Analysis of spatial variability and influencing factors of arsenic in groundwater of Hetao Plain, Inner Mongolia
-
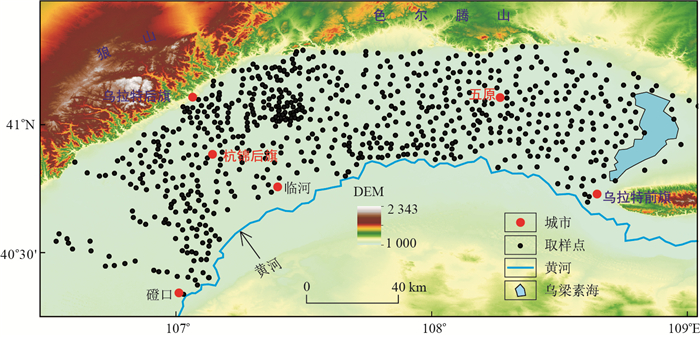
摘要: 河套平原是我国地方性砷中毒最为严重的地区之一。基于河套平原浅层地下水的砷含量数据,利用地统计学中半变异函数分析法,对地下水砷含量的空间分布及其异质性特征进行了分析,并探讨其空间变异性的影响因素。结果显示,河套平原地下水砷含量整体上呈由南向北递增的趋势,在假设各向同性条件下,砷含量残差项的空间分布符合纯块金效应模型,在所测尺度上(2~4 km)为随机分布,不存在空间自相关性,短距离内变异较大;地下水砷含量的分维数较大(D=1.999),进一步说明该尺度上变异显著。地下水砷含量与沉积物中有机质关系密切。晚第四纪以来,河套平原北部山区的新构造运动和盆地沉积环境变迁形成多种成因、形态复杂的沉积相,导致有机质埋藏条件的高度空间变异性,进而导致地下水砷含量的高度空间变异。河套平原缓慢的地下水径流条件有利于砷元素空间变异性的维持。河套地区地下水砷的空间异质性研究,对有效预测未知地区饮水型砷暴露潜在风险、精准防控地方病和保障供水安全具有重要的科学意义。Abstract: Hetao Plain is one of the most serious area of local arsenic poisoning in China.Based on shallow groundwater arsenic samples, the paper used the semivariogram to reveal the spatial distribution and heterogeneity of groundwater arsenic concentration, and further discussed the influencing factors.The results show that the arsenic concentration in groundwater generally increases from south to north in the Hetao Plain.The residual groundwater arsenic concentration is fitted to the pure nugget effect model under the assumption of isotropic conditions, which means it is random on the measured scale, so there is no spatial autocorrelation and the variance is great in short distances.The fractal dimension value is large(D=1.999), further indicating the distinct variation of groundwater arsenic concentration within the measured scale.Groundwater arsenic is closely related to organic matters in sediments.Since the Late Quaternary, the tectonic movements of the northern mountains and changes in the sedimentary environment of the basin has caused multiple sedimentary facies, resulting in a high degree of spatial variability in burial conditions of organic matters.The high spatial variability of organic matters characteristics further leads to high spatial variability of groundwater arsenic concentration.The slow groundwater flow plays an important role in maintaining this pattern.This article focuses on the spatial heterogeneity of groundwater arsenic in the Hetao area, which has scientific significance for effectively predicting the potential risk of arsenic exposure in drinking water in unknown areas, accurately preventing endemic diseases and ensuring water supply safety.
-
Key words:
- arsenic concentration /
- groundwater /
- spatial variability /
- organic matters /
- Hetao Plain
-
表 1 河套平原地区地下水砷质量浓度的统计特征值
Table 1. Statistical characteristics of As concentration in groundwater across the Hetao Plain
样点数 均值 标准差 最小值 最大值 变异系数 ρ(As)/(mg·L-1) 753 0.072 7 0.142 0 0 1.368 0 1.952 5 表 2 五原西北部海子堰地区钻探沉积物的有机物(C、N)及砷质量浓度
Table 2. Organic matters (C, N) and arsenic contents of the sediment cores in Haiziyan area, northwest of Wuyuan
取样编号 岩性 采样深度/m w(TOC)/% w(TN)/% w(C+N)/% w(As)/(mg·kg-1) 1 地表土壤 0 0.909 9 0.047 9 0.957 8 12.2 2 淤泥质砂 5 0.117 6 0.012 9 0.130 5 10.2 3 淤泥质黏土 6.5 0.493 2 0.020 4 0.513 6 19.1 4 淤泥质黏土 9.2 0.278 3 0.031 2 0.309 5 20.9 5 粉细沙 12 0.125 0 0.004 4 0.129 4 9.1 6 淤泥质黏土 15.1 0.326 3 0.023 4 0.349 7 15.9 7 淤泥质黏土 18.5 0.594 9 0.030 5 0.625 4 17.1 8 中细砂 20.7 0.038 7 0.004 7 0.043 4 6.8 9 中细砂 25 0.036 3 0.005 7 0.042 0 8.0 10 淤泥质砂 30.3 0.074 7 0.006 6 0.081 3 9.5 11 细砂 33.5 0.036 8 0.006 0 0.042 8 7.7 12 细砂 36 0.047 8 0.006 6 0.054 4 8.5 13 黏土 41.5 0.458 8 0.033 3 0.492 1 47.1 14 中细砂 45 0.041 5 0.006 9 0.048 4 6.0 15 中细砂 48 0.036 6 0.006 3 0.042 9 6.3 16 黏土 49.5 0.377 6 0.033 2 0.410 8 47.1 17 中细砂 58 0.035 2 0.005 7 0.040 9 6.5 18 中细砂 71.4 0.039 2 0.004 9 0.044 1 7.2 -
[1] 沈雁峰, 孙殿军, 赵新华, 等.中国饮水型地方性砷中毒病区和高砷区水砷筛查报告[J].中华地方病学杂志, 2005, 24(2):172-175. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-4955.2005.02.019 [2] Nickson R T, McArthur J M, Burgess W G, et al.Arsenic poisoning of Bangladesh groundwater[J].Nature, 1998, 395:338. doi: 10.1038/26387 [3] Deng Y M, Wang Y X, Ma T.Isotope and minor element geochemistry of high arsenic groundwater from Hangjinhouqi, the Hetao Plain, Inner Mongolia[J].Applied Geochemistry, 2009, 24(4):587-599. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.12.018 [4] Guo H M, Zhang Y, Xing L N, et al.Spatial variation in arsenic and fluoride concentrations of shallow groundwater from the town of Shahai in the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia[J].Applied Geochemistry, 2012, 27(11):2187-2196. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2012.01.016 [5] 张扬, 郭华明, 贾永峰, 等.内蒙古河套平原典型高砷区地下水中砷的演化规律[J].水文地质工程地质, 2017, 44(2):15-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201702003.htm [6] 余倩, 谢先军, 马瑞, 等.地下水系统中砷迁移富集过程的水文地球化学模拟[J].地质科技情报, 2013, 32(6):116-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201306019.htm [7] 张俊文, 马腾, 冯亮, 等.微生物介导下高砷地下水系统的氧化还原分带性概念模型[J].地质科技情报, 2015, 34(5):153-159. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201505024.htm [8] 高存荣, 刘文波, 冯翠娥, 等.干旱、半干旱地区高砷地下水形成机理研究:以中国内蒙古河套平原为例[J].地学前缘, 2014, 21(4):13-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201404003.htm [9] Yang S Z, Guo H M, Tang X H, et al.Distribution of abnormal groundwater arsenic in Hetao Plain, Inner Mongolia[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2008, 15(1):242-249. [10] 鲁守刚, 邓娅敏, 张美雁, 等.基于多元统计分析的高砷地下水水化学特征研究:以内蒙古杭锦后旗为例[J].中国农村水利水电, 2014(12):40-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2014.12.011 [11] Guo H M, Zhang Y, Jia Y F, et al.Dynamic behaviors of water levels and arsenic concentration in shallow groundwater from the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 135:130-140. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2012.06.010 [12] Guo H M, Zhang B, Zhang Y.Control of organic and iron colloids on arsenic partition and transport in high arsenic groundwaters in the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia[J].Applied Geochemistry, 2011, 26(3):360-370. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.12.009 [13] Dong Y H, Ma T, Li J L, et al.Arsenic releasing from poly-metallic sulfide deposits at Hetao Plain, China[J].Geochemistry International, 2018, 56(12):1179-1188. doi: 10.1134/S001670291812011X [14] He J, Ma T, Deng Y M, et al.Environmental geochemistry of high arsenic groundwater at western Hetao Plain, Inner Mongolia[J].Frontiers of Earth Science, 2009, 3(1):63-72. doi: 10.1007/s11707-009-0004-x [15] Maguffin S C, Kirk M F, Daigle A R, et al.Substantial contribution of biomethylation to aquifer arsenic cycling[J].Nature Geoscience, 2015, 8(4):290-293. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2383 [16] Mcarthur J M, Banerjee D M, Hudson-Edwards K A, et al.Natural organic matter in sedimentary basins and its relation to arsenic in anoxic ground water:The example of West Bengal and its worldwide implications[J].Applied Geochemistry, 2004, 19(8):1255-1293. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.02.001 [17] 郭华明, 倪萍, 贾永锋, 等.原生高砷地下水的类型、化学特征及成因[J].地学前缘, 2014, 21(4):1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201404002.htm [18] Danyar S, Yudong S, Jumakeld M.Influence of groundwater level change on vegetation coverage and their spatial variation in arid regions[J].Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2004, 14(3):323-329. doi: 10.1007/BF02837413 [19] Zhang H Y, Wang X S.The impact of groundwater depth on the spatial variance of vegetation index in the Ordos Plateau, China:A semivariogram analysis[J].Journal of Hydrology, 2020, 588:125096. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125096 [20] 徐伟嘉, 钟流举, 何芳芳.等.基于变异函数的大气污染物空间分布特征分析[J].环境科学与技术, 2014, 37(12):73-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS201412017.htm [21] 王军, 傅伯杰, 邱扬, 等.黄土丘陵小流域土壤水分的时空变异特征半变异函数[J].地理学报, 2000, 67(4):428-438. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2000.04.005 [22] 杜志勇, 刘苑秋, 郑诗樟, 等.退化红壤区不同模式重建森林土壤水分空间变异性[J].水土保持学报, 2007, 21(5):101-105. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2007.05.024 [23] 吴才聪, 胡冰冰, 赵明, 等.基于无人机影像和半变异函数的玉米螟空间分布预报方法[J].农业工程学报, 2017, 09:92-99. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NYGU201709011.htm [24] Phillips J D.Measuring complexity of environmental gradients[J].Vegetatio, 1986, 64(2/3):95-102. doi: 10.1007/BF00044785 [25] Palmer M W.Fractal geometry:A tool for describing spatial patterns of plant communities[J].Vegetatio, 1988, 75(1/2):91-102. [26] 陈健, 倪绍祥, 李静静, 等.植被叶面积指数遥感反演的尺度效应及空间变异性[J].生态学报, 2006, 26(5):1502-1508. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2006.05.027 [27] 江颖慧, 焦利民, 张博恩.城市地表温度与NDVI空间相关性的尺度效应[J].地理科学进展, 2018, 37(10):62-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKJ201810006.htm [28] 张先, 贺为民, 沈京秀, 等.内蒙古河套断陷带及其邻区地壳磁性构造特征[J].地震工程学报, 1995, 1:31-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ501.004.htm [29] 王谦身, 滕吉文, 王光杰, 等.内蒙古阴山地区特异区域重磁场与深部构造[J].地球物理学报, 2005, 48(2):314-320. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2005.02.012 [30] 李建彪, 冉勇康, 郭文生.河套盆地托克托台地湖相层研究[J].第四纪研究, 2005, 25(5):630-639. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2005.05.012 [31] Guo H M, Yang S Z, Tang X H, et al.Groundwater geochemistry and its implications for arsenic mobilization in shallow aquifers of the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2008, 393(1):131-144. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.12.025 [32] Zawadzki J, Cieszewski C J, Zasada M, et al.Applying geostatistics for investigations of forest ecosystems using remote sensing imagery[J].Silva Fenn, 2005, 39(4):599-618. [33] Krige D G.A study of gold and uranium distribution patterns in the Klerksdorp gold field[J].Geoexploration, 1966, 4(1):43-53. doi: 10.1016/0016-7142(66)90010-X [34] Chen L J, Feng Q.Geostatistical analysis of temporal and spatial variations in groundwater levels and quality in the Minqin oasis, Northwest China[J].Environ.Earth Sci., 2013, 70(3):1367-1378. doi: 10.1007/s12665-013-2220-7 [35] Bachmaier M, Backes M.Variogram or semivariogram variance or semivariance Allan variance or introducing a new term[J].Mathematical Geosciences, 2011, 43(6):735-740. doi: 10.1007/s11004-011-9348-3 [36] Hani A, Pazira E, Manshouri M, et al.Spatial distribution and mapping of risk elements pollution in agricultural soils of southern Tehran, Iran[J].Plant Soil & Environment, 2010, 56(6):288-296. [37] McBradney A B, Webster R.Choosing functions for semi-variograms of soil properties and fitting them to sampling estimates[J].Journal of Soil Science, 1986, 37:617-639. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.1986.tb00392.x [38] Burrough P A.Multiscale sources of spatial variation in soil.Ⅱ.A non-Brownian fractal model and its application in soil survey[J].European Journal of Soil Science, 1983, 34(3):599-620. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.1983.tb01058.x [39] 彭润民, 翟裕生, 韩雪峰, 等.内蒙古狼山造山带构造演化与成矿响应[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(3):679-688. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200703016.htm [40] 郭秉成, 孙振洲, 郭婧.内蒙古中部色尔腾山地区成矿地质条件分析[J].西部资源, 2011(6):56-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBZY201106052.htm [41] 杨发.河套断陷带第四纪活动特征[C]//国家地震局.鄂尔多斯周缘活动断裂系.北京: 地震出版社, 1988. [42] He X L, Zhang X J, He Z X, et al.Late Quaternary alluvial fan terraces:Langshan, Inner Mongolia, China[J].Geomorphology, 2017, 286(1):34-44. [43] Jia L Y, Zhang X J, He Z X, et al.Late Quaternary climatic and tectonic mechanisms driving river terrace development in an area of mountain uplift:A case study in the Langshan area, Inner Mongolia, northern China[J].Geomorphology, 2015, 234:109-121. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2014.12.043 [44] 周青硕, 张绪教, 叶培盛, 等.河套地区全新世黄河古河道的分布及期次划分[J].地质力学学报, 2017, 23(3):339-347. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2017.03.002 [45] 杨洁, 林年丰, 卞建民, 等.内蒙河套平原砷中毒病区砷的环境地球化学研究[J].水文地质工程地质, 1996, 23(1):49-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG601.015.htm [46] 杨元策.内蒙古高砷含水层沉积物有机质特征研究[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015. [47] 于凯.高砷地下水系统中有机质来源及其对砷动态变化的影响研究[D].武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2016. [48] Zhou Y Z, Guo H M, Zhang Z, et al.Characteristics and implication of stable carbon isotope in high arsenic groundwater systems in the northwest Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia, China[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 163:70-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.05.018 [49] Yang Y J, Yuan X F, Deng Y M, et al.Seasonal dynamics of dissolved organic matter in high arsenic shallow groundwater systems[J].Journal of Hydrology, 2020, 589:125120. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125120 [50] 袁晓芳, 邓娅敏, 杜尧, 等.江汉平原高砷地下水稳定碳同位素特征及其指示意义[J].地质科技通报, 2020, 39(5):156-163. http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10061.shtml [51] 包凤琴, 李佑国, 郝晓琳, 等.内蒙古河套地区地球化学分区及特征[J].地质科技情报, 2015, 34(2):1-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2015.02.001 [52] 刘晓彤, 张绪教, 叶培盛, 等.河流沉积分析在浅覆盖第四纪填图中的应用以内蒙古河套地区1:50000填图试点为例[J].地质力学学报, 2016, 22(4):868-881. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.04.006 [53] Cao W G, Guo H M, Zhang Y L, et al.Control of paleochannels on groundwater arsenic distribution in shallow aquifers of alluvial plain in the Hetao Basin, China[J].Science of The Total Environment, 2018, 613/614:958-968. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.182 -





 下载:
下载: