Characteristics and source mechanism of geothermal field in Cuona, Tibet
-
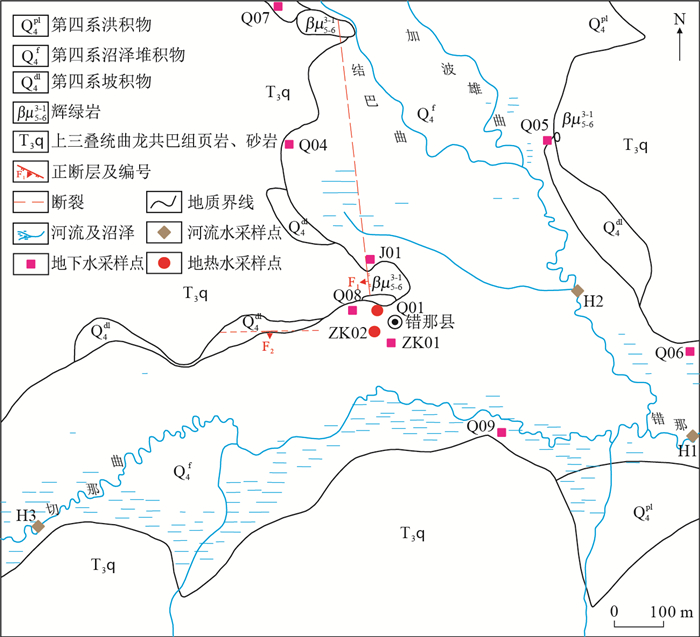
摘要: 错那县位于西藏自治区山南地区南部、喜马拉雅山脉中段,是我国重要的边境口岸。为了研究错那地区地热田的水化学特征与物源机制,通过对研究区的温泉点水样的水化学数据进行化验分析,结合研究区的地热地质条件,使用piper三线图和Gibbs图等分析了水化学特征和物质来源。在阐明几种主要的地热温度计原理和适用条件的基础上,利用各种地球化学温度计和多矿物平衡图解法对研究区地下热水进行了温度估算。基于综合分析,最终得出热储温度为117℃左右,分析出地下热水的水化学类型以HCO3-Na型为主,并进行了相应的地热资源评价。这有助于查明地下热水物质来源,探明该地区地热资源,以便在今后为该地区的地热资源开发利用提供技术支持,同时也推动了生态环境的保护和能源结构的逐步改变。Abstract: Cuona county is located in the south of shannan region of Tibet and the middle of the Himalayas, which is an important border port in China. To study the characteristics and source mechanism of geothermal field in Cuona, we use hydrochemical meathods such as piper and Gibbs to analyze the hydrogeochemical characteristics and main material sources of the hot springs water with geothermal geological conditions. The temperature of reservoir in the research area is calculated by geothermometers and graphic method of multi-mineral balance after a detailed introduction of the principles of several methods.The comprehensive analysis results indicate that the geothermal reservoir temperature is about 117℃ and the study area is of HCO3-Na type. The next step is to evaluate the resources. The research work we have done can identify main material sources and resources, provide technical support for the development and utilization of geothermal resources, meanwhile, promote ecological environmental protection and change energy structure in this region.
-
Key words:
- Tibet /
- geothermal field /
- hydrogeochemical characteristic /
- source mechanism
-
表 1 研究区主要水化学组分测试结果
Table 1. Results of major hydrochemical properties of water samples in the study area
序号 水样编号 ρ(TDS)/(mg·L-1) 阳离子ρB/(mg·L-1) 阴离子ρB/(mg·L-1) SiO2 Sr pH T/℃ 属性 原始值 平均值 Li+ K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ NO3- CO32- Cl- SO42- F- HCO3- ρB/(mg·L-1) 1 H1 132.94 101.53 0.027 1.25 3.52 25.68 2.10 0.50 0 1.42 14.62 0.28 73.39 6.88 0.192 7.76 15 河流水 2 H2 142.67 0.020 0.70 3.62 25.68 2.92 < 0.02 — 1.42 3.85 0.17 91.41 9.01 0.196 8.00 17 3 H3 28.98 0.020 0.37 0.75 3.21 0 0.35 0 0.71 0.38 0.26 14.81 4.77 0.064 8.10 14 4 J01 234.11 308.35 0.020 1.23 9.92 40.14 3.89 6.70 0 7.09 25.01 0.22 124.88 9.24 - 7.86 5 地下水 5 ZK01 506.34 0.305 4.73 124.56 17.64 0.97 0.10 15.12 29.78 119.17 4.60 157.42 11.80 0.230 8.20 22.5 6 Q04 344.67 0.064 1.75 42.51 32.10 6.82 1.70 0 8.58 44.25 1.30 181.53 15.81 0.389 7.77 13 7 Q05 388.85 0.350 1.88 67.74 22.47 5.84 0.40 0 17.02 86.25 1.80 151.92 22.79 0.369 7.90 23 8 Q06 225.20 0.043 0.40 2.57 38.52 7.79 3.30 0 7.10 19.24 0.02 131.32 11.58 0.515 7.84 9 9 Q07 234.46 0.030 0.31 4.39 36.92 8.76 1.90 0 7.70 4.25 0.04 149.35 16.26 0.586 7.80 9 10 Q08 367.21 0.144 2.75 49.98 32.10 5.84 0.45 0 12.41 62.56 1.70 168.66 22.08 0.506 7.90 19 11 Q09 165.96 0.041 0.41 14.49 17.66 2.92 0.75 0 6.21 19.24 0.28 74.67 16.99 0.227 8.03 8 12 ZK02 327.25 361.95 0.235 1.61 62.86 13.83 0.97 0.20 29.64 12.76 43.25 3.30 78.83 68.20 0.063 8.93 55 地热水 13 Q01 396.65 2.790 3.59 83.25 11.24 0.97 4.50 17.73 3.19 96.20 4.70 83.68 69.10 0.146 8.83 56 表 2 错那研究区温泉热储温度计算结果
Table 2. Calculation results of hot springs geothermal temperature in the study area of Cuona, Tibet
实验编号 二氧化硅温度计 钠钾温度计 钾镁温度计 钠钾钙温度计 t/℃ Q01 118 133 71 727 ZK02 116 96 53 581 平均值 117 115 62 654 -
[1] 王贵玲, 张薇, 梁继运, 等. 中国地热资源潜力评价[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(4): 449-459. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201704002.htmWang G L, Zhang W, Liang J Y, et al. Evaluation of geothermal resources potential in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(4): 449-459(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201704002.htm [2] 王贵玲, 张发旺, 刘志明. 国内外地热能开发利用现状及前景分析[J]. 地球学报, 2000, 21(2): 134-139. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2000.02.004Wang G L, Zhang F W, Liu Z M. Development and utilization of geothermal resources at home and abroad present situation and prospect analysis[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2000, 21(2): 134-139(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2000.02.004 [3] 章铭陶. 古堆热田初探: 西藏高原地热考察散记之一[J]. 地理知识, 1977, 17(5): 14-18.Zhang T M. Preliminary study on Gudui geothermal field: Geothermal survey of Tibet Plateau[J]. Geographical Knowledge, 1977, 17(5): 14-18(in Chinese with English abstract). [4] 朱梅湘, 徐勇. 西藏羊八井地热田水热蚀变[J]. 地质科学, 1989, 24(2): 162-175, 214. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.1989.02.001Zhu M X, Xu Y. Hydrothermal alteration in the Yangbajain geothermal field, Tibet[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 1989, 24(2): 162-175, 214(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.1989.02.001 [5] 杨期隆. 西藏羊八井地热田侧向舌型系统[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1994, 21(4): 48-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG404.013.htmYang Q L. The lateral tongue type of geothermal system in the Yangbajain geothermal field, Tibet[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 1994, 21(4): 48-51(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG404.013.htm [6] 佟伟, 廖志杰, 刘时彬, 等. 西藏温泉志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000.Tong W, Liao Z J, Liu S B, et al. Thermal springs in Tibet[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2000(in Chinese with English abstract). [7] 李振清, 侯增谦, 聂凤军, 等. 西藏地热活动中铯的富集过程探讨[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(9): 1457-1464. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.09.019Li Z Q, Hou Z Q, Nie F J, et al. Enrichment of element cesium during modern geothermal action in Tibet, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2006, 80(9): 1457-1464(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.09.019 [8] 周立. 西藏中部典型温泉特征[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2012.Zhou L. Characteristics of the typical hot springs in the central Tibet[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2012(in Chinese with English abstract). [9] 刘昭. 西藏尼木-那曲地热带典型高温地热系统形成机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2014.Liu Z. The forming mechanism of typical high-temperature geothermal systems in Nimu-Naqu geothermal belt, Tibet[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2014(in Chinese with English abstract). [10] 王思琪. 西藏古堆高温地热系统水文地球化学过程与形成机理[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017.Wang S Q. Hydrogeochemical processes and genesis machenism of high-temperature geothermal system in Gudui, Tibet[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2017(in Chinese with English abstract). [11] 章旭, 郝红兵, 刘康林, 等. 西藏加查象牙泉水文地球化学特征及成因[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2019, 46(4): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201904002.htmZhang X, Hao H B, Liu K L, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation of the Ivory Spring in Jiacha County of Tibet[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(4): 1-9(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201904002.htm [12] 郭宁, 刘昭, 男达瓦, 等. 西藏昌都觉拥温泉水化学特征及热储温度估算[J]. 地质论评, 2020, 66(2): 499-509. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202002022.htmGuo N, Liu Z, Nan D W, et al. The characteristics and reservoir temperatures of hot springs in Jueyong, Chamdo, Xizang(Tibet)[J]. Geological Review, 2020, 66(2): 499-509(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202002022.htm [13] Tannock L, 王亚, 李景富, 等. 广东河源断裂带地热成因及与构造关系初探[J]. 地质力学学报, 2019, 25(3): 400-411. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201903007.htmTannock L, Wang Y, Li J F, et al. A preliminary study on the mechanics and tectonic relationship to the geothermal field of the Heyuan fault zone in Guangdong Province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 25(3): 400-411(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201903007.htm [14] Kose R. Geothermal energy potential for power generation in Turkey: A case study in Simav, Kutahya[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2007, 11(3): 497-511. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2005.03.005 [15] 刘仕娟. 西藏错那中高温地热流体物源分析[D]. 石家庄: 河北地质大学, 2016.Liu S J. The provenance analysis of the medium-high temperature geothermal fluid in Cona, Tibet[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei GEO University, 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). [16] 孙红丽, 马峰, 刘昭, 等. 西藏高温地热显示区氟分布及富集特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(1): 251-259. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201501045.htmSun H L, Ma F, Liu Z, et al. The distribution and enrichment characteristics of fluoride in geothermal active area in Tibet[J]. China Environmental Science, 2015, 35(1): 251-259(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201501045.htm [17] 付中彪, 何宁洁, 鲍征宇, 等. 赣南地区水稻: 根系土系统中硒含量影响因素分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(5): 220-229. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905024.htmFu Z B, He N J, Bao Z Y, et al. Analysis of influencing factors of selenium content in rice-root soil system in southern Jiangxi[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(5): 220-229(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905024.htm [18] 刘基, 高敏, 靳德武, 等. 榆神矿区地表水水化学特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(7): 354-361. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTKJ202007041.htmLiu J, Gao M, Jin D W, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of surface water and analysis on influence factors in Yushen mining area[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(7): 354-361(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTKJ202007041.htm [19] 孙红丽, 马峰, 蔺文静, 等. 西藏高温地热田地球化学特征及地热温标应用[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(3): 171-177. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201503024.htmSun H L, Ma F, Lin W J, et al. Geochemical characteristics and geothermometer application in high temperature geothermal field in Tibet[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(3): 171-177(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201503024.htm [20] 梁杏, 张婧玮, 蓝坤, 等. 江汉平原地下水化学特征及水流系统分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 21-33. http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9922.shtmlLiang X, Zhang J W, Lan K, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and analysis of groundwater flow systems in Jianghan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 21-33(in Chinese with English abstract). http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9922.shtml [21] Brown G H. Glacier meltwater hydrochemistry[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2002, 17(7): 855-883. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(01)00123-8 [22] 邢文乐, 马瑞, 孙自永, 等. 敦煌盆地地下水水化学特征及水质评价[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(5): 196-202. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201605027.htmXing W L, Ma R, Sun Z Y, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of groundwater in the Dunhuang Basin, Northwestern China[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(5): 196-202(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201605027.htm [23] 胡静, 涂良全, 刘会平. 河南省九龙山汤池温泉地热地质特征及成因机制[J]. 地质科技情报, 2012, 31(4): 86-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201204016.htmHu J, Tu L Q, Liu H P. Geological features and formation mechanism of Tangchi hot spring in Jiulongshan mountain area[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2012, 31(4): 86-90(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201204016.htm [24] Fournier R O. Chemical geothermometers and mixing models for geothermal systems[J]. Geothermics, 1977, 5(1): 41-50. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0375650577900074 [25] Arnósson S, Andrésdóttir A. Processes controlling the distribution of boron and chlorine in natural waters in Iceland[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(20): 4125-4146. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00278-8 [26] Wang L H, Dong Y H, Xie Y X, et al. Distinct groundwater recharge sources and geochemical evolution of two adjacent subbasins in the lower Shule River Basin, northwest China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2016, 24(8): 1967-1979. doi: 10.1007/s10040-016-1456-1 [27] Gibbs R J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry[J]. Science, 1970, 170: 1088-1090. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1088 [28] 刘峰, 李忠勤, 郝嘉楠, 等. 额尔齐斯河源春季水化学及稳定同位素特征研究[J]. 冰川冻土, 2020, 42(1): 234-242. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT202001021.htmLiu F, Li Z Q, Hao J N, et al. Study on the hydrochemical and stable isotope characteristics at the headwaters of the Irtysh River in spring[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2020, 42(1): 234-242(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT202001021.htm [29] Tóth J. Groundwater as a geologic agent: An overview of the causes, processes, and manifestations[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 1999, 7(1): 1-14. doi: 10.1007/s100400050176 [30] Peiffer L, Wanner C, Spycher N, et al. Optimized multicompo-nent vs. classical geothermometry: Insights from modelling studies at the Dixie Valley geothermal area[J]. Geothermics, 2014, 51: 154-169. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2013.12.002 [31] Ballantyne J M, Moore J N. Arsenic geochemistry in geothermal systems[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1988, 52(2): 475-483. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(88)90102-0 [32] Dotsika E, Poutoukis D, Raco B. Fluid geochemistry of the Methana Peninsula and Loutraki Geothermal area, Greece[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2010, 104(3): 97-104. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2010.01.001 [33] Saibi H, Ehara S. Temperature and chemical changes in the fluids of the Obama geothermal field in response to field utilization[J]. Geothermics, 2010, 39(3): 228-241. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2010.06.005 [34] Truesdell A H, Haizlip J R, Armannsson H, et al. Origin and transport of chloride in superheated Geothermal steam[J]. Geothermics, 1989, 18(1): 295-304. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0375650589900394 [35] Armienta M A, Rodríguez R, Ceniceros N, et al. Groundwater quality and geothermal energy. The case of Cerro Prieto Geothermal Field, México[J]. Renewable Energy, 2014, 63: 236-254. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2013.09.018 [36] Grassi S, Amadori M, Pennisi M, et al. Identifying sources of B and As contamination in surface water and groundwater downstream of the Larderello geothermal-industrial area[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2014, 509: 66-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.11.003 [37] Nordstrom D K, Jenne E A. Fluorite solubility equilibria in selected geothermal waters[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1977, 41(2): 175-188. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(77)90224-1 [38] 李明礼, 多吉, 王祝, 等. 西藏日多温泉水化学特征及其物质来源[J]. 中国岩溶, 2015, 34(3): 209-216. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201503002.htmLi M L, Duo J, Wang Z, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and material sources of Riduo thermal spring in Tebit[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2015, 34(3): 209-216(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201503002.htm [39] 袁晓芳, 邓娅敏, 杜尧, 等. 江汉平原高砷地下水稳定碳同位素特征及其指示意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(5): 156-163. http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10061.shtmlYuan X F, Deng Y M, Du Y, et al. Characteristics of stable carbon isotopes and its implications on arsenic enrichment in shallow groundwater of the Jianghan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(5): 156-163(in Chinese with English abstract). http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10061.shtml [40] 王彩会, 左丽琼, 荆慧, 等. 江苏东海温泉热储温度估算[J]. 地质学刊, 2015, 39(1): 111-115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2015.01.111Wang C H, Zuo L Q, Jing H, et al. Estimation of geothermal reservoir temperature for the Donghai hot spring in Jiangsu[J]. Journal of Geology, 2015, 39(1): 111-115(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2015.01.111 [41] 徐世光, 郭远生. 地热学基础[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009.Xu S G, Guo Y S. Fundamentals of geothermal science[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009(in Chinese with English abstract). [42] Giggenbach W F. Geothermal solute equilibria: Derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindicators[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1988, 52(12): 2749-2765. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(88)90143-3 [43] Giggenbach W F. Geothermal gas equilibria[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1980, 44(12): 2021-2032. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(80)90200-8 [44] Verma S P, Santoyo E. New improved equations for Na/K, Na/Li and SiO2 geothermometers by Outlier detetion and rejection[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 1997, 79(1): 9-23. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0377027397000243 [45] Chandrajith R, Barth J A C, Subasinghe N D, et al. Geochemical and isotope characterization of geothermal spring waters in Sri Lanka: Evidence for steeper than expected geothermal gradients[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2013, 476: 360-369. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.11.004 [46] 丁仲礼. 固体地球科学研究方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013.Ding Z L. Research methods of solid Earth science[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2013(in Chinese with English abstract). [47] Reed M, Spycher N. Calculation of pH and mineral equilibria in hydrothermal waters with application to geothermometry and studies of boiling and dilution[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1984, 48(7): 1479-1492. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(84)90404-6 [48] 王莹, 周训, 于湲, 等. 应用地热温标估算地下热储温度[J]. 现代地质, 2007, 21(4): 605-612. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.04.003Wang Y, Zhou X, Yu Y, et al. Application of geothermometers to calculation of temperature of geothermal Reservoirs[J]. Geoscience, 2007, 21(4): 605-612(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.04.003 [49] 吴红梅, 孙占学. 地热系统中矿物-流体化学平衡的计算[J]. 华东地质学院学报, 2000, 23(1): 39-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3504.2000.01.009Wu H M, Sun Z X. Calculation of the fluid-rock equilibrium state in the geothermal system[J]. Journal of East China Geological Institute, 2000, 23(1): 39-42(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3504.2000.01.009 [50] 刘军强. 应用地热温标估算热储温度: 以嵊州崇仁热水为例[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2014, 26(5): 129-132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2014.05.043Liu J Q. Estimation of heat storage temperature using geothermal temperature scale: Take Shengzhou Chongren hot water as an example[J]. West China Exploration Engineering, 2014, 26(5): 129-132(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2014.05.043 [51] 黄珣, 李晓, 余中友, 等. 康定中谷地区热储特征及温度计算[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护, 2018, 29(4): 96-104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2018.04.017Huang X, Li X, Yu Z Y, et al. Thermal storage characteristics and temperature calculation in Zhonggu area, Kangding[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 2018, 29(4): 96-104(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2018.04.017 [52] 张振国, 何江涛, 王磊, 等. 衡水地区深层地下水水化学特征及其演化过程[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(3): 565-573. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201803014.htmZhang Z G, He J T, Wang L, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution processes of deep groundwater in Hengshui area[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(3): 565-573(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201803014.htm -





 下载:
下载: