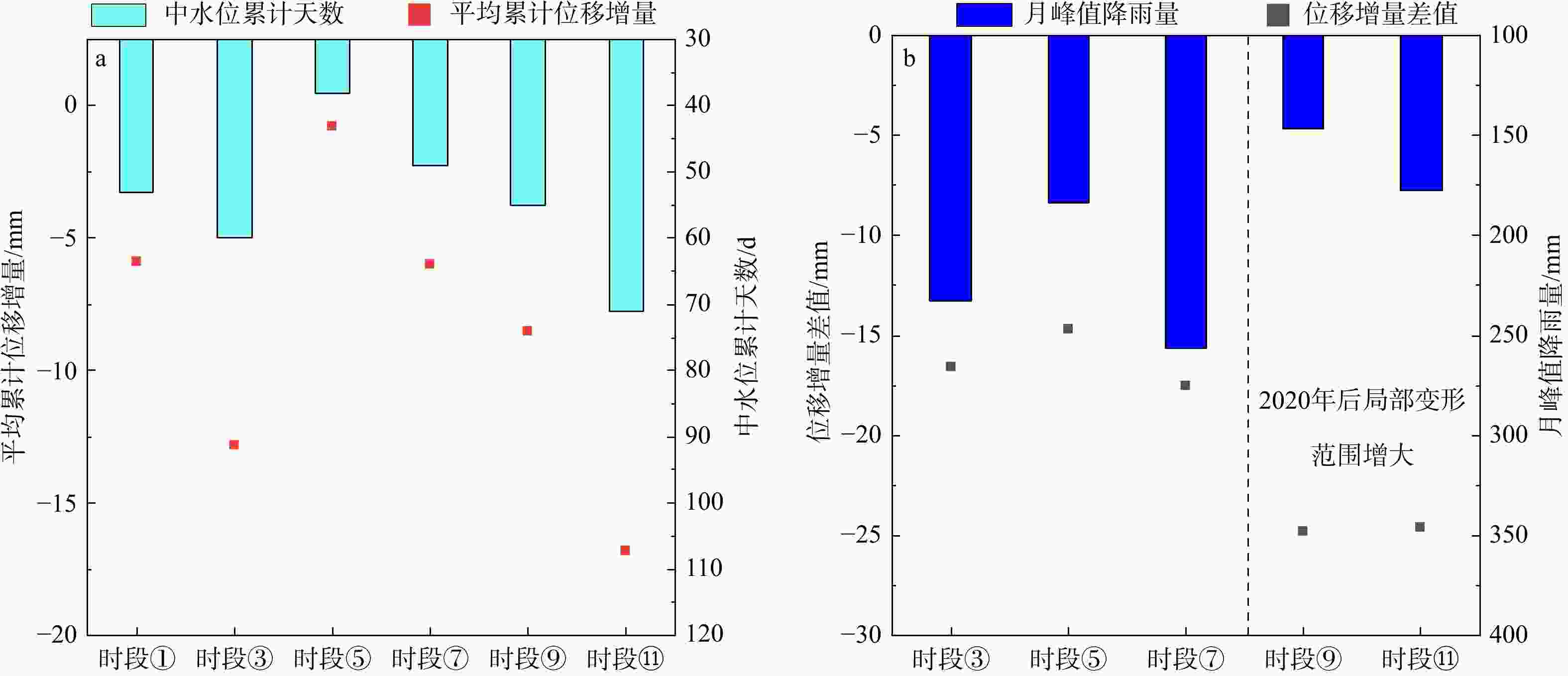
mm② 2017/09/08-2018/03/07 159 131 208.6 −29.9 ④ 2018/09/03-2019/03/02 155 130 138.2 −22.1 ⑥ 2019/09/10-2020/03/08 148 96 163.2 −18.0 ⑧ 2020/09/04-2021/03/03 152 124 161.6 −19.3 ⑩ 2021/09/11-2022/03/10 175 124 51.4 −29.1 表 4 蠕滑变形阶段统计表
Table 4. Statistical table of creep deformation stage
时段
序号时间 库水下降期中
水位(≥160 m)
累计天数/d月峰值
降雨量/
mm平均累计
位移增量/
mm累计位移
增量峰值/
mm① 2017/03/12-2018/09/08 53 数据缺失 −5.9 −28.9 ③ 2018/03/07-2018/09/03 60 233.0 −12.8 −29.4 ⑤ 2019/03/02-2019/09/10 38 183.6 −0.8 −15.5 ⑦ 2020/03/08-2020/09/04 49 256.6 −6.0 −23.5 ⑨ 2021/03/03-2021/09/11 55 146.6 −8.5 −33.3 ⑪ 2022/03/10-2022/09/06 71 177.6 −16.8 −41.4 -
[1] 唐辉明. 重大滑坡预测预报研究进展与展望[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(6):1-13.TANG H M. Advance and prospects of major landslides prediction and forecasting[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(6):1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 殷坤龙,张桂荣. 地质灾害风险区划与综合防治对策[J]. 安全与环境工程,2003,10(1):32-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1556.2003.01.010YIN K L,ZHANG G R. Risk zonation of geo-hazards and its comprehensive control[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2003,10(1):32-35. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1556.2003.01.010 [3] 黄润秋,向喜琼,巨能攀. 我国区域地质灾害评价的现状及问题[J]. 地质通报,2004,23(11):1078-1082. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.11.005HUANG R Q,XIANG X Q,JU N P. Assessment of China's regional geohazards:Present situation and problems[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2004,23(11):1078-1082. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.11.005 [4] 朱鸿鹄,王佳,李厚芝,等. 基于数据挖掘的三峡库区特大滑坡变形关联规则研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2022,30(5):1517-1527.ZHU H H,WANG J,LI H Z,et al. Association rule analysis for giant landslide deformation of the Three Gorges Reservoir region based on data mining[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022,30(5):1517-1527. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 徐潇宇. 三峡库区地质灾害防治系统运行机制研究[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学(武汉),2013.XU X Y. Research on the operation mechanism of the system dealing with the prevention and control of geological hazards in Three Gorges Reservoir area[D]. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences (Wuhan),2013. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 李振洪,朱武,余琛,等. 雷达影像地表形变干涉测量的机遇、挑战与展望[J]. 测绘学报,2022,51(7):1485-1519. doi: 10.11947/j.issn.1001-1595.2022.7.chxb202207031LI Z H,ZHU W,YU C,et al. Interferometric synthetic aperture radar for deformation mapping:Opportunities,challenges and the outlook[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica,2022,51(7):1485-1519. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11947/j.issn.1001-1595.2022.7.chxb202207031 [7] 唐亚明,张茂省,薛强,等. 滑坡监测预警国内外研究现状及评述[J]. 地质论评,2012,58(3):533-541. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2012.03.014TANG Y M,ZHANG M S,XUE Q,et al. Landslide monitoring and early-warning:An overview[J]. Geological Review,2012,58(3):533-541. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2012.03.014 [8] 许强,董秀军,李为乐. 基于天−空−地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):957-966.XU Q,DONG X J,LI W L. Integrated space-air-ground early detection,monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):957-966. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 张毅. 基于InSAR技术的地表变形监测与滑坡早期识别研究:以白龙江流域中游为例[D]. 兰州:兰州大学,2018.ZHANG Y. Detecting ground deformation and investigating landslides using InSAR technique:Taking middle reach of Bailong River Basin as an example[D]. Lanzhou:Lanzhou University,2018. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] FERRETTI A,PRATI C,ROCCA F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2001,39(1):8-20. doi: 10.1109/36.898661 [11] BERARDINO P,FORNARO G,LANARI R,et al. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2002,40(11):2375-2383. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.803792 [12] HOOPER A,ZEBKER H,SEGALL P,et al. A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other natural terrains using InSAR persistent scatterers[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2004,31(23):1-5. [13] 张亚迪,李煜东,董杰,等. 时序InSAR技术探测芒康地区滑坡灾害隐患[J]. 遥感学报,2019,23(5):987-996. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20198025ZHANG Y D,LI Y D,DONG J,et al. Landslide hazard detection in Markam with time-series InSAR analyses[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin,2019,23(5):987-996. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11834/jrs.20198025 [14] ZHOU C,CAO Y,YIN K L,et al. Landslide characterization applying Sentine l-1 images and InSAR technique:The Muyubao landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area,China[J]. Remote Sensing,2020,12(20):3385. doi: 10.3390/rs12203385 [15] 朱同同,史绪国,周超,等. 利用2016−2020年Sentine l-1数据监测与分析三峡库区树坪滑坡稳定性[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2021,46(10):1560-1568.ZHU T T,SHI X G,ZHOU C,et al. Stability monitoring and analysis of the Shuping landslide in the Three Gorges area with Sentine l-1 images from 2016 to 2020[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2021,46(10):1560-1568. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] ZHANG T T,LI B,GAO Y,et al. Massive glacier-related geohazard chains and dynamics analysis at the Yarlung Zangbo River downstream of southeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2023,82(11):426. doi: 10.1007/s10064-023-03423-w [17] ZHANG X C,CHEN L X,ZHOU C. Deformation monitoring and trend analysis of reservoir bank landslides by combining time-series InSAR and Hurst index[J]. Remote Sensing,2023,15(3):619. doi: 10.3390/rs15030619 [18] 范景辉,邱阔天,夏耶,等. 三峡库区范家坪滑坡地表形变InSAR监测与综合分析[J]. 地质通报,2017,36(9):1665-1673. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.09.018FAN J H,QIU K T,XIA Y,et al. InSAR monitoring and synthetic analysis of the surface deformation of Fanjiaping landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2017,36(9):1665-1673. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.09.018 [19] 赵超英,刘晓杰,张勤,等. 甘肃黑方台黄土滑坡InSAR识别、监测与失稳模式研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):996-1007.ZHAO C Y,LIU X J,ZHANG Q,et al. Research on loess landslide identification,monitoring and failure mode with InSAR technique in Heifangtai,Gansu[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):996-1007. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 朱智富,甘淑,张荐铭,等. 结合SBAS-InSAR技术及信息熵的苍山地质滑坡隐患识别[J]. 测绘通报,2022(11):13-19.ZHU Z F,GAN S,ZHANG J M,et al. Identification of geological potential landslides in Cang Mountain by combining SBAS-InSAR technique and information entropy[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping,2022(11):13-19. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] TSIRONI V,GANAS A,KARAMITROS I,et al. Kinematics of active landslides in Achaia (Peloponnese,Greece) through InSAR time series analysis and relation to rainfall patterns[J]. Remote Sensing,2022,14(4):844. doi: 10.3390/rs14040844 [22] 赵蓓蓓,黄海峰,邓永煌,等. 基于Sentine l-1A的三峡库区范家坪滑坡InSAR监测分析[J]. 人民长江,2022,53(10):103-107.ZHAO B B,HUANG H F,DENG Y H,et al. InSAR monitoring analysis on Fanjiaping landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir area based on Sentine l-1A[J]. Yangtze River,2022,53(10):103-107. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 包馨,张瑞,刘安梦云,等. 联合升降轨时序InSAR的金沙江滑坡群隐患识别[J]. 北京理工大学学报,2023,43(11):1135-1145.BAO X,ZHANG R,LIU A M Y,et al. Identification of Jinsha River landslide hazards by time-series InSAR with combined ascending and descending orbit data[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology,2023,43(11):1135-1145. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 杨沛璋,崔圣华,裴向军,等. 基于SBAS-InSAR和光学遥感影像的大型倾倒变形体变形演化[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(6):63-75.YANG P Z,CUI S H,PEI X J,et al. Deformation and evolution of large dumping bodies based on SBAS-InSAR and optical remote sensing images[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(6):63-75. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 刘涛,张明,王立朝,等. 甘肃舟曲江顶崖古滑坡形成演化机理与堆积体稳定性评价[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(3):266-278.LIU T,ZHANG M,WANG L C,et al. Formation and evolution mechanism of the ancient landslide and stability evaluation of the accumulation body in Jiangdingya,Zhouqu County,Guansu Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(3):266-278. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 张凯翔,张占荣,于宪煜. SBAS-InSAR和PS-InSAR技术在鲁西南某线性工程沿线地面沉降成因分析中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(4):65-76.ZHANG K X,ZHANG Z R,YU X Y. Application of SBAS-InSAR and PS-InSAR technologies in analysis of landslide subsidence along a linear infrastructure in southwestern Shandong[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(4):65-76. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] YAO J M,YAO X,LIU X H. Landslide detection and mapping based on SBAS-InSAR and PS-InSAR:A case study in Gongjue County,Tibet,China[J]. Remote Sensing,2022,14(19):4728. doi: 10.3390/rs14194728 [28] ZHANG J L,YANG R,QI Y,et al. A study on the monitoring of landslide deformation disasters in Wenxian County,Longnan City based on different time-series InSAR techniques[J]. Natural Hazards,2024,120(13):11851-11875. doi: 10.1007/s11069-024-06663-5 [29] 张富灵. 库水及降雨作用下滑移−弯曲型滑坡形成条件与演化机制研究:以木鱼包滑坡为例[D]. 湖北宜昌:三峡大学,2021.ZHANG F L. Study on formation conditions and evolution mechanism of sliding bending landslide under reservoir water and rainfall:A case study of Muyubao landslide[D]. Yichang Hubei:China Three Gorges University,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 魏瑞琦. 三峡库区木鱼包滑坡变形机理分析及稳定性预测评价[D]. 湖北宜昌:三峡大学,2022.WEI R Q. Analysis of deformation mechanism and stability prediction evaluation of Muyubao landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir area[D]. YichangHubei:China Three Gorges University,2022. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] GABRIEL A K,GOLDSTEIN R M,ZEBKER H A. Mapping small elevation changes over large areas:Differential radar interferometry[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Solid Earth),1989,94(B7):9183-9191. doi: 10.1029/JB094iB07p09183 [32] USAI S,KLEES R. SAR interferometry on a very long time scale:A study of the interferometric characteristics of man-made features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,1999,37(4):2118-2123. doi: 10.1109/36.774730 [33] HOOPER A,BEKAERT D,SPAANS K,et al. Recent advances in SAR interferometry time series analysis for measuring crustal deformation[J]. Tectonophysics,2012,514:1-13. [34] 姜兆英,于胜文,陶秋香. StaMPS-MTI技术在地面沉降监测中的应用[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2017,52(2):295-302. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.02.012JIANG Z Y,YU S W,TAO Q X. Application of StaMPS-MTI technology in monitoring ground subsidence[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University,2017,52(2):295-302. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.02.012 [35] 郑坤,聂运菊,罗跃,等. StaMPS-MTI技术在上海市地面沉降监测中的应用[J]. 江西科学,2019,37(1):108-111.ZHENG K,NIE Y J,LUO Y,et al. Application of StaMPS-MTI in Shanghai land subsidence monitoring[J]. Jiangxi Science,2019,37(1):108-111. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] 冯文凯,易小宇,孟睿,等. 三峡库区木鱼包滑坡不同库水升降速率变形响应离心模型试验研究[J]. 水利学报,2021,52(5):578-588.FENG W K,YI X Y,MENG R,et al. Study on deformation response of Muyubao landslide in Three Gorges region under different water fluctuation rates by centrifugal model test[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2021,52(5):578-588. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] HUANG F M,CHEN J W,LIU W P,et al. Regional rainfall-induced landslide hazard warning based on landslide susceptibility mapping and a critical rainfall threshold[J]. Geomorphology,2022,408:108236. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2022.108236 [38] 赵玉,陈丽霞,梁梦姣. 基于LSTM_TCN模型的降雨型滑坡时间概率预测及气象预警建模[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(2):201-214.ZHAO Y,CHEN L X,LIANG M J. Temporal probability prediction and meteorological early warning modeling of rainfall-induced landslide based on LSTM_TCN model[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(2):201-214. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 王佳,朱鸿鹄,叶霄,等. 考虑时滞效应的库区滑坡位移预测:以新铺滑坡为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2022,30(5):1609-1619.WANG J,ZHU H H,YE X,et al. Prediction of reservoir landslide displacements considering time lag effect:A case study of the Xinpu landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area,China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022,30(5):1609-1619. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 邓茂林,易庆林,韩蓓,等. 长江三峡库区木鱼包滑坡地表变形规律分析[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(8):3145-3152.DENG M L,YI Q L,HAN B,et al. Analysis of surface deformation law of Muyubao landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2019,40(8):3145-3152. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: