Sedimentary characteristics and significance in hydrocarbon exploration of sandy debris flow in Meishan Formation of the northern Lingshui Sag, Qiongdongnan Basin
-
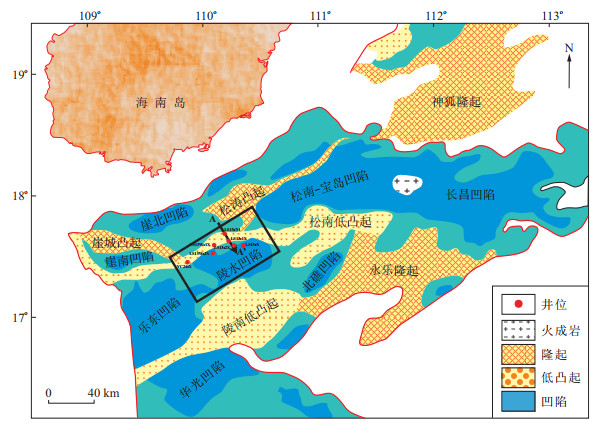
摘要: 通过岩心描述以及粒度、薄片资料的综合分析,结合区域古地貌特征、地震相研究成果,详细论述了琼东南盆地陵水凹陷北部梅山组砂质碎屑流砂岩沉积构造特征及识别标志,并在此基础上建立了研究区砂质碎屑流沉积模式。研究区梅山组砂质碎屑流砂岩主要为厚层块状构造粉砂岩-极细砂岩以及具有丰富同生变形构造的粉砂质泥岩、泥岩与粉砂岩互层2种岩性组合,成因为陆架坡折之上的三角洲前缘、前三角洲沉积物发生整体性"冻结"滑动、滑塌再沉积所形成,其平面分布主要受陆架坡折所控制,大致呈平行于陆架坡折带分布的舌形形态。结合区域油气成藏要素研究认为研究区砂质碎屑流砂岩可通过沟源断层沟通深部烃源岩,形成下生上储型岩性油气藏,为琼东南盆地大中型油气藏勘探突破的重点领域。Abstract: Through comprehensive analysis of core description, core slice observation and grain size data, in combination with regional palaeogeomorphology and seismic facies study, the sedimentary structure characteristics and its identification mark of the Meishan Formation sandy debris flow in northern Lingshui Sag of Qiongdongnan Basin were discussed in details.The sedimentary model of sandy debris flow in the study area is then established based on its sedimentary environment and characteristics.Two main lithological associations developed in sandy debris flow sedimentation in the Meishan Formation, which were thick massive bedding siltstone to very fine sandstone without sedimentary structure and silty mudstone, mudstone and siltstone interbeds with abundant contemporaneous deformation structure.These lithological associations formed during the process when the sediments of the delta front and the pre-delta on the shelf went frozen sliding as whole and collapsed and deposited again as sandy debris flow.Their distribution was mainly controlled by the shelf break and roughly distributed parallel to the shelf break showing tongue shaped outline.Combined with regional hydrocarbon accumulation elements study, it was thought the sandy debris flow sandstone in the study area could form lower-generation and upper-reservoir type lithological reservoirs with faults connecting to deep source rock, and this would be an important exploration break through to realize the exploration breakthrough in finding large and medium-sized oil and gas reservoirs in Qiongdongnan Basin.
-
图 9 陵水凹陷北部砂质碎屑流砂岩地震反射特征典型剖面
Figure 9. Typical seismic reflection characteristics of sandy debris flow sandstone in the northern Lingshui Sag (section position as shown in Fig. 1, A-A′)
-
[1] Purvis K, Kao J, Flanagan K, et al.Complex reservoir geometries in a deepwater clastic sequence, Gryphon Field, UKCS:Injection structures, geological modeling and reservoir simulation[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2002, 19(2):161-179. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(02)00003-X [2] Hursta D.Fluidization and injection in the deepwater sandstones of the Eocene Alba Formation(UK.North Sea)[J].Sedimentology, 2004, 51(3):503-529. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.2004.00634.x [3] Shanmugam G, Shrivastava S K.Sandydebrites and tidalites of Pliocene reservoir sands in upper slope canyon environments, offshore Krishna Godavari Basin(India):Implications[J].Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2009, 79(9):736-756. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2009.076 [4] 李相博, 刘化清, 陈启林, 等.大型坳陷湖盆沉积坡折带特征及其对砂体与油气的控制作用:以鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组为例[J].沉积学报, 2010, 28(4):717-729. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201004008.htm [5] 袁珍, 李文厚, 范萌萌, 等.深水块状砂岩沉积特征及其成因机制探讨:以鄂尔多斯盆地东南缘上三叠统长6油层组为例[J].地质科技情报, 2011, 30(4):43-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2011.04.006 [6] 李相博, 刘化清, 完颜容, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组砂质碎屑流储集体的首次发现[J].岩性油气藏, 2009, 21(4):19-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2009.04.003 [7] 张建新, 范彩伟, 谭建财, 等.莺歌海盆地中新世沉积体系演化特征及勘探意义[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6):51-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906008.htm [8] 王华, 陈思, 巩天浩, 等.牵引流化重力流沉积过程与堆积机制:以渤海湾盆地歧口凹陷为例[J].地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1):95-104. http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9930.shtml [9] Shanmugam G.Perception vs. reality in deep water exploration[J].World Oil, 1996, 217:37-41. http://scitation.aip.org/getabs/servlet/GetabsServlet?prog=normal&id=SEGEAB000015000001001922000001&idtype=cvips&prog=normal [10] Shanmugam G.50 Years of the turbidite paradigm(1950s-1990s):Deep water processes and facies models:A critical perspective[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2000, 17:285-342. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(99)00011-2 [11] Amy L A, Talling P J, Peakall J, et al.Bed geometry used to test recognition criteria of turbidites and(sandy)debrites[J].Sedimentary Geology, 2005, 179(1/2):163-174. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0037073805001740 [12] Migeon S, Ducassou E, Le Gonidec Y, et al.Lobe construction and sand/mud segregation by turbidity currents and debris flows on the western Nile deep sea fan(Eastern Mediterranean)[J].Sedimentary Geology, 2010, 229(3):124-143. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2010.02.011 [13] 陈宇航, 朱增伍, 贾鹏, 等.重力流沉积砂岩的成因、改造及油气勘探意义[J].地质科技情报, 2017, 36(5):148-155. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201705020.htm [14] 鲜本忠, 安思奇, 施文华.水下碎屑流沉积:深水沉积研究热点与进展[J].地质论评, 2014, 60(1):39-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201401005.htm [15] 高红灿, 郑荣才, 魏钦廉, 等.碎屑流与浊流的流体性质及沉积特征研究进展[J].地球科学进展, 2012, 27(8):815-827. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201208000.htm [16] 范彩伟, 李绪深, 刘昆, 等.琼东南盆地乐东、陵水凹陷中新统岩性地层圈闭成藏条件[J].中国海上油气, 2016, 28(2):53-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201602006.htm [17] 谢玉洪, 范彩伟, 周家雄, 等.琼东南盆地中中新世重力流海底扇沉积特征及控制因素[J].天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(2):220-228. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201602004.htm [18] 左倩媚, 张道军, 王亚辉, 等.琼东南盆地深水区新近系海底扇沉积特征与资源潜力[J].海洋学报, 2016, 38(11):105-116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2016.11.010 [19] 朱伟林, 张功成, 高乐.南海北部大陆边缘盆地油气地质特征与勘探方向[J].石油学报, 2008, 29(1):1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200801002.htm [20] 王振峰, 李绪深, 孙志鹏, 等.琼东南盆地深水区油气成藏条件和勘探潜力[J].中国海上油气, 2011, 23(1):7-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201101001.htm [21] Coussot P, Meunier M.Recognition, classification and mechanical description of debris flows[J].Earth Science Reviews, 1996, 40(3/4):209-227. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0012825295000658 [22] Talling P J, Masson D G, Sumner E J, et al.Subaqueous sediment density flows:Depositional processes and deposit types[J].Sedimentology, 2012, 59:1937-2003. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.2012.01353.x [23] 李相博, 刘化清, 张忠义, 等.深水块状砂岩碎屑流成因的直接证据:"泥包砾"结构:以鄂尔多斯盆地上三叠统延长组研究为例[J].沉积学报, 2014, 32(4):611-622. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201404001.htm [24] 刘忠保, 张春生, 龚文平, 等.牵引流砂质载荷沿陡坡滑动形成砂质碎屑流沉积模拟研究[J].石油天然气学报, 2008, 30(6):30-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX200806007.htm [25] 王颖, 王晓州, 王英民, 等.沉积物理模拟实验在确定重力流临界坡度中的应用[J].成都理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 37(4):463-468. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201004017.htm [26] 何云龙, 解习农, 李俊良, 等.琼东南盆地陆坡体系发育特征及其控制因素[J].地质科技情报, 2010, 29(2):118-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201002022.htm [27] Mohrig D, Ellis C, Parker G, et al.Hydroplaning of subaqueous debris flows[J].GSA Bulletin, 1998, 110:387-394. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1998GSAB..110..387M [28] Talling P J.Hybrid submarine flows comprising turbidity current and cohesive debris flow:Deposits, theoretical and experimental analyses, and generalized models[J].Geosphere, 2013, 9(3):460-488. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2013Geosp...9..460T [29] 邹才能, 陶士振, 袁选俊, 等."连续型"油气藏及其在全球的重要性:成藏、分布与评价[J].石油勘探与开发, 2009, 36(6):669-682. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200906003.htm [30] 邹才能, 陶士振, 袁选俊, 等.连续型油气藏形成条件与分布特征[J].石油学报, 2009, 30(3):324-331. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200903003.htm [31] 沈怀磊, 张功成, 孙志鹏, 等.琼东南盆地深水区富气凹陷形成控制因素与勘探实践:以陵水凹陷为例[J].石油学报, 2013, 34(增刊2):83-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2013S2011.htm [32] 黄保家, 李绪深, 王振峰, 等.琼东南盆地深水区烃源岩地球化学特征与天然气潜力[J].中国海上油气, 2012, 24(4):1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201204002.htm -





 下载:
下载: