Experimental study about the gas slip flow in Longmaxi shales from the southern Sichuan Basin
-
摘要: 针对页岩储层气体滑脱效应特征及其影响机制不清问题,选取四川盆地长宁地区志留系龙马溪组页岩样品,开展了低温氮气吸附孔隙结构表征实验,并利用非稳态脉冲衰竭方法测量了不同围压下氦气、氮气在页岩岩心上的气体渗透率,分析了平均孔隙压力、气体类型、围压对滑脱效应的影响,建立了滑脱因子的预测关系式。结果表明:压力低于2.5 MPa时,页岩气体滑脱效应不能忽略。由于“分子筛效应”的影响,页岩克氏渗透率与测试流体介质类型有关,以氦气为流动介质测试得到的克氏渗透率大于以氮气为流动介质的测试结果。滑脱效应与气体类型有关,龙马溪组页岩的氦气滑脱因子约为氮气滑脱因子的1.7倍。利用滑脱因子计算得到围压为10~40 MPa时,氦气在页岩上的有效渗流孔径为113~166 nm,氮气的有效渗流孔径为66~99 nm,均远大于液氮吸附法测试的平均孔径。建立了龙马溪组页岩气体滑脱因子与克氏渗透率的幂函数关系,为页岩气流动模型的建立提供了基础。Abstract: In order to clarify the gas slip flow effect and its influencing mechanism of shale gas reservoirs, low-temperature nitrogen adsorption measurements were performed on the Silurian Longmaxi Formation shales from the Sichuan Basin. Pore structure characteristics of shales were described based on nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms. Non-steady state gas flow experiments on gas shales were carried out to obtain the apparent permeability coefficients of helium and nitrogen. The effects of pore pressure, gas types, confining pressure on gas slippage were discussed. Results show that gas slippage cannot be neglected when the pore pressure is less than 2.5 MPa. The Klinkenberg corrected permeability coefficients of shales are gas-dependent due to the "molecular sieving effect". The Klinkenberg corrected permeability of helium on shales is larger than that of using nitrogen. Gas slippage factors are also related to gas types. Helium slippage factor of shales is about 1.7 times of nitrogen slippage factor. The effective transport pore diameter of helium on shales with the confining pressure being 10-40 MPa ranges from 113 to 166 nm, while that of nitrogen is between 66 and 99 nm. These values are significantly larger than that derived from low-temperature nitrogen adsorption. A power function is utilized to fit the gas slippage factor and permeability of shales and can be used to predict gas flow in shales.
-
Key words:
- shale /
- slippage effect /
- permeability /
- transport pore diameter /
- Sichuan Basin
-
页岩气作为一种重要的非常规油气资源近年来已经成为全球能源勘探开发的热点。页岩储层特征精细描述和流体渗流能力表征是实现页岩气藏有效开发的关键问题之一[1-3]。页岩储层孔隙结构复杂,孔隙类型多样。页岩中大量发育的微纳米级孔隙导致页岩储层流体赋存和流动行为异常复杂。常规油气储层孔隙直径多在微米以上,微米级孔隙通道中气体分子的平均自由程远小于孔隙尺寸,滑脱效应微弱。在页岩纳米尺度空间下,气体分子平均自由程与孔隙尺寸相当,气体分子与纳米级孔隙孔壁的碰撞增强,这将引起气体渗透能力增强。因此,页岩纳米级孔隙中的气体滑脱效应严重。页岩储层气体流动主要发生于滑脱流和弱过渡流阶段[4]。弄清页岩气体滑脱效应的存在条件和影响机制对页岩气藏产能预测具有重要意义。
目前,关于国内外页岩气藏的研究主要集中在页岩气资源潜力、孔隙结构、气体吸附和产能预测等方面[5-11],但对页岩储层气体流动方面的研究还不够深入,尤其是少有页岩气流动的实验数据发表[12-17]。页岩基质渗透率极低,常规的稳态渗流理论和测试方法不再完全适用于致密页岩。测定页岩渗透率的非稳态技术包括GRI(Gas Research Institute)压力衰竭法、脉冲衰竭法以及解吸流动法等[18-19]。一些学者利用非稳态渗流实验,在页岩气滑脱效应研究的基础上,建立了考虑气体滑脱效应的页岩气井产能预测模型[20-21]。笔者选取四川盆地长宁地区龙马溪组页岩样品,通过自主研发的致密流体渗流实验装置,开展氦气和氮气在页岩岩心中的非稳态渗透率测试,得到不同应力条件下气体在页岩中的表观渗透率,结合液氮吸附法测量的孔径分布,分析龙马溪组页岩气体滑脱效应的影响因素,计算气体流动时的有效渗流孔径,并建立滑脱因子与岩心渗透率的关系式,以期为我国四川盆地龙马溪组页岩气藏的有效开发提供依据。
1. 样品和方法
1.1 实验样品
实验岩心采自四川盆地南部长宁地区下志留统龙马溪组。龙马溪组页岩样品为浅灰色粉砂质页岩,气测孔隙度为8.4%。采用D/max-2500PC全自动粉末X射线衍射仪对样品进行矿物成分检测,结果显示:页岩样品中黏土矿物质量分数最高,为45.5%;黏土矿物以伊利石为主(质量分数达35%);石英和方解石质量分数次之,分别为20.3%、23.3%。此外,页岩样品还含有一定的长石、白云石、黄铁矿等。采用碳硫分析仪测得页岩样品的w(TOC)为0.96%。用油浸显微镜测试页岩沥青质体反射率,转换得到等效镜质体反射率约为2.8%,表明样品处于高过成熟阶段。
采用比表面与孔径分析仪对龙马溪组页岩样品进行77 K温度下的低温氮气吸附实验以测定孔径分布。以相对压力为横坐标、液氮吸附量为纵坐标,绘制氮气吸附-解吸等温线。利用氮气吸附-解吸数据,根据Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET)公式和Barrett-Joyner-Halenda(BJH)方法分别计算样品的总比表面积和BJH孔径分布[22]。BET比表面积公式如下:
P/P0V(1−P/P0)=1VmC+C−1VmC⋅PP0 (1) 式中:P为氮气压力(Pa);P0为77 K温度下氮气饱和蒸气压(Pa);V为氮气吸附量(cm3/g);Vm为单分子层饱和吸附量(cm3/g);C为BET方程常数(无因次)。
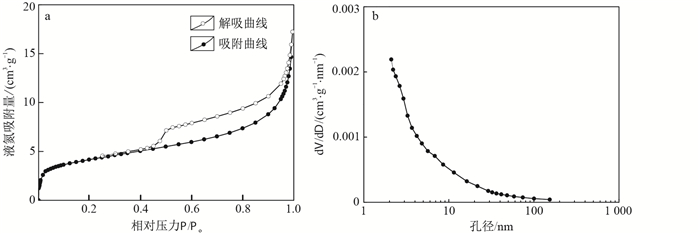
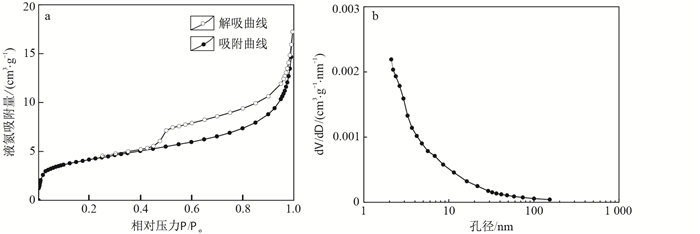
由页岩样品的低温低压氮气吸附-解吸曲线(图 1-a)可知,当相对压力(P/P0)为0.42~1.0时,液氮吸附-解吸曲线出现滞后环,表明龙马溪组页岩的介孔(2 nm < 孔径 < 50 nm)发育良好。当相对压力为0.05~0.30时,用多点BET法计算获得页岩的比表面积为14.95 m2/g。而致密砂岩(如Berea砂岩等)比表面积大约只有1 m2/g[23]。因此,相对于砂岩,页岩的比表面积非常大,是砂岩的十几倍。巨大的比表面积为气体的吸附存储提供了基础。由最高相对压力时的液氮吸附量和比表面积计算获得页岩的平均孔径为7 nm。采用BJH方法,以孔径为横坐标、孔容随孔径的变化率为纵坐标,绘制页岩样品的孔径分布曲线如图 1-b,可以看出,样品的孔径比较复杂,但总体来说,页岩孔径集中分布在小于10 nm的范围内。
1.2 非稳态气测渗透率测试
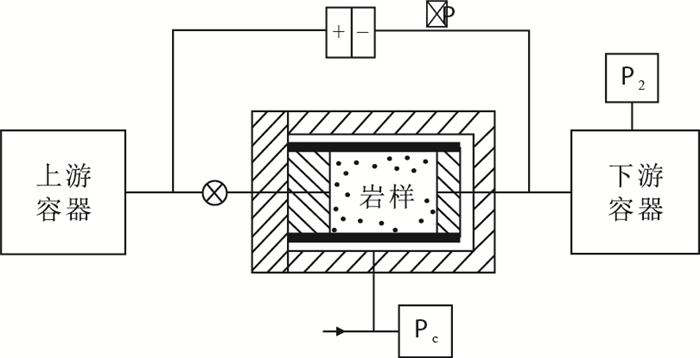
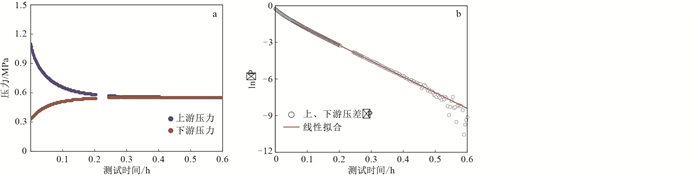
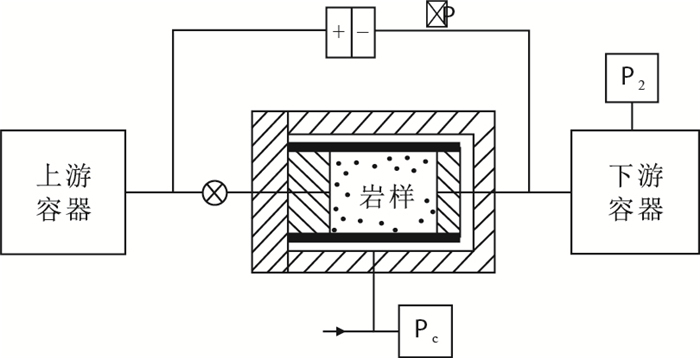
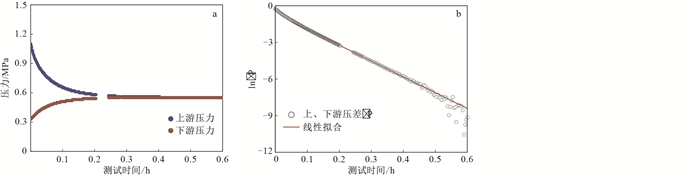
由于页岩岩心非常致密,传统的稳态测试方法不一定能准确测量致密岩心的渗透率。本次研究采用非稳态脉冲衰竭方法测量龙马溪组页岩气测渗透率(图 2)。与稳态渗透率测试方法不同,非稳态脉冲渗透率技术主要利用高精度的压力传感器(2个)或者压差传感器(1个)监测压力脉冲随时间的变化情况,从而缩短了测试时间,同时提高了计量精度。非稳态渗流测试过程中,对岩心夹持器上游引入小的压力脉冲(0.1~0.5 MPa),让上游压力脉冲通过岩心夹持器传播到下游,同时记录压力脉冲随时间的变化,最终上下游容器达到压力平衡(图 3)。结合非稳态渗流理论,根据上下游压差随时间的半对数关系计算致密岩石渗透率[18]。本次实验过程中,岩心夹持器的围压(Pc)依次设置为40,30,20,10 MPa。每个围压阶段,通过多次压力脉冲的引入,改变岩心孔隙压力,进而计算不同孔隙压力下的气体渗透率。为了分析气体类型对滑脱效应的影响,在室温下分别采用氦气和氮气2种气体对页岩进行测试。同时,考虑到流体在不同压力下的物理性质会发生变化,尤其是气体黏度,因此在数据处理过程中,采用变气体黏度进行计算。气体黏度数据通过查询美国国家标准与技术研究院(NIST)数据库得到。
1.3 滑脱效应
考虑气体流动时存在滑脱效应,Klinkenberg[24]建立了岩心的气测渗透率与等效液体渗透率的关系式:
Kg=K∞(1+bPm) (2) 式中:Kg为气测渗透率(m2);K∞为等效液体渗透率或克氏渗透率(m2);Pm为平均孔隙压力(Pa);b为气体滑脱因子,取决于气体性质和岩石孔隙结构(Pa)。
对于气体在圆柱形毛管内的流动,滑脱因子的表达式为:
b=4CλPmr (3) 式中:λ为气体分子平均自由程(m);r为毛管渗流半径(m);C为近似为1的常数(Adzumi常数)(无因次)。
2. 页岩非稳态气测渗透率
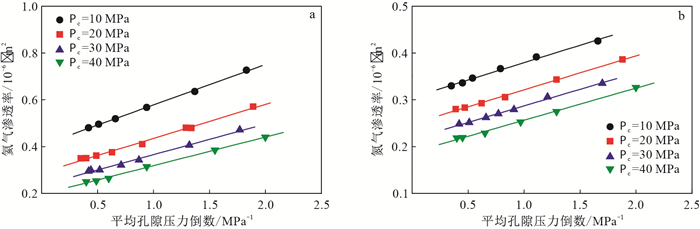
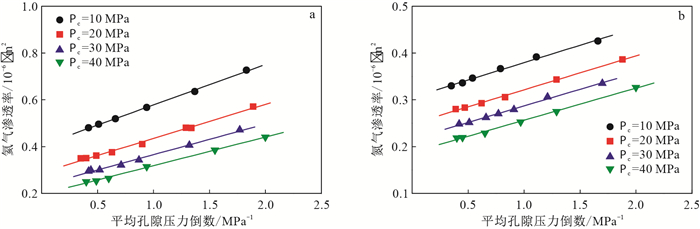
图 4为不同围压下龙马溪组页岩非稳态气测渗透率的Klinkenberg效应关系曲线,可以看出,不同围压(Pc)下,龙马溪组页岩的氦气和氮气的表观渗透率与平均孔隙压力倒数均呈现良好的线性关系,满足Klinkenberg方程,这也进一步说明了页岩储层气体流动处于滑脱流阶段。通过拟合直线的斜率和截距,可以计算页岩克氏渗透率和滑脱因子(表 1)。随着围压从10 MPa增大到40 MPa,利用氦气测试的龙马溪组页岩的克氏渗透率从0.40×10-6 μm2降低至0.20×10-6 μm2。同时,每个围压下,氦气与氮气测试得到的克氏渗透率并不相等。从龙马溪组页岩的测试结果来看,氦气测试得到的克氏渗透率高于氮气测试得到的克氏渗透率。不过,由不同气体得到的克氏渗透率的差别随着围压的增大有逐渐减小的趋势。围压为10 MPa时,氦气测试得到的克氏渗透率为0.40×10-6 μm2,氮气测试得到的克氏渗透率为0.31×10-6 μm2;围压为40 MPa时,氦气与氮气测试得到的克氏渗透率几乎相等。这种由于测试气体的不用造成岩石克氏渗透率的差别主要与页岩的“分子筛效应”有关[25]。氦气分子直径为0.29 nm,小于氮气分子直径(0.42 nm)。因此,氦气分子能够在氮气分子不能进入的页岩孔隙通道内流动。这种“分子筛效应”造成分子直径小的气体得到的克氏渗透率偏大。
表 1 龙马溪组页岩氦气和氮气测试的克氏渗透率、滑脱因子和等效渗流孔径Table 1. Klinkenberg-corrected permeability of helium and nitrogen, slip factors and equivalent seepage pore diameter围压
Pc/MPa氦气 氮气 克氏渗透率/
10-6 μm2滑脱因子/
MPa渗流孔径①/
nm克氏渗透率/
10-6 μm2滑脱因子/
MPa渗流孔径①/
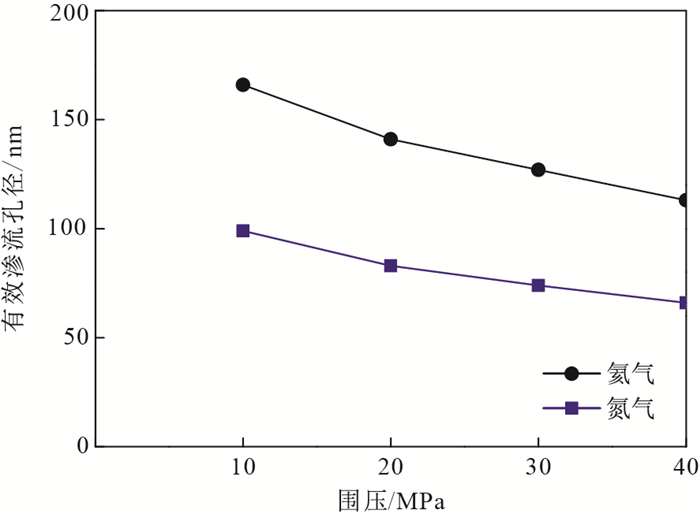
nm10 0.40 0.43 166 0.31 0.24 99 20 0.29 0.50 141 0.25 0.29 83 30 0.23 0.56 127 0.22 0.33 74 40 0.20 0.63 113 0.19 0.37 66 注:①为等效渗流孔径,是根据滑脱因子的表达式(3)转换得到 3. 页岩气体滑脱效应影响因素
3.1 平均孔隙压力
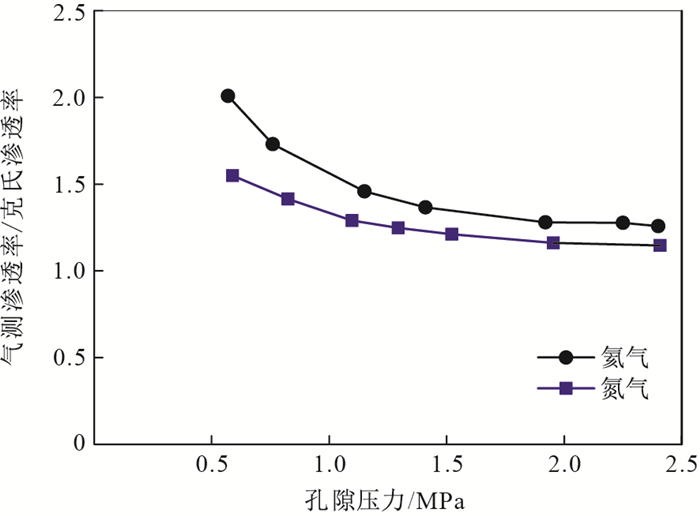
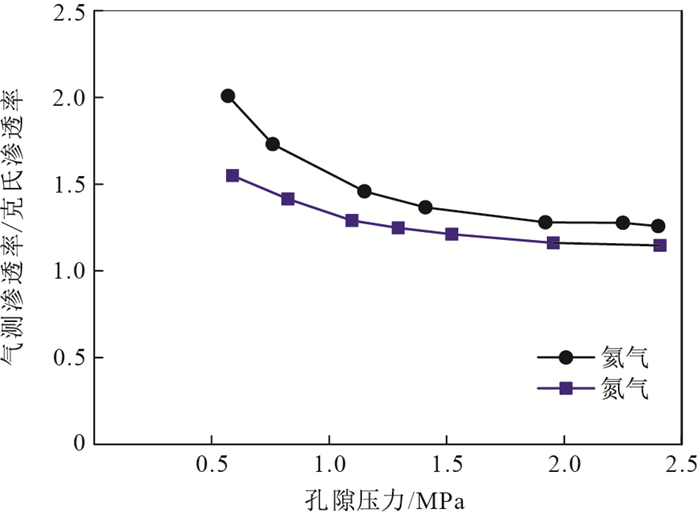
以围压为30 MPa为例,分析滑脱效应对页岩气测渗透率的影响(图 5),可以看出,平均孔隙压力较低时,气测渗透率/克氏渗透率比值较大,滑脱效应显著;而随着平均孔隙压力增加,滑脱效应逐渐减弱。实验过程中,孔隙压力为1 MPa时,氦气和氮气滑脱效应对气测渗透率的贡献大于30%。当孔隙压力大于2.5 MPa时,气测渗透率/克氏渗透率比值趋于1,滑脱效应可以忽略。
3.2 气体类型
从表 1可知,不同类型气体得到的滑脱因子存在差别。围压为40 MPa时,氦气在龙马溪组页岩上的滑脱因子为0.63 MPa,远大于氮气的滑脱因子(0.37 MPa)。不同围压下,氦气的滑脱因子约为氮气滑脱因子的1.7倍。这主要是由于一方面,受“分子筛效应”的影响,氦气分子能够进入更小的孔隙空间;另一方面,滑脱效应与气体分子的平均自由程有关。结合分子平均自由程的表达式,可以看出气体滑脱因子与气体黏度成正比,与气体相对分子质量的平方根成反比。通过查询NIST数据库可知,25℃和1 MPa时,氦气和氮气的黏度分别为1.98×10-5,1.78×10-5 Pa·s,计算得到氦气和氮气的平均分子自由程之比约为2.1,与滑脱因子的比值较为接近。
3.3 围压与有效渗流孔径
实验测试温度下,当围压从10 MPa增大到40 MPa时,龙马溪组页岩的氦气滑脱因子从0.43 MPa增大到0.63 MPa,氮气滑脱因子从0.24 MPa增加到0.37 MPa(表 1)。这主要反映了随着围压的增加,页岩样品受到的有效应力增强,孔隙流动通道被压缩,滑脱效应增强。
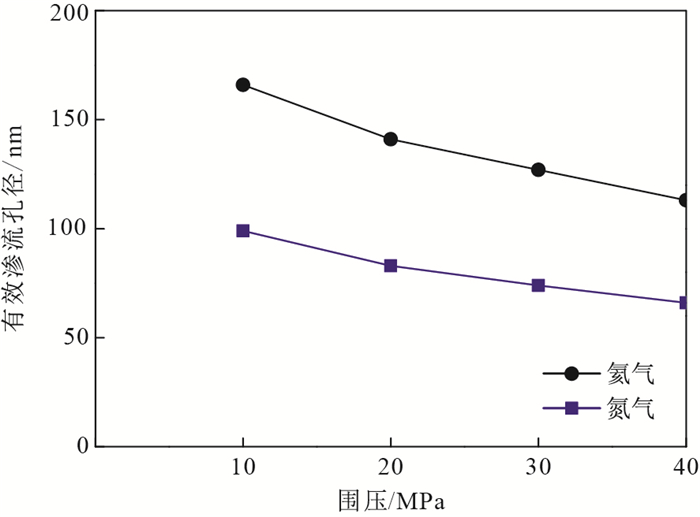
由公式(3)可知,根据滑脱因子及气体分子平均自由程可以计算页岩样品的有效渗流孔径,计算结果见表 1和图 6。当围压从10 MPa增加到40 MPa时,氦气在龙马溪组页岩的有效渗流孔径从166 nm降低至113 nm,氮气的有效渗流孔径从99 nm降低至66 nm,反映了有效压力增强对孔道的压缩。需要指出的是,非稳态渗流实验测试采用的是岩心柱,而液氮吸附实验通常采用粉末样品。与氮气测试的孔径分布曲线和平均孔径相比,龙马溪组页岩的有效渗流孔径远大于液氮吸附法测试的平均孔径。因此,我们认为液氮吸附法测试的孔径和比表面积主要反映了吸附气的影响,而滑脱效应计算得到的孔径则为气体实际渗流孔径。从不同围压下龙马溪组页岩的有效渗流孔径可以看出,尽管页岩纳米级孔隙发育,但对气体渗流起主要作用的依然是孔径大于50 nm以上的大孔。因此,对于页岩气开发而言,应当加强对页岩中孔径在50 nm以上的大孔隙、微裂缝中气体的流动研究。
3.4 滑脱因子经验关系式
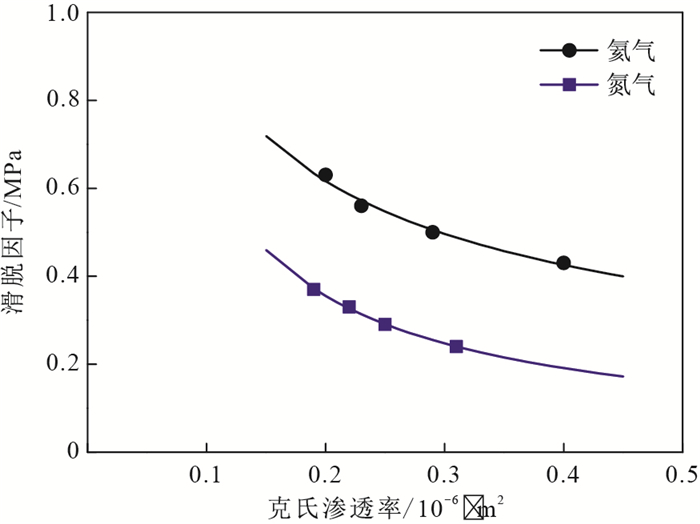
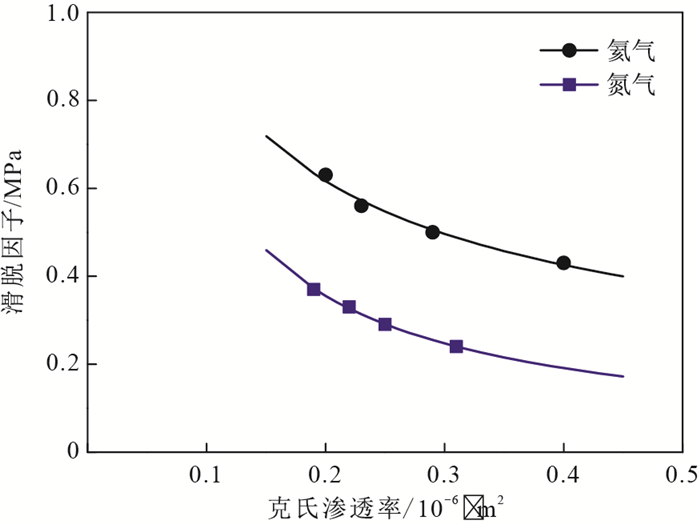
图 7为气体滑脱因子与龙马溪组页岩克氏渗透率的关系曲线,可以看出,不同围压下,氦气和氮气的滑脱因子与克氏渗透率呈现较好的幂函数关系,拟合得到的相关系数均达到0.99以上。
氦气:b=0.261K−0.534∞ (4) 氮气:b=0.0843K−0.894∞ (5) 龙马溪组页岩滑脱因子的幂函数经验关系与Letham等[26]和Fink等[27]对Eagle Ford页岩和Bossier页岩研究的滑脱因子关系式一致,所区别的是关系式中的幂指数不相等。理论上,对于平行毛管束模型,滑脱因子与岩石渗透率关系式的幂指数一般为-0.5。对于页岩岩心,滑脱因子的幂指数从-0.43到-0.89均有见到,这可能与页岩岩心的孔隙形态和孔隙连通性有关。
4. 结论
(1) 龙马溪组页岩气体流动存在滑脱效应。采用非稳态脉冲渗透率方法测试围压为10~40 MPa时,龙马溪组页岩的氦气克氏渗透率为0.40×10-6~0.20×10-6 μm2,氦气滑脱因子为0.43~0.63 MPa;氮气克氏渗透率为0.31×10-6~0.19×10-6 μm2,氮气滑脱因子为0.24~0.37 MPa。由于“分子筛效应”的影响,氦气测试得到的克氏渗透率大于氮气测试得到的克氏渗透率。
(2) 龙马溪组页岩气体滑脱效应与气体类型有关。气体滑脱因子与气体黏度成正比,与气体相对分子质量的平方根成反比。不同围压情况下,龙马溪组页岩的氦气滑脱因子约为氮气滑脱因子的1.7倍。
(3) 利用滑脱因子计算得到氦气在龙马溪组页岩中的有效渗流孔径为113~166 nm,氮气的有效渗流孔径为66~99 nm,远大于液氮吸附法测试的平均孔径。龙马溪组页岩气体滑脱因子与克氏渗透率呈幂函数关系,该关系式可以为页岩气体滑脱效应研究和产能预测提供基础。
-
表 1 龙马溪组页岩氦气和氮气测试的克氏渗透率、滑脱因子和等效渗流孔径
Table 1. Klinkenberg-corrected permeability of helium and nitrogen, slip factors and equivalent seepage pore diameter
围压
Pc/MPa氦气 氮气 克氏渗透率/
10-6 μm2滑脱因子/
MPa渗流孔径①/
nm克氏渗透率/
10-6 μm2滑脱因子/
MPa渗流孔径①/
nm10 0.40 0.43 166 0.31 0.24 99 20 0.29 0.50 141 0.25 0.29 83 30 0.23 0.56 127 0.22 0.33 74 40 0.20 0.63 113 0.19 0.37 66 注:①为等效渗流孔径,是根据滑脱因子的表达式(3)转换得到 -
[1] 邹才能, 杨智, 崔景伟, 等. 页岩油形成机制、地质特征及发展对策[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(1): 14-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201301003.htm [2] 马新华, 谢军. 川南地区页岩气勘探开发进展及发展前景[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201801020.htm [3] 聂海宽, 张金川, 李玉喜. 四川盆地及其周缘下寒武统页岩气聚集条件[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(6): 959-967. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8719.2011.06.020 [4] Javadpour F, Fisher D, Unsworth M. Nano-scale gas flow in shale gas sediments[J]. Journal of Canadian Petroleum Technology, 2007, 46(10): 54-60. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/250092811_Nanoscale_Gas_Flow_in_Shale_Gas_Sediments [5] 陈林, 陈孝红, 张保民, 等. 鄂西宜昌地区五峰组-龙马溪组页岩储层特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 54-61. http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9974.shtml [6] 杨峰, 宁正福, 胡昌蓬, 等. 页岩储层微观孔隙结构特征[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(5): 301-311. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201302013.htm [7] 蔡全升, 陈孝红, 王传尚, 等. 上奥陶统五峰组-下志留统龙马溪组黑色岩系笔石赋存特征与堆积模式[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 43-53. http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9973.shtml [8] 刘安, 陈孝红, 李培军, 等. 宜昌天阳坪断裂两侧页岩气保存条件对比研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 10-19. http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9970.shtml [9] 孙中良, 王芙蓉, 侯宇光, 等. 潜江凹陷潜江组页岩中可溶有机质赋存空间表征及影响因素分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6): 81-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906011.htm [10] 乔辉, 贾爱林, 贾成业, 等. 页岩气储层关键参数评价及进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(2): 157-163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201802022.htm [11] 程璇, 徐尚, 郝芳, 等. 松辽盆地嫩江组富有机质页岩有机孔隙成因[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(4): 62-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904008.htm [12] Yang F, Ning Z F, Wang Q, et al. Pore structure characteristics of Lower Silurian shales in the southern Sichuan Basin, China: Insights to pore development and gas storage mechanism[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2016, 156(3): 12-24. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166516215301002 [13] Javadpour F. Nanopores and apparent permeability of gas flow in mudrocks (shales and siltstone)[J]. Journal of Canadian Petroleum Technology, 2009, 48(8): 16-21. doi: 10.2118/09-08-16-DA [14] 周红, 郭超华, 朱芳冰, 等. 灰关联法在页岩气资源丰度敏感性研究中的应用[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(4): 196-201. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201804027.htm [15] 端祥刚, 胡志明, 常进, 等. 页岩储层气体流动能力实验研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 2019, 26(3): 143-147. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2019.03.027 [16] Wu K L, Li X F, Guo C H, et al. A unified model for gas transfer in nanopores of shale-gas reservoirs: Coupling pore diffusion and surface diffusion[J]. SPE Journal, 2016, 21(5): 1-29. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/299522550_A_Unified_Model_for_Gas_Transfer_in_Nanopores_of_Shale-Gas_Reservoirs_Coupling_Pore_Diffusion_and_Surface_Diffusion [17] Fathi E, Akutlu I Y. Lattice Boltzmann method for simulation of shale gas transport in kerogen[J]. SPE Journal, 2012, 18(1): 27-37. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/254534945_Lattice_Boltzmann_Method_for_Simulation_of_Shale_Gas_Transport_in_Kerogen [18] Cui X, Bustin A M M, Bustin R M. Measurements of gas permeability and diffusivity of tight reservoir rocks: Different approaches and their applications[J]. Geofluids, 2009, 9(2): 208-223. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-8123.2009.00244.x [19] Firouzi M, Alnoaimi A, Kovscek A, et al. Klinkenberg effect on predicting and measuring helium permeability in gas shales[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2014, 123(3): 62-68. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166516213002115 [20] 高树生, 于兴河, 刘华勋, 等. 滑脱效应对页岩气产能影响的分析[J]. 天然气工业, 2011, 31(4): 55-58. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2011.04.013 [21] Clarkson C R, Nobakht M, Kaviani D, et al. Production analysis of tight-gas and shale-gas reservoirs using the dynamic-slippage concept[J]. SPE Journal, 2012, 17(1): 230-242. doi: 10.2118/144317-PA [22] Gregg S J, Sing K S W. Adsorption, surface area and porosity[M]. New York: Academic Press, 1982. [23] 杨建, 康毅力, 桑宇, 等. 致密砂岩天然气扩散能力研究[J]. 西南石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2009, 31(6): 76-79. doi: 10.3863/j.issn.1674-5086.2009.06.016 [24] Klinkenberg L J. The permeability of porous media to liquids and gas[J]. Drilling and Production Practice, 1941, 2(2): 200-213. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10020711264 [25] Ross D J K, Bustin R M. Impact of mass balance calculations on adsorption capacities in microporous shale gas reservoirs[J]. Fuel, 2007, 86(17): 2696-2706. http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/el/00162361/2007/00000086/00000017/art00010 [26] Letham E A, Bustin R M. Klinkenberg gas slippage measurements as a means for shale pore structure characterization[J]. Geofluids, 2015, 16(6): 264-278. doi: 10.1111/gfl.12147 [27] Fink R, Krooss B M, Amann-Hildenbrand A. Stress-dependence of porosity and permeability of the Upper Jurassic Bossier shale: An experimental study[C]//Rutter E H, Mecklenburgh J, Taylor K G. Geomechanical and petrophysical properties of mudrocks. London: Geological Society, 2017: 107-130. 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 吴迪,宋开鑫,曹启坤,翟文博,苗丰. 考虑CO_2吸附和滑脱效应影响的页岩渗透率演化机制研究. 实验力学. 2024(01): 115-125 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 王莉,吴珍云,尹宏伟,董少春,毕晨洁,杨秀磊,王福远,刘松. 含盐沉积盆地挤压盐构造及其对油气成藏的意义. 地质科技通报. 2021(05): 136-150 .  本站查看
本站查看其他类型引用(4)
-






 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:
 百度学术
百度学术