Three-dimensional comprehensive model and deep prediction of the Jinqingding gold deposit, Muping-Rushan metallogenic belt, Shandong, China
-
摘要: 探讨山东牟平-乳山成矿带金青顶金矿区成矿元素地球化学场三维分布特征,总结成矿规律,建立三维综合找矿模型,为金矿深部成矿预测提供更为丰富的信息,指导矿山生产与发展方向。针对金青顶矿区深部找矿问题,在全面收集已有地质、矿产资料的基础上,结合野外实地调查,应用三维建模与可视化技术、构造叠加晕及地质统计学理论与方法,构建矿床地质、地球化学场等方面的三维综合找矿模型,将金青顶矿床的预测评价研究拓展到三维空间,揭示了区内成矿地质特征和地球化学异常表征,据此探讨了矿体及地球化学场的三维空间分布规律。并在此基础上,开展了矿区的地质-地球化学综合信息分析与深部预测评价,减少了深部预测的不确定性。矿体三维模型显示,矿体呈现中间宽两端窄的形态,有向深部尖灭的趋势。三维地球化学场分布特征显示,Au、As、Sb、Hg、Cu、W、Sn、Co、Ni元素及组合因子主要分布于矿体浅部,向深部呈现元素场强度下降的趋势;Mo、Bi元素主要分布于矿体深部;Ag、Pb、Zn元素分布较分散,存在多个矿化中心。地质-地球化学三维模型显示,组合因子高得分区域与组合矿物富集区域相符合,Au成矿作用主要发生于矿体浅部,深部成矿作用减弱。应用格里戈良分带指数法求取Ⅱ号金矿体的原生晕垂向分带序列为Sb-Cu-Ni-Au-Sn-W-Hg-As-Co-Ag-Zn-Pb-Mo-Bi,该序列与单一期次成矿垂向分带序列进行对比无明显反常现象,指示Ⅱ号矿体当前开采深度以下成矿潜力不高。研究结果显示,在综合找矿模型指导下,基于三维地球化学空间场晕模型的三维地质、地球化学异常信息的展示、提取与综合分析,可以有效地评价深部成矿潜力,为深部成矿预测研究提供了新思路,有利于指导矿山工作的部署。综合分析认为金青顶Ⅱ号主矿体在-1 200 m以下找矿潜力一般,不宜继续进行大规模的深部探矿。Abstract: The study of the three-dimensional(3D) distribution characteristics of ore-forming element geochemical field in Jinqingding gold deposit, Mouping-Rushan metallogenic belt, Shandong Province, summarizes the metallogenic law and establishes a 3D comprehensive prospecting model. It provides richer information for deep prediction and guides the direction of mine production and development. In this study, 3D modelling of the deposit and its geochemical field was carried out. Guided by the prospecting model of this deposit, the 3D geological bodies and 3D geochemical model of ore bodies were built up in this study based on comprehensive analysis upon the geological and geochemical data in this deposit, by using 3D modelling visualization technology and geostatistics. These models reveal the ore bodies features and geochemical characterization of this deposit. In order to reduce the uncertainty of the deep prospecting information, the 3D modelling of the Jinqingding gold deposit was carried out by the comprehensive information analysis and prediction of geology and geochemistry in the study area. The 3D model of the ore body shows that the ore body is wide in the middle and narrow at ends, and tends to narrow and disappear to the deep. The distribution characteristics of the geochemical field show that the elements and combination factors of Au, As, Sb, Hg, Cu, W, Sn, Co, Ni are distributed in the shallow part of the ore bodies, showing a decreasing trend of element-field strength to the deep. The characteristics of Mo and Bi are distributed deep in the ore bodies. The characteristics of Ag, Pb, and Zn are more scattered and there are multiple metallogenic centers. The 3D model of the combination geochemical field shows that the metallogenesis of gold occurred in the shallow area of the ore bodies, while it weakened in the deep. The results show that guided by the comprehensive prospecting model, the display, extraction and comprehensive analysis of 3D geological and geochemical anomaly information based on the 3D geochemical field model effectively evaluate the potential of deep prospecting and provide the evidences for deep prospecting prediction. The comprehensive analysis results show that the prospecting potential of the No.2 orebody of the Jinqingding gold deposit below -1 200 m is low-expected, and it is inappropriate to continue deep exploration massively.
-
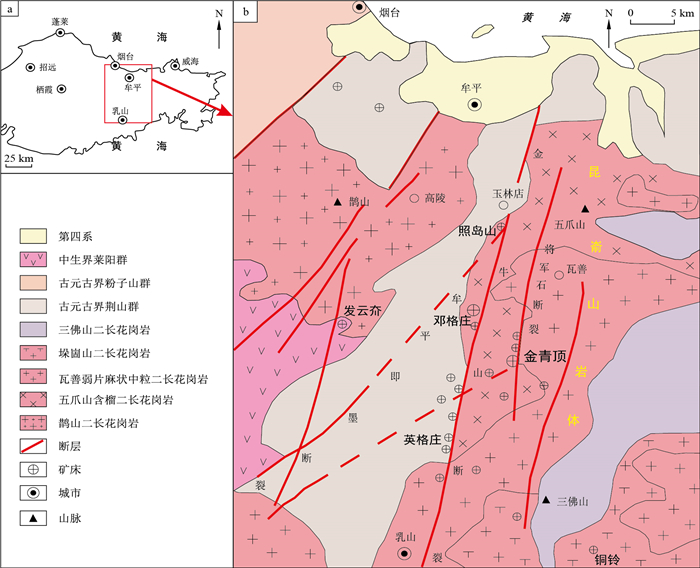
图 1 山东牟乳地区区域地质略图(底图据文献[10]修改)
Figure 1. Regional geological sketch of the Muping-Rushan area, Shandong
图 14 金青顶金矿构造叠加晕模式图(底图据文献[9]修改)
Figure 14. Structural superimposed halo model of the Jinqingding gold deposit
表 1 数据类型及数量
Table 1. Data type and quantity
数据类型 数量 区域地质图 7张 地形地质图 12张 垂直纵投影图 40张 中段地质图 40张 勘探线剖面图 89张 采样点化验数据 1 027组 数据库 3个 表 2 金青顶金矿构造叠加晕元素分带参数
Table 2. Parameters of structure superimposed halo elements of the Jinqingding gold deposit
元素 Au As Sb Ag Cu Pb Zn Bi Mo Co Ni W Sn Hg wB/10-6 wB/10-9 外带 0.5 10 0.8 5 20 30 80 0.8 6 20 10 10 5 20 中带 5 20 1.5 10 80 120 200 3 15 40 20 20 10 40 内带 10 80 3 20 480 480 800 12 25 60 40 40 20 80 高浓带 20 320 6 40 960 960 1 600 36 100 120 80 80 40 160 表 3 因子分析总方差特征表
Table 3. Total variance feature of factor analysis
成分 初始特征值 提取平方和载入 旋转平方和载入 合计 方差/% 累积/% 合计 方差/% 累积/% 合计 方差/% 累积/% F1 5.189 37.067 37.067 5.189 37.067 37.067 4.686 33.469 33.469 F2 2.052 14.656 51.724 2.052 14.656 51.724 2.096 14.971 48.440 F3 1.600 11.430 63.153 1.600 11.430 63.153 2.060 14.714 63.153 表 4 旋转后因子载荷矩阵
Table 4. Rotated factor load matrix
元素 成分 F1 F2 F3 Au 0.866 0.056 0.121 As 0.827 0.115 0.111 Sb 0.289 -0.049 0.672 Hg 0.647 -0.128 0.519 Ag 0.839 0.319 -0.093 Cu 0.486 0.085 0.489 Pb 0.140 0.880 -0.019 Zn 0.210 0.694 0.103 Bi 0.674 0.200 -0.336 Mo 0.090 0.709 -0.029 Co 0.902 0.121 0.081 Ni 0.649 0.190 0.088 W -0.220 -0.117 0.748 Sn -0.018 0.301 0.605 -
[1] Houlding S W. 3D geoscience modeling: Computer techniques for geological characterization[M]. London: Springer-Verlag, 1993. [2] 毛先成. 三维数字矿床与隐伏矿体立体定量预测研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2006.Mao X C. Research on 3D digital deposit and stereo quantitative prediction of concealed ore body[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2006 (in Chinese with English abstract). [3] 王守民. 三维可视化技术在数字矿山中的应用研究[J]. 世界有色金属, 2019, 26(7): 12, 14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO201907007.htmWang S M. Application research of 3D visualization technology in digital mine[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2019, 26(7): 12, 14 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO201907007.htm [4] Zhang Z Q, Wang G W, Ma Z B, et al. Interactive 3D modeling by integration of geoscience datasets for exploration targeting in Luanchuan Mo polymetallic district, China[J]. Natural Resources Research, 2018, 27(3): 315-346. doi: 10.1007/s11053-017-9353-4 [5] 王方里. 三维地质建模技术在地勘找矿中的应用[J]. 世界有色金属, 2020, 27(14): 145-146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2020.14.067Wang F L. Application of 3D geological modeling technology in geological prospecting[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2020, 27(14): 145-146 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2020.14.067 [6] 陈麒玉, 刘刚, 何珍文, 等. 面向地质大数据的结构-属性一体化三维地质建模技术现状与展望[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(4): 51-58. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9999.shtmlChen L Y, Liu G, He Z W, et al. Current situation and prospect of structure-attribute integrated 3D geological modeling technology for geological big data[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(4): 51-58 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9999.shtml [7] Fisher L A, Cleverley J S, Pownceby M, et al. 3D representation of geochemical data, the corresponding alteration and associated REE mobility at the Ranger uranium deposit, Northern Territory, Australia[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2013, 48(8): 947-966. doi: 10.1007/s00126-013-0463-6 [8] 李惠, 禹斌, 魏江, 等. 矿区深部盲矿预测新突破: 构造叠加晕找盲矿法[J]. 矿产勘查, 2019, 10(12): 3070-3073. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2019.12.033Li H, Yu B, Wei J, et al. New breakthrough in the prediction of deep blind ore in mining area: Structural superimposed halo for blind ore method[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2019, 10(12): 3070-3073 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2019.12.033 [9] 李惠, 禹斌, 李德亮, 等. 构造叠加晕找盲矿法及研究方法[J]. 地质与勘探, 2013, 49(1): 154-161. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201301017.htmLi H, Yu B, Li D L, et al. Prediction of blind ore bodies using structural superimposed halo and research methods[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2013, 49(1): 154-161 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201301017.htm [10] 陈海燕. 胶东金青顶金矿成因矿物学与深部远景研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2010.Chen H Y. Genetic mineralogy and deep prospects of Jinqingding gold deposit in Rushan, east Shandong Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2010 (in Chinese with English abstract). [11] 刘善宝. 山东乳山金青顶金矿田成矿规律及其成矿远景研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2005.Liu S B. Themetallegenic regularity of the Jinqingding gold deposit field and ore prospecting, in Rushan, Shandong Province[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2005 (in Chinese with English abstract). [12] 宋波. 山东乳山金矿带金矿矿床成因与找矿标志分析[J]. 世界有色金属, 2019, 26(17): 82, 84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO201917053.htmSong B. The genesis and prospecting marks of the gold deposits in Shandong's Rushan gold belt[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2019, 26(17): 82, 84 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO201917053.htm [13] 宋明春, 林少一, 杨立强, 等. 胶东金矿成矿模式[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39(2): 215-236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202002002.htmSong M C, Lin S Y, Yang L Q et al. Metallogenic model of Jiaodong peninsula gold deposits[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2020, 39(2): 215-236 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202002002.htm [14] Hu R Z, Burnard P G, Bi X W, et al. Helium and argon isotope geochemistry of alkaline intrusion-associated gold and copper deposits along the Red River-Jinshajiang fault belt, SW China[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 203: 305-317. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2003.10.006 [15] Cai Y C, Fan H R, Santosh M, et al. Evolution of the lithospheric mantle beneath the southeastern North China Craton: Constraints from mafic dikes in the Jiaobei terrain[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 24(2): 601-621. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.11.013 [16] Deng J, Yang L Q, David I G, et al. An integrated mineral system model for the gold deposits of the giant Jiaodong Province, eastern China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 208(9): 274-295. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012825220303202 [17] 张铭, 谭俊, 王怀洪, 等. 山东范家庄金矿床S、Pb同位素组成及对成矿物质来源的示踪[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(4): 124-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904013.htmZhang M, Tan J, Wang H H, et al. Sulfur and lead isotopic compositions of the Fanjiazhuang gold deposit and their implications for sources of ore-forming materials, Shandong Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(4): 124-133 (in Chinese with English abstract https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904013.htm [18] Bi S J, Zhao X F. 40Ar/39Ar dating of the Jiehe gold deposit in the Jiaodong Peninsula, Eastern North China Craton: Implications for regional gold metallogeny[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 86(6): 639-651. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=721f61ba027502db893467aa5e8ed5a7 [19] Li L, Li S R, Santosh M, et al. Dyke swarms and their role in the genesis of world-class gold deposits: Insights from the Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 130(15): 2-22. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Sheng-Rong_Li/publication/305385799_Dyke_swarms_and_their_role_in_the_genesis_of_world-class_gold_deposits_Insights_from_the_Jiaodong_peninsula_China/links/57a407f108ae455e8534d6b8.pdf [20] Li S R, Santosh M, Zhang H F, et al. Inhomogeneous lithospheric thinning in the central North China Craton: Zircon U-Pb and S-He-Ar isotopic record from magmatism and metallogeny in the Taihang Mountains[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23(1): 141-160. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.006 [21] Liu S, Hu R Z, Gao S, et al. Petrogenesis of Late Mesozoic mafic dykes in the Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern North China Craton and implications for the foundering of lower crust[J]. Lithos, 2009, 113(3/4): 621-639. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493709002801 [22] 宋英昕, 宋明春, 孙伟清, 等. 胶东金矿成矿时代及区域地壳演化: 基性脉岩的SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(5): 908-919. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201805013.htmSong Y X, Song M C, Sun W Q, et al. Metallogenic epoch and regional crust evolution in the Jiaodong gold deposit, Shandong Province: Evidence from SHRIMP zircon U-Pb ages of mafic dykes[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2018, 37(5): 908-919 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201805013.htm [23] 刘执腾. 山东地区金矿床地球化学找矿模型[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018.Liu Z T. Geochemical exploration model of gold deposits in Shandong Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2018 (in Chinese with English abstract). [24] Xu W G, Fan H R, Yang K F, et al. Gold mineralizing efficiency during hydrothermal alteration of the Mesozoic granitoids in the northwest Jiaodong Peninsula: Contrasting conditions between the Guojialing and Linglong plutons[J]. Chemie der Erde - Geochemistry - Interdisciplinary Journal for Chemical Problems of the Geosciences and Geoecology, 2017, 77(3): 387-398. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009281916302938 [25] 李胜荣, 陈光远, 绍伟, 等. 胶东乳山金矿田成因矿物学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1996.Li S R, Chen G Y, Shao W, et al. Genetic mineralogy of Rushan gold field in Jiaodong[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1996 (in Chinese). [26] Stephanie E M, Andrew G T, Roberto F W, et al. Implications of pyrite geochemistry for gold mineralisation and remobilisation in the Jiaodong gold district, northeast China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 71(12): 150-168. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Andrew_Tomkins4/publication/276486183_Implications_of_pyrite_geochemistry_for_gold_mineralisation_and_remobilisation_in_the_Jiaodong_gold_district_northeast_China/links/55ea14a108aeb6516265e28d.pdf [27] 崔举超. 胶东牟-乳金成矿带成因矿物学研究及其找矿意义[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2012.Cui J C. Genetic mineralogy in gold ore-forming belt of Muping-Rushan in Jiaodong[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2012 (in Chinese with English abstract). [28] Hu F F, Fan H R, Yang J H, et al. Mineralizing age of the Rushan lode gold deposit in the Jiaodong Peninsula: SHRIMP U-Pb dating on hydrothermal zircon[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(3): 1629-1636. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/86894X/2004015/10501983.html [29] 尹升, 张海芳, 王芳, 等. 山东金青顶金矿床Ⅱ号矿体成矿特征[J]. 山东国土资源, 2015, 31(11): 9-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2015.11.003Yin S, Zhang H F, Wang F, et al. Metallogenic characteristics of No. Ⅱ orebody in Jinqingding gold deposit in Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2015, 31(11): 9-14 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2015.11.003 [30] Ma L, Jiang S Y, Hofmann A W, et al. Lithospheric and asthenospheric sources of lamprophyres in the Jiaodong Peninsula: A consequence of rapid lithospheric thinning beneath the North China Craton?[J]. Geochinica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 124(1): 250-271. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016703713005449 [31] Chen B H, Deng J, Wei H T, et al. Trace element geochemistry in quartz in the Jinqingding gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Implications for the gold precipitation mechanism[J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(5): 326-336. doi: 10.3390/min9050326 [32] Chen H Y, Li S R, Zhang X B, et al. Wallrock alteration and gold mineralization in the Jinqingding gold deposit, eastern Shandong Province[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy Petrology & Geochemistry, 2012, 31(1): 5-13. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/281527290_Wall_rock_alteration_and_gold_mineralization_in_the_Jinqingding_gold_deposit_eastern_Shandong_province [33] Li N, Song X L, Xiao K Y, et al. Part Ⅱ: A demonstration of integrating multiple-scale 3D modelling into GIS-based prospectivity analysis: A case study of the Huayuan-Malichang district, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 95(4): 292-305. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136817309927 [34] 李惠. 山东省乳山金青顶金矿跟踪研究报告[R]. 河北保定: 中国冶金地质总局地球物理勘查院物探中心, 2010.Li H. Tracking research report ofJinqingding gold deposit in Rushan, Shandong Province[R]. Baoding Hebei: Geophysical Exploration Center, Geopysical Exploration Academy of China Metallurgical Geology Bureau, 2010. [35] Chen J P, Shi R, Chen Z P, et al. 3D positional and quantitative prediction of the Xiaoqinling gold ore belt in Tongguan, Shanxi, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 86(3): 653-660. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2012.00693.x [36] 王恺其, 肖凡. 多点地质统计学的理论、方法、应用及发展现状[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6): 256-268. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906031.htmWang K Q, Xiao F. Multiple-points geostatistics: A review of theories methods and applications[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(6): 256-268 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906031.htm [37] 刘乐, 杨智. 基于钻孔数据的三维地质建模空间插值方法的对比研究[J]. 能源技术与管理, 2019, 44(3): 162-164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9943.2019.03.063Liu L, Yang Z. Comparative study on spatial interpolation methods of 3D geological modeling based on borehole data[J]. Energy Technology and Management, 2019, 44(3): 162-164 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9943.2019.03.063 [38] 林成贵, 程志中, 吕志成, 等. 甘肃省早子沟金矿原生晕分带特征及深部找矿预测[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2020, 50(1): 70-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202001006.htmLin C G, Cheng Z Z, Lü Z C, et al. Characteristics of primary halo zonation and deep ore prediction in Zaozigou gold deposit, Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2020, 50(1): 70-84 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202001006.htm -





 下载:
下载: