Confirmation and genesis of the Middle Eocene tectonic transformation in northwestern margin of Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin
-
摘要: 通过西湖凹陷西北缘断裂体系、构造格局、火成岩演变等构造条件综合分析,首次明确了区内中始新世存在构造变革。研究结果表明,构造变革在平湖组底界形成了显著的不整合,主要表现为削平、削超,愈向西邻近长江坳陷不整合愈发显著;构造变革前后西湖凹陷格局发生了显著变化,在杭州斜坡带主要表现为大断裂走向由早期差异到后期逐步趋同,最终导致早期分隔、多沉积中心在后期连片统一。认为中始新世这期构造变革作用的发生与周缘板块俯冲调整有关,构造变革期在时间上与西部印度板块俯冲引发高原隆升和东部太平洋板块俯冲转向、后撤作用相同步,是在西部挤压作用逐步增强背景下,盆地由整体拉张背景到西压、东张的差异化发育转变作用的主要响应。在西湖凹陷内这种构造变革作用具有广泛性,在平湖组与下伏宝石组地层的烃源岩特征上形成差异,对油气资源差异富集的贡献需要做更深入的研究。Abstract: Comprehensive analyses of faulting systems, basin tectonic framework and igneous rock evolution were conducted to confirm the existence of the Middle Eocene tectonic transformation in northwestern margin of Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin.The results show that the tectonic transformation has formed remarkable unconformities in the bottom of Pinghu Formation, and the main performances of these unconformities are flattening and overshooting. The more westward the adjacent Yangtze Depression, the more obvious the unconformity is. In addition, the tectonic framework of Xihu Depression has changed remarkably before and after the tectonic transformation, and the main performance of the change is the trend of the large scale fracture from the early difference to the later one in the Hangzhou Slope Belt. This eventually led to the unification of early multi-segregated sedimentary centers in later stages. Accordingly, we suggest that the occurrence of tectonic transformation during the Middle Eocene is related to the adjustment of the subduction of the surrounding plates. The period of tectonic transformation is synchronous with the uplift of the plateau causing by the subduction of Indian plate in the west, and it is also synchronous with the diversion and retreat of the Pacific plate subduction in the east. Therefore, under the background of increasing extrusion in the west, the tectonic transformation responses to differential development transition from the whole tension to western extrusion and eastern tension. In Xihu Depression, this tectonic transformation is widespread, and as a result, the characteristics of source rocks in Pinghu Formation and underlying Baoshi Formation are different. The contribution of this difference to differential enrichment of oil and gas resources needs to be further studied.
-
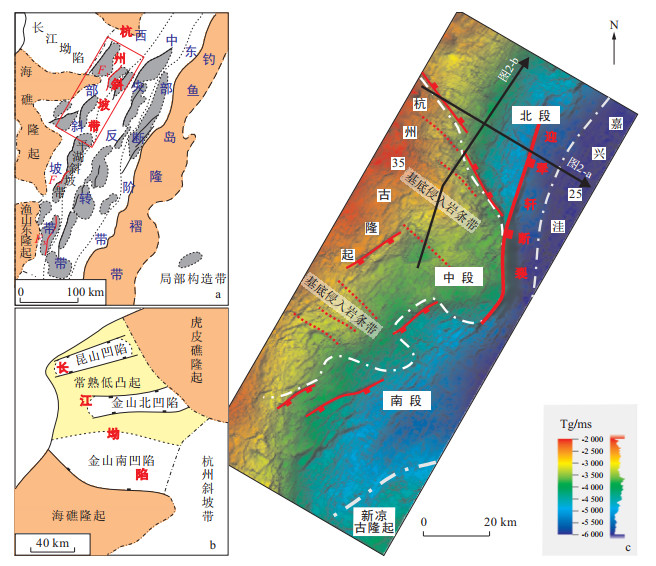
图 2 过杭州斜坡带北段典型地震剖面(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 2. Typical seismic profile of the north of Hangzhou Slope Belt
图 3 杭州斜坡带北段不整合界面地震反射特征(剖面位置见图 2)
Figure 3. Seismic reflection characteristics of unconformity interface in the north of Hangzhou Slope Belt
表 1 西湖凹陷及邻区构造演化简表
Table 1. Tectonic evolution of Xihu Depression and its adjacent area

-
[1] 周心怀, 蒋一鸣, 唐贤君.西湖凹陷成盆背景、原型盆地演化及勘探启示[J].中国海上油气, 2019, 31(3):1-10. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-gc201903001 [2] 蒋一鸣.西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带平湖组碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄及米兰科维奇旋回:对源-汇系统及沉积演化的约束[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6):133-140. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93477A/20196/7100580445.html [3] 李上卿.东海西湖凹陷新生代地质构造特征与演化[J].海洋石油, 2000, 20(2):8-14. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200000739088 [4] 顾惠荣, 陈琳琳.东海陆架西湖凹陷宝石一井深层微体化石及地层意义[J].古生物学报, 2003, 42(4):620-623. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gswxb200304013 [5] 李三忠, 余珊, 赵淑娟, 等.东亚大陆边缘的板块重建与构造转换[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(3):65-94. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201303008 [6] Zhu Weilin, Zhong Kai, Fu Xiaowei, et al. The formation and evolution of the East China Sea Shelf Basin:A new view[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 190:89-111. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.12.009 [7] 刘景彦, 姜亮.东海西湖凹陷第三系主要不整合面的特征、剥蚀量的分布及其意义[J].现代地质, 1999, 13(4):432-438. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=3663552 [8] 王子煜, 张明利.东海西湖凹陷新生界主要不整合面地层剥蚀厚度恢复[J].地质论评, 2005, 51(3):309-318. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlp200503011 [9] 索艳慧, 李三忠, 戴黎明, 等.东亚及其大陆边缘新生代构造迁移与盆地演化[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(8):2602-2618. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201208025 [10] 索艳慧, 李三忠, 曹现志, 等.中国东部中新生代反转构造及其记录的大洋板块俯冲过程[J].地学前缘, 2017, 24(4):249-267. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201704023 [11] 张建培, 张田, 唐贤君.东海陆架盆地类型及其形成的动力学环境[J].地质学报, 2014, 88(11):2033-2043. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201411002 [12] 任建业.中国近海海域新生代成盆动力机制分析[J].地球科学, 2018, 43(10):3337-3361. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201810002 [13] 刘金水, 廖宗廷, 贾健谊, 等.东海陆架盆地地质结构及构造演化[J].上海地质, 2003, 24(3):1-6. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=shdz200303001 [14] 任建业.渤海湾盆地东营凹陷S6'界面的构造变革意义[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2004, 29(1):72-76. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=9043675 [15] 王家豪, 王华, 肖敦清, 等.陆相伸展性盆地二级层序的厘定[J].石油学报, 2009, 30(6):869-875. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb200906012 [16] 蒋一鸣, 何新建, 张绍亮.东海陆架盆地"反转改造"构造迁移演化特征[J].长江大学学报:自科版, 2016, 13(26):1-7. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjdxxb-rkxb201626002 [17] 万天丰.古构造应力场[M].北京:地质出版社, 1988:22-52. [18] 岳桥, 施炜, 廖昌珍, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地周边断裂运动学分析与晚中生代构造应力体制转换[J].地质学报, 2006, 80(5):639-647. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200605002 [19] 张敏强, 徐发, 张建培, 等.西湖凹陷裂陷期构造样式及其对沉积充填的控制作用[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(5):67-72. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201105010 [20] 吴晓智, 齐雪峰, 唐勇, 等.东西准噶尔火山岩成因类型与油气勘探方向[J].中国石油勘探, 2009, 14(1):1-9. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsykt200901001 [21] 杨传胜, 李刚, 杨长清.东海陆架盆地及其邻域岩浆岩时空分布特征[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(3):125-133. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201203016 [22] 唐贤君, 蒋一鸣, 张绍亮.平湖斜坡带火山岩层发育构造环境及油气地质意义[J].地质科技情报, 2018, 37(1):27-36. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201801004 [23] 袁伟, 徐旭辉, 周小进.西湖凹陷平湖组时代新认识:来自火山岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄的证据[J].高校地质学报, 2014, 20(3):407-414. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GXDX201403006.htm [24] 孙卫东, 凌明星, 汪方跃, 等.太平洋板块俯冲与中国东部中生代地质事件[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2008, 27(3):218-225. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwysdqhxtb200803002 [25] 杨文达, 崔征科, 张异彪, 等.东海地质与矿产[M].北京:海洋出版社, 2010. [26] 能源, 杨桥, 张克鑫, 等.苏北盆地高邮凹陷晚白垩世-新生代构造沉降史分析与构造演化[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 2009, 29(2):25-32. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yxgdl200902004 [27] Dewey J F, Helman M L, Knott S D, et al.Models of development of the Alpine Chain, kinematics of the western Mediterranean[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 45:265-283. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.045.01.15 [28] Molnar P, Boos W R, Battisti D S, et al. Orographic controls on climate and paleoclimate of Asia:Thermal and mechanical roles for the Tibetan Plateau[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 38:77-102. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-040809-152456 [29] 罗照华, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 等.青藏高原新生代形成演化的整合模型:来自火成岩的约束[J].地学前缘, 2006, 13(4):196-211. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/98600x/20064/22369608.html [30] 张克信, 王国灿, 洪汉烈, 等.青藏高原新生代隆升研究现状[J].地质通报, 2013, 32(1):1-18. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201301001 [31] 雷超, 任建业, 张静.南海构造变形分区及成盆过程[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(4):744-762. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201504016 [32] 孙珍, 钟志洪, 周蒂.莺歌海盆地构造演化与强烈沉降机制的分析和模拟[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2007, 32(3):347-356. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=24414425 [33] 谢文彦, 张一伟, 孙珍, 等.琼东南盆地新生代发育机制的模拟研究[J].地学前缘, 2008, 15(2):232-241. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200802026 [34] 胡阳, 吴智平, 钟志洪, 等.珠江口盆地珠一坳陷始新世中-晚期构造变革特征及成因[J].石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(5):779-785. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syytrqdz201605019 [35] 唐贤君, 蒋一鸣, 张建培, 等.东海盆地西湖凹陷平北区断陷层断裂特征及其对圈闭的控制[J].海洋地质前沿, 2019, 35(8):34-43. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzdt201908005 -





 下载:
下载: