Hydrocarbon generation characteristics and signification of source rock in different oil-rich depressions in the eastern part of the Bohai Sea
-
摘要: 渤海海域东部发育多个富油凹陷,具有较大的生烃潜力,由于各凹陷形成和发育过程不同,导致不同凹陷、不同层段烃源岩热演化和生、排烃特征具有明显差异。通过对渤海海域东部3个富油凹陷多套烃源岩进行埋藏史、热史和生、排烃史研究,厘定了渤中凹陷、渤东凹陷和庙西凹陷烃源岩生、排烃时间以及演化特征。结果表明:①渤海海域东部地区不同构造单元烃源岩热演化程度具有"西高东低"的趋势,渤中凹陷最早生烃时间为31.5 Ma,渤东凹陷和庙西凹陷最早生烃时间分别为28.2,11.2 Ma,渤中凹陷最早排烃时间为27.8 Ma,而渤东凹陷和庙西凹陷最早排烃时间分别为20.9,6.7 Ma;②渤中凹陷烃源岩热演化程度较高,现今主要为储层提供天然气,为环渤中凹陷地区形成天然气藏和凝析气藏提供了气源;渤东凹陷、庙西凹陷热演化程度依次降低,为储层提供大量油源,盆地边缘地区主要以油藏为主。Abstract: There are numerous oil-rich depressions in the eastern part of the Bohai Sea, which have a large hydrocarbon generation potential.Due to differences in the formation and development of these depressions, the thermal evolution and hydrocarbon generation and expulsion characteristics of the source rocks in different depressions and intervals are quite different.By studying the burial history, thermal history, and hydrocarbon generation and expulsion history of multiple sets of source rocks in three oil-rich depressions in eastern Bohai Sea, this paper determines the source rock generation, hydrocarbon expulsion timing and evolution characteristics of the Bozhong Depression, Bodong Depression and Miaoxi Depression.The results indicate that: ① The thermal evolution of source rocks in individual tectonic units in the eastern Bohai Sea has a general end of "high in the west and low in the east".The earliest hydrocarbon generation time in the Bozhong Depression is 34.4 Ma, while that for the Bodong and Miaoxi depressions are 30.8 Ma and 14.2 Ma, respectively.The earliest hydrocarbon expulsion time of the Bozhong Depression is 27.8 Ma, while that for the Bodong and Miaoxi depressions are 20.9 Ma and 6.7 Ma, respectively; ② The source rock in the Bozhong Depression has a relatively high degree of thermal evolution, and now it mainly provides natural gas to the reservoirs, which provides a gas source for the formation of natural gas reservoirs and condensate gas reservoirs in the Bozhong area.The degree of thermal evolution in the Bodong Depression and Miaoxi Depression gradually decreases, which provides a large amount of oil source for the reservoirs.The marginal areas of the basin are mainly oil reservoirs.
-
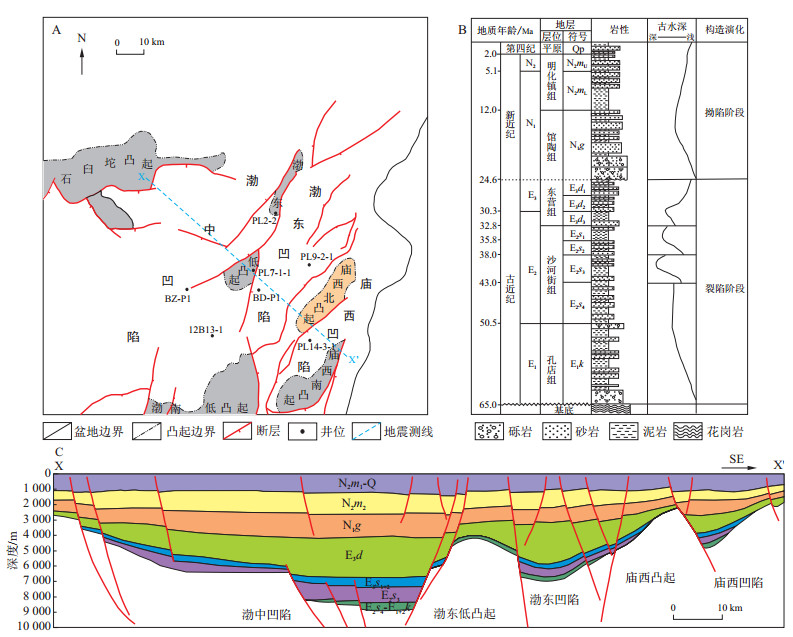
图 1 渤海海域东部地质综合图(据文献[15]修改)
A.研究区平面分布图;B.岩性综合柱状图;C.地震剖面图
Figure 1. Comprehensive geological map of the eastern part of the Bohai Sea
表 1 一维地质模型建立的主要输入参数(据文献[24-32]数据整理)
Table 1. Main input parameters for the establishment of one-dimensional geological model
层位 沉积时间 主要岩性 BZ-P1 BD-P1 PL14-3-1 开始/Ma 结束/Ma 顶深/m 底深/m 剥蚀/m w(TOC)/% HI/(mg·g-1) 顶深/m 底深/m 剥蚀/m w(TOC)/% HI/(mg·g-1) 顶深/m 底深/m 剥蚀/m w(TOC)/% HI/(mg·g-1) 第四系 Qp 2.0 0 灰黄色泥岩与灰绿色粉细砂岩互层 0 640 0 528 0 441 新近系 N2m 12.0 2.0 棕红色泥岩与砂岩互层 640 3 316 528 2 850 441 1 730 N1g 23.0 12.0 灰绿色泥岩、砂砾岩 3 316 4 412 2 850 3 356 1 730 2 475 古近系 E3d1 27.4 23.0 砂岩与泥岩互层 4 412 4 986 100 3 356 3 824 50 600 E3d2 30.3 27.4 深灰色泥页岩 4 986 5 607 1.06 350 3 824 4 360 0.66 320 2 475 3 187 1.30 340 E3d3 32.8 30.3 深灰色泥页岩 5 607 6 334 1.69 450 4 360 5 309 1.99 434 3 187 3 729 2.01 400 E2s1-2 39.5 32.8 泥页岩与白云岩薄互层 6 334 7 632 100 2.83 400 5 309 6 058 150 1.95 550 3 729 4 002 50 2.13 350 E2s3 42.0 39.5 深灰色泥岩 7 632 9 527 150 2.65 550 6 058 7 012 200 2.92 563 4 002 4 412 375 3.00 550 E2s4+ E1-2k 65.0 42.0 紫红色泥岩夹砂岩 9 527 11 107 7 012 7 866 4 412 4 634 表 2 研究区烃源岩地球化学数据(据文献[25, 27, 34-41]数据整理)
Table 2. Geochemical data of source rocks in the study area
凹陷名称 层位 w(TOC)/% (S1+S2)/(mg·g-1) HI/(mg·g-1) 有机质类型 Tmax/℃ 渤中凹陷 E2s3 0.21~1.96 2.02~7.27 50~550 Ⅱ1、Ⅱ2 422~442 E2s1-2 0.42~2.57 6.85~14.92 260~580 Ⅱ1 425~443 E3d3 1.26~3.28 8.01~12.45 220~600 Ⅱ1 425~445 E3d2 1.43~5.14 8.22~24.63 160~700 Ⅱ1 524~440 庙西凹陷 E2s3 0.82~0.97 1.68~2.05 210~412 Ⅱ1、Ⅱ2 / E2s1-2 1.82~2.25 2.36~12.02 226~508 Ⅱ1、Ⅱ2 430~445 E3d3 0.76~3.11 2.64~21.35 220~680 Ⅰ、Ⅱ1 436~445 E3d2 1.99~4.04 9.81~26.34 477~637 Ⅰ、Ⅱ1 431~436 渤东凹陷 E2s3 1.32 / 412 Ⅱ2 / E2s1-2 2.01 11.85 470 Ⅱ1 435~445 E3d3 1.93 10.61 311 Ⅱ1 440 E3d2 2.96 / 556 Ⅱ1 / 表 3 渤海湾盆地不同时期沉积水界面温度和平均大地热流值[43-44]
Table 3. Sedimentary water interface temperature and average terrestrial heat flow in different periods of the Bohai Bay Basin
时间/Ma 65 42 38 32 23.3 5.3 0 SWIT/℃ 23.66 23.22 23.10 22.13 21.02 17.01 16.90 HF/(mW·m-2) 69.01 83.56 82.95 78.52 71.62 63.92 62.93 表 4 渤中凹陷、渤东凹陷和庙西凹陷不同剥蚀厚度下的烃源岩成熟度相对误差
Table 4. Relative error of maturity of source rocks under different denudation thicknesses in Bozhong, Bodong and Miaoxi depressions
剥蚀厚度/m 0 150 初始值 450 600 烃源岩成熟度相对误差/% 渤中凹陷 E2s3 0.49 0 0 0 0.24 E2s1-2 0 0 0 -0.34 0.34 E3d3 -0.52 0 0 -0.52 -0.52 E3d2 0.71 1.42 0 -0.71 1.42 渤东凹陷 E2s3 -0.39 0 0 0.39 0 E2s1-2 0.56 0.56 0 1.12 0 E3d3 0 0 0 0 0 E3d2 -1.01 -1.01 0 -2.02 0 庙西凹陷 E2s3 -1.21 -0.61 0 0 0 E2s1-2 -0.74 0 0 0.74 0 E3d3 0 -0.93 0 0 0.93 E3d2 -1.30 0 0 1.30 0 表 5 渤中凹陷、渤东凹陷和庙西凹陷不同热流值下的烃源岩成熟度相对误差
Table 5. Relative error of maturity of source rocks under different heat flow values in Bozhong, Bodong and Miaoxi depressions
热流值改变量/(mW·m-2) -10 -5 初始值 +5 +10 烃源岩成熟度相对误差/% 渤中凹陷 E2s3 -19.90 -8.74 0 5.58 9.71 E2s1-2 -31.96 -19.26 0 15.12 29.21 E3d3 -32.64 -22.15 0 19.17 40.93 E3d2 -29.79 -14.89 0 19.15 42.55 渤东凹陷 E2s3 -36.72 -24.88 0 19.14 37.11 E2s1-2 -34.83 -22.76 0 21.35 45.51 E3d3 -32.59 -18.52 0 20.00 45.19 E3d2 -25.25 -16.47 0 16.16 36.36 庙西凹陷 E2s3 -28.49 -18.71 0 17.58 36.35 E2s1-2 -26.67 -14.07 0 17.04 36.30 E3d3 -23.36 -15.05 0 14.02 32.71 E3d2 -16.88 -10.00 0 10.39 23.38 -
[1] 文志刚, 何文祥, 米立军, 等. 利用盆地模拟技术评价渤东凹陷下第三系油气勘探潜力[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2004, 15(4): 379-382. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2004.04.011Wen Z G, He W X, Mi L J, et al. Evaluating on hydrocarbon exploration potential of Lower Tertiary in Bodong Depression by basin modelling technique[J]. Natural Gas Geosicience, 2004, 15(4): 379-382(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2004.04.011 [2] 薛永安, 李慧勇. 渤海海域深层太古界变质岩潜山大型凝析气田的发现及其地质意义[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018, 30(3): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201803001.htmXue Y A, Li H Y. Large condensate gas field in deep Archean metamorphic buried hill in Bohai Sea: Discovery and geological significance[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2018, 30(3): 1-9(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201803001.htm [3] 李慧勇, 徐云龙, 王飞龙, 等. 渤海海域深层潜山油气地球化学特征及油气来源[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(1): 45-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201901006.htmLi H Y, Xu Y L, Wang F L, et al. Geochemical characteristics and sources of oil and gas in deep buried hill, Bohai Sea area[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(1): 45-56(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201901006.htm [4] 崔海忠, 王飞龙, 王清斌, 等. 蓬莱20-2油田原油地球化学特征与油源分析[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2019, 33(6): 47-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2019.06.011Cui H Z, Wang F L, Wang Q B, et al. Geochemical characteristics and oil source analysis of crude oil in Penglai 20-2 Oilfield[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2019, 33(6): 47-52(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2019.06.011 [5] 薛永安, 邓运华, 王德英, 等. 蓬莱19-3特大型油田成藏条件及勘探开发关键技术[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(9): 1125-1146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201909010.htmXue Y A, Deng Y H, Wang D Y, et al. Reservoir formation conditions and key exploration & development technologies in PL 19-3 Giant Oilfield[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(9): 1125-1146(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201909010.htm [6] 高喜龙, 肖贤明, 赵必强, 等. 渤海湾盆地渤中凹陷下第三系烃源岩生烃史[J]. 沉积学报, 2004, 22(2): 359-364. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2004.02.025Gao X L, Xiao X M, Zhao B Q, et al. Petroleum generation history of Lower Tertiary source rocks from the Bozhong Depression of the Bohaiwan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2004, 22(2): 359-364(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2004.02.025 [7] 何文祥, 米立军, 文志刚, 等. 渤东凹陷烃源岩生烃潜力研究[J]. 天然气工业, 2005, 25(5): 14-17. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2005.05.004He W X, Mi L J, Wen Z G, et al. Hydrocarbon generation potential of the source rocks in Bodong Sag[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2005, 25(5): 14-17(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2005.05.004 [8] 邹华耀, 周心怀, 郝芳. 渤中地区蓬莱19-3油田油源分析及其成藏与勘探意义[J]. 西安石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2009, 24(1): 13-16, 108-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-064X.2009.01.003Zou H Y, Zhou X H, Hao F. Oil origin analysis of PL19-3 Oil field, Bozhong area and its significance to oil accumulation and exploration[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University: National Science Edition, 2009, 24(1): 13-16, 108-109(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-064X.2009.01.003 [9] 左银辉, 邱楠生, 庞雄奇, 等. 渤海海域沙三段烃源灶演化特征研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2010, 53(10): 2415-2426. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.10.015Zuo Y H, Qiu N S, Pang X Q, et al. Hydrocarbon kitchen evolution of E2s3 source rock of the Bohai Offshore area[J]. Earth and Planetary Physics, 2010, 53(10): 2415-2426(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.10.015 [10] 周毅, 张通彩. 渤中, 渤东凹陷结构认识及有利勘探方向[J]. 中国海上油气: 地质, 1997, 11(6): 432-438. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD199706011.htmZhou Y, Zhang T C. Geological configuration and potential exploration areas of Bozhong and Bodong sags[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas: Geology, 1997, 11(6): 432-438(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD199706011.htm [11] 杨永才, 李友川. 渤海湾盆地渤中凹陷烃源岩地球化学与分布特征[J]. 矿物岩石, 2012, 32(4): 65-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS201204009.htmYang Y C, Li Y C. The geochemical characteristics and distribution of source rocks of the Bozhong Sag in Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2012, 32(4): 65-72(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS201204009.htm [12] 何文祥, 文志刚, 孙磉礅. 渤东凹陷PL2-2-1井区烃源岩生排烃门限研究[J]. 江汉石油学院学报, 2004, 26(2): 11-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2004.02.004He W X, Wen Z G, Sun S D. Source rock hydrocarbon generation and expulsion threshold in Well PL2-2-1 of Bodong Depression[J]. Journal of Jianghan Petroleum Institute, 2004, 26(2): 11-12(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2004.02.004 [13] 宗奕, 梁建设, 刘丽芳. 庙西凹陷构造特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2012, 24(1): 36-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2012.01.007Zong Y, Liang J S, Liu L F. Structural characteristics of Miaoxi Sag[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2012, 24(1): 36-39(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2012.01.007 [14] 田立新, 吴国强, 张金辉. 渤海东部庙西地区隆凹结构的形成及与油气聚集的关系[J]. 石油实验地质, 2014, 36(1): 56-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201401011.htmTian L X, Wu G Q, Zhang J H. Formation of uplifts and sags in Miaoxi area of eastern Bohai Sea and their relationship with hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2014, 36(1): 56-63(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201401011.htm [15] Hao F, Zhou X H, Zhu Y M, et al. Mechanisms of petroleum accumulation in the Bozhong sub-basin, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Part 1: Origin and occurrence of crude oils[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2009, 26(8): 1528-1542. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2008.09.005 [16] 胡志伟, 杨海风, 韩自军, 等. 渤海海域渤中34-9油田火山岩特征及其对油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3): 208-218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903022.htmHu Z W, Yang H F, Han Z J, et al. Characteristics of volcanic rocks and their control actions on hydrocarbon accumulation of Bozhong 34-9 Oilfield in Bohai Sea[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(3): 208-218(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903022.htm [17] 李欢, 王清斌, 庞小军, 等. 致密砂砾岩储层裂缝形成及储层评价: 以黄河口凹陷沙二段为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(1): 176-185. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201901019.htmLi H, Wang Q B, Pang X J, et al. Fracture generation and reservoir evaluation of tight glutenite reservoir: A case study of second Member of Shahejie Formation in Huanghekou Depression[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(1): 176-185(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201901019.htm [18] 何仕斌, 朱伟林, 李丽霞. 渤中坳陷沉积演化和上第三系储盖组合分析[J]. 石油学报, 2001, 22(2): 38-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200102007.htmHe S B, Zhu W L, Li L X. Sedimentary evolution and Neogene reservoir-seal assemblage analysis of Bozhong Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2001, 22(2): 38-43(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200102007.htm [19] 王华, 陈思, 巩天浩, 等. 牵引流化重力流沉积过程与堆积机制: 以渤海湾盆地歧口凹陷为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 95-104. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9930.shtmlWang H, Chen S, Gong T H, et al. Sedimentary process and accumulation mechanism of traction fluidization gravity flow: An example from Qikou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 95-104(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9930.shtml [20] 赵俊峰, 刘池洋, 韩少甲, 等. 渤中凹陷古近纪沙三段沉积期原盆面貌恢复[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(增刊1): 194-202. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE2013S1092.htmZhao J F, Liu C Y, Han S J, et al. Restoration of the original sedimentary extent of Bozhong Sag during the sedimentary period of the third Member of Shahejie Formation in Paleogene[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013, 87(S1): 194-202(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE2013S1092.htm [21] 吴磊, 徐怀民, 季汉成. 渤海湾盆地渤中凹陷古近系沉积体系演化及物源分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(1): 81-88. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200601018.htmWu L, Xu H M, Ji H C. Evolution of sedimentary system and analysis of sedimentary source in Paleogene of Bozhong Sag, Bohai Bay[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(1): 81-88(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200601018.htm [22] 刘丽芳, 林青, 吴克强, 等. 渤海海域渤东地区烃源特征及资源潜力[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2015, 31(9): 28-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201509004.htmLiu L F, Lin Q, Wu K Q, et al. Characteristics of hydrocarbon source rocks and resource potential in the Bodong region of Bohai Sea Basin[J]. Marine Geological Frontiers, 2015, 31(9): 28-37(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201509004.htm [23] 刘可禹, 刘建良. 盆地和含油气系统模拟(BPSM)研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 石油科学通报, 2017, 2(2): 161-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYKE201702001.htmLiu K Y, Liu J L. Current status and future development trends of Basin and Petroleum System Modeling(BPSM)[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2017, 2(2): 161-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYKE201702001.htm [24] 官大勇, 王昕, 刘朋波, 等. 渤海海域庙西南凸起沙河街组低渗透砂岩储层特征及控制因素[J]. 地质科技情报, 2013, 32(2): 58-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201302007.htmGuan D Y, Wang X, Liu P B, et al. Low permeability reservoir characteristics and controlling factors of the South Uplift of Miaoxi in Bohai Bay[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2013, 32(2): 58-61(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201302007.htm [25] Hao F, Zou H Y, Gong Z S, et al. Petroleum migration and accumulation in the Bozhong sub-basin, Bohai Bay Basin, China: Significance of preferential petroleum migration pathways(PPMP) for the formation of large oilfields in lacustrine fault basins[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2007, 24(1): 1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2006.10.007 [26] 章森桂, 张允白, 严惠君. 《中国地层表》(2014)正式使用[J]. 地层学杂志, 2015, 39(4): 359-366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201504002.htmZhang S G, Zhang Y B, Yan H J. Introduction to the stratigraphic chart of China(2014)[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2015, 39(4): 359-366(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201504002.htm [27] Hao F, Zhou X H, Zhu Y M, et al. Lacustrine source rock deposition in response to co-evolution of environments and organisms controlled by tectonic subsidence and climate, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2011, 42(4): 323-339. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2011.01.010 [28] 韩少甲, 赵俊峰, 刘池洋, 等. 渤海海域庙西凹陷古近纪沙三段沉积期原盆面貌恢复[J]. 地质论评, 2014, 60(2): 339-347. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201402011.htmHan S J, Zhao J F, Liu C Y, et al. Restoration of the original sedimentary extent of Miaoxi Sag in Bohai Sea during the sedimentary period of the third Member of Shahejie Formation in Paleogene[J]. Geological Review, 2014, 60(2): 339-347(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201402011.htm [29] 万桂梅, 汤良杰, 周心怀, 等. 郯庐断裂带在渤海海域渤东地区的构造特征[J]. 石油学报, 2009, 30(3): 342-346. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2009.03.004Wan G M, Tang L J, Zhou X H, et al. Tectonic characteristics of the Tanlu fault zone in Bodong area of Bohai Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2009, 30(3): 342-346(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2009.03.004 [30] 李祖辉, 郑彦鹏, 支鹏遥, 等. 渤海东南部深地震探测与地壳结构研究新进展: OBS2013剖面数据处理分析[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2015, 30(3): 1402-1409. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201503054.htmLi Z H, Zheng Y P, Zhi P Y, et al. The new progress of deep seismic survey and crustal structure in southeast of Bohai Sea: Based on the data processing and analysis of OBS2013 line[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2015, 30(3): 1402-1409(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201503054.htm [31] 孙晓静. 渤海庙西凹陷重点探井古近沉积岩相特征分析[D]. 黑龙江大庆: 东北石油大学, 2015.Sun X J. Research of Paleogene and analysis of sedimentary characteristics by key wells of Bohai Bay Miaoxi Depression[D]. Daqing Heilongjiang: Northeast Petroleum University, 2015(in Chinese with English abstract). [32] 陈江欣, 侯方辉, 李日辉, 等. 渤海海域中西部新构造运动特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(4): 83-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201804007.htmChan J X, Hou F H, Li R H, et al. Neotectonics in the western and central Bohai Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(4): 83-91(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201804007.htm [33] Pepper A S, Corvi P J. Simple kinetic models of petroleum formation. Part I: Oil and gas generation from kerogen[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1995, 12(3): 291-319. doi: 10.1016/0264-8172(95)98381-E [34] Hao F, Zhou X H, Zhu Y M, et al. Charging of oil fields surrounding the Shaleitian uplift from multiple source rock intervals and generative kitchens, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2010, 27(9): 1910-1926. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.07.005 [35] Tian J Q, Hao F, Zhou X H, et al. Charging of the Penglai 9-1 oil field, Bohai Bay Basin, China: Functions of the delta on accumulating petroleum[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 57: 603-618. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.07.007 [36] Xu S, Hao F, Xu C G, et al. Hydrocarbon migration and accumulation in the northwestern Bozhong subbasin, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 172: 477-488. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.09.084 [37] 文志刚, 唐友军, 宋换新, 等. 渤海海域中部地区天然气组成与成因类型[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2005, 32(4): 111-113. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.04.018Wen Z G, Tang Y J, Song H X, et al. Composition and origin of natural gases in central Bohai Sea area, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2005, 32(4): 111-113(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.04.018 [38] 贾楠, 刘池洋, 张东东. 渤海湾盆地庙西凹陷烃源岩评价及油源分析[J]. 西北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 43(3): 461-465. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-274X.2013.03.025Jia N, Liu C Y, Zhang D D. Study on hydrocarbon source rock characteristics and oil-source correlation in Miaoxi Depression, Bohaiwan Basin[J]. Journal of Northwest University: Natural Science Edition, 2013, 43(3): 461-465(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-274X.2013.03.025 [39] 姚佳, 陈保柱, 张敏, 等. 庙西北洼东营组烃源岩地球化学特征及意义[J]. 长江大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 13(6): 8-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJDL201617002.htmYao J, Chen B Z, Zhang M, et al. Geochemical characteristics and the significance of the source rocks in Dongying Formation of the Northern Depression of Miaoxi Sag[J]. Journal of Yangtze University: Natural Science Edition, 2016, 13(6): 8-12(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJDL201617002.htm [40] 周心怀, 张如才, 李慧勇, 等. 渤海湾盆地渤中凹陷深埋古潜山天然气成藏主控因素探讨[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 41(1): 42-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201701005.htmZhou X H, Zhang R C, Li H Y, et al. Major controls on natural gas accumulation in deep-buried hills in Bozhong Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Natural Science Edition, 2017, 41(1): 42-50(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201701005.htm [41] 韩金虎, 郭小文, 王学军, 等. 渤南洼陷不同来源原油分布规律及主要控制因素[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 83-92. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10074.shtmlHan J H, Guo X W, Wang X J, et al. Distribution rule and main controlling factors of crude oil from different sources in Bonan Sag[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 83-92(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10074.shtml [42] Guo Y C, Pang X Q, Dong Y X, et al. Hydrocarbon generation and migration in the Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, eastern China: Insight from basin and petroleum system modeling[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 77: 140-150. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.08.033 [43] Wygrala B P. Integrated study of an oil field in the southern Po Basin[D]. Northern Italy: University K ln, 1989. [44] 邱楠生, 左银辉, 常健, 等. 中国东西部典型盆地中-新生代热体制对比[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(1): 157-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201501015.htmQiu N S, Zuo Y H, Chang J, et al. Characteristics of Meso-Cenozoic thermal regimes in typical eastern and western sedimentary basins of China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(1): 157-168(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201501015.htm [45] 朱伟林, 米立军, 高阳东, 等. 中国近海近几年油气勘探特点及今后勘探方向[J]. 中国海上油气, 2009, 21(1): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD200901002.htmZhu W L, Mi L J, Gao Y D, et al. Recent features and future directions of offshore hydrocarbon exploration in China[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2009, 21(1): 1-8(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD200901002.htm [46] 龚再升. 中国近海新生代盆地至今仍然是油气成藏的活跃期[J]. 石油学报, 2005, 26(6): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200506000.htmGong Z S. Cenozoic China offshore basins keeping active hydrocarbon accumulation to present[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2005, 26(6): 1-6(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200506000.htm [47] 王奇, 邹华耀, 周心怀, 等. 渤海海域烃源岩的生气潜力与天然气成因分析[J]. 高校地质学报, 2017, 23(2): 304-314. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201702013.htmWang Q, Zou H Y, Zhou X H, et al. Gas potential of source rocks and origin of natural gases in Bohai Sea[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2017, 23(2): 304-314(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201702013.htm [48] 陈晓艳, 田福清, 邹华耀, 等. 湖相烃源岩热演化生烃研究: 基于冀中坳陷烃源岩加水热模拟实验[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(1): 103-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201801010.htmChen X Y, Tian F Q, Zou H Y, et al. Study on hydrocarbon-generation of lacustrine source rocks based on hydrous pyrolysis experiments of source rocks from Jizhong Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2018, 29(1): 103-113(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201801010.htm [49] 李儒峰, 张刚雄, 阮小飞. 渤海海域古近系-新近系不整合剥蚀量恢复研究[J]. 地质论评, 2012, 58(3): 542-552. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201203016.htmLi R F, Zhang G X, Ruan X F. Study on the recovery of erosion quantity of unconformities of Paleogene-Neogene in Bohai Sea area[J]. Geological Review, 2012, 58(3): 542-552(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201203016.htm [50] 何丽娟. 辽河盆地新生代多期构造热演化模拟[J]. 地球物理学报, 1999, 12(1): 62-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX901.006.htmHe L J. Mutiple tectono-thermal modeling of Liaohe Basin in the Cenozoic[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 1999, 12(1): 62-68(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX901.006.htm [51] 邱楠生, 苏向光, 李兆影, 等. 济阳坳陷新生代构造-热演化历史研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2006, 49(4): 1127-1135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200604025.htmQiu N S, Su X G, Li Z Y, et al. The Cenozoic tectono-thermal evolution of Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, East China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2006, 49(4): 1127-1135(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200604025.htm [52] Hantschel T, Kauerauf A I. Fundamentals of basin and petroleum systems modeling[M]. Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media, 2009. [53] Hakimi M H, Abdullah W H. Thermal maturity history and petroleum generation modelling for the Upper Jurassic Madbi source rocks in the Marib-Shabowah Basin, western Yemen[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 59: 202-216. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S026481721400258X [54] 张学军, 邹育良, 霍秋立. 流体包裹体在松辽盆地成藏期次研究中的应用[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2008, 13(4): 50-55, 2-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY200804012.htmZhang X J, Zou Y L, Huo Q L. Application of fluid inclusions to period research on oil and gas accumulation in Songliao Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2008, 13(4): 50-55, 2-3(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY200804012.htm [55] 蒋有录, 房磊, 谈玉明, 等. 渤海湾盆地东濮凹陷不同区带油气成藏期差异性及主控因素[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(6): 1321-1331. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201506014.htmJiang Y L, Fang L, Tan Y M, et al. Differences and main controlling factors of accumulation periods in Dongpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Geological Review, 2015, 61(6): 1321-1331(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201506014.htm -





 下载:
下载: