Lithology prediction of tight sandstone formation using GS-LightGBM hybrid machine learning model
-
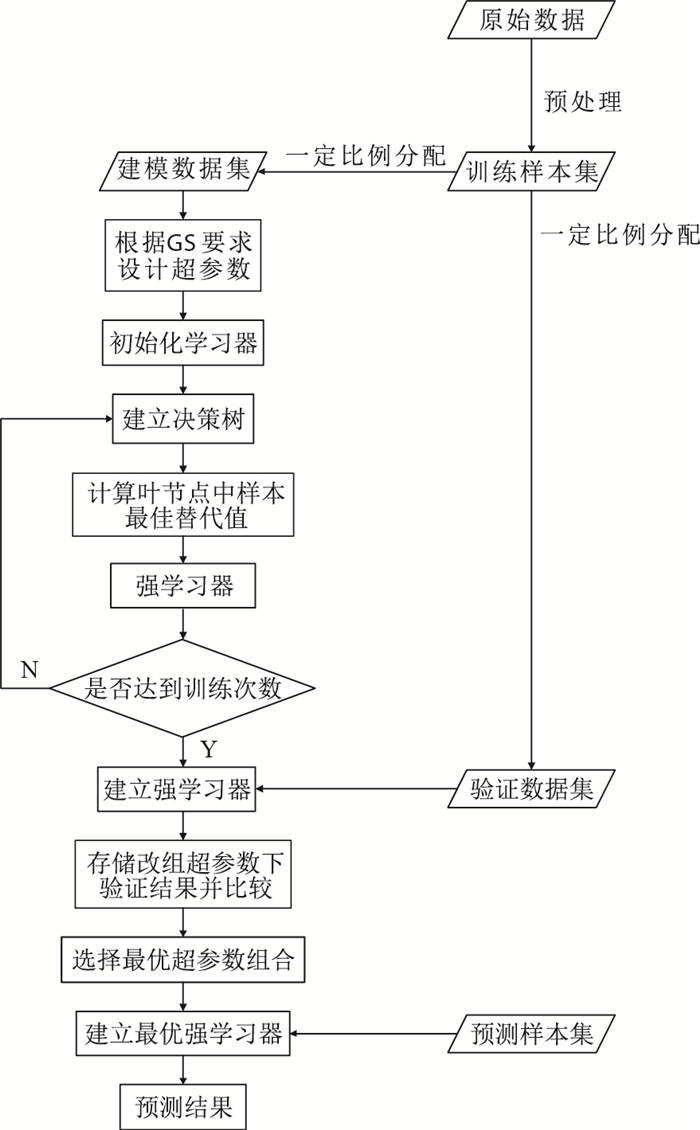
摘要: 以交会图为代表的传统岩性识别图版无法适用于致密砂岩地层,其主要原因是大部分地层岩性的测井响应特征相似度高,难以基于图版分析被有效识别。LightGBM较传统模式识别模型能更高效地解决问题,为此采用该模型识别致密砂岩地层岩性。由于LightGBM在建模时利用了较多的超参数,导致预测结果难以保证为最优,所以采用GS算法进行优化,进而提出GS-LightGBM。实验目的层为姬塬油田西部长4+5段致密砂岩地层。提出模型的预测能力通过设计两个实验来验证。为突出验证效果,实验中加入SVM和XGBoost作为对比模型。实验结果显示,GS-XGBoost和GS-LightGBM的准确率、F1-score和AUC指标相接近,都最高,但GS-LightGBM的计算时间只有GS-XGBoost的约1/23。实验结果表明,GS-LightGBM模型可在不失精度的情况下,能快速给出预测结果,具备了在致密砂岩地层岩性识别研究上的应用价值和推广性。Abstract: Classic lithology predictors, represented by crossplot, are generally ineffective for tight sandstone formation, mainly due to a point that most lithologies present extremely similar logging responses and thus are rather difficult to be analyzed effectively via crossplot.Compared to classic pattern recognizers, LightGBM shows higher efficiency in data process, therefore it is employed to make a solution for lithology prediction of tight sandstone formation.As LightGBM utilizes many hyper-parameters during modeling, easily causing an issue that the predicted results are not reliable enough, GS algorithm is adopted to solve optimization and further a hybrid machine learning model GS-LightGBM is proposed.The tight sandstone formation of member of Chang 4+5 in western Jiyuan Oilfield is validation targets, and two experiments are designed to reveal prediction capability of the proposed model.In order to highlight validation effect, SVM and XGBoost are introduced as comparative predictors.Experimental results manifest GS-XGBoost and GS-LightGBM have the similar and also the highest marks in the prediction performance of accuracy, F1-score, and AUC, while computing time of GS-LightGBM is only 1/23 shorter than that of GS-XGBoost.The results demonstrate the proposed model is capable to rapidly figure out the predicted lithologies based on guarantee of high prediction accuracy, proving its better applicable prospect and generalization in the study field of lithology prediction of tight sandstone formation.
-
Key words:
- tight sandstone formation /
- lithology prediction /
- SVM model /
- XGBoost model /
- LightGBM model /
- GS optimizing algorithm
-
表 1 测井曲线数据统计参数
Table 1. Statistical parameters produced by logging data
测井曲线 Q1 Q3 IQR LIF UIF AC/(μs·m-1) 218.42 242.12 35.55 182.87 277.66 DEN/(g·cm-3) 2.45 2.63 0.26 2.20 2.88 GR/API 84.82 116.51 47.53 37.29 164.04 PE/(b·e-1) 2.68 3.43 1.12 1.56 4.56 AT90/(Ω·m) 7.22 16.11 13.32 -6.10 29.43 SP/mV 64.83 81.70 25.32 39.51 107.02 表 2 各验证模型、GS优化算法初始参数设置和各验证模型超参数优化结果
Table 2. Initial parameter settings of all validated models and GS optimizing algorithm, and optimal results of hyper-parameters of all validated models
验证模型 SVM XGBoost LightGBM 参数初始化
(是否为超参数)惩罚系数(c)=1(是);
核函数=RBF1 (否);
核函数平滑因子(σ)=0.1 (是)S=100 (是);
η=0.1 (是);
最大回归树深度
max_depth=3 (是) 2;
λ=0.1 (是);
叶节点最小样本权重之和
min_chile_weight =0.001 (否) 3;
最小分裂梯度下降值
δ=0.001 (否) 4;
损失函数=对数似然损失函数(否)S=100 (是);
η=0.1 (是);
max_depth=3 (是);
λ=0.1 (是);
叶节点最大数目
num_leaves=2 (是) 5;
叶节点样本最少数量
min_data_in_leaf=5 (是) 6;
min_chile_weight=0.001 (否);
桶数max_bin=2 (是) 7;
每桶最小样本数量
min_data_in_bin=1 (是) 8;
损失函数=对数似然损失函数(否)GS参数设置
(左界限,右界限,步长)c (1, 100, 0.2);
σ(0.1, 1, 0.05)S (100, 5000, 50);
η (0.1, 1, 0.05);
max_depth (3, 10, 1);
λ (0.1, 10, 0.1)S (100, 5000, 50);
η(0.1, 1, 0.05);
max_depth (3, 10, 1);
λ(0.1, 10, 0.1);
num_leaves (2, 1024, ×2) 9;
min_data_in_leaf (5, 100, 5);
max_bin (2, 255, ×2);
min_data_in_bin (1, 100, 5)超参数最优结果 c=9.2;
σ=0.8S=1500;
η=0.2;
max_depth=8;
λ=0.3S=1300;
η=0.35;
max_depth=7;
λ=0.3;
num_leaves=64;
min_data_in_leaf=20;
max_bin=8;
min_data_in_bin=31注:1.Radial Basis Function (径向基函数); 2.回归树最大分裂次数;3.如果叶节点中样本二阶导之和小于该值,则剪掉该叶节点;4.如果叶节点中样本对应的梯度下降值之和小于该值,则停止分裂;5.如果叶节点个数超过该值,则停止分裂;6.如果叶节点中样本容量小于该值,则剪掉该叶节点;7.Historgram算法寻找最佳分裂点时所用桶的数量以该值为准;8.如果桶中样本容量小于该值,则弃用该桶;9.“×2”表示以2倍速度增长 表 3 实验中各模型综合评价信息
Table 3. Summary of comprehensive evaluation information of all validated models produced in the experiments
验证
模型GS-SVM GS-XGBoost GS-LightGBM 准确率/% 平均
AUC计算时间/s 准确率/% 平均
AUC计算时间/s 准确率/% 平均
AUC计算时间/s 实验1 67.66 0.79 139.87 88.50 0.91 553.31 87.78 0.91 22.95 实验2 70.53 0.81 175.32 92.81 0.93 859.35 92.61 0.93 37.54 -
[1] 周林, 刘皓天, 周坤, 等. 致密砂岩储层"甜点"识别及评价方法[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(4): 165-173. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10012.shtmlZhou L, Liu H T, Zhou K, et al. "Sweet spot" identification and evaluation of tight sandstone reservoir[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(4): 165-173(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10012.shtml [2] 李峰峰, 郭睿, 余义常. 层序地层划分方法进展及展望[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(4): 215-224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904022.htmLi F F, Guo R, Yu Y C. Progress and prospect of the division of sequence stratigraphy[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(4): 215-224(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904022.htm [3] 刘惠民, 郑金凯, 赵文山, 等. 深层致密砂岩储层脆性指数评价新方法[J]. 地质力学学报2019, 25(4): 492-500. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201904005.htmLiu H M, Zheng J K, Zhao W S, et al. A new method for evaluation brittleness index of deep tight sandstone reservoir[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 25(4): 492-500(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201904005.htm [4] 韦阿娟. 渤海海域中生界火成岩岩性测井识别技术及应用[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(6): 207-213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201506030.htmWei A J. Well-logging identification technique and its application in Mesozoic igneous rocks in Bohai Sea area[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(6): 207-213(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201506030.htm [5] 赵建, 高福红. 测井资料交会图法在火山岩岩性识别中的应用[J]. 世界地质, 2003, 22(2): 136-140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2003.02.006Zhao J, Gao F H. Application of crossplots based on well log data in identifying volcanic lithology[J]. Global Geology, 2003, 22(2): 136-140(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2003.02.006 [6] 吴磊, 徐怀民, 季汉成. 基于交会图和多元统计法的神经网络技术在火山岩识别中的应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2006, 41(1): 81-86. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7210.2006.01.016Wu L, Xu H M, Ji H C. Application of neural network technique based on crossplot and multielement statistics to recognition of volcanic rocks[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2006, 41(1): 81-86(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7210.2006.01.016 [7] 范训礼, 戴航, 张新家, 等. 神经网络在岩性识别中的应用[J]. 测井技术, 1999, 23(1): 50-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1338.1999.01.012Fan X L, Dai H, Zhang X J, et al. Application of neural network in lithology identification[J]. Well Logging Technology, 1999, 23(1): 50-52(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1338.1999.01.012 [8] 李政宏, 刘永福, 张立强, 等. 数据挖掘方法在测井岩性识别中的应用[J]. 断块油气藏, 2019, 26(6): 713-718. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201906008.htmLi Z H, Liu Y F, Zhang L Q, et al. Application of data mining method in lithology identification using well log[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2019, 26(6): 713-718(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201906008.htm [9] Chen T, Guestrin C. XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining. New York, USA: ACM, 2016. [10] 卢新卫, 金章东. 前馈神经网络的岩性识别方法[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1999, 20(1): 82-84. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.1999.01.019Lu X W, Jin Z D. Method of lithologic recognizing based on feedforward neural network[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 1999, 20(1): 82-84(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.1999.01.019 [11] 张洪, 邹乐君, 沈晓华. BP神经网络在测井岩性识别中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2002, 38(6): 63-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200206015.htmZhang H, Zou L J, Shen X H. The application of BP neural network in well lithology identification[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2002, 38(6): 63-65(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200206015.htm [12] 林香亮, 朱建伟, 刘光涛, 等. 基于PCA-SVM的砂砾岩岩性识别[J]. 长江大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 17(1): 21-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1409.2020.01.005Lin X L, Zhu J W, Liu G T, et al. Lithologic identification of glutenite based on PCA-SVM[J]. Journal of Yangtze University: Natural Science Edition, 2020, 7(1): 21-26(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1409.2020.01.005 [13] 石锁, 余继峰, 曹慧涛, 等. 基于高斯核SVM的地层岩性识别: 以东濮凹陷上古生界碎屑岩为例[J]. 中国科技论文, 2020, 15(1): 112-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2020.01.017Shi S, Yu J F, Cao H T, et al. Reservoir lithology identification based on SVM using radial basis function: An example of Upper Paleozoic clastic rock in Dongpu Sag[J]. China Science Paper, 2020, 15(1): 112-118(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2020.01.017 [14] Dev V A, Eden M R. Formation lithology classification using scalable gradient boosted decision trees[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2019, 128: 392-404. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098135419302200 [15] Sun Z, Jiang B, Li X, et al. A data-driven approach for lithology identification based on parameter-optimized ensemble learning[J]. Energies, 2020, 13(15): 3903. doi: 10.3390/en13153903 [16] Ke G L, Meng Q, Finley T, et al. Light GBM: A highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the 31st international conference on neural information processing systems. California, USA: ACM, 2017. [17] Zhang X X, Deng T, Jia G Z. Nuclear spin-spin coupling constants prediction based on XGboost and lightGBM algorithms[J]. Molecular Physics, 2019, 118(14): 1-10. doi: 10.1080/00268976.2019.1696478 [18] 韩学辉, 卢时林, 支乐菲, 等. 应用最小二乘支持向量机识别J13井区杜家台油层岩性[J]. 特种油气藏, 2011, 18(6): 18-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2011.06.005Han X H, Lu S L, Zhi L F, et al. Identification of the lithology of Dujiatai Formation in Well J13 block with east squares support vector machine[J]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 2011, 18(6): 18-21(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2011.06.005 [19] 邓呈祥, 高文利, 潘和平, 等. 庐枞矿集区科学钻探的岩性识别方法[J]. 物探与化探, 2015, 39(6): 1144-1149. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201506008.htmDeng C X, Gao W L, Pan H P, et al. Lithologic identification method in scientific drilling of the Luzong ore district[J]. Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 39(6): 1144-1149(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201506008.htm [20] Tukey J W. Mathematics and the picturing of data[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the international congress of mathematicians. Vancouver, USA: BC, 1975. [21] Han S, Horsfield B, Zhang J, et al. Hydrocarbon generation kinetics of lacustrine Yanchang shale in southeast Ordos Basin, North China[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2014, 28(9): 5632-5639. doi: 10.1021/ef501011b [22] Liu H, Li X, Liao J, et al. Genesis of the high gamma sandstone of the Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin[J]. China Petroleum Science, 2013, 10(1): 50-54. doi: 10.1007/s12182-013-0248-7 [23] Li J, Zhou S, Li Y, et al. Effect of organic matter on pore structure of mature lacustrine organic-rich shale: A case study of the Triassic Yanchang shale, Ordos Basin, China[J]. Fuel, 2016, 185: 421-431. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.07.100 -





 下载:
下载: