Geological conditions and the main controlling factors for the tight oil accumulation in Liushagang Formation of Fushan Depression, Beibuwan Basin
-
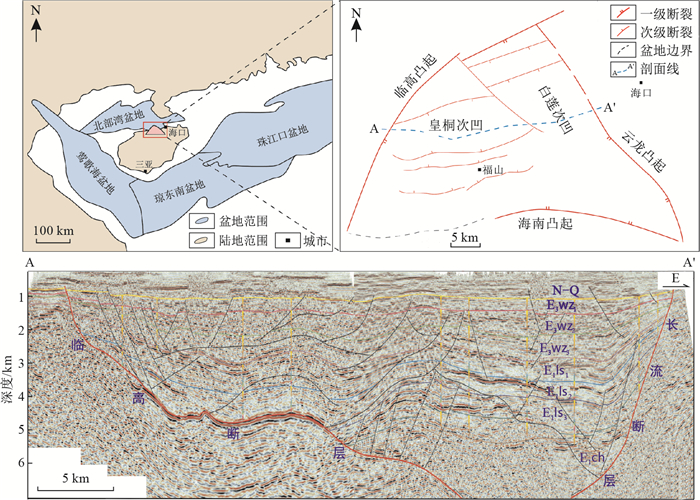
摘要: 查明北部湾盆地福山凹陷流沙港组致密油成藏条件并分析其控制因素,对于进一步明确致密油分布、厘定有利探区具有重要的指导意义。基于地震、录井、测井、岩心及分析化验等资料的综合分析,对北部湾盆地福山凹陷流沙港组有效烃源岩、有利储层、源储匹配关系等进行了研究。结果表明,流沙港组在最大湖泛期于皇桐和白莲两次凹内形成优质烃源岩,具有有机质丰度高、热演化程度适中的特点,提供了致密油形成的物质基础;受多物源供给影响,致密砂岩深入两次凹内,具有源储叠置、分布广泛的特点,溶蚀孔隙与构造裂缝发育,有利于致密油的近源运移与富集;主要烃源岩进入生油高峰期时凹陷构造已基本定型,无大型断裂发育,相对稳定的构造条件有利于致密油形成和保存。因此,福山凹陷流沙港组具备致密油成藏的有利条件,致密油纵向上主要分布在流一下亚段和流二段,平面上主要分布在皇桐次凹和白莲次凹,其形成和分布主要受控于优质烃源岩展布、富溶蚀孔隙"甜点"储层分布及有利的源-储叠置组合。Abstract: Unravelling the accumulation conditions and their controlling factors for the tight oil in the Liushagang Formation, Fushan Depression, Beibuwan Basin, is critical for the further evaluation of the tight oil distribution and the favorable exploration area.Based on comprehensive analysis of seismic, well logging, core and lab tests in this study, the effective source rocks, favorable reservoir, and the source-reservoir matching relations were investigated.It can be proposed that the high-quality source rocks were formed in Huangtong, Bailian two sub-sags during the maximum lake flooding periods in Liushagang depositional stage and were characterized as high organic content and moderate degree of thermal evolution, and thus they provide the material basis for the formation of tight oil; due to the influence of multi-source supply, tight sandstones penetrated into these two sub-sags and they were widely distributed with superimposed source-reservoir assemblages. The development of dissolution pores and structural fractures was favorable for the migration and enrichment of tight oil; the tectonic conditions of the sag were relatively stable and no major fault system was active when the main sources entered peak oil window, and thus the relatively stable tectonic environment enabled the formation and preservation of tight oil accumulations.Therefore, the Liushagang Formation of the Fushan Depression have favorable geological conditions for the formation of tight oil, which mainly distribute in the lower L1 submember and L2 member vertically and Huangtong and Bailian sub-sags horizontally.The distribution of high-quality source rocks, the distribution of "sweet point" reservoirs being rich in dissolution pores and favorable superimposed source-reservoir assemblages are the three main controlling factors for the formation and distribution of tight oil in Liushagang Formation of Fushan Depression, Beibuwan Basin.
-
Key words:
- tight oil /
- main controlling factor /
- Liushagang Formation /
- Fushan Depression /
- Beibuwan Basin
-
图 7 福山凹陷西部永7井埋藏史(a)及Ro演化史图(b)
地层代号同图 2
Figure 7. Burial and thermal history of Well Yong 7 from the western Fushan Depression
表 1 福山凹陷流沙港组烃源岩地球化学参数特征
Table 1. Geochemical parameters of the source rocks from the Liushagang Formation, Fushan Depression
残余有机碳 氯仿沥青"A" 总烃wB/10-6 生烃潜量(S1+S2)/(mg·g-1) 烃源岩质量分级 wB/% 流一段 范围值 0.18~2.61 0.004 8~0.179 2 58~1 121 0.52~6.25 次优质烃源岩 平均值 1.23 0.075 1 424 2.50 流二段 范围值 0.64~6.0 0.013 2~0.247 0 204~1 519 0.50~29.28 优质-高丰度烃源岩 平均值 1.61 0.109 7 612 4.56 流三段 范围值 0.12~4.73 0.009 4~0.226 2 14~1 580 1.88~9.31 优质烃源岩 平均值 1.43 0.105 5 616 3.79 -
[1] 孙龙德, 邹才能, 贾爱林, 等. 中国致密油气发展特征与方向[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(6): 1015-1026. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201906002.htmSun L D, Zou C N, Jia A L, et al. Development characteristics and orientation of tight oil and gas in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(6): 1015-1026(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201906002.htm [2] 邹才能, 杨智, 朱如凯, 等. 中国非常规油气勘探开发与理论技术进展[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(6): 979-1007. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2015.06.001Zou C N, Yang Z, Zhu R K, et al. Unconventional oil and gas exploration and development in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(6): 979-1007(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2015.06.001 [3] 林森虎, 邹才能, 袁选俊, 等. 美国致密油开发现状及启示[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2011, 23(4): 25-30, 64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2011.04.005Lin S H, Zou C N, Yuan X J, et al. Status quo of tight oil exploitation in the United States and its implication[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2011, 23(4): 25-30, 64(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2011.04.005 [4] Cipolla C, Lewis R, Maxwell S, et al. Appraising unconventional resource plays: Separating reservoir quality from completion effectiveness[C]//Anon. International petroleum technology conference. Bangkok, Thailand: [s. n. ], 2011. [5] Jarvie D M. Unconventional oil petroleum systems: Shales and shale hybrids[M]. Calgary: AAPG, 2011. [6] 贾承造, 邹才能, 李建忠, 等. 中国致密油评价标准、主要类型、基本特征及资源前景[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(3): 343-350. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201203000.htmJia C Z, Zou C N, Li J Z, et al. Assessment criteria, main types, basic features and resource prospects of the tight oil in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(3): 343-350(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201203000.htm [7] 邹才能, 杨智, 陶士振, 等. 纳米油气与源储共生型油气聚集[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(1): 13-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201201003.htmZou C N, Yang Z, Tao S Z, et al. Nano-hydrocarbon and the accumulation in coexisting source and reservoir[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(1): 13-26(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201201003.htm [8] 杜金虎, 何海清, 杨涛, 等. 中国致密油勘探进展及面临的挑战[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2014, 19(1): 1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2014.01.001Du J H, He H Q, Yang Tao, et al. Progress in China's tight oil exploration and challenges[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2014, 19(1): 1-9(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2014.01.001 [9] 匡立春, 王霞田, 郭旭光, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组致密油地质特征与勘探实践[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2015, 36(6): 629-634. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201506002.htmKuang L C, Wang X G, Guo X G, et al. Geological characteristics and exploration practice of tight oil of Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2015, 36(6): 629-634(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201506002.htm [10] 宋效文, 周立宏, 文开丰, 等. 零值剥离法在致密油甜点体预测中的应用: 以沧东凹陷G108井区Ek-2~2为例[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2016, 51(6): 1195-1201, 1052. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ201606020.htmSong X W, Zhou L H, Wen K F, et al. Tight oil sweet spot prediction with zero stripping: An example of Ek-2~2 in Well G108 Block, Cangdong Sag[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2016, 51(6): 1195-1201, 1052(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ201606020.htm [11] 孙龙德, 邹才能, 贾爱林, 等. 中国致密油气发展特征与方向[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(6): 1015-1026. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201906002.htmSun L D, Zou C N, Jia A L, et al. Development characteristics and orientation of tight oil and gas in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(6): 1015-1026(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201906002.htm [12] 邹才能, 杨智, 何东博, 等. 常规-非常规天然气理论、技术及前景[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(4): 575-587. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201804005.htmZou C N, Yang Z, He D B, et al. Theory, technology and prospects of conventional and unconventional natural gas[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(4): 575-587(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201804005.htm [13] 朱如凯, 邹才能, 吴松涛, 等. 中国陆相致密油形成机理与富集规律[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(6): 1168-1184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201906002.htmZhu R K, Zou C N, Wu S T, et al. Mechanism for generation and accumulation of continental tight oil in China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(6): 1168-1184(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201906002.htm [14] Cao Z, Liu G, Xiang B, et al. Geochemical characteristics of crude oil from a tight oil reservoir in the Lucaogou Formation, Jimusar Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2017, 101: 39-72. doi: 10.1306/05241614182 [15] 靳军, 杨召, 依力哈木·尔西丁, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷致密油储层纳米孔隙特征及其含油性[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(5): 1594-1601. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201805021.htmJin J, Yang Z, Erxiding Y, et al. Nanopore characteristics and oil-bearing properties of tight oil reservoirs in Jimusar Sag, Jggar Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(5): 1594-1601(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201805021.htm [16] 唐红娇, 杨立辉, 朱峰, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组致密油分子尺寸及结构特征[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(5): 1587-1593. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201805020.htmTang H J, Yang L H, Zhu F, et al. Molecularsize and structure characteristics of tight oil of Lucaogou Formation in Jimusar Depression[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(5): 1587-1593(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201805020.htm [17] 马铨峥, 杨胜来, 杨龙, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组致密储层微观孔隙特征[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2020, 39(6): 16-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK202006002.htmMa Q Z, Yang S L, Yang L, et al. Characteristics of the micro-pore in Lucaogou-Formation tight reservoir of Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2020, 39(6): 16-23(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK202006002.htm [18] 王俞策, 曹剑, 陶柯宇, 等. 准噶尔盆地芦草沟组致密油系统油源对比与成藏非均质性研究[J]. 南京大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 56(3): 322-337. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJDZ202003003.htmWang Y C, Cao J, Tao K Y, et al. Oil-source correlation and accumulation heterogeneity of tight oils in the Middle PermianLucaogou Formation, Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Nanjing University: Natural Science Edition, 2020, 56(3): 322-337(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJDZ202003003.htm [19] 朱如凯, 邹才能, 张鼐. 致密砂岩气藏储层成岩流体演化与致密成因机理: 以四川盆地上三叠统须家河组为例[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2009, 39(3): 327-339. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3045.2009.03.018Zhu R K, Zou C N, Zhang N, et al. Diagenetic fluid evolution and tight genetic mechanism of tight sandstone gas reservoir: A case study of Xujiahe Formation of Upper Triassic in Sichuan Basin[J]. Science China: Earth Science, 2009, 39(3): 327-339(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3045.2009.03.018 [20] 邹才能, 杨智, 陶士振, 等. 纳米油气与源储共生型油气聚集[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(1): 13-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201201003.htmZou C N, Yang Z, Tao S Z, et al. Nano-hydrocarbon and the accumulation in coexisting source and reservoir[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(1): 13-26(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201201003.htm [21] 杨学峰, 雷启鸿, 吴新伟, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地致密油储层启动压力梯度对比分析[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2020, 36(1): 310-317.Yang X F, Lei Q H, Wu X W, et al. Comparative study on threshold pressure gradient of tight oil reservoirs in Ordos Basin[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2020, 36(1): 310-317(in Chinese with English abstract). [22] 刘惠民, 郑金凯, 赵文山, 等. 深层致密砂岩储层脆性指数评价新方法[J]. 地质力学学报, 2019, 25(4): 492-500. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201904005.htmYang H M, Zheng J K, Zhao W S, et al. A new method for evaluating brittleness index of deep tight sandstone reservoir[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 25(4): 492-500(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201904005.htm [23] 谢升洪, 李伟, 冷福, 等. 致密砂岩储层可动流体赋存规律及制约因素研究: 以鄂尔多斯盆地华庆油田长6段储层为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(5): 105-114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905011.htmXie S H, Li W, Leng F, et al. Distribution and controlling factors of movable fluid in tight sandstone reservoir: Taking Chang 6 Formation of Huaqing Oilfield in Ordos Basin as an example[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(5): 105-114(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905011.htm [24] 周林, 刘皓天, 周坤, 等. 致密砂岩储层"甜点"识别及评价方法[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(4): 165-173. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10012.shtmlZhou L, Liu H T, Zhou K, et al. "Sweet spot" identification and evaluation of tight sandstone reservoir[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(4): 165-173(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10012.shtml [25] 冯越, 黄志龙, 李天军, 等. 吐哈盆地胜北洼陷七克台组二段致密油成藏条件[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2020, 32(6): 97-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202006009.htmFeng Y, Huang Z L, Li T J, et al. Tight oil accumulation conditions of the second member of Qiketai Formation in Shengbei sub-sag, Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2020, 32(6): 97-108(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202006009.htm [26] Ju W, Li Z, Sun W, et al. In-situ stress orientations in the Xiagou tight oil reservoir of Qingxi Oilfield, Jiuxi Basin, northwestern China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 98: 258-269. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.08.020 [27] Gan H, Wang H, Shi Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genetic origin of crude oil in the Fushan Sag, Beibuwan Basin, South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2000, 112: 104-114. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264817219305628 [28] 黄娅, 孙盼科, 万金彬, 等. 福山油田流沙港组微观孔喉结构评价及其主控因素研究[J]. 长江大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 13(26): 8-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1409(s).2016.26.003Huang Y, Sun P K, Wan J B, et al. Microscopic pore structureevalution and main controlling factors of Liushagang reservoir in Fushan Oilfield[J]. Journal of Yangtze University: Natural Science Edition, 2016, 13(26): 8-13(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1409(s).2016.26.003 [29] Liu E, Wang H, Li Y, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and tectonic setting of sublacustrine fans in a half-graben rift depression, Beibuwan Basin, South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 52: 9-21. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.01.008 [30] Li Y, Lin S, Wang H, et al. Depositional setting analysis using seismic sedimentology: Example from the Paleogene Lishagang sequence in the Fushan Depression, South China Sea[J]. Geodesy Geodynamics, 2017, 8: 347-355. doi: 10.1016/j.geog.2017.05.001 [31] 薛海涛, 田善思, 王伟明, 等. 页岩油资源评价关键参数: 含油率的校正[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014, 37(1): 15-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201601004.htmXue H T, Tian S S, Wang W M, et al. Correction of oil content: One key parameter in shale oil resource assessment[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 37(1): 15-22(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201601004.htm [32] 王敏. 页岩油评价的关键参数及求取方法研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2013, 53(9): 1689-1699. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201401020.htmWang M. Key parameter and calculation in shale oil reservoir evaluation[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 53(9): 1689-1699(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201401020.htm [33] Berner U, Faber E, Scheeder G, et al. Primary cracking of algal and landplant kerogens: Kinetic models of isotope variations in methane, ethane and propane[J]. Chem. Geol., 1995, 126: 233-245. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(95)00120-4 [34] Wood D A. Kerogen conversion and thermal maturity modelling of petroleum generation: Integrated analysis applying relevant kerogen kinetics[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 89: 313-329. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.10.003 -





 下载:
下载: