Main controlling factors and development model of the Miocene marine source rocks in Yinggehai Basin
-
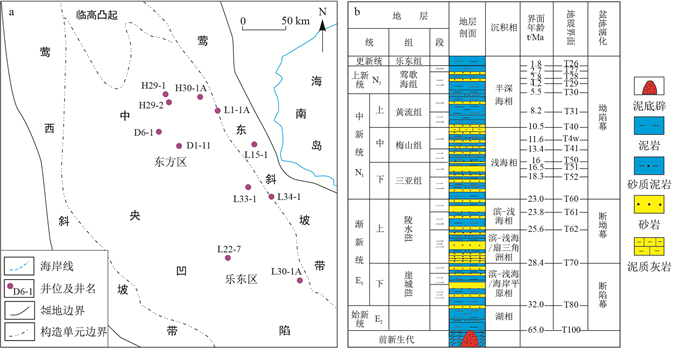
摘要: 中新统海相烃源岩是中国近海莺歌海盆地主要油气供给层段,也是我国新生代海相烃源岩的典型代表。综合利用地质、地球化学和古生物等资料,在烃源岩有机地球化学特征分析的基础上,探讨了莺歌海盆地中新统海相烃源岩发育的主控因素,并建立了相应的形成模式。结果表明,莺歌海盆地发育中等-好级别的中新统海相烃源岩,并具有较强的横向与纵向非均质性;中新统海相烃源岩受古气候、古生产力、水介质条件、沉积速率及海平面变化等因素的综合影响,发育以莺东斜坡带梅山组、三亚组为代表的海相陆源型和以东方区、乐东区梅山组为代表的海相内源型2种模式,其中以海相内源型烃源岩生烃条件最为优越。Abstract: The Miocene marine source rock is the main oil and gas supplier of the Yinggehai Basin and the typical representative of the Cenozoic marine source rocks in China.Based on comprehensive analysis of geological, geochemical and paleontological data and the study of the geochemical characteristics of the source rocks, the paper discusses the main controlling factors and establishes models of the development of the Miocene marine source rocks in Yinggehai Basin.The results show that medium-good Miocene marine source rocks are developed with strong lateral and vertical heterogeneity in Yinggehai Basin.And the Miocene marine source rocks in Yinggehai Basin are influenced by paleoclimate, paleoproductivity, water medium conditions, sedimentation rate and sea level changes.Two models of the type of marine terrestrial source represented by Meishan Formation and Sanya Formation in Yingdong slope belt and the type of marine endogenous type represented by Meishan Formation in Dongfang area and Ledong area are developed, in contrast, the latter hydrocarbon generation conditions are more excellent.
-
图 6 莺歌海盆地生源构成堆积图(数据源自文献[17])
Figure 6. Accumulation diagram of organic matter source composition of the Yinggehai Basin
表 1 莺歌海盆地中新统海相烃源岩生物标志化合物统计
Table 1. Statistics of biomarkers of the Miocene marine source rocks in Yinggehai Basin
层位 区域 样品数 CPI (C21+C22)/(C28+C29) 姥鲛烷/植烷 范围 平均 范围 平均 范围 平均 梅山组 东方区 21 1.03~2.10 1.21 0.66~10.72 5.01 0.24~0.51 0.37 乐东区 27.91~38.52 33.22 0.53~0.75 0.64 莺东斜坡带 0.98~15.09 4.17 0.32~1.50 0.92 三亚组 东方区 7 1.07~1.99 1.30 1.60~5.33 2.88 0.90~2.39 1.58 莺东斜坡带 0.51 2.16 表 2 莺歌海盆地古生产力恢复参数及结果统计
Table 2. List of calculation parameters and calculation results of paleo-productivity of the Miocene marine source rocks in Yinggehai Basin
层位 区域 井号 沉积速率/
(m·Ma-1)w(TOC)/% 孔隙度/% 沉积物密度/
(g·cm-3)古海洋生产力/
(g·cm-2·a-1)古海洋生产力平均
值/(g·cm-2·a-1)梅山组 东方区 H29-2 406.15 0.75 0.19 0.22 58.35 58.35 乐东区 L22-7 215.60 0.71 0.10 0.22 71.32 146.02 L30-1A 63.05 2.09 0.09 0.22 220.72 莺东
斜坡带L1-1A 215.60 0.76 0.16 0.22 74.18 83.51 L33-1 63.05 0.65 0.15 0.22 92.84 三亚组 L1-1A 111.39 0.65 0.19 0.22 74.58 82.70 L34-1 57.12 0.66 0.21 0.22 90.82 表 3 莺歌海盆地古盐度指标Sr/Ba比值统计
Table 3. Statistics of Sr/Ba ratio of paleosalinity index in Yinggehai Basin
层位 区域 井位 深度
h/mSr Ba Sr/Ba Sr/Ba
均值wB/% 梅山组 东方区 H30-1A 1 777 0.05 0.6 0.083 3 8.87 H30-1A 1 801 0.05 0.5 0.010 0 H30-1A 1 848 0.05 0.6 0.083 3 莺东
斜坡带L34-1 2 489 0.05 1.0 0.050 0 6.46 L34-1 2 556 0.05 0.8 0.062 5 L34-1 2 580 0.05 0.6 0.083 3 L34-1 2 604 0.05 0.8 0.062 5 三亚组 莺东
斜坡带L34-1 2 772 0.05 1.0 0.050 0 4.20 L34-1 2 811 0.05 1.0 0.050 0 L34-1 2 844 0.05 1.0 0.050 0 L34-1 2 871 0.05 1.0 0.050 0 L34-1 2 655 0.05 5.0 0.010 0 -
[1] 贾怀存, 康洪全, 管红, 等. 南大西洋两岸盆地海相烃源岩特征与控制因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(3): 143-150. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201903014.htm [2] 张水昌, 张宝民, 边立曾, 等. 中国海相烃源岩发育控制因素[J]. 地学前缘, 2005, 12(3): 39-48. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2005.03.006 [3] Abell P I, Nyamweru C K. Paleoenvironments in the Chalbi Basin of Kenya[J]. Chemical Geology, 2013, 72: 283-291. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0168962288900413 [4] Adegoke A K, Andreu B, Abdullah W H. et al. Geochemical characterisation of Fika Formation in the Chad (Bornu)Basin, northeastern Nigeria: Implications for depositional environment and tectonic setting[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2014, 43: 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.01.008 [5] Chen Zhipeng, Cui Junpeng, Ren Zhanli, et al. Paleoenvironment and mechanism of organic-matter enrichment in the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation shale in the Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica: English Edition, 2017, 93(3): 505-519. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/86253X/201903/7002355530.html [6] 刘邦, 潘校华, 万仑坤, 等. 东尼日尔盆地Tenere坳陷上白垩统海相烃源岩评价及勘探潜力[J]. 海相油气地质, 2012, 17(1): 29-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2012.01.005 [7] 孙涛, 王建新, 孙玉梅, 等. 西非塞内加尔盆地海相优质烃源岩控制因素讨论[J]. 海洋石油, 2017, 37(4): 41-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2017.04.041 [8] 聂明龙, 徐树宝, 方杰, 等. 阿姆河盆地侏罗系海相烃源岩地化特征及与中国海相烃源岩比较[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(3): 216-227. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201703020.htm [9] 方杰, 徐树宝, 吴蕾, 等. 阿姆河右岸地区侏罗系海相烃源岩生烃潜力[J]. 海相油气地质, 2014, 19(1): 8-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2014.01.002 [10] 兰蕾. 南海南部盆地烃源岩特征及其对含油气性的影响[J]. 地质科技通报, 2019, 38(4): 23-29. http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9829.shtml [11] 赵志刚. 南海中南部主要盆地油气地质特征[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018, 30(4): 49-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201804006.htm [12] 田杨, 叶加仁, 杨宝林, 等. 东海陆架盆地丽水凹陷油气成藏规律及区带优选[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(4): 639-653. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201604009.htm [13] 叶加仁, 刘金水, 徐陈杰, 等. 东海西湖凹陷西次凹天然气资源分级评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(3): 1-9. http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10017.shtml [14] 李晓唐, 于书友, 何家雄, 等. 南海西北部莺歌海盆地古近系烃源条件及石油地质意义[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(12): 20-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201612003.htm [15] 徐新德, 杨计海, 刘海钰, 等. 莺歌海盆地浅海环境下烃源岩有机质形成机制[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(8): 2643-2653. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201908010.htm [16] 王元, 李贤庆, 王刚, 等. 莺琼盆地中新统海相烃源岩地球化学特征及生烃潜力评价[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(3): 500-510. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201803008.htm [17] 王元. 莺琼盆地烃源岩生源构成、生烃潜力及其控藏作用研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2018. [18] 于兴河, 李胜利, 乔亚蓉, 等. 南海北部新生代海陆变迁与不同盆地的沉积充填响应[J]. 古地理学报, 2016, 18(3): 349-366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201603005.htm [19] Hurchison C. Marginal basin evolution: The southern South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2004, 21(9): 1129-1148. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2004.07.002 [20] Li Youchuan, Mi Lijun, Zhang Gongcheng, et al. The formation and distribution of source rocks for deep water area in the northern of South China Sea[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2011, 29(5): 970-979. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201105018.htm [21] 何家雄, 陈伟煌, 李明兴. 莺-琼盆地天然气成因类型及气源剖析[J]. 中国海上油气: 地质, 2000, 14(6): 398-404. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2000.06.005 [22] 黄保家, 肖贤明, 董伟良. 莺歌海盆地烃源岩特征及天然气生成演化模式[J]. 天然气工业, 2002, 22(1): 26-30. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2002.01.007 [23] 侯读杰, 张善文, 肖建新, 等. 陆相断陷湖盆优质烃源岩形成机制与成藏贡献: 以济阳坳陷为例[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2008: 1-242. [23] 卢双舫, 张敏. 油气有机地球化学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2008: 1-273. [24] 陈义才, 沈忠民, 罗小平, 等. 石油与天然气有机地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007: 1-275. [25] Muller P J, Suess E. Productivity, sedimentation rate and sedimentary organic matter in the oceans. I: Organic carbon preservation[J]. Deep Sea Research, 1979, 26(12): 1347-1362. doi: 10.1016/0198-0149(79)90003-7 [26] Hou Yuguang, Hw Sheng, Yang Xianghua, et al. Geochemical characteristics and development model of transitional source rocks during the continental margin rifting stage, Bonaparte Basin[J]. Australia Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2015, 37(3): 375-382. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201503018.htm [27] Feng Ziqi, Liu Dan, Huang Shipeng, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of natural gas in the Yan′an gas field, Ordos Basin, China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2016, 102: 67-76. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2016.10.008 [28] Li Wenhao, Zhang Zhihuan. Paleoenvironment and its control of the formation of Oligocene marine source rocks in the deep-water area of the northern South China Sea[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2018, 31(10): 10598-10611. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b01681 [29] 熊小辉, 肖加飞. 沉积环境的地球化学示踪[J]. 地球与环境, 2011, 29(3): 405-414. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201103021.htm [30] 丁次乾. 矿场地球物理[M]. 山东东营: 中国石油大学出版社, 2008: 1-369. [31] Schuhe S, Mangelsdorf K, Rullkoetter J. Organic matter preservation on the Pakistan continental margin as revealed by biomarker geochemistry[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2000, 31: 1005-1022. doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(00)00108-X [32] 叶加仁, 赵牛斌, 杨宝林, 等. 涠西南凹陷流沙港组烃源岩生产力及发育模式[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 105-113. http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9931.shtml [33] 高志前, 樊太亮, 李岩, 等. 塔里木盆地寒武系、奥陶系烃源岩发育模式及分布规律[J]. 现代地质, 2006, 20(1): 69-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2006.01.008 [34] 田景春, 陈洪德, 张翔, 等. 凝缩段特征及其与烃源岩的关系: 以中国南方海相震旦系、中三叠统为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2006, 27(3): 378-383. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2006.03.013 [35] 刘宝珺, 余光明. 岩相地理学教程试用版[M]. 成都: 地质矿产部岩相古地理工作协作组, 2010: 1-205. [36] 汤艳杰, 贾建业, 谢先德. 黏土矿物的环境意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2002, 9(2): 337-344. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2002.02.011 -





 下载:
下载: