Research progress and prospects of the stages, genesis and fluid evolution of micro-fracture veins in petroliferous basins
-
摘要: 沉积岩石中断裂与裂缝是含油气盆地流体活动的重要通道,断裂与裂缝中充填的不同期次、不同类型的矿物脉体是烃-水-岩相互作用的产物,记录了断裂、裂缝形成过程中不同期次流体性质、组分、来源以及温压场、氧化还原环境等信息,为研究沉积盆地断裂发育、流体动力场特征、物理化学环境及封闭与保存条件等地层古流体活动、动态演化过程提供了重要线索。系统总结了含油气盆地微观裂缝脉体流体活动示踪、演化的基本方法及其地质应用现状,认为目前主要集中在三个方面:①通过对裂缝脉体充填的成岩矿物岩石学观察,分析成岩矿物类型、结构及形成的相对次序;②通过对脉体成岩矿物的同位素、微量-稀土元素、流体包裹体等地球化学测试,示踪成脉古流体性质、来源、温压-氧化还原环境等;③通过对脉体成岩矿物放射性同位素(如U-Pb、Re-Os等)的测试,精确确定脉体形成时间,结合区域构造演化探讨脉体形成过程、流体动力场环境及其动态演化过程。最后分析了现有研究方法存在的问题,探讨今后的发展趋势及地质应用前景,以期为含油气盆地古流体演化及其与油气运移、聚集与保存等油气成藏机理的研究提供参考。Abstract: Faults and fractures in sedimentary rocks are important channels for fluid activities in petroliferous basins.Different stages and types of mineral veins filled in fractures are the product of hydrocarbon-water-rock interactions, recording the formation process of faults and fractures fluid properties, components, sources, temperature and pressure fields, redox environment and other information in different stages of the process. They provide important clues to study the development of faults in sedimentary basins, the characteristics of fluid dynamic fields, physical and chemical environments.This paper systematically summarizes the basic methods of fluid activity tracing and evolution of fracture veins in petroliferous basins and their current geological applications, and believes that they are mainly concentrated in three aspects: First, through the petrological observation of diagenetic minerals filled with fracture veins, to analyze the type, structure and relative order of formation of diagenetic minerals; the second is to trace the nature, source, temperature and pressure of vein-forming paleo-fluids through geochemical tests such as isotopes, trace rare earth elements, and fluid inclusions of vein diagenetic minerals- redox environment, etc.; the third is to accurately determine the formation time of veins by testing radioisotopes of diagenetic minerals in veins(such as U-Pb, Re-Os, etc.), and discuss vein formation processes and hydrodynamic fields based on regional structural evolution environment and its dynamic evolution process.Finally, the problems of existing research methods are analyzed, and the future development trends and geological application prospects are discussed, in order to provide references for the study of the evolution of paleofluid in petroliferous basins and their relationship with hydrocarbon migration and accumulation and preservation.
-
Key words:
- rare earth elements /
- paleofluid evolution /
- diagenetic sequence /
- fracture vein /
- petroliferous basin
-
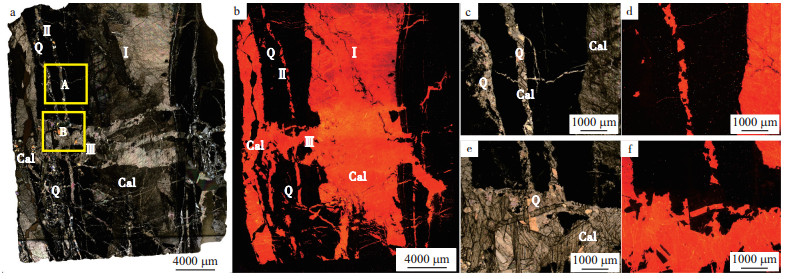
图 1 四川盆地涪陵地区梓里场区块五峰组-龙马溪组页岩裂缝脉体微观发育特征
图a, c, e为透射光; 图b, d, f为对应的阴极光;图c,e分别对应图a中A、B区域;Q为石英,Cal为方解石;图b见方解石呈橙红色或橘黄色阴极光,石英不发光。Ⅰ.早期低角度方解石脉;Ⅱ.石英与方解石共生脉;Ⅲ.晚期高角度方解石脉
Figure 1. Microscopic development characteristics of shale fracture veins in Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation of Zilichang block in Fuling area, Sichuan Basin
图 4 典型自然环境和矿物中稀土元素的PAAS标准化配分模式[45]
Figure 4. PAAS standardized distribution model of REE in typical natural environments and minerals
表 1 流体包裹体成分分析方法、特点、影响因素及其局限性
Table 1. Analysis methods, characteristics, influencing factors and limitations of fluid inclusion composition
分析类别 测试方法 方法特点 影响因素及局限性 资料来源 单个包裹体成分分析 非破坏性分析 激光拉曼光谱分析(LRM) 用途:气烃包裹体、CO2包裹体成分确定
特点:定性-半定量,微区微量,高分辨率影响因素:荧光干扰
局限性:测定成分有限,未能实现C6+液态烃的分析文献[18] 傅里叶变换红外光谱分析(FTIR) 用途:含油气包裹体中的有机成分确定
特点:定性,测试结果具有很好的重复性,可以消除一些矿物和有机荧光的影响影响因素:流体包裹体大小、形状
局限性:流体包裹体中离子态元素无法定量文献[31] 同步辐射X射线荧光(SXRF) 用途:流体包裹体中微量元素成分确定
特点:定量,较高的空间分辨率,能谱连续,多元素同时检出影响因素:主矿物对入射荧光束的X射线吸收
局限性:价格昂贵,检测限较高,仅适用于原子序数大于13的元素文献[32] 核微探针分析(PIXE和PIGE) 用途:流体包裹体中的微量元素成分确定
特点:定量,高灵敏度,多元素同时检出影响因素:流体包裹体形状、内部结构
局限性:PIXE适用于重元素分析,PIGE适用于轻元素分析文献[33] 破坏性分析 激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子质谱(LA-ICP-MS) 用途:流体包裹体中的常、微量元素,Sr和Pb同位素确定
特点:定量,高灵敏度、低检出限、多元素同时检出影响因素:剥蚀热量、流体包裹体大小
局限性:定量校正技术的适用性不足文献[17, 21] 群体包裹体成分分析 色谱-质谱分析:压碎法、爆裂-萃取法 用途:流体包裹体中气相成分、阴阳离子数确定
特点:定量,速度快,准确度高影响因素:样品处理要求高
局限性:数据代表性差,仅适用于同世代且具有良好代表性的流体包裹体文献[34] 表 2 古流体活动时间确定方法、特点、影响因素及其局限性
Table 2. Methods, characteristics, influencing factors and limitations of determining the time of paleofluid activity
研究方法 方法特点 影响因素及局限性 资料来源 流体包裹体分析法 均一温度法 用途:叠合盆地多源、多期流体活动时间
特点:间接定年影响因素:埋藏史-热史、成岩环境
局限性:测试结果具有多解性、人为性强文献[70] 40Ar-39Ar法 用途:伴生矿物形成时间
特点:直接定年影响因素:流体包裹体丰度及其K含量
局限性:测定流体包裹体K含量难度大文献[53] 原油或沥青U-Pb、Rb-Sr、Sm-Nd同位素测年 用途:油气生成、运移的年龄
特点:直接确定原油或沥青的年龄影响因素:样品中放射性同位素的富集和分离
局限性:目前只做到了沥青和干酪根中放射性同位素的分离文献[56, 71] 原油或沥青Re-Os同位素定年 用途:油气生成、运移的年龄
特点:精确厘定油气运移和充注的时限,有效示踪烃源岩影响因素:在自然界丰度低,分离和提纯困难
局限性:仅适用于晚期成藏、单期改造的油气藏文献[58, 72] 方解石LA-MC-ICP-MS微区原位U-Pb放射性同位素定年 用途:不同期次方解石形成年龄
特点:准确率高,避免了不同期次、成岩矿物混合的影响影响因素:矿物中U/Pb含量
局限性:缺乏广泛认可的标准样品用于数据校正文献[66-67] 自生矿物热释光、ESR定年 用途:晚期成藏的年龄
特点:间接定年,准确度高影响因素:自生矿物分离提纯难
局限性:仅适用于与油气藏伴生的石英脉、方解石脉,年龄范围较年轻文献[68-69] -
[1] Curtis J B. Fractured shale-gas systems[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2002, 86(11): 1921-1938. http://www.nrcresearchpress.com/servlet/linkout?suffix=refg13/ref13&dbid=16&doi=10.1139%2Fcjes-2014-0188&key=10.1306%2F61EEDDBE-173E-11D7-8645000102C1865D [2] Rossi C, Marfil R, Ramseyer K, et al. Facies-related diagenesis and multiphase siderite cementation and dissolution in the reservoir sandstones of the Khatatba Formation, Egypt's western desert[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2001, 71(3): 459-472. doi: 10.1306/2DC40955-0E47-11D7-8643000102C1865D [3] 赵靖舟, 李军, 徐泽阳. 沉积盆地超压成因研究进展[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(9): 973-998. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201709001.htmZhao J Z, Li J, Xu Z Y. Advances in the origin of overpressures in sedimentary basins[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(9): 973-998(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201709001.htm [4] 苗凤彬, 彭中勤, 汪宗欣, 等. 雪峰隆起西缘下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩裂缝发育特征及主控因素[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 31-42. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9972.shtmlMiao F B, Peng Z Q, Wang Z X, et al. Development characteristics and major controlling factors of shale fractures in the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation, western margin of Xuefeng Uplift[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 31-42(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9972.shtml [5] 苟启洋, 徐尚, 郝芳, 等. 基于成像测井的泥页岩裂缝研究: 以焦石坝区块为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 193-200. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10085.shtmlGou Q Y, Xu S, Hao F, et al. Research on mud shale fractures based on image logging: A case study of Jiaoshiba area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 193-200(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10085.shtml [6] 苟启洋, 徐尚, 郝芳, 等. 纳米CT页岩孔隙结构表征方法: 以JY-1井为例[J]. 石油学报, 2018, 39(11): 1253-1261. doi: 10.7623/syxb201811005Gou Q Y, Xu S, Hao F, et al. Characterization method of shale pore structure based on nano CT: A case study of Well JY-1[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2018, 39(11): 1253-1261(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.7623/syxb201811005 [7] Pierson B J. The control of cathodoluminescence in dolomite by iron and manganese[J]. Sedimentology, 2006, 28(5): 601-610. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1981.tb01924.x [8] 陈红汉, 吴悠, 朱红涛, 等. 塔中地区北坡中-下奥陶统早成岩岩溶作用及储层形成模式[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(10): 1231-1246. doi: 10.7623/syxb201610003Chen H H, Wu Y, Zhu H T, et al. Eogenetic karstification and reservoir formation model of the Middle-Lower Ordovician in the northeast slope of Tazhong uplift, Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(10): 1231-1246(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.7623/syxb201610003 [9] Becker S P, Eichhubl P, Laubach S E, et al. A 48 my history of fracture opening, temperature, and fluid pressure: Cretaceous Travis Peak Formation, East Texas Basin[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2010, 122(7/8): 1081-1093. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2010GSAB..122.1081B [10] 卢焕章, 范宏瑞, 倪培, 等. 流体包裹体[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004.Lu H Z, Fan H R, Ni P, et al. Fluid inclusions[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004(in Chinese with English abstract). [11] Bakker R J. Raman spectra of fluid and crystal mixtures in the systems H2O, H2O-NaCl and H2O-MgCl2 at low temperatures: Applications to fluid-inclusion research[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 2004, 42(5): 1283-1314. doi: 10.2113/gscanmin.42.5.1283 [12] Mernagh T P, Wilde A R. The use of the laser Raman microprobe for the determination of salinity in fluid inclusions[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1989, 53(4): 765-771. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(89)90022-7 [13] 倪培, 丁俊英, 饶冰. 人工合成H2O及NaCl-H2O体系流体包裹体低温原位拉曼光谱研究[J]. 科学通报, 2006(9): 1073-1078. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.09.012Ni P, Ding J Y, Rao B. In-situ cryogenic Raman spectroscopic studies on the synthetic fluid inclusions in the systems H2O and NaCl-H2O[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006(9): 1073-1078(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.09.012 [14] 陈小兰, 周振柱, 韩作振, 等. 低温拉曼光谱分析流体包裹体盐度的条件约束[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2017, 37(8): 2446-2451. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201708026.htmChen X L, Zhou Z Z, Han Z Z, et al. The constraints on the method of using cryogenic Raman spectroscopy to determine the salinities of fluid inclusions[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(8): 2446-2451(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201708026.htm [15] Jones D M, Macleod G. Molecular analysis of petroleum in fluid inclusions: A practical methodology[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2000, 31(11): 1163-1173. doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(00)00115-7 [16] Ping H W, Li C Q, Chen H H, et al. Overpressure release: Fluid inclusion evidence for a new mechanism for the formation of heavy oil[J]. Geology, 2020, 48(8): 803-807. doi: 10.1130/G47227.1 [17] Pettke T, Oberli F, Audétat A, et al. Recent developments in element concentration and isotope ratio analysis of individual fluid inclusions by laser ablation single and multiple collector ICP-MS[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2011, 44: 10-38. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S016913681100134X [18] Frezzotti M L, Tecce F, Casagli A. Raman spectroscopy for fluid inclusion analysis[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 112: 1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2011.09.009 [19] Tsui T F, Holland H D. The analysis of fluid inclusions by laser microprobe[J]. Economic Geology, 1979, 74(7): 1647-1653. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.74.7.1647 [20] 施伟军, 席斌斌, 秦建中, 等. 单体油气包裹体激光剥蚀在线成分分析技术: 以塔河油田奥陶系储层为例[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(2): 196-206. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201602005.htmShi W J, Xi B B, Qin J Z, et al. Online laser ablation compositional analysis technique for single hydrocarbon inclusion: A case study of the Ordovician reservoirs in Tahe Oilfield, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(2): 196-206(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201602005.htm [21] Volk H, Fuentes D, Fuerbach A, et al. First on-line analysis of petroleum from single inclusion using ultrafast laser ablation[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2010, 41(2): 74-77. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2009.05.006 [22] Liu D H, Xiao X M, Mi J K, et al. Determination of trapping pressure and temperature of petroleum inclusions using PVT simulation software: A case study of Lower Ordovician carbonates from the Lunnan Low Uplift, Tarim Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2003, 20(1): 29-43. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(03)00047-3 [23] Aplin A C, Macleod G, Larter S R, et al. Combined use of Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy and PVT simulation for estimating the composition andphysical properties of petroleum in fluid inclusions[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1999, 16(2): 97-110. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(98)00079-8 [24] 王瑀辉. 渝东南彭水地区龙马溪组地层压力演化[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2018.Wang Y H. Evolution of formation fluid pressure in Longmaxi Formation, Pengshui area, Southeast Chongqing[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum(Beijing), 2018(in Chinese with English abstract). [25] Lin F, Bodnar R, Becker S. Experimental determination of the Raman CH4 symmetric stretching(ν1) band position from 1650 bar and 0.3-22℃: Application to fluid inclusion studies[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(15): 3746-3756. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.05.016 [26] Lu W, Chou I, Burruss R, et al. A unified equation for calculating methane vapor pressures in the CH4-H2O system with measured Raman shifts[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(16): 3969-3978. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.06.004 [27] Duan Z H, Møller N, Weare J H. An equation of state for the CH4-CO2-H2O system: Ⅰ. Pure systems from 0 to 1000℃ and 0 to 8000 bar[J]. Pergamon, 1992, 56(7): 2605-2617. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/001670379290347L [28] Duan Z H, Møller N, Weare J H. An equation of state for the CH4-CO2-H2O system: Ⅱ. Mixtures from 50 to 1000℃ and 0 to 1000 bar[J]. Pergamon, 1992, 56(7): 2619-2631. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/001670379290348M [29] 高键, 何生, 易积正. 焦石坝页岩气田中高密度甲烷包裹体的发现及其意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2015, 36(3): 472-480. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201503018.htmGao J, He S, Yi J Z. Discovery of high density methane inclusions in Jiaoshiba shale gas field and its significance[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2015, 36(3): 472-480(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201503018.htm [30] 施伟军, 席斌斌. 应用包裹体技术恢复气藏古压力[J]. 石油实验地质, 2016, 38(1): 128-134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201601019.htmShi W J, Xi B B. Calculation of paleo-pressure in gas reservoirs using fluid inclusions[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2016, 38(1): 128-134(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201601019.htm [31] Pironon J, Thiery R, Ougougdal M A, et al. FT-IR measurements of petroleum fluid inclusions: Methane, n-alkanes and carbon dioxide quantitative analysis[J]. Geofluids, 2001, 1(1): 2-10. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-8123.2001.11002.x [32] Rankin A H, Ramsey M H, Coles B, et al. The composition of hypersaline, iron-rich granitic fluids based on laser-ICP and synchrotron-XRF microprobe analysis of individual fluid inclusions in topaz, Mole granite, eastern Australia[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1992, 56(1): 67-79. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(92)90117-2 [33] Anderson A J, Ckark A H, Ma X P, et al. Proton-induced X-ray and gamma-ray emission analysis of unopened fluid inclusions[J]. Economic Geology, 1989, 84(4): 924-939. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.84.4.924 [34] Hall P A, Watson A F R, Garner G V, et al. An investigation of micro-scale sealed vessel thermal extraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry(MSSV-GC-MS) and micro-scale sealed vessel pyrolysis-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry applied to a standard reference material of an urban dust/organics[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 1999, 235(1): 269-276. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969799002041 [35] Eichhubl P, Boles J R. Focused fluid flow along faults in the Monterey Formation, coastal California[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2000, 112(11): 1667-1679. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(2000)112<1667:FFFAFI>2.0.CO;2 [36] Worden R H, Benshatwan M S, Potts G J, et al. Basin-scale fluid movement patterns revealed by veins: Wessex Basin, UK[J]. Geofluids, 2016, 16(1): 149-174. doi: 10.1111/gfl.12141 [37] Azmy K, Veizer J, Wenzel B, et al. Silurian strontium isotope stratigraphy[J]. GSA Bulletin, 1999, 111(4): 475-483. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1999)111<0475:SSIS>2.3.CO;2 [38] Dogramaci S S, Herczeg A L. Strontium and carbon isotope constraints on carbonate-solution interactions and inter-aquifer mixing in groundwaters of the semi-arid Murray Basin, Australia[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2002, 262(1/4): 50-67. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022169402000215 [39] Fietzke J, Eisenhauer A. Determination of temperature-dependent stable strontium isotope(88Sr/86Sr) fractionation via bracketing standard MC-ICP-MS[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2006, 7(8), DOI: 10.1029/2006-GC001243. [40] Veizer J, Ala D, Azmy K, et al. 87Sr/86Sr, δ13C and δ18O evolution of Phanerozoic seawater[J]. Chemical Geology, 1991, 161: 59-88. [41] 郑永飞. 稳定同位素体系理论模式及其矿床地球化学应用[J]. 矿床地质, 2001, 20(1): 57-70, 85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2001.01.007Zheng Y F. Theoretical modeling of stable isotope systems and its applications to geochemistry of hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2001, 20(1): 57-70, 85(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2001.01.007 [42] 钱一雄, 沙旭光, 李慧莉, 等. 塔里木盆地塔中西部加里东中、晚期构造-层序结构与奥陶系碳酸盐岩储集体分布[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(1): 260-274. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201301023.htmQian Y X, Sha X G, Li H L, et al. An approach to Caledonian unconformities and sequence stratigraphic patterns and distribution of reservoirs of Ordovician carbonate in the western Tazhong area, Tarim Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(1): 260-274(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201301023.htm [43] Caja M A, Permanyer A, Marfil R, et al. Fluid flow record from fracture-fill calcite in the Eocene limestones from the South-Pyrenean Basin(NE Spain) and its relationship to oil shows[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2006, 89(1/3): 27-32. [44] Lottermoser B G. Rare earth elements and hydrothermal ore formation processes[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 1992, 7(1): 25-41. doi: 10.1016/0169-1368(92)90017-F [45] Tostevin R, Shields G A, Tarbuck G, et al. Effective use of cerium anomalies as a redox proxy in carbonate-dominated marine settings[J]. Chemical Geology, 2016, 438: 146-162. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.06.027 [46] Bau M, M ller P. Rare earth element fractionation in metamorphogenic hydrothermal calcite, magnesite and siderite[J]. Mineralogy & Petrology, 1992, 45(45): 231-246. doi: 10.1007%2FBF01163114 [47] 杨建, 王国芝, 李娜, 等. 川东南二叠系区域盖层沥青来源稀土元素示踪[J]. 云南地质, 2011, 30(2): 226-228. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1885.2011.02.029Yang J, Wang G Z, Li Na, et al. The REE tracer of pitch origin Permian regional super imposition bed in SE Sichuan[J]. Yunnan Geology, 2011, 30(2): 226-228(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1885.2011.02.029 [48] 金之钧, 朱东亚, 孟庆强, 等. 塔里木盆地热液流体活动及其对油气运移的影响[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(3): 1048-1058. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201303026.htmJin Z J, Zhu D Y, Meng Q Q, et al. Hydrothermal activites and influences on migration of oil and gas in Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(3): 1048-1058(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201303026.htm [49] 何顺, 秦启荣, 周吉羚, 等. 川东南DS地区龙马溪组页岩裂缝发育特征及期次解析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2): 101-109. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902012.htmHe S, Qin Q R, Zhou J L, et al. Shale fracture characteristics and its application of the Longmaxi Formation in DS area, Southeast Sichuan[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(2): 101-109(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902012.htm [50] Parnell J, Carey P, Duncan W. History of hydrocarbon charge on the Atlantic margin: Evidence from fluid-inclusion studies, West of Shetland[J]. Geology, 1998, 26(9): 807-810. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1998)026<0807:HOHCOT>2.3.CO;2 [51] Bourdet J, Burruss R C, Chou I M, et al. Evidence for a palaeo-oil column and alteration of residual oil in a gas-condensate field: Integrated oil inclusion and experimental results[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 142: 362-385. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.07.022 [52] 吴河勇, 云建兵, 冯子辉, 等. 松辽盆地深层CO2气藏40Ar/39Ar成藏年龄探讨[J]. 科学通报, 2010, 55(8): 693-697. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201008007.htmWu H Y, Yun J B, Feng Z H, et al. CO2 gas emplacement age in the Songliao Basin: Insight from volcanic quartz 40Ar-39Ar stepwise crushing[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(8): 693-697(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201008007.htm [53] Qiu H N, Wu H Y, Yun J B, et al. High-precision40Ar/39Ar age of the gas emplacement into the Songliao Basin[J]. Geology, 2011, 39(5): 451-454. doi: 10.1130/G31885.1 [54] 刘昭茜, 梅廉夫, 邱华宁, 等. 中扬子地块南缘半坑古油藏成藏期及破坏期的40Ar/39Ar年代学约束[J]. 科学通报, 2011, 56(33): 2782-2790. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201133008.htmLiu Z Q, Mei L F, Qiu H N, et al. 40Ar/39Ar geochronology constraints on hydrocarbon accumulation and destruction periods in the Bankeng paleo-reservoir in the southern margin of the middle Yangtze block[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(33): 2782-2790(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201133008.htm [55] Nguyen T H, Nevolko P A, Pham T D, et al. Age and genesis of the W-Bi-Cu-F(Au) Nui Phao deposit, Northeast Vietnam: Constrains from U-Pb and Ar-Ar geochronology, fluid inclusions study, S-O isotope systematic and scheelite geochemistry[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 123: 103578. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103578 [56] Zhu B Q, Zhang J L, Tu X L, et al. Pb, Sr and Nd isotopic features in organic matter from China and their implications for petroleum generation and migration[J]. Geotectonica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65(15): 2555-2570. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00608-1 [57] 沈传波, Selby D, 梅廉夫, 等. 油气成藏定年的Re-Os同位素方法应用研究[J]. 矿物岩石, 2011, 31(4): 87-93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2011.04.014Shen C B, Selby D, Mei L F, et al. Advances in the study of Re-Os geochronology and tracing of hydrocarbon generation and accumulation[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2011, 31(4): 87-93(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2011.04.014 [58] Selby D, Creaser R A, Dewing K, et al. Evaluation of bitumen as a187Re-187Os geochronometer for hydrocarbon maturation and migration: A test case from the Polaris MVT deposit, Canada[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 235(1): 1-15. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X05001202 [59] Lillis P G, Selby D. Evaluation of the rhenium-osmium geochronometer in the Phosphoria petroleum system, Bighorn Basin of Wyoming and Montana, USA[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2013, 118: 312-330. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2013.04.021 [60] Corrick A J, Selby D, Mckirdy D M, et al. Remotely constraining the temporal evolution of offshore oil systems[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 1327. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37884-x [61] 李欣尉, 李超, 周利敏, 等. 贵州正安县奥陶系-志留系界线碳质泥岩Re-Os同位素精确厘定及其古环境反演[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(2): 251-261. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS202002012.htmLi X W, Li C, Zhou L M, et al. Accurate determination of the age of the carbonaceous mudstone of the Ordovician-Silurian boundary in Zheng'an County, Guizhou Province by Re-Os isotope dating method and its application in paleoenvironmental inversion[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(2): 251-261(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS202002012.htm [62] Chen X C, Hu R Z, Bi X W, et al. Cassiterite LA-MC-ICP-MS U/Pb and muscovite40Ar/39Ar dating of tin deposits in the Tengchong-Lianghe tin district, NW Yunnan, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2014, 49(7): 843-860. doi: 10.1007/s00126-014-0513-8 [63] 梁文博, 郭瑞清, 刘桂萍, 等. 新疆库鲁克塔格西段橄榄辉长岩脉LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(1): 58-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201901007.htmLiang W B, Guo R Q, Liu G P, et al. LA-ICP MS zircon U-Pb age and geochemistry of the olivine gabbro dike in the western segment of Kuruktag, Xinjiang and its tectonic significance[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(1): 58-67(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201901007.htm [64] Li Q, Parrish R R, Horstwood M S A, et al. U-Pb dating of cements in Mesozoic ammonites[J]. Chemical Geology, 2014, 376: 76-83. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.03.020 [65] 郭小文, 陈家旭, 袁圣强, 等. 含油气盆地激光原位方解石U-Pb年龄对油气成藏年代的约束: 以渤海湾盆地东营凹陷为例[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(3): 284-291. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202003005.htmGuo X W, Chen J X, Yuan S Q, et al. Constraint of in-situ calcite U-Pb dating by laser ablation on geochronology of hydrocarbon accumulation in petroliferous basins: A case study of Dongying Sag in the Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(3): 284-291(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202003005.htm [66] Mangenot X, Gasparrini M, Gerdes A, et al. An emerging thermochronometer for carbonate-bearing rocks: Δ47/(U-Pb)[J]. Geology, 2018, 46(12): 1067-1070. doi: 10.1130/G45196.1 [67] Roberts N M, Walker R J. U-Pb geochronology of calcite-mineralized faults: Absolute timing of rift-related fault events on the northeast Atlantic margin[J]. Geology, 2016, 44(7): 531-534. doi: 10.1130/G37868.1 [68] Beerten K, Stesmans A. ESR dating of sedimentary quartz: Possibilities and limitations of the single-grain approach[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2007, 2(1): 373-380. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1871101406000045 [69] Aydas C, Engin B, Aydin T. Radiation-induced signals of gypsum crystals analysed by ESR and TL techniques applied to dating[J]. Nuclear Inst. and Methods in Physics Research, 2011, 269(4): 417-424. doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2010.12.074 [70] Bourdet J, Pironon J. Strain response and re-equilibration of CH4-rich synthetic aqueous fluid inclusions in calcite during pressure drops[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2008, 72(12): 2946-2959. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2008.04.012 [71] Parnell J, Swainbank I. Pb-Pb dating of hydrocarbon migration into a bitumen-bearing ore deposit, North Wales[J]. Geology, 1990, 18(10): 1028-1030. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1990)018<1028:PPDOHM>2.3.CO;2 [72] Creaser R A, Sannigrahi P, Chacko T, et al. Further evaluation of the Re-Os geochronometer in organic-rich sedimentary rocks: A test of hydrocarbon maturation effects in the Exshaw Formation, Western Canada Sedimentary Basin[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2002, 66(19): 3441-3452. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(02)00939-0 -





 下载:
下载: