Stratigraphic lithology identification based on no-dig Logging While Drilling system and random forest
-
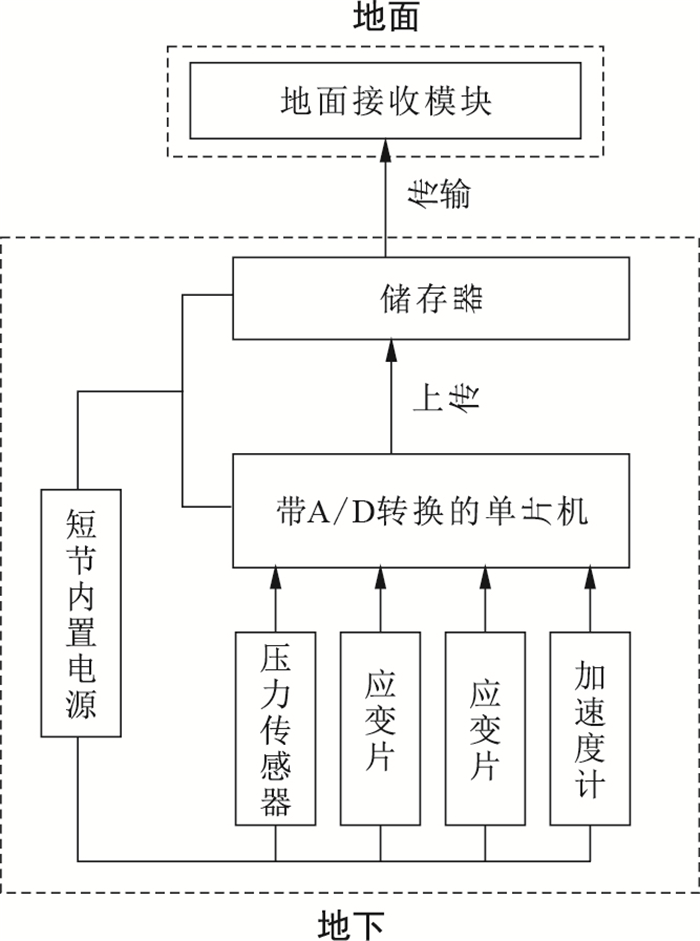
摘要: 通过自主研发设计的非开挖随钻检测系统,采集非开挖钻进参数,进行非开挖钻进实时地层岩性识别,为非开挖施工提供安全信息保证。针对非开挖工程工勘资料缺乏,掘进地层岩性难以判断的问题,提出了一种基于非开挖随钻检测系统实时采集数据,利用随机森林算法建立地层识别模型,通过模型去识别未知地层,并将识别结果可视化展示。通过非开挖随钻检测系统在工程现场的实际应用,获得了包括钻速、扭矩、转速、拉力、泵压、泵量等钻进敏感参数作为训练样本,利用随机森林算法对采集的钻进参数进行训练,构造决策树与随机森林,对钻进参数进行分类,建立了以典型非开挖地层岩性分类为目标的分类模型,分别确定了杂填土、黏土、粉细砂、砾石和淤泥的地层分类标签。进一步,基于机器学习的分类结果,利用PCA主成分分析将地层识别特征降维至三维,实现了地层岩性识别结果的三维展示。将预测模型应用于实际工程,以验证其有效性。结果表明,该方法能在非开挖实时钻进条件下快速识别钻进地层,识别正确率高达92%。该研究成果通过采集导向随钻参数,识别非开挖掘进段地层岩性,为非开挖扩孔阶段钻具选型、泥浆设计等提供了重要信息。Abstract: Through the self-developed and designed no-dig Logging While Drilling(LWD) system, it can collect the parameters of no-dig drilling, identify the real-time formation lithology of no-dig drilling, and provide safety information guarantee for no-dig construction.In view of the lack of prospecting data in no-dig engineering, it is difficult to determine the lithology of the excavation stratum.A real-time data acquisition system based on the no-dig LWD system is proposed.The random forest algorithm is used to establish the stratum identification model, and identify the unknown strata.The identification results are displayed visually.Through the practical application of the detection while drilling system in the engineering field, the drilling sensitive parameters including Rate of Penetration(ROP), torque, rotation speed, pulling force, pump pressure and pump volume are obtained as training samples.The random forest algorithm is used to train the collected drilling parameters, and the decision tree and random forest are constructed to classify the drilling parameters.A classification model aiming at the classification of typical no-dig strata is established, and the classification labels of miscellaneous fill, clay, silty fine sand, gravel and silt are determined respectively.Furthermore, based on the classification results of machine learning, PCA principal component analysis is used to reduce the dimension of strata recognition features to three-dimensional, and realize the three-dimensional display of formation lithology identification results.The prediction model is applied to practical engineering to verify its effectiveness.The results show that the method can quickly identify the drilling formation under the condition of no-dig real-time drilling, and the recognition accuracy is as high as 92%.The research results provide important information for the selection of no-dig mud and no-dig reaming stage.
-
Key words:
- no-dig /
- logging while drilling /
- random forest /
- strata recognition
-
图 6 随机森林算法实现流程[13]
Figure 6. Implementation process of random forest algorithm
表 1 随钻数据举例
Table 1. Examples of data while drilling
识别特征 钻速/(m·h-1) 扭矩/(N·m) 转速/(r·min-1) 轴向力/MPa 泥浆压力/MPa 杂填土 7.0 13 025 120 6.0 4.0 6.8 12 661 115 5.9 3.9 7.2 13 212 126 6.1 4.1 7.0 13 174 124 6.2 4.1 7.3 13 300 136 6.4 4.3 黏土 10.0 3 830 130 4.0 2.6 12.0 4 042 140 4.4 2.9 13.0 4 217 150 4.6 2.8 12.0 3 794 142 4.2 2.7 9.0 3 835 122 3.8 2.3 粉细砂 8.0 7 014 120 5.0 3.0 7.0 6 056 110 4.1 2.1 7.4 6 537 115 4.5 2.5 7.2 6 208 112 4.2 2.2 8.6 7 615 126 5.6 3.6 砾石 2.0 15 363 100 8.0 4.2 2.1 15 507 105 8.1 4.2 2.2 15 766 110 8.3 4.2 2.4 15 982 120 8.3 4.3 1.8 15 006 90 7.9 4.1 淤泥 5.0 10 892 140 2.0 4.0 5.2 11 254 142 2.0 4.1 5.1 11 146 138 2.0 3.9 4.8 10 793 130 2.0 3.8 5.4 11 404 150 2.0 4.4 表 2 扭矩数据运算展示节选
Table 2. Excerpt of torque data operation display
编号 扭矩/(N·m) 地层岩性 1 12 661 杂填土 2 13 174 杂填土 3 4 042 黏土 4 3 794 黏土 5 7 014 粉细砂 6 6 537 粉细砂 7 15 507 砾石 8 15 982 砾石 9 11 254 淤泥 10 10 793 淤泥 表 3 模型精确度验证数据
Table 3. Validation data of model accuracy
识别特征 钻速/(m·h-1) 扭矩/(N·m) 转速/(r·min-1) 轴向力/MPa 泥浆压力/MPa 工勘岩性 岩性识别 识别结果 1 10.0 4 102 139 4.0 2.6 黏土 粉质黏土 正确 2 2.0 17 100 98 7.0 4.1 砾石 弱胶结砾岩 正确 3 5.0 11 100 140 1.9 4.0 淤泥 淤泥 正确 4 7.1 13 061 122 5.9 4.1 杂填土 杂填土 正确 5 7.9 6 899 114 5.0 3.0 粉细砂 粉砂 正确 6 13.0 4 200 148 4.5 2.9 黏土 粉质黏土 正确 7 1.8 15 831 108 7.8 4.0 砾石 中胶结砾岩 正确 8 5.1 11 156 144 2.0 4.1 淤泥 淤泥 正确 9 6.9 12 856 118 5.8 4.0 杂填土 杂填土 正确 10 8.3 7 320 126 5.2 3.3 粉细砂 粉细砂 正确 11 9.0 3 825 121 3.8 2.2 黏土 粉质黏土 正确 12 2.1 15 930 113 8.2 4.2 砾石 杂填土 错误 -
[1] 颜纯文. 我国非开挖行业现状与展望[J]. 探矿工程: 岩土钻掘工程, 2010(10): 56-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7428.2010.10.013Yan C W. Currentstatus of trenchless industry in China and the prospect[J]. Exploration Engineering: Rock & Soil Drilling and Tunneling, 2010(10): 56-60(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7428.2010.10.013 [2] 刘军. 非开挖水平定向钻进铺管施工技术及工程应用研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2004.Liu J. Construction technology and project application study of no-dig horizontal directional drilling dipe paving[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2004(in Chinese with English abstract). [3] 冯锐, 张鹏, 苏树尧, 等. 大口径长距离钢顶管注浆减阻技术: 以黄浦江上游水源地连通管工程为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(4): 174-180. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10013.shtmlFeng R, Zhang P, Su S Y, et al. Resistance reduction by grouting to large diameter and long distance steel pipe jacking: A case study of pipe jacking project in the upstreem water source area of Huangpu River[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(4): 174-180(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10013.shtml [4] 谭卓英, 李文, 岳鹏君, 等. 基于钻进参数的岩土地层结构识别技术与方法[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2015, 37(7): 1328-1333. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201507023.htmTan Z Y, Li W, Yue P J, et al. Techniques and approaches for identification of geoformation structure based on diamond drilling parameters[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 37(7): 1328-1333(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201507023.htm [5] 李章林, 吴冲龙, 张夏林, 等. 地质科学大数据背景下的矿体动态建模方法探讨[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(4): 59-68. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10000.shtmlLi Z L, Wu L C, Zhang X L, et al. Discussion on dynamic orebody modeling method with geological science big data[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(4): 59-68(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10000.shtml [6] 佟晶, 张婉, 张玄杰, 等. 基于航空重、磁数据的南黄海海相地层分布特征识别[J]. 中国地质调查, 2020, 7(5): 95-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDC202005011.htmTong J, Zhang W, Zhang X J, et al. Characteristics of marine strata distribution in South Yellow Sea based on airborne gravity and magnetic data[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2020, 7(5): 95-106(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDC202005011.htm [7] 宋康明, 姜阳厚, 谭志祥, 等. 基于随机森林方法的岩石节理粗糙度系数研究[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(3): 263-267. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201803035.htmSong K M, Jiang Y H, Tan Z X, et al. Method to calculate the joint roughness coefficient based on random forest[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(3): 263-267(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201803035.htm [8] 张幼振, 张宁, 邵俊杰, 等. 基于钻进参数聚类的含煤地层岩性模糊识别[J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(8): 2328-2335. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201908007.htmZhang Y B, Zhang N, Shao J J, et al. Fuzzy identification of coal-bearing strata lithology based ondrilling parameter clustering[J]. Journal of Coal Industry, 2019, 44(8): 2328-2335(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201908007.htm [9] Sair K, Jamai R, Aali N. Review of ground characterization by using instrumented drills for under-ground mining and construction[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2016, 49(2): 585-602. doi: 10.1007/s00603-015-0756-4 [10] 向杰, 陈建平, 肖克炎, 等. 基于机器学习的三维矿产定量预测: 以四川拉拉铜矿为例[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(12): 2010-2021. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201912010.htmXiang J, Chen J P, Xiao K Y, et al. 3D metallogenic prediction based on machine learning: A casestudy of the Lala copper deposit in Sichuan Province[J]. Bulletin of Geology, 2019, 38(12): 2010-2021(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201912010.htm [11] 王建刚. 基于机器学习的航空高光谱遥感岩性识别技术研究[D]. 北京: 核工业北京地质研究院, 2020.Wang J G. Research on lithology recognition technology of aerial hyperspectral remote sensing based on machine learning[D]. Beijing: Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology, 2020(in Chinese with English abstract). [12] 房昱纬, 吴振君, 盛谦, 等. 基于超前钻探测试的隧道地层智能识别方法[J]. 岩土力学, 2020, 41(7): 2494-2503. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202007036.htmFang Y W, Wu Z J, Sheng Q, et al. Intelligent recognition of tunnel stratum based on advanced drilling tests[J]. Geotechnical Mechanics, 2020, 41(7): 2494-2503(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202007036.htm [13] 曹正凤. 随机森林算法优化研究[D]. 北京: 首都经济贸易大学, 2004.Cao Z F. Study on optimization of random forests algorithm[D]. Beijing: Capital University of Economics and Trade, 2004(in Chinese with English abstract). [14] Jan P, Bernard D B, Niko E C V, et al. Random forests as a tool for ecohydrological distribution modelling[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2007, 207(2/4): 304-318. [15] Lee S L A, Kouzania A Z, Hu E J. Random forest based lung nodule classification aided by clustering[J]. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 2010, 34(7) 535-542. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2010.03.006 [16] Auret L, Aldrich C. Change point detection in time series data with random forests[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2010, 18(8): 990-1002. doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2010.04.005 [17] Meinshausen N. Quantile regression forests[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2006, 7(6): 13-14. http://www.ams.org/mathscinet-getitem?mr=2274394 [18] Dietterich T. An experimental comparison of three methods for constructing ensembles of decision trees: Bagging, boosting and randomization[J]. Machine Learning, 2000, 40(2): 139-157. doi: 10.1023/A:1007607513941 [19] 肖勇, 赵云, 涂治东, 等. 基于改进的皮尔逊相关系数的低压配电网拓扑结构校验方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2019, 47(11): 37-43. doi: 10.7667/PSPC20191106Xiao Y, Zhao Y, Tu Z D, et al. Topology checking method for low voltage distribution network based on improved Pearson correlation coefficient[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2019, 47(11): 37-43(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.7667/PSPC20191106 [20] 刘士琛. 面向推荐系统的关键问题研究及应用[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2014.Liu S T. Research on the key issues for the recommender systems[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2014(in Chinese with English abstract). -





 下载:
下载: