Research on mud shale fractures based on image logging: A case study of Jiaoshiba area
-
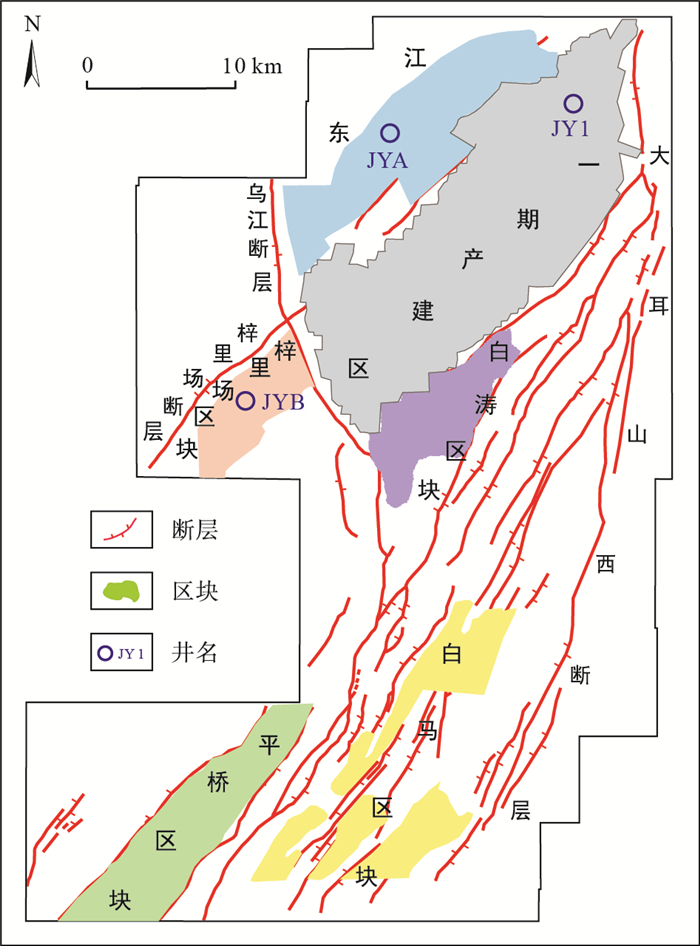
摘要: 富有机质泥页岩裂缝类型及其发育分布特征是影响页岩气聚集与散失的重要因素。基于岩心观测和高分辨微电阻率成像测井(FMI),对焦石坝区块2口关键井(JYA井和JYB井)裂缝发育特征进行了精细标定与定量解释,并在此基础上联合含气性资料简要探讨了裂缝对页岩含气性的影响。研究结果表明,JYA井和JYB井主力层段及下伏地层裂缝差异较小,均以层理缝为主,但上覆盖层具有明显差异。JYA井上覆盖层天然裂缝发育程度较低,以高阻缝为主,高导缝和断层次之,三者的倾角变化范围分别为20.31°~75.83°(平均44.65°)、16.65°~61.17°(平均39.43°)和36.41°。裂缝线密度最高为0.6条/m,其中断层仅为0.025条/m,页岩系统封闭能力较好,压裂投产为高产井。JYB井上覆盖层天然裂缝发育程度较高,且以断层为主,高阻缝和高导缝次之,三者的倾角分别介于13.71°~72.23°(平均37°)、6.9°~78.49°(平均37.9°)和13.53°~61°(平均32°)之间。裂缝线密度高达0.98条/m,其中断层线密度约为0.654条/m,页岩系统封闭能力较差,压裂投产为低产井。裂缝发育类型及其程度决定了不同区块页岩气保存条件与页岩气富集程度。Abstract: The fracture type, development and distribution characteristics of organic-rich mud shale are important factors that affect the accumulation and dissipation of shale gas.Based on core observation and high resolution micro-resistivity image logging (FMI), the fracture development characteristics of two key wells (JYA well and JYB well) in Jiaoshiba area were described and quantitatively interpreted.Besides, the influence of fracture on shale gas-bearing property is discussed in combination with gas-bearing data.The results show that there is little difference between JYA well and JYB well in main formation and underlying formation, and the bedding fracture is the main one, but the seal condition has obvious difference.The natural fracture of the direct seal of the JYA well is relatively low, mainly high-resistance fracture, followed by high-conductivity fracture and fault.The dip angle is 20.31°-75.83° (average 44.65°), 16.65°-61.17° (average 39.43°) and 36.41°, respectively.The line density of fracture in JYA well is 0.6 bar/ m, of which fault is 0.025 bar/m.The sealing condition of JYA well is well, and the production fracturing is high-yield.However, the natural fracture of the seal condition of the JYB well is relatively high, and mainly fault, followed by high-resistance fracture and high-conductivity fracture.The dip angle is 13.71°-72.23° (average 37°), 6.9°-78.49° (average 37.9°) and 13.53°-61° (average 32°), respectively. The linear density of fracture in JYB well can reach 0.98 bar/ m, of which fault is 0.654 bar/ m.The sealing condition of JYB well is low, and the production fracturing is low-yield.Fracture type and its degree determine the condition of shale gas preservation and the degree of shale gas enrichment in different blocks.
-
Key words:
- shale gas /
- micro-resistivity image logging /
- fracture /
- gas bearing /
- preservation condition /
- Jiaoshiba area
-
图 2 微电阻率成像测井测量原理和裂缝表征示意图(据文献[38], 有修改)
Figure 2. Sketch map of FMI and fracture characterization
-
[1] Zhang L C, Lu S F, Jiang S, et al.Effect of shale lithofacies on pore structure of the Wufeng-Longmaxi shale in southeast Chongqing, China[J].Energy Fuels, 2018, 32(6):6603-6618. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=c104d62f9be434915282d90a43ea7205 [2] 程璇, 徐尚, 郝芳, 等.松辽盆地嫩江组富有机质页岩有机孔隙成因[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(4):62-69. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/dzkjqb201904008 [3] Yi J Z, Bao H Y, Zheng A W, et al.Main factors controlling marine shale gas enrichment and high-yield wells in South China:A case study of the Fuling shale gas field[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 103:114-125. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/64330a3769bc98a0042b13f8943ce307 [4] Ross D J K, Bustin R M, The importance of shale composition and pore structure upon gas storage potential of shale gas reservoirs[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2009, 26(6):916-927. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264817208001153 [5] Slatt R M, O'Brien N R, Pore types in the Barnett and Woodford gas shales:Contribution to understanding gas storage and migration pathways in fine-grained rocks[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2011, 95(12):2017-2030. http://www.springerlink.com/content/g41vv3w061410121/ [6] He Z L, Li S J, Nie H K, et al.The shale gas "sweet window":"The cracked and unbroken" state of shale and its depth range[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 101:334-342. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264817218305038 [7] Gale J F W, Reed R M, Holder J.Natural fractures in the Barnett shale and their importance for hydraulic fracture treatments[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(4):603-622. [8] 龙鹏宇, 张金川, 唐玄, 等.泥页岩裂缝发育特征及其对页岩气勘探和开发的影响[J].天然气地球科学, 2016, 22(3):525-532. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=38333575 [9] Zeng W T, Zhang J C, Ding W L, et al.Fracture development in Paleozoic shale of Chongqing area (South China).Part one:Fracture characteristics and comparative analysis of main controlling factors[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 75:251-266. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912013003623 [10] 吕文雅, 曾联波, 刘静, 等.致密低渗透储层裂缝研究进展[J].地质科技情报, 2016, 35(4):74-83. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKQ201604012.htm [11] 蒲泊伶, 董大忠, 牛嘉玉, 等.页岩气储层研究新进展[J].地质科技情报, 2014, 33(2):98-104. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKQ201402017.htm [12] 陈彦虎, 蒋龙聪, 胡俊, 等.页岩储层裂缝型孔隙定量预测的新方法[J].地质科技情报, 2018, 37(1):115-121. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201801015 [13] 黄继新, 彭仕宓, 王小军, 等.成像测井资料在裂缝和地应力研究中的应用[J].石油学报, 2006, 27(6):65-69. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SYXB200606013.htm [14] 聂昕, 邹长春, 杨玉卿, 等.测井技术在页岩气储层力学性质评价中的应用[J].工程地球物理学报, 2012, 9(4):433-439. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdqwlxb201204012 [15] 赖锦, 王贵文, 郑新华, 等.油基泥浆微电阻率扫描成像测井裂缝识别与评价方法[J].油气地质与采收率, 2015, 22(6):47-54. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90849X/201506/666500251.html [16] 王松, 王贵文, 赖锦, 等.塔北地区一间房组碳酸盐岩储层测井识别方法及应用[J].地球物理学进展, 2018, 33(6):2462-2470. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQWJ201806035.htm [17] 车世琦.四川盆地涪陵地区页岩裂缝测井定量识别[J].特种油气藏, 2017, 24(6):72-78. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_tzyqc201706014.aspx [18] 王敏, 朱家俊, 余光华, 等.罗家地区泥页岩岩相特征及测井分析技术[J].测井技术, 2013, 37(4):426-431. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cjjs201304018 [19] 周正龙, 王贵文, 冉冶, 等.致密油储集层岩性岩相测井识别方法:以鄂尔多斯盆地合水地区三叠系延长组7段为例[J].石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(1):61-69. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SKYK201601008.htm [20] 赖锦, 韩能润, 贾云, 等.基于测井资料的辫状河三角洲沉积储层精细描述[J].中国地质, 2018, 45(2):304-318. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201802007 [21] 谢芳, 张承森, 刘瑞林, 等.碳酸盐岩缝洞储集层电成像测井产量预测[J].石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(2):349-356. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SKYK201802020.htm [22] Guo T L.The fuling shale gas field: A highly productive Silurian gas shale with high thermal maturity and complex evolution history, southeastern Sichuan Basin, China[J].Interpretation, 2015, 3(2):25-34. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/276914908_The_Fuling_Shale_Gas_Field__A_highly_productive_Silurian_gas_shale_with_high_thermal_maturity_and_complex_evolution_history_southeastern_Sichuan_Basin_China [23] Feng W P, Wang F Y, Guan J, et al.Geologic structure controls on initial productions of lower Silurian Longmaxi shale in South China[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 91:163-178. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264817218300011 [24] Wang G C, Long S X, Ju Y W, et al.Application of horizontal wells in three-dimensional shale reservoir modeling:A case study of Longmaxi-Wufeng shale in Fuling gas field, Sichuan Basin[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2018, 102(11):2333-2354. http://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/aapgbull/article-pdf/102/11/2333/4524110/bltn17144.pdf [25] Gou Q Y, Xu S, Hao F, et al.Full-scale pores and micro-fractures characterization using FE-SEM, gas adsorption, nano-CT and micro-CT:A case study of the Silurian Longmaxi Formation shale in the Fuling area, Sichuan Basin, China[J].Fuel, 2019, 253:167-179. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236119306763 [26] Zheng X W, Zhang B Q, Sanei H, et al.Pore structure characteristics and its effect on shale gas adsorption and desorption behavior[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 100:165-178. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264817218304513 [27] Yang F, Xu S, Hao F, et al.Petrophysical characteristics of shales with different lithofacies in Jiaoshiba area, Sichuan Basin, China:Implications for shale gas accumulation mechanism[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 109:394-407. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264817219302806 [28] Ma Y, Guo X, Guo T, et al.The Puguang gas field:New giant discovery in the mature Sichuan Basin, southwest China[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(5):627-643. http://www.nrcresearchpress.com/servlet/linkout?suffix=refg39/ref39&dbid=16&doi=10.1139%2Fcjes-2014-0188&key=10.1306%2F11030606062 [29] Hao F, Guo T L, Zhu Y M, et al.Evidence for multiple stages of oil cracking and thermochemical sulfate reduction in the Puguang gas field, Sichuan Basin, China[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2008, 92(5), 611-637. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/249897958_Evidence_for_multiple_stages_of_oil_cracking_and_thermochemical_sulfate_reduction_in_the_Puguang_gas_field_Sichuan_Basin_China?ev=auth_pub [30] 郭彤楼.涪陵页岩气田发现的启示与思考[J].地学前缘, 2016, 23(1):29-43. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DXQY201601005.htm [31] 苟启洋, 徐尚, 郝芳, 等.纳米CT页岩孔隙结构表征方法:以JY-1井为例[J].石油学报, 2018, 39(11):1253-1261. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_syxb201811005.aspx [32] 孙健, 罗兵.四川盆地涪陵页岩气田构造变形特征及对含气性的影响[J].石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(6):809-818. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syytrqdz201606002 [33] 郭旭升, 胡东风, 魏祥峰, 等.四川盆地焦石坝地区页岩裂缝发育主控因素及对产能的影响[J].石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(6):799-808. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syytrqdz201606001 [34] Chen L, Lu Y C, Jiang S, et al.Heterogeneity of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi marine shale in the southeast Sichuan Basin of China[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 65:232-246. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264817215001233 [35] Gou Q Y, Xu S.Quantitative evaluation of free gas and adsorbed gas content of Wufeng-Longmaxi shales in the Jiaoshiba area, Sichuan Basin, China[J].Advances in Geo-Energy Research, 2019, 3(3):258-267. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzxb-e201902011 [36] Li S J, Yuan Y S, Sun W, et al.Formation and destruction mechanism as well as major controlling factors of the Silurian shale gas overpressure in the Sichuan Basin, China[J].Journal of Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 1(4):287-294. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2468256X16300499 [37] 童亨茂.成像测井资料在构造裂缝预测和评价中的应用[J].天然气工业, 2006, 26(9):58-61. http://www.trqgy.cn/EN/abstract/abstract10136.shtml [38] 屈海洲, 张福祥, 王振宇, 等.基于岩心-电成像测井的裂缝定量表征方法:以库车坳陷ks2区块白垩系巴什基奇克组砂岩为例[J].石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(3):425-432. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syktykf201603013 [39] Lyu W Y, Zeng L B, Liu Z Q, et al.Fracture responses of conventional logs in tight-oil sandstones:A case study of the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in southwest Ordos Basin, China[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2016, 100(9):1399-1417. http://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/aapgbull/article-pdf/100/9/1399/3343779/BLTN15129.pdf [40] Brekke H, MacEachern J A, Roenitz T, et al.The use of microresistivity image logs for facies interpretations:An example in point-bar deposits of the McMurray Formation, Alberta, Canada[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2017, 101(5):655-682. http://archives.datapages.com/data/bulletns/aop/2016-11-07/aapgbltn16014aop.html [41] Fernandez-Ib'añez F, DeGraff J M, Ibrayev F.Integrating borehole image logs with core:A method to enhance subsurface fracture characterization[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2018, 102(6):1067-1090. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=49e0d79ae88b2ebe2bdde7348e955154 [42] 郭旭升, 胡东风, 李宇平, 等.涪陵页岩气田富集高产主控地质因素[J].石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(4):481-491. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90664X/201704/672755310.html [43] Zhang K, Song Y, Jia C Z, et al.Vertical sealing mechanism of shale and its roof and floor and effect on shale gas accumulation: A case study of marine shale in Sichuan Basin, the Upper Yangtze area[J].Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 175:743-754. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0920410519300099 [44] Jin Z J, Nie H K, Liu Q Y, et al.Source and seal coupling mechanism for shale gas enrichment in Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation-Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in Sichuan Basin and its periphery[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 97:78-93. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/325660470_Source_and_seal_coupling_mechanism_for_shale_gas_enrichment_in_upper_Ordovician_Wufeng_Formation_-_Lower_Silurian_Longmaxi_Formation_in_Sichuan_Basin_and_its_periphery [45] 刘莉, 包汉勇, 李凯, 等.页岩储层含气性评价及影响因素分析:以涪陵页岩气田为例[J].石油实验地质, 2018, 40(1):58-64. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SYSD201801010.htm [46] 苟启洋, 徐尚, 郝芳, 等.基于灰色关联的页岩储层含气性综合评价因子及应用:以四川盆地焦石坝区块为例[J].天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(7):1045-1052. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_trqdqkx201907013.aspx [47] 苟启洋, 徐尚, 郝芳, 等.基于微米CT页岩微裂缝表征方法研究[J].地质学报, 2019, 93(9):2372-2382. http://www.geojournals.cn/dzxbe/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2019058&flag=1 -





 下载:
下载: