Review on geoscience time series big data similarity measurement and index method
-
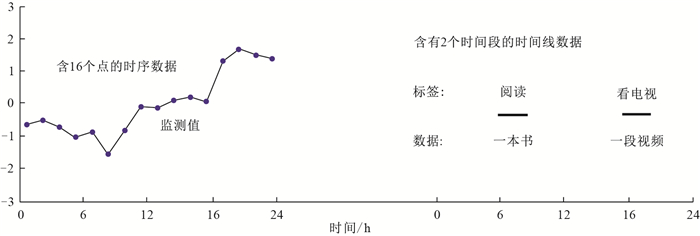
摘要: 地学时序大数据具有多传感器、多目标、多分辨率、多类型的多源异构特征,是地学领域机器学习与数据挖掘的重要数据来源,分为基于时点和基于时段的两大类时序数据。现有时序数据的相似性度量与索引研究主要聚焦在前者。时序数据表达方法的核心思想是降维处理,是相似性度量与索引方法的基础,主要包括基于域变换和模型的表达方法和基于极限分段思想的表达方法。相似性度量的核心是相似性距离计算,主要分为锁步度量和弹性度量。它为时序数据索引中索引项的聚合与划分提供了基本准则。多源异构地学时序大数据的高效相似性度量与分布式索引方法是地学大数据领域未来的重要研究方向。Abstract: Geoscience time series big data is a kind of multi-sensor, multi-target, multi-resolution, multi-type, and multi-source heterogeneous time data, and is an important data source for machine learning and data mining in the field of geosciences. Geosciences time series data has two categories: the time point data set, and the time interval data set. The main data representation methods, similarity measurements and data indexing methods of existing time series data focus on time-points-based time series data. The core idea of the representation method for time series data is dimensionality reduction. It is the basis of similarity measurement and indexing method, including domain-transformation-based, model-based and pieces-based representation methods. The key of similarity measurement is the similarity distance including lock-step measurement and elasticity measurement. It provides a basic guideline for the aggregation and division of index items in the index of time series data. The efficient similarity measurement and distributed indexing method of multi-source heterogeneous time series big data will be an important further direction in the field of geosciences big data.
-
Key words:
- time series data /
- big data /
- representation /
- index /
- similarity measurement
-
图 2 PAA与SAX示意图[51]
Figure 2. The relationship between PAA and SAX
表 1 时序数据的主要表示方法
Table 1. Main representation methods for time-series data
表示方法 发表时间 所属类型 算法复杂度 资料来源 离散傅立叶变换(DFT) 1993 T1 O(n(log(n))) 文献[14-15] 离散小波变换(DWT) 1999 T1 O(n) 文献[16-17] 奇异值分解(SVD) 1997 T2 O(Mn2) 文献[18] 离散余弦变换(DCT) 1997 T1 N 文献[18] 分片线性近似(PLA) 1998 T2 O(n(log(n))) 文献[19] 隐马尔科夫模型(HMMs) 1998 T4 N 文献[20] 分片聚合近似(PAA) 2000 T1 O(n) 文献[21] 分片常量近似(PCA) 2000 T2 N 文献[22] 自适应分片常量近似(APCA) 2002 T2 O(n) 文献[23] 感知重要点(PIP) 2001 T1 N 文献[24] 切比雪夫多项式(CHEB) 2004 T1 N 文献[25] 符号化近似(SAX) 2003 T2 O(n) 文献[26-27] 剪切数据(Clipped Data) 2005 T3 N 文献[28] 可索引分片线性近似(IPLA) 2007 T1 N 文献[29] 自动回归模型 2012 T4 N 文献[30] 移动-分裂-合并(MSM) 2013 T1 N 文献[31] 基于树的表示方法 2015 T3 N 文献[32] 基于图形内容的DTW(SC-DTW) 2015 T1 N 文献[33] 基于本地自动模式的表示方法 2016 T4 N 文献[34] 基于网格的表示方法 2019 T4 N 文献[35] N.作者没有列出;T1.非数据自适应型表示方法; T2.数据自适应表示方法;T3.数据指示型表示方法; T4.基于模型的表示方法 -
[1] He Z, Kraak M J, Huisman O, et al.Parallel indexing technique for spatio-temporal data[J].Isprs Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2013, 78:116-128. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2013.01.014 [2] He Z, Wu C, Liu G, et al.Decomposition tree:A spatio-temporal indexing method for movement big data[J].Cluster Computing, 2015, 18(4):1481-1492. doi: 10.1007/s10586-015-0475-3 [3] He Z, Ma X.A distributed indexing method for timeline similarity query[J].Algorithms, 2018, 11(4):19-41. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=MDPI000000169415 [4] 吴冲龙, 刘刚, 王力哲, 等.基于大数据的城市地质环境智能监管思路与方法[J].地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1):157-163. http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9936.shtml [5] 吴冲龙, 刘刚.大数据与地质学的未来发展[J].地质通报, 2019, 38(7):1081-1088. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201907001 [6] 吴冲龙, 刘刚, 周琦, 等.地质科学大数据统合应用的基本问题[J].地质科技通报, 2020, 39(4):1-11. http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9993.shtml [7] 陈国旭, 田宜平, 张夏林, 等.基于勘探剖面的三维地质模型快速构建及不确定性分析[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2):275-280. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201902033 [8] 张文彪, 段太忠, 刘彦锋, 等.定量地质建模技术应用现状与发展趋势[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3):1-9. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201903029 [9] 刘刚, 吴冲龙, 何珍文, 等.面向地质时空大数据表达与存储管理的数据模型研究[J].地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1):164-174. http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9937.shtml [10] Brehmer M, Lee B, Bach B, et al.Timelines revisited:A design space and considerations for expressive storytelling[J].IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2017, 23(9):2151-2164. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2016.2614803 [11] Li C, Li B, Bhuiyan M Z A, et al.FluteDB:An efficient and scalable in-memory time series database for sensor-cloud[J].Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2018, 122:95-108. doi: 10.1016/j.jpdc.2018.07.021 [12] Noury A, Amini M.An access and inference control model for time series databases[J].Future Generation Computer Systems, 2019, 92:93-108. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2018.09.057 [13] Aghabozorgi S, Seyed Shirkhorshidi A, Teh Y W.Time-series clustering:A decade review[J].Information Systems, 2015, 53:16-38. doi: 10.1016/j.is.2015.04.007 [14] Agrawal R, Faloutsos C, Swami A.Efficient similarity search in sequence databases[C]//Lomet D B.Foundations of data organization and algorithms.FODO 1993.Lecture Notes in Computer Science.Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1993: 69-84. [15] Faloutsos C, Ranganathan M, Manolopoulos Y.Fast subsequence matching in time-series databases[J].Sigmod Rec., 1994, 23(2):419-429. doi: 10.1145/191843.191925 [16] Kin-Pong C, Ada Wai-Chee F.Efficient time series matching by wavelets[C]//Masaru K, Michael P, Calton P.Proceedings of the 15th international conference on data engineering (Cat No99CB36337), F 23-26 March 1999.Washington D.C.: IEE Computer Society, 1999: 126-133. [17] Kawgoe K, Ueda T.A similarity search method of time series data with combination of fourier and wavelet transforms[C]//Mchael P, Alessardro A.Proceedings of the ninth international symposium on temporal representation and Reasoning (TIME'02).Washington: IEEE Computer Society, 2002: 86-98. [18] Korn F, Jagadish H V, Faloutsos C.Efficiently supporting ad hoc queries in large datasets of time sequences[J].Sigmod Rec., 1997, 26(2):289-300. doi: 10.1145/253262.253332 [19] Keogh E J, Pazzani M J.An enhanced representation of time series which allows fast and accurate classification, clustering and relevance feedback[C]//Rakesh A, Paul E S.The 4th international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining.New York: AAAI Press, 1998: 239-241. [20] Azzouzi M, Nabney I.Analysing time series structure with hidden Markov models, neural networks for signal processing Ⅷ[C]//Mahesan N, Elizabeth W, Tony C, et al.Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE Signal Processing Society Workshop.New York: IEEE Computer Society Press, 1998: 402-408. [21] Yi B K, Faloutsos C.Fast time sequence indexing for arbitrary Lp norms[C]//Amr E A, Michael L B, Sharma C, et al.Proceedings of the 26th international conference on very large data bases.San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc, 2000: 385-394. [22] Keogh E J, Pazzani M J.A simple dimensionality reduction technique for fast similarity search in large time series databases[M].Berlin, Heidelberg:Springer, 2000. [23] Chakrabarti K, Keogh E, Mehrotra S, et al.Locally adaptive dimensionality reduction for indexing large time series databases[J].ACM Trans Database Syst., 2002, 27(2):188-228. doi: 10.1145/568518.568520 [24] Chung F L, Fu T C, Luk R, et al.Flexible time series pattern matching based on perceptually important points[C]//Hector L, Bernhard N, Ron B, et al.International joint conference on artificial intelligence workshop on learning from temporal and spatial data.San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann, 2001: 1-7. [25] Cai Y, Ng R.Indexing spatio-temporal trajectories with Chebyshev polynomials[C]//Arnd C K, Stefan D.Proceedings of the 2004 ACM SIGMOD international conference on management of data.Paris: ACM, 2004: 599-610. [26] Lin J, Keogh E, Lonardi S, et al.A symbolic representation of time series, with implications for streaming algorithms[C]//Mohamned J Z, Charu C A.Proceedings of the 8th ACM SIGMOD workshop on research issues in data mining and knowledge discovery.San Diego, California: ACM, 2003: 2-11. [27] Lin J, Keogh E, Wei L, et al.Experiencing SAX:A novel symbolic representation of time series[J].Data Mining Knowledge Discovery, 2007, 15(2):107-144. http://nar.oxfordjournals.org/external-ref?access_num=10.1007/s10618-007-0064-z&link_type=DOI [28] Ratamahatana C J, Keogh E, Bagnall A, et al.A novel bit level time series representation with implication of similarity search and clustering[C]//Tu B H, David C, Huan L.Advances in knowledge discovery and data mining PAKDD 2005.Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2005: 771-777. [29] Chen Q, Chen L, Lian X, et al.Indexable PLA for efficient similarity search[C]//Wolfgang K, Erich J N.Proceedings of the 33rd international conference on very large data bases.Vienna, Austria: VLDB Endowment.2007: 435-446. [30] Serra J, Kantz H, Serra X, et al.Predictability of music descriptor time series and its application to cover song detection[J].Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, IEEE Transactions on, 2012, 20:514-525. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=b267ec14db1c90d4e0b6cd5a9ca85568 [31] Stefan A, Athitsos V, Das G.The move-split-merge metric for time series[J].IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng., 2013, 25(6):1425-1438. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2012.88 [32] Baydogan M G, Runger G.Learning a symbolic representation for multivariate time series classification[J].Data Mining Knowledge Discovery, 2015, 29(2):400-422. doi: 10.1007/s10618-014-0349-y [33] Zhang Z, Tang P, Duan R.Dynamic time warping under pointwise shape context[J].Information Sciences, 2015, 315:88-101. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2015.04.007 [34] Baydogan M G, Runger G.Time series representation and similarity based on local autopatterns[J].Data Mining Knowledge Discovery, 2016, 30(2):476-509. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=3239893eea2eb9924ed78f89e25691e2 [35] Ye Y Q, Jiang J, Ge B F, et al.Similarity measures for time series data classification using grid representation and matrix distance[J].Knowledge Information Systems, 2019, 60(2):1105-1134. doi: 10.1007/s10115-018-1264-0 [36] Har-Peled S, Raichel B.Net and prune:A linear time algorithm for euclidean distance problems[J].J.ACM, 2015, 62(6):1-35. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2831230 [37] Oregi I, Pérez A, Del Ser J, et al.On-line elastic similarity measures for time series[J].Pattern Recognition, 2019, 88:506-517. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.12.007 [38] 陈海燕, 刘晨晖, 孙博.时间序列数据挖掘的相似性度量综述[J].控制与决策, 2017, 32(1):1-11. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kzyjc201701001 [39] 王一舒, 袁野, 刘萌, 等.大规模时序图数据的查询处理与挖掘技术综述[J].计算机研究与发展, 2018, 55(9):1889-902. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jsjyjyfz201809005 [40] Bai S, Qi H D, Xiu N.Constrained best euclidean distance embedding on a sphere:A matrix optimization approach[J].SIAM Journal on Optimization, 2015, 25(1):439-467. doi: 10.1137/13094918X [41] Junejo I N, Junejo K N, Aghbari Z A.Silhouette-based human action recognition using SAX-Shapes[J].The Visual Computer, 2014, 30(3):259-269. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c9eeb52a7e591c430b542d28131dd133 [42] Hsu C J, Huang K S, Yang C B, et al.Flexible dynamic time warping for time series classification[J].Procedia Computer Science, 2015, 51(28):38-42. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=2771883c82adae9bff875df64ae86ef6 [43] Roggen D, Cuspinera L P, Pombo G, et al.Limited-memory warping LCSS for real-time low-power pattern recognition in wireless nodes[M].Cham:Springer International Publishing, 2015. [44] Chairunnanda P, Gopalkrishnan V, Lei C.Enhancing edit distance on real sequences filters using histogram distance on fixed reference ordering[C]//Tang Y Y, Wang S P, Lorette G, et al.Proceedings of the 18th international conference on pattern recognition (ICPR'06), F 20-24 Aug.Los Alamtes: IEEE, 2006: 582-585. [45] Chen L, Ng R.On the marriage of Lp-norms and edit distance[C]//Mario A N, Özsu M T, Donald K, et al.Proceedings of the thirtieth international conference on very large data bases-Volume 30.Toronto, Canada: VLDB Endowment, 2004: 792-803. [46] Sun Y, Li J, Liu J, et al.An improvement of symbolic aggregate approximation distance measure for time series[J].Neurocomputing, 2014, 138:189-198. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.01.045 [47] Abughali I K A, Minz S.Binarizing change for fast trend similarity based clustering of time series data[M].Cham:Springer International Publishing, 2015. [48] Nakamura T, Taki K, Nomiya H, et al.A shape-based similarity measure for time series data with ensemble learning[J].Pattern Analysis and Applications, 2013, 16(4):535-548. doi: 10.1007/s10044-011-0262-6 [49] He X, Shao C, Xiong Y.A new similarity measure based on shape information for invariant with multiple distortions[J].Neurocomputing, 2014, 129:556-569. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2013.09.003 [50] Ares J, Lara J A, Lizcano D, et al.A soft computing framework for classifying time series based on fuzzy sets of events[J].Information Sciences, 2016, 330:125-144. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2015.10.014 [51] Kondylakis H, Dayan N, Zoumpatianos K, et al.Coconut:A scalable bottom-up approach for building data series indexes[J].Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 2018, 11(6):1-14. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/323869978_Coconut_A_Scalable_Bottom-Up_Approach_for_Building_Data_Series_Indexes [52] Shieh J, Keogh E.iSAX:Disk-aware mining and indexing of massive time series datasets[J].Data Mining Knowledge Discovery, 2009, 19(1):24-57. http://www.springerlink.com/content/7357q35x63121n56/ [53] Camerra A, Palpanas T, Shieh J, et al.iSAX 2.0: Indexing and mining one billion time series[C]//Geoffrey I W, Liu B, Zhang C, et al.Proceedings of the 10th IEEE international conference on data mining.ICDM 2010, December 14, 2010- December 17, 2010, Sydney, NSW, Australia.Sydney: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc, 2010: 58-67. [54] Zoumpatianos K, Idreos S, Palpanas T.ADS:The adaptive data series index[J].The VLDB Journal, 2016, 25(6):843-66. doi: 10.1007/s00778-016-0442-5 [55] Yagoubi D E, Akbarinia R, Masseglia F, et al.DPiSAX: Massively distributed partitioned iSAX[C]//Raju G, Ning X, Dong G Z, et al.Proceedings of the 17th IEEE international conference on data mining, ICDM 2017, November 18- November 21, 2017, New Orleans USA.New Orleans: IEEE Computer Society Press, 2017: 1135-1140. [56] 曾碧贵, 叶少珍.时间序列数据摘要与索引机制[J].工业控制计算机, 2017, 30(1):59-60. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gykzjsj201701026 [57] Camerra A, Shieh J, Palpanas T, et al.Beyond one billion time series:Indexing and mining very large time series collections with iSAX2+[J].Knowledge Information Systems, 2014, 39(1):123-151. doi: 10.1007/s10115-012-0606-6 [58] Keogh E, Chakrabarti K, Pazzani M, et al.Dimensionality reduction for fast similarity search in large time series databases[J].Knowledge Information Systems, 2001, 3(3):263-286. doi: 10.1007/PL00011669 [59] Yagoubi D E, Akbarinia R, Masseglia F, et al.Massively distributed time series indexing and querying[J].IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2018, 11:1-14 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8528881/ [60] Kaufmann M, Manjili A A, Vagenas P, et al.Timeline index: A unified data structure for processing queries on temporal data in SAP HANA[C]//Kenneth R, Divesh S.Proceedings of the 2013 ACM SIGMOD international conference on management of data.New York: ACM, 2013: 1173-1184. [61] 何锦源.TQIndex: 面向超大规模数据进行时序检索的高效数据索引结构[D].广州: 中山大学, 2015. [62] Leon-Alcaide P, Rodriguez-Benitez L, Castillo-Herrear E, et al.An evolutionary approach for efficient prototyping of large time series datasets[J].Information Sciences, 2020, 511:74-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.09.044 [63] Palpanas T.Evolution of a Data Series Index[C]//Flouris G, Laurent D, Plexousakis D, et al.International workshop on information search, integration, and personalization.Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2020: 68-83. [64] Ye Y Q, Jiang J, Ge B F, et al.Similarity measures for time series data classification using grid representation and matrix distance[J].Knowledge and Information Systems, 2019, 60(2):1105-1134. doi: 10.1007/s10115-018-1264-0 -





 下载:
下载: