Fault modeling based on the semantic constraint of geological big data
-
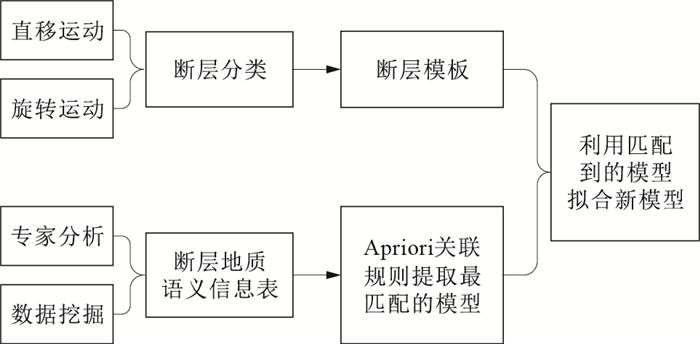
摘要: 断层作为一种重要的地质构造,在自然界中普遍存在。在地质体三维建模中,断层处理的难点主要在于数据获取不易。如今,在地质大数据条件下,可以利用不同地质语义约束来推测断层的产状。但由于断层构造往往十分复杂,要利用地质大数据对断层构造进行约束建模,需厘清断层的形态分类及其数据模型。通过研究断层的分类,提取出影响断层产状的要素,将这些要素作为断层数据模型的组成部分,在地质大数据挖掘中作为挖掘目标,形成断层地质语义信息表,为后续断层建模提供数据支撑。在此基础上,提出一种新的断层建模思路,即将断层看成一个整体,通过Apriori算法对断层地质语义信息表进行分类,找到每个断层的标准模型。然后,利用断层地质语义信息表对该断层模型进行几何形态约束,形成符合特定地质语义的断层模型。最后,通过断层牵引构造的平滑过渡,将断层镶嵌在已经建好的地层格架模型中,完成断层的三维建模。Abstract: Faults, as an important geological structure, are ubiquitous in nature.In 3d modeling of geological body, the difficulty of fault processing lies in obtaining data.Nowadays, under the condition of geological big data, different geological semantic constraints can be used to predict the occurrence of faults.However, as fault structures are often very complex, it is necessary to clarify the morphological classification of faults and their data models in order to use geological big data for constraint modeling of fault structures. This paper studies classification of faults and extracts factors that affect occurrence of faults. These factors are taken as part of fault data model and as mining target in the big data mining of geology. They can constitute table of geological semantic information of faults to provide data support for subsequent fault modeling.On this basis, a new fault modeling idea is proposed, that is, fault is regarded as a whole, and section fault geological semantic information table is classified by Aprirori algorithm to find standard model of each fault. Then, the fault model is constrained by geometric form by using the fault semantic information table to form a fault model with the specific geological semantics. Finally, through smooth transition of the fault traction structure, the fault is embedded in established stratigraphic framework model to complete three-dimensional modeling of the fault.
-
表 1 断层地质语义信息
Table 1. Fault geological semantic information
字段名称 说明 数据类型 Fault_ID 断层名称 Long Char Fault_Attribute 断层属性 Char Fault_Level 断层级别 Int Fault_Position_X 断层插入起始位置 (Double, Double, Double) Fault_Position_Y 断层插入终止位置 (Double, Double, Double) Fault_Strike 断层走向 (Double, Double) Fault_Dipangle 断层地层倾角 Double Fault_Interval 地层断距 Double Fault_Ver_Interval 铅直地层断距 Double Fault_Hor_Interval 水平地层断距 Double Fault_Nor_componet 正断层分量 Double Fault_Thr_componet 逆断层分量 Double Fault_Lef_component 左行断层分量 Double Fault_Rig_Component 右行断层分量 Double Fault_Rot_Position 旋转轴位置 (Double, Double) Fault_Rot_Angle 旋转倾角 Double Fault_Pin_Position 断层尖灭位置 (Double, Double) -
[1] 何珍文, 吴冲龙, 刘刚, 等.地质空间认知与多维动态建模结构研究[J].地质科技情报, 2012, 31(6):46-51. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKQ201206009.htm [2] 翁正平.复杂地质体三维模型快速构建及更新技术研究[D].武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2008. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10491-1013354269.htm [3] 陈麒玉.基于多点地质统计学的三维地质体随机建模方法研究: 以闽江口地区第四纪沉积体系建模为例[D].武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2018. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10491-1018817151.htm [4] Keith T.Challenges and trends for geological modelling and visualization[J].Bulletin of Engineering Geology & the Environment, 2006, 65:109-127. http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-foreign_other_thesis/020416214200.html [5] 朱良峰, 潘信, 吴信才, 等.地质断层三维可视化模型的构建与实现技术[J].软件学报, 2008, 19(8):2004-2015. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=rjxb200808012 [6] 朱良峰, 潘信.地质断层三维构模技术研究[J].岩土力学, 2008, 29(1):274-278. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ytlx200801051 [7] 李忠权, 刘顺.构造地质学[M].北京:地质出版社, 2010. [8] 武强, 徐华.虚拟地质建模及可视化[M].北京:科学出版社, 2011. [9] 杨洋, 潘懋, 吴耕宇, 等.一种新的轮廓线三维地质表面重建方法[J].地球信息科学学报, 2015, 17(3):253-259. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxxkx201503001 [10] 唐丙寅, 吴冲龙, 李新川.一种基于TIN-CPG混合空间数据模型的精细三维地质模型构建方法[J].岩土力学, 2017, 38(4):1218-1225. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ytlx201704037 [11] 吴冲龙, 刘刚, 王力哲, 等.基于大数据的城市地质环境智能监管思路与方法[J].地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1):157-163. http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9936.shtml [12] 田宜平, 刘维安, 张夏林.基于等角度变化比例投影的矿体轮廓线自动匹配方法研究[J].地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1):175-180. http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9938.shtml [13] 刘刚, 吴冲龙, 何珍文, 等.面向地质时空大数据表达与存储管理的数据模型研究[J].地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1):164-174. http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9937.shtml [14] 陈国旭, 田宜平, 张夏林, 等.基于勘探剖面的三维地质模型快速构建及不确定性分析[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2):275-280. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201902033 [15] 张文彪, 段太忠, 刘彦锋, 等.定量地质建模技术应用现状与发展趋势[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3):1-9. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201903029 [16] 吴冲龙, 刘刚, 张夏林, 等.地质科学大数据及其利用的若干问题探讨[J].科学通报, 2016, 61(16):1797-1807. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201616010 [17] 田宜平, 刘志峰, 赵攀, 等.水电三维地质模型中各地质要素的建模方法[J].地质学刊, 2012, 36(3):320-325. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jsdz201203017 [18] 田宜平, 毛小平, 张志庭, 等."玻璃油田"建设与油气勘探开发信息化[J].地质科技情报, 2012, 31(6):16-22. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93477A/20126/44012102.html [19] 吴冲龙, 刘刚.大数据与地质学的未来发展[J].地质通报, 2019, 38(7):1082-1088. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201907001 [20] 吴冲龙, 刘刚."玻璃地球"建设的现状、问题、趋势与对策[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(7):1281-1287. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201507005 [21] 朱合华, 郑国平, 吴江斌, 等.基于钻孔信息的地层数据模型研究[J].同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2003, 31(5):535-539. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=tjdxxb200305007 [22] 严俊, 魏迎奇, 蔡红, 等.基于钻孔数据的三维地质模型智能建模方法[J].水力发电, 2015, 41(2):25-28. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=slfd2015020008 [23] Benito B R, Alberto C, Agustrin M D, et al. A novel geometric approach for 3-D geological modeling[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology & the Environment, 2014, 73:551-567. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9120b22cfccae35c2bf858b4a9ce39bc [24] 陈明娥, 涂江涛.基于规则库的三维地质自动建模技术研究[J].测绘通报, 2017(9):120-125. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=chtb201709027 [25] 张慧, 刘刚, 陈麒玉.带约束的体元属性插值方法与可视化表达[J].地质科技情报, 2017, 36(6):267-272. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201706031 [26] 倪凤娟, 郭福生, 黎广荣, 等.内蒙古塔木素地区断层活动性研究:来自断层泥及围岩主量元素及碳氧同位素的证据[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(4):166-174. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKQ201904017.htm [27] Gong J, Cheng P, Wang Y. Three-dimensional modeling and application in geological exploration engineering[J]. Computers and Geosciences, 2004, 30(4):391-404. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2003.06.003 [28] Fan Q, Ju N P, Xiang X Q, et al.Landslides hazards assessment with weights of evidence-A case study in Guizhou, China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2014, 22(3):474-481. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gcdzxb201403022 [29] 王静.基于QuantyView和多源数据的滑坡体三维地质建模技术研究[D].武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10491-1014164902.htm [30] De Rienzo F, Oreste P, Pelizza S. Subsurface geological geotechnical modeling to sustain underground civil planning[J]. Engineering Geology, 2008, 96(1):187-204. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S001379520700227X [31] 王柏林.基于关联规则的数据挖掘方法的研究[D].武汉: 华中科技大学, 2017. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10487-1018970195.htm -





 下载:
下载: