Sedimentary characteristics and model of shallow sea sandy debrisflow: A case study of Ying Ⅱ Member in the Dongfang 1-1 Gas Field, Yinggehai Basin
-
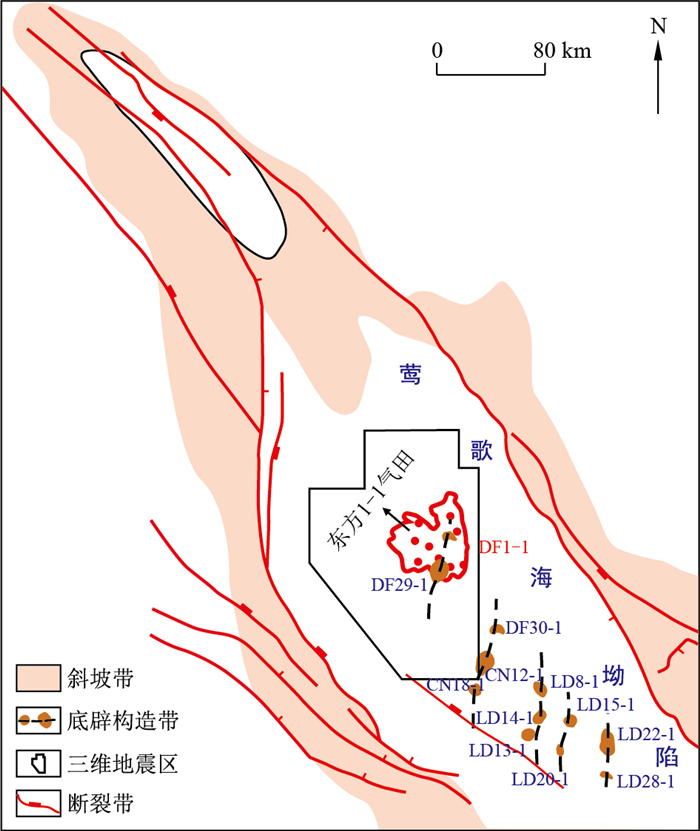
摘要: 莺歌海盆地东方气田莺二段发育浅海砂质碎屑流,对其沉积特征与模式的研究具有重要意义。从岩心精细描述入手,结合测井曲线特征、地震剖面、地球化学实验,综合国内外重力流研究进展,确定了研究区浅海砂质碎屑流的岩心、测井、地震相特征,并通过分析研究区沉积背景,进一步探讨了东方气田莺二段ⅡL、ⅢU气组浅海砂质碎屑流的沉积模式。研究结果表明:该区砂质碎屑流的岩心相为富漂浮泥岩碎屑的块状砂岩、"泥包砾"等典型砂质碎屑流特征;测井相上表现为齿化现象十分严重的逆粒序漏斗型及无粒序钟型-漏斗型复合型特征;地震相上表现为中振幅平行席状反射和低频平行-亚平行空白反射特征;剖面上呈席状和平缓透镜状展布。研究厘定了研究区砂质碎屑流为西侧三角洲前缘由于风暴作用引起沉积物滑塌再搬运和北侧红河洪水重力流共同作用形成的浅海砂质碎屑流沉积模式。Abstract: There is shallow sea sandy debris flow in Ying Ⅱ Member in Dongfang 1-1 Gas Field, Yinggehai Basin.Based on the detailed description of cores, combined with well logs, seismic section, geochemical experiments and the research progress of gravity flow, the core, logging and seismic facies characteristics of shallow sea sandy debris flow in the study area are determined.By analyzing the sedimentary background of the study area, the sedimentary mechanism of shallow sea sandy clastic flow in ⅡL and ⅢU gas groups of Ying Ⅱ Member in Dongfang Gas Field is further discussed.It is found that it is characterized massive sandstone rich in mudstone floating debris and "mud-coated intraclasts", which are typical sandy clastic flow characteristics, in core facies, funnel type and bell-funnel type which jugged acutely in logging facies, medium amplitude parallel sheet reflection and low frequency parallel sub parallel blank reflection in seismic facies, sheet and flat lenticular distribution on the section.The results show that the sandy debris flow in the study area is the sedimentary mechanism of the shallow sea sandy debris flow formed by the combined action of the west delta front sediment collapse and re-transportation caused by the storm and the Red River flood gravity flow on the north side.
-
图 3 DF1-1-11井浮游有孔虫质量分数、古水深曲线及层位标定图[17]
Figure 3. Percentage contents of planktonic foraminifera, paleobathymetric curve and horizon calibration map of Well DF1-1-11
图 4 莺歌海盆地三大物源区及东方1-1气田锆石年龄分布图[35] (n为样品数)
Figure 4. Zircon age distribution of Dongfang 1-1 Gas Field the three provenance areas of Yinggehai Basin
图 5 莺歌海盆地莺二段物源搬运路径图[35]
Figure 5. Provenance transport route of Ying Ⅱ Member, Yinggehai Basin
图 6 莺歌海盆地东方1-1气田莺二段浅海砂质碎屑流沉积构造及沉积背景分析
a.块状砂岩富漂浮泥岩碎屑,3井ⅡL气组,1 297.5 m;b.块状砂岩富漂浮泥岩碎屑,3井ⅢU气组,1 334.2 m;c.砂质碎屑流“泥包砾”结构,3井ⅢU气组,1 336.2 m;d.槽状交错层理,5井ⅡU气组,1 441.2 m;e.风暴序列,3井ⅢU气组,①平行层理,②洼状层理,③包卷层理,④丘状层理;f.生物逃逸构造,2井ⅢU气组,1 347.4 m;g.生物潜穴构造,3井ⅢU气组,1 376.5 m;h.砂质碎屑流“泥包砾”结构,3井ⅢU气组,1 336.2 m;i.槽状交错层理,8井ⅢU气组,1 460.5 m;j.韵律层理,3井ⅢU气组,1 369 m
Figure 6. Sedimentary structure of sandy debris flow and sedimentary background analysis of Ying Ⅱ Member in Dongfang 1-1 Gas Field, Yinggehai Basin
-
[1] Shanmugam G. 50 years of the turbidite para-digm(1950s—1990s): Deep-water processes and facies models: A critical perspective[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2000, 17(2): 285-342. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(99)00011-2 [2] 鲜本忠, 安思奇, 施文华. 水下碎屑流沉积: 深水沉积研究热点与进展[J]. 地质论评, 2014, 60(1): 39-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201401005.htmXian B Z, An S Q, Shi W H. Subaqueous debris flow: Hotspots and advances of deep-water sedimentation[J]. Geological Review, 2014, 60(1): 39-51(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201401005.htm [3] 邹才能, 赵政璋, 杨华, 等. 陆相湖盆深水砂质碎屑流成因机制与分布特征: 以鄂尔多斯盆地为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(6): 1065-1075. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200906007.htmZou C N, Zhao Z Z, Yang H, et al. Genetic mechanism and distribution of sandy debris flows in terrestrial lacustrine basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(6): 1065-1075(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200906007.htm [4] 李相博, 付金华, 陈启林, 等. 砂质碎屑流概念及其在鄂尔多斯盆地延长组深水沉积研究中的应用[J]. 地球科学进展, 2011, 26(3): 286-294. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201103009.htmLi X B, Fu J H, Chen Q L, et al. The concept of sandy debris flow and its application in the Yanchang Formation deep water sedimentation of the Ordos Basin[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2011, 26(3): 286-294(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201103009.htm [5] 李相博, 刘化清, 张忠义, 等. 深水块状砂岩碎屑流成因的直接证据: "泥包砾"结构: 以鄂尔多斯盆地上三叠统延长组研究为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 32(4): 611-622. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201404001.htmLi X B, Liu H Q, Zhang Z Y, et al. "Argillaceous parcel" structure: A direct evidence of debris flow origin of deep-water massive sandstone of Yanchang Formation, Upper Triassic, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2014, 32(4): 611-622(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201404001.htm [6] Li X B, Yang Z L, Wang J, et al. Mud-coated intraclasts: A criterion for recognizing sandymass-transport deposits: Deep-lacustrine massive sandstone of the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, Central China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 129: 98-116. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.06.007 [7] 廖建波, 李相博, 赵惠周, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组深水块状砂岩"泥包砾"结构成因机制[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 41(4): 46-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201704006.htmLiao J B, Li X B, Zhao H Z, et al. Genetic mechanism of mud-coated intraclasts within deep-water massive sandstone in Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Natural Science Edition, 2017, 41(4): 46-53(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201704006.htm [8] Xian B Z, Wang J H, Liu J P, et al. Classification and sedimentary characteristics oflacustrine hyperpycnal channels: Triassic outcrops in the south Ordos Basin, central China[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2018, 368: 68-82. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2018.03.006 [9] Xu Q H, Shi W Z, Xie X Y, et al. Deep-lacustrine sandy debrites and turbidites in the Lower Triassic Yanchang Formation, southeast Ordos Basin, central China: Facies distribution and reservoir quality[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 77: 1095-1107. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.08.011 [10] 陈飞, 胡光义, 孙立春, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地富县地区上三叠统延长组砂质碎屑流沉积特征及其油气勘探意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2012, 30(6): 1042-1052. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201206005.htmChen F, Hu G Y, Sun L C, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and the significance of petroleum exploration of sandy debris flows of Yanchang Formation of the Upper Triassin, Fuxian area, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(6): 1042-1052(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201206005.htm [11] 鲜本忠, 万锦峰, 姜在兴, 等. 断陷湖盆洼陷带重力流沉积特征与模式: 以南堡凹陷东部东营组为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(6): 121-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201201015.htmXian B Z, Wan J F, Jiang Z X, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and model of gravity flow deposition in the depressed belt of rift lacustrine basin: A case study from Dongying Formation in Nanpu Depression[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(1): 121-135(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201201015.htm [12] 杨田, 操应长, 王艳忠, 等. 深水重力流类型、沉积特征及成因机制: 以济阳坳陷沙河街组三段中亚段为例[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(9): 1048-1059. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201509003.htmYang T, Cao Y C, Wang Y Z, et al. Types, sedimentary characteristics and genetic mechanisms of deep-water gravity flows: A case study of the middle submember in Member 3 of Shahejie Formation in Jiyang Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(9): 1048-1059(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201509003.htm [13] Zhao X Z, Pu X G, Zhou L H, et al. Geologic characteristics of deep water deposit sand exploration discoveries in slope zones of fault lake basin: A case study of Paleogene Shahejie Formation in Banqiao-Qibei slope, Qikou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(2): 171-182. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(17)30022-8 [14] 张庆石, 张革, 陈彬滔, 等. 松辽盆地坳陷期湖底扇沉积特征与分布规律: 以英台地区青山口组为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(3): 318-325. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201403003.htmZhang Q S, Zhang G, Chen B T, et al. Deposition characteristics and distribution pattern of sublaucustrine fan in Qingshankou Formation, Songliao Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2014, 25(3): 318-325(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201403003.htm [15] 杨棵, 朱筱敏, 刘宇, 等. 浊积岩和砂质碎屑流岩关键识别标志及辽河盆地岩心实例[J]. 古地理学报, 2020, 22(3): 483-492. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX202003008.htmYang K, Zhu X M, Liu Y, et al. Key signatures of turbidite and sandy debris and core examples in Liaohe Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography: Chinese Edition, 2020, 22(3): 483-492(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX202003008.htm [16] 郑荣才, 李云, 戴朝成, 等. 白云凹陷珠江组深水扇砂质碎屑流沉积学特征[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2012, 42(6): 1581-1589. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201206002.htmZheng R C, Li Y, Dai C C, et al. Depositional features of sandy debris flow of submarine fan in Zhujiang Formation, Baiyun Sag[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2012, 42(6): 1581-1589(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201206002.htm [17] 李安琪, 叶绮, 王真真, 等. 琼东南盆地陵水凹陷北部梅山组砂质碎屑流沉积特征及油气地质意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 110-118. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10097.shtmlLi A Q, Ye Q, Wang Z Z, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and significance in hydrocarbon exploration of sandy debris flow in Meishan Formation of the northern Lingshui Sag, Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 110-118(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10097.shtml [18] 李楠, 李国辉, 吴长江, 等. 坡折带控制下的砂质碎屑流对油气勘探的意义: 以四川盆地上三叠统须家河组为例[J]. 四川地质学报, 2014, 34(4): 505-509. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCDB201404006.htmLi N, Li G H, Wu C J, et al. The application of sandy debris flow under the contrl of slope break to oil-gas exploration[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2014, 34(4): 505-509(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCDB201404006.htm [19] 袁静, 梁绘媛, 梁兵, 等. 湖相重力流沉积特征及发育模式: 以苏北盆地高邮凹陷深凹带戴南组为例[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(3): 348-359. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201603007.htmYuan J, Liang H Y, Liang B, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and development model of lacustrine gravity flow: A case study of Dainan Formation in deep sag belt of Gaoyou Depression, Northern Jiangsu Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(3): 348-359(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201603007.htm [20] 余烨, 王莉, 尹太举, 等. 下刚果盆地早白垩世巴雷姆晚期深水重力流沉积的发现及意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2020, 22(4): 620-634. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX202004002.htmYu Y, Wang L, Yin T J, et al. Discovery and significance of deep-water gravity-flow deposits of the Late Barremian of Early Cretaceous in Lower Congo Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography: Chinese Edition, 2020, 22(4): 620-634(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX202004002.htm [21] 王颖, 王晓州, 王英民, 等. 沉积物理模拟实验在确定重力流临界坡度中的应用[J]. 成都理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2010, 37(4): 463-468. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201004017.htmWang Y, Wang X Z, Wang Y M, et al. Determination of the gravity flow critical gradient using sedimentary simulation experiment[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology: Science & Technology Edition, 2010, 37(4): 463-468(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201004017.htm [22] Lee H J, Syvitski J P M, Parker G, et al. Distinguishing sediment waves from slope failure deposits: Field examples, including the "Humboldt slide" and modeling results[J]. Marine Geology, 2002, 192(13): 79-104. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/James_Syvitski/publication/222317246_Distinguishing_sediment_waves_from_slope_failure_deposits_field_examples_including_the_'Humboldt_slide'_and_modelling_results/links/09e41502eabf805560000000.pdf [23] 裴羽, 何幼斌, 李华, 等. 高密度浊流和砂质碎屑流关系的探讨[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(6): 1281-1293. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201506010.htmPei Y, He Y B, Li H, et al. Discuss about relationship between high-density turbidity current and sandy debris flow[J]. Geological Review, 2015, 61(6): 1281-1293(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201506010.htm [24] Gee M J R, Masson D G, Watts A B, et al. The Saharan debris flow: An insight into the mechanics of long runout submarine debris flows[J]. Sedimentology, 1999, 46(2): 317-335. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Martin_Gee/publication/263562771_The_Saharan_debris_flow_An_insight_into_the_mechanics_of_long_runout_submarine_debris_flows/links/5644274008aef646e6ca6bbc/The-Saharan-debris-flow-An-insight-into-the-mechanics-of-long-runout-submarine-debris-flows.pdf [25] Shanmugam G. 深水砂体成因研究新进展[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(3): 294-301. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201303007.htmShanmugam G. New perspectives on deep-water sandstones: Implications[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(3): 294-301(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201303007.htm [26] 金杰华, 操应长, 王健, 等. 深水砂质碎屑流沉积: 概念-沉积过程与沉积特征[J]. 地质论评, 2019, 65(3): 689-702. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201903016.htmJin J H, Cao Y C, Wang J, et al. Deep-water sandy debris flow deposits: Concepts, sedimentary processes and characteristics[J]. Geological Review, 2019, 65(3): 689-702(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201903016.htm [27] Mulder T, Chapron E. Flood deposits in continental and marine environments: Character and significance[J]. AAPG Studies in Geology, 2011, 61: 1-30. http://swbplus.bsz-bw.de/bsz37052196Xinh.pdf;jsessionid=4252A327F9793E5383FF5E150A66522A?1438277983121 [28] Mutti E, Tinterri R, Benevelli G, et al. Deltaic, mixed and turbidite sedimentation of ancient foreland basins[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2003, 20: 733-755. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035416601010_3e04.html [29] Girard F, Ghienne J F, Rubino J L. Occurrence of hyperpycnal flows and hybrid event beds related to glacial outburst events in a Late Ordovician proglacial delta(Murzuq Basin, SW Libya)[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2012, 82: 688-708. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2012JSedR..82..688G [30] 龚再升. 中国近海含油气盆地新构造运动和油气成藏[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2004, 25(2): 133-138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200402002.htmGong Z S. Neotectonic movement and hydrocarbon accumulation in petroliferous basins, offshore China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2004, 25(2): 133-138(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200402002.htm [31] 任建业, 雷超. 莺歌海-琼东南盆地构造-地层格架及南海动力变形分区[J]. 地球物理学报, 2011, 54(12): 3303-3314. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201112030.htmRen J Y, Lei C. Teetonie stratigraphic framework of Yinggehai-Qiongdongnan Basin sand its impliection for tectonic province division in South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2011, 54(12): 3303-3314(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201112030.htm [32] 谢玉洪. 莺琼盆地区中央峡谷源头沉积特征及油气勘探前景[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(5): 69-78. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10052.shtmlXie Y H. Sedimentary characteristics and hydrocarbon exploration potential of the upstream of the Central Canyon in the Yinggehai and Qiongdongnan basins[J]. Bulletin of Geological Scienceand Technology, 2020, 39(5): 69-78(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10052.shtml [33] 何家雄, 黄火尧, 陈龙操. 莺歌海盆地泥底辟发育演化与油气运聚机制[J]. 沉积学报, 1994, 12(3): 120-129. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB403.014.htmHe J X, Huang H R, Chen L C. The formation and evolution of mud diapir and its relationship with hydrocarbon accumulation mechanism in Yinggehai Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1994, 12(3): 120-129(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB403.014.htm [34] 何卫军, 谢金有, 刘新宇, 等. 莺歌海盆地DF1-1-11井有孔虫生物地层与沉积环境研究[J]. 地层学杂志, 2011, 35(1): 81-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201101015.htmHe W J, Xie J Y, Liu X Y, et al. Foraminiferal biostratigraphy and sedimentary environment reconstruction based on paleontological data from bore hole DF1-1-11, Yinggehai Basin[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2011, 35(1): 81-87(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201101015.htm [35] 王策. 莺歌海盆地上中新统-更新统储层物源识别: 来自碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学制约[D]. 广州: 中国科学院研究生院, 广州地球化学研究所, 2016.Wang C. Provence discrimination of Upper Miocene to Pleistocene reservoirs in the Yinggehai Basin: Constrains from detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of sedimentary rocks[D]. Guangzhou: Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, 2016 (in Chinese with English abstract). [36] 王策, 梁新权, 付建刚, 等. 莺歌海盆地莺歌海组二段碎屑锆石U-Pb定年及其物源意义[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(增刊1): 716-717. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP2015S1337.htmWang C, Liang X Q, Fu J G, et al. U-Pb dating of detrital zircons from the second member of the Yinggehai Formation in the Yinggehai Basin and its provenance significance[J]. Geological Review, 2015, 61(S1): 716-717(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP2015S1337.htm [37] Wang C, Liang X Q, Xie Y H, et al. Provenance of Upper Miocene to Quaternary sediments in the Yinggehai-Songhong Basin, South China Sea: Evidence from detrital zircon U-Pb ages[J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 355: 202-217. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000036544190010_df71.html -





 下载:
下载: