The thrust-decollement structure in western Guizhou and its control of Pb-Zn deposit
-
摘要: 黔西地区位于上扬子地块西南缘,大地构造处于古特提斯构造域与太平洋构造域共同控制与影响的区域。该区广泛出露中上泥盆统-下三叠统(D2-T1)碳酸盐岩为主的沉积岩,下伏下泥盆统与志留系巨厚页岩和粉砂岩,构成了该区的底部滑脱层。在D2-T1碳酸盐岩为主的强硬岩层中夹有的页岩-粉砂岩、炭质页岩构成了次级滑脱层。在中生代,受上述两大构造域远程复合作用,黔西地区发生了多次构造活动与叠加变形。在挤压收缩过程中,强硬层与软弱层之间的滑脱作用形成了黔西地区复杂的构造格局。不同阶段不同规模的逆冲滑脱作用(顺层滑脱→切层滑脱→小型逆冲→大型逆冲)对铅锌富集起到了不同的控制作用。顺层滑脱形成了与层理一致的铅锌富集;切层滑动(小型逆冲)控制了稍陡于岩层的铅锌矿富集;小型平移或张性断层控制了陡倾铅锌矿的富集;而大型逆冲断层则控制了大型、超大型铅锌矿床的富集。因此,逆冲滑脱作用是控制黔西铅锌矿床富集的最重要因素。Abstract: The western Guizhou area is located in the southwest margin of the upper Yangtze Block, which is influenced both by the Tethys tectonic process and the Pacific tectonic process. The most widely exposed sedimentary rocks in this area are mainly the Middle and Upper Devonian-Lower Triassic (D2-T1) carbonate. The Lower Devonian and Silurian shale and siltstones are overlaid to constitute the bottom detachment layer in this area. Shale, siltstones and carbonaceous shale in D2-T1 carbonate hard rock form the secondary detachment layer. In the Mesozoic, due to the remote recombination of the above two tectonic process, many tectonic activities and superimposed deformation occurred in western Guizhou. In the extrusion process, the decollements between the hard and the weak layer formed the complex tectonic pattern. The different scale thrust-decollement in different stage (interlayer decollement-multi detachment-small thrust-large thrust) has different effects for Pb and Zn enrichment. Pb and Zn enrichment was formed by interlayer decollement in accordance with bedding. Furtherly, multi detachment (small thrust) controls Pb-Zn enrichment slightly steeper than the strata. Small parallel displacement or tensile faults control the enrichment of steeply dipping lead-zinc deposits, whereas the large thrust faults control the enrichment of large and very large Pb-Zn deposits. Therefore, the thrust-decollement is the most important factor to control the enrichment of Pb-Zn deposit in western Guizhou.
-
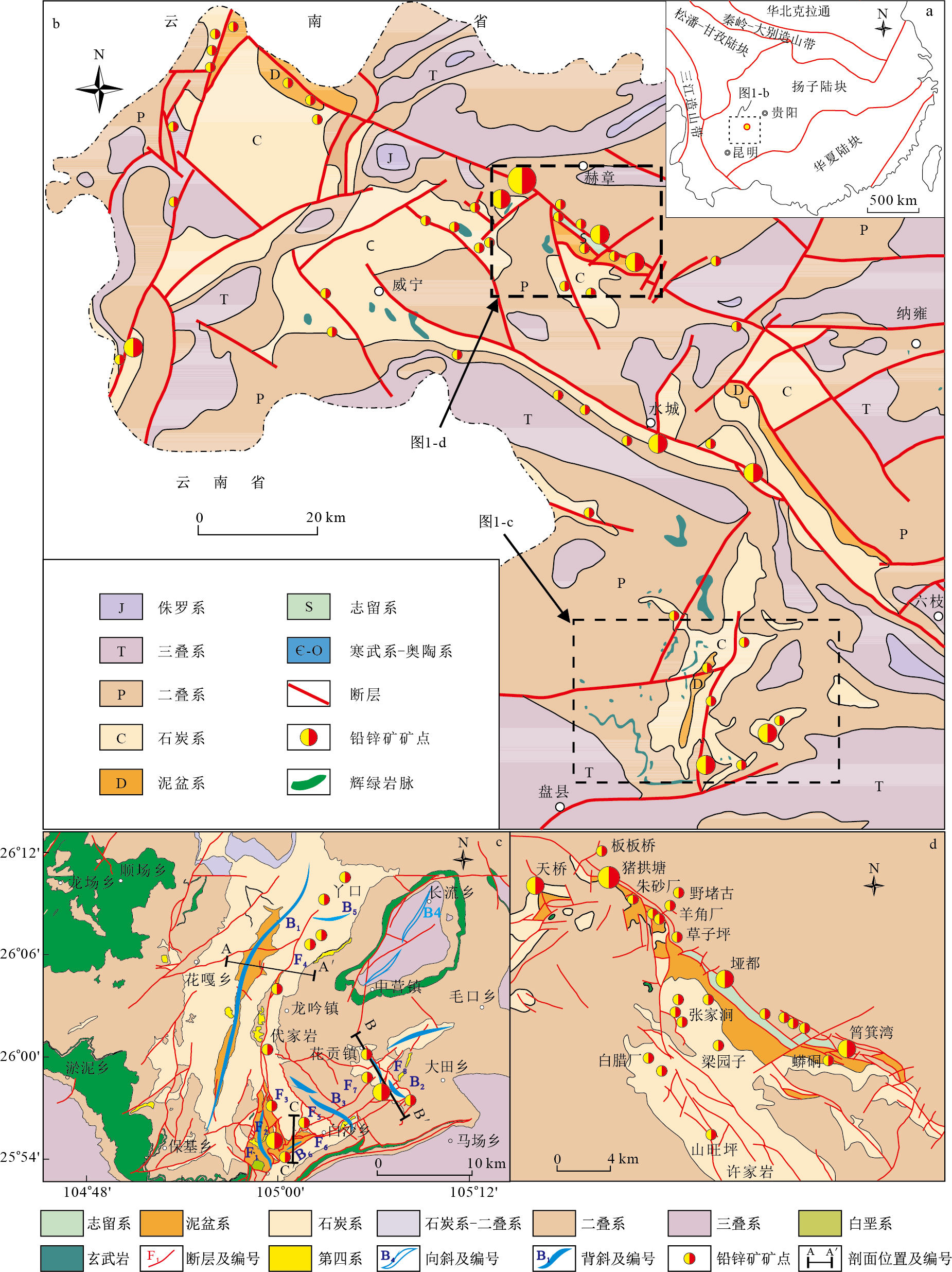
图 5 滑脱与逆冲构造及其对铅锌矿体的控制
a.格所背斜深谷中泥盆系不协调褶皱; b.打屋坝组(C2w)不协调滑脱构造; c, d.顺层滑动控制矿层; e.切层滑动控制矿层; f.逆冲滑动控制矿层; 地层代号同图 3;S1.劈理;Gn.方铅矿;Sp.闪锌矿;Lm.褐铁矿
Figure 5. The thrust-decollement structure and its control of Pb-Zn deposit
-
[1] Zhou J X, Wang X C, Wilde S A.New insights into the metallogeny of MVT Zn-Pb deposits:A case study from the Nayongzhi in South China, using field data, fluid compositions, and in situ S-Pb isotopes[J].American Mineralogist, 2018, 103(1):91-108. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/msa/ammin/article-abstract/103/1/91/525794/New-insights-into-the-metallogeny-of-MVT-Zn-Pb [2] 金中国, 周家喜, 黄智龙, 等.贵州普定那雍枝铅锌矿矿床成因:S和原位Pb同位素证据[J].岩石学报, 2016, 32(11):3441-3455. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201611016.htm [3] Zhou J X, Luo K, Wang X C.Ore genesis of the Fule Pb-Zn deposit and its relationship with the Emeishan Large Igneous Province:Evidence from mineralogy, bulk C-O-S and in situ S-Pb isotopes[J].Gondwana Research, 2018, 54:161-179. https://espace.curtin.edu.au/handle/20.500.11937/59431 [4] 周家喜, 黄智龙, 周国富, 等.黔西北天桥铅锌矿床热液方解石C、O同位素和REE地球化学[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2012, 36(1):93-101. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201201012 [5] 朱路艳, 苏文超, 沈能平, 等.黔西北地区铅锌矿床流体包裹体与硫同位素地球化学研究[J].岩石学报, 2016, 32(11):3431-3440. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201611015 [6] 黄林, 郭阳, 王生伟, 等.贵州五指山特大型铅锌矿床成矿流体特征及其地质意义[J].矿物岩石, 2018, 38(4):39-48. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwys201804006 [7] Laubscher H P.Folds development in the Jura[J].Tectonophysics, 1977, 37(4):337-362. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201205007 [8] Sommaruga A.Decollement tectonics in the Jura foreland fold and thrust belt[J].Maine and Petroleum Geology, 1999, 16(2):111-134. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fa9615942bb8d1f86752a5427f081ae9 [9] Yan D P, Zhou M F, Song H L, et al.Origin and tectonic significance of a Mesozoic multi-layer over-thrust system within the Yangtze Block (South China)[J].Tectonophysics, 2003, 361(3/4):239-254. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=069fcc1d9ed52deee632dc3893af5507 [10] Jamison W R.Geometric analysis of fold development in overthrust terranes[J].Journal of Structural Geology, 1987, 9(2):207-219. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0191814187900265 [11] 朱志澄, 宋鸿林.构造地质学[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1990:197-198. [12] Ma X, Yang K G, Li X G, et al.Neoproterozoic Jiangnan Orogeny in southeast Guizhou, South China:Evidence from U-Pb ages for detrital zircons from the Sibao Group and Xiajiang Group[J].Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2016, 53(3):219-230. doi: 10.1139/cjes-2015-0052#.XvqvjPkyaRw [13] 张国伟, 郭安林, 王岳军, 等.中国华南大陆构造与问题[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2013, 43(10):1553-1582. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201310003 [14] Wang Y J, Zhang F F, Fan W M, et al.Tectonic setting of the South China Block in the early Paleozoic:Resolving intracontinental and ocean closure models from detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology[J].Tectonics, 2010, 29(6):. doi: 10.1029/2010TC002750 [15] 邓新, 杨坤光, 刘彦良, 等.黔中隆起性质及其构造演化[J].地学前缘, 2010, (3):79-89. doi: 10.2174-187152409788452090/ [16] 贵州省地质调查院.中国区域地质志:贵州志[M].北京:地质出版社, 2017:271-276, 972-973. [17] 罗金海.紫云-罗甸-南丹裂陷带的构造演化及其地质意义[D].西安: 西北大学, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10697-2010118617.htm [18] 张德民, 何良伦, 曾广乾, 等.黔西罐子窑地区叠加变形及其对铅锌矿床的控制作用[J].贵州地质, 2014, 31(4):241-251. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzdz201404001 [19] 周启永.普安旋卷构造体系及其控矿规律研究[J].贵州地质, 1991, 8(2):130-140. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GZDZ199102004.htm [20] 陈学敏.论贵州西部扭动构造[J].贵州地质, 2009, 26(1):13-18. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzdz200901003 [21] 杨坤光, 李学刚, 戴传固, 等.断层调整与控制作用下的叠加构造变形:以贵州地区燕山期构造为例[J].地质科技情报, 2012, 31(5):50-56. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKQ201205008.htm [22] 何良伦, 赵锋, 柏光辉, 等.贵州省猪拱塘超大型铅锌矿床的发现及其找矿意义[J].中国地质调查, 2019, 6(3):29-36. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdzdc201903004 [23] 兰安平, 任厚州, 刘雨, 等.黔西北五指山地区加里东期盲冲断层的厘定及其找矿意义[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2):14-24. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkjqb201902002 [24] 杨兴玉, 任厚州, 刘雨, 等.黔西北五指山地区叠加构造变形特征对铅锌矿成矿的控制[J].现代地质, 2018, 32(4):739-749. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xddz201804011 [25] Li B, Zhou J X, Huang Z L, et al.Geological, rare earth elemental and isotopic constraints on the origin of the Banbanqiao Zn-Pb deposit, southwest China[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 111:100-112. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=82d340255dc2d095891b1e31b9838fe7 [26] 肖宪国, 黄智龙, 周家喜, 等.黔西北筲箕湾铅锌矿床成矿物质来源:Pb同位素证据[J].矿物岩石, 2012, 32(2):294-298. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwxb201202018 [27] 杜远生, 黄虎, 杨江海, 等.晚古生代-中三叠世右江盆地的格局和转换[J].地质论评, 2013, 59(1):1-10. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp201301001 [28] Bao Z W, Li Q, Wang C Y.Metal source of giant Huize Zn-Pb deposit in SW China:New constraints from in situ Pb isotopic compositions of galena[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 91:824-836. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136817302809 -





 下载:
下载: