Progress of deep learning in oil and gas reservoir geological modeling
-
摘要: 随着大数据和以深度学习为基础的人工智能技术的快速发展,油气藏地质建模逐步从传统的两点地质统计建模、基于目标建模、多点地质统计建模和基于沉积过程建模进入智能地质建模阶段。以深度学习为基础的智能地质建模主要采用对抗生成网络建立三维地质模型,目前这些研究集中在网络结构和算法的完善,特别是对地震和测井等各类数据的条件化,少量研究侧重于样本数据的获取。目前研究中采用的训练样本大多是基于目标或基于沉积过程方法模拟得到的合成数据,为了真正将该技术应用实际地下油气藏,需要更加关注真实样本数据的获取。仅靠深度神经网络这种统计学习方法实现技术突破的难度较大,研发通用的人工智能地质建模器是未来的主要发展方向,其中统计学习与符号学习相结合可能是实现该技术的必经道路。Abstract: With the rapid development of big data and deep learning based on artificial intelligence technology, reservoir geological modeling has gradually moved from traditional two-point geostatistical modeling, object-based modeling, multi-point geostatistical modeling, and sedimentary process-based modeling to intelligent geological modeling stage.Intelligent geological modeling based on deep learning mainly uses adversarial generation networks to build a 3D geological model.At present, these studies focus on the improvement of network architectures and algorithms, especially the conditioning of various types of observed data such as seismic and well logging.Few studies focus on sample data obtaining.At present, most of the training samples used in the research are synthetic data based on object modeling or sedimentary process methods.To truly apply this technology to actual underground oil and gas reservoirs, more attention needs to be paid on the acquisition of real sample data.We believe a general artificial intelligence geological modeler is the main direction in the future.However, it is difficult to achieve technological breakthroughs only by the statistical learning method of deep neural networks.The combination of statistical learning and symbol learning may be the only way to realize this technology.
-
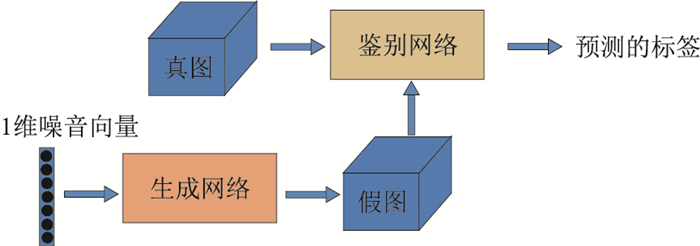
表 1 卷积对抗生成网络结构
Table 1. Network structure generated by convolution countermeasure
鉴别网络(D) 生成网络(G) 通道64卷积核4×4, 步长2 线性函数100×2048 通道128卷积核4×4, 步长2 通道256转置卷积核4×4, 步长2 通道256卷积核4×4, 步长2 通道128转置卷积核4×4, 步长2 通道32卷积核4×4, 步长2 通道64转置卷积核4×4, 步长2 线性函数2048×1 通道1转置卷积核4×4, 步长2 -
[1] 吴胜和, 李宇鹏. 储层地质建模的现状与展望[J]. 海相油气地质, 2007, 12(3): 53-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2007.03.009Wu S H, Li Y P. Reservoir modeling: Current situation and development prospect[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2007, 12(3): 53-60(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2007.03.009 [2] 张文彪, 段太忠, 刘彦锋, 等. 定量地质建模技术应用现状与发展趋势[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3): 270-281. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903029.htmZhang W B, Duan T Z, Liu Y F, et al. Application status and development trend of quantitative geological modeling[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(3): 270-281(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903029.htm [3] 尹艳树, 张昌民, 李玖勇, 等. 多点地质统计学研究进展与展望[J]. 古地理学报, 2011, 13(2): 245-252. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201102015.htmYin Y S, Zhang C M, Li J Y, et al. Progress and prospect of multiple-point geostatistics[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2011, 13(2): 245-252(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201102015.htm [4] 王鹏飞, 高振南, 李俊飞, 等. 基于数理统计方法的地质模型不确定性评价[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2): 291-269. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902035.htmWang P F, Gao Z N, Li J F, et al. Uncertainty evaluation of geology model based on mathematics statistics[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(2): 291-269(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902035.htm [5] 田启川, 王满丽. 深度学习算法研究进展[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2019(22): 25-33. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1908-0359Tian Q C, Wang M L. Research progress on deep learning algorithms[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2019(22): 25-33(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1908-0359 [6] 李苍柏, 范建福, 宋相龙. 深度学习在地质学上的应用[J]. 地质学刊, 2018, 42(1): 115-121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2018.01.015Li C B, Fan J F, Song X L. A study on application of deep learning in geology[J]. Journal of Geology, 2018, 42(1): 115-121(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2018.01.015 [7] Al-Anazi A, Gates I. A support vector machine algorithm to classify lithofacies and model permeability in heterogeneous reservoirs[J]. Engineering Geology, 2010, 114(3): 267-277. [8] Korjani M, Popa A, Grijalva E, et al. A new approach to reservoir characterization using deep learning neural networks[C]//Anon. SPE western regional meeting. Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2016. [9] 郝扬, 周景润, 蔡璇. 卷积神经网络在石油勘探开发领域的应用研究[J]. 信息系统工程, 2020, 323(11): 140-142.Hao Y, Zhou J R, Cai X. Research on application of convolutional neural network in the field of petroleum exploration and development[J]. Information System Engineering, 2020, 323(11): 140-142(in Chinese with English abstract). [10] 付超, 林年添, 张栋, 等. 多波地震深度学习的油气储层分布预测案例[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(1): 293-303. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201801026.htmFu C, Lin N T, Zhang D, et al. Prediction of reservoirs using multi-component seismic data and the deep learning method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018, 61(1): 293-303(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201801026.htm [11] 刘力辉, 陆蓉, 杨文魁. 基于深度学习的地震岩相反演方法[J]. 石油物探, 2019, 58(1): 127-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYWT201901015.htmLiu L H, Lu R, Yang W K. Seismic lithofacies inversion based on deep learning[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2019, 58(1): 127-133(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYWT201901015.htm [12] Canchumuni S A, Emerick A A, Pacheco M A. Integration of ensemble data assimilation and deep learning for history matching facies models[C]//Anon. Offshore Technology Conference, Society of Petroleum Engineers, Brasil, 2017. [13] 陈麒玉, 刘刚, 何珍文, 等. 面向地质大数据的结构-属性一体化三维地质建模技术现状与展望[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(4): 51-58. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9999.shtmlChen Q Y, Liu G, He Z W, et al. Current situation and prospect of structure-attribute integrated 3D geological modeling technology for geological big data[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(4): 51-58(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9999.shtml [14] Strebelle S B, Journel A G. Reservoir modeling using multiple-point statistics[C]//Anon. SPE annual technical conference and exhibition. [S. l. ]: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2001. [15] Mariethoz G, Caers J. Multiple-point geostatistics: Stochastic modeling with training images[M]. Oxford, UK: John Wiley & Sons, 2014. [16] 王恺其, 肖凡. 多点地质统计学的理论、方法、应用及发展现状[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6): 256-268. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906031.htmWang K Q, Xiao F. Multiple-ponits geostatistics: A review of theories, methods and applications[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(6): 256-268(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906031.htm [17] Hinton G E, Osindero S, Teh Y W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets[J]. Neural Computation, 2006, 18(7): 1527-1554. http://database.oxfordjournals.org/external-ref?access_num=10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527&link_type=DOI [18] Kingma D P, Welling M. Auto-encoding variational bayes[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on learning representations, Banff, AB, Canada, 2014. [19] Canchumuni S W A, Emerick A A, Pacheco M A C. Towards a robust parameterization for conditioning facies models using deep variational autoencoders and ensemble smoother[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2019, 128: 87-102. [20] Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]//Anon. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2014. [21] Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]//Anon. International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Cham: Springer, 2015. [22] Salimans T, Goodfellow I, Zaremba W, et al. Improved techniques for training gans[C]//Anon. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2016. [23] Arjovsky M, Chintala S, Bottou L. Wasserstein GAN[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the 34th international conference on machine learning, 2017. [24] Zhong Z, Sun A Y, Jeong H. Predicting CO2 plume migration in heterogeneous formations using conditional deep convolutional generative adversarial network[J]. Water Resources Research, 2019, 55(7): 5830-5851. doi: 10.1029/2018WR024592 [25] Laloy E, Hérault R, Jacques D, et al. Training-image based geostatistical inversion using a spatial generative adversarial neural network[J]. Water Resources Research, 2018, 54(1): 381-406. http://arxiv.org/abs/1708.04975v2 [26] Chavdarova T, Fleuret F. SGAN: An alternative training of generative adversarial networks[C]//Anon. Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition(Cvpr). IEEE, 2018. [27] Chan S, Elsheikh A H. Parametric generation of conditional geological realizations using generative neural networks[J]. Computational Geosciences, 2019, 23(5): 925-952. doi: 10.1007/s10596-019-09850-7 [28] Li Q, Aguilera R. Unsupervised statistical learning with integrated pattern-based geostatistical simulation[C]//Anon. SPE western regional meeting. [S.l.]: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2018. [29] Mosser L, Dubrule O, Blunt M J. Reconstruction of three-dimensional porous media using generative adversarial neural networks[J]. Physical Review E., 2017, 96(4): 043309. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/29347591 [30] Mosser L, Dubrule O, Blunt M J. Stochastic reconstruction of an oolitic limestone by generative adversarial networks[J]. Transport in Porous Media, 2018, 125(1): 81-103. doi: 10.1007/s11242-018-1039-9 [31] 谢鹏飞. 基于深度学习的地质统计学反演方法[D]. 武汉: 长江大学, 2019.Xie P F. Geostatistical inversion method based on deep learning[D]. Wuhan: Yangtze University, 2019(in Chinese with English abstract). [32] Mosser L, Dubrule O, Blunt M J. Stochastic seismic waveform inversion using generative adversarial networks as a geological prior[J]. Mathematical Geosciences, 2020, 52(1): 53-79. [33] Dupont E, Zhang T, Tilke P, et al. Generating realistic geology conditioned on physical measurements with generative adversarial networks[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1802.03065, 2018. [34] Mosser L, Dubrule O, Blunt M J. Conditioning of three-dimensional generative adversarial networks for pore and reservoir-scale models[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1802.05622, 2018. [35] Yeh R A, Chen C, Lim T Y, et al. Semantic image inpainting with deep generative models[C]//Anon. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition(CVPR). IEEE, 2017. [36] Zhang T F, Tilke P, Dupont E, et al. Generating geologically realistic 3D reservoir facies models using deep learning of sedimentary architecture with generative adversarial networks[J]. Petroleum Science, 2019, 16(3): 541-549. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&filename=SYKX201903006 [37] Ruffino C, Hérault R, Laloy E, et al. Pixel-wise conditioned generative adversarial networks for image synthesis and completion[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2002.01281, 2020. [38] Chan S, Elsheikh A H. Parametrization of stochastic inputs using generative adversarial networks with application in geology[J]. Frontiers in Water, 2020, 2(5): 1-21. http://arxiv.org/abs/1904.03677 [39] Song S, Mukerji T, Hou J. Geological facies modeling based on progressive growing of generative adversarial networks(GANs)[J]. EarthArXiv. June 22. doi: 10.31223/osf.io/ycufs. [40] Song S, Mukerji T, Hou J. Conditional facies modeling using an improved progressive growing of generative adversarial networks(GANs)[J]. non-peer reviewed preprint submitted to EarthArXiv, DOI: 10.31223/osf.io/fm24b. [41] Deutsch C V, Wang L. Hierarchical object-based stochastic modeling of fluvial reservoirs[J]. Mathematical Geology, 1996, 28(7): 857-880. doi: 10.1007/BF02066005 [42] Korjani M, Popa A, Grijalva E, et al. A new approach to reservoir characterization using deep learning neural networks[C]//Anon. SPE western regional meeting. [S.l.]: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2016. [43] 侯晓琳. 深度学习在地质储层属性预测中的应用研究[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2020, 37(4): 40-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYRJ202004008.htmHou X L. Application on deep learning in geological reservoir properties prediction[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2020, 37(4): 40-47(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYRJ202004008.htm [44] Saikia P, Baruah R D, Singh S K, et al. Artificial neural networks in the domain of reservoir characterization: A review from shallow to deep models[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2020, 135: 104357. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098300418305417 [45] Nesvold E, Mukerji T. Geomodeling using generative adversarial networks and a database of satellite imagery of modern river deltas[C]//Anon. Petroleum Geostatistics 2019. European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers, 2019. [46] 吴冲龙, 刘刚, 周琦, 等. 地质科学大数据统合应用的基本问题[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(4): 1-11. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9993.shtmlWu L C, Liu G, Zhou Q, et al. Fundamental problems of integrated application of big data in geoscience[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(4): 1-11(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9993.shtml [47] Pesaresi M, Syrris V, Julea A. A new method for earth observation data analytics based on symbolic machine learning[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(5): 391-399. http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/doaj/20724292/2016/00000008/00000005/art00046 -





 下载:
下载: