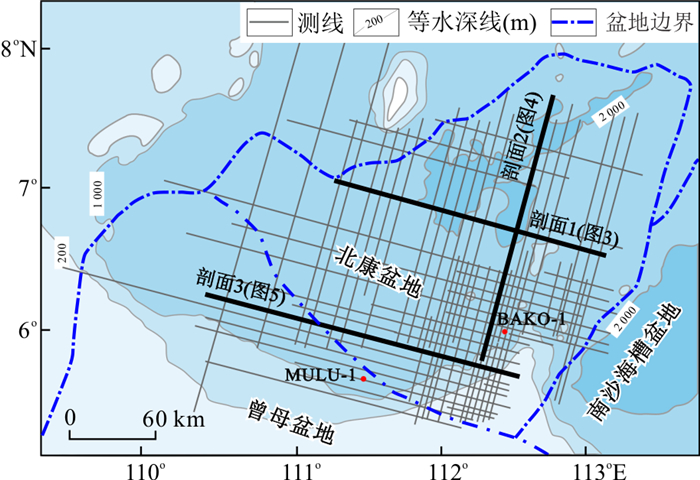
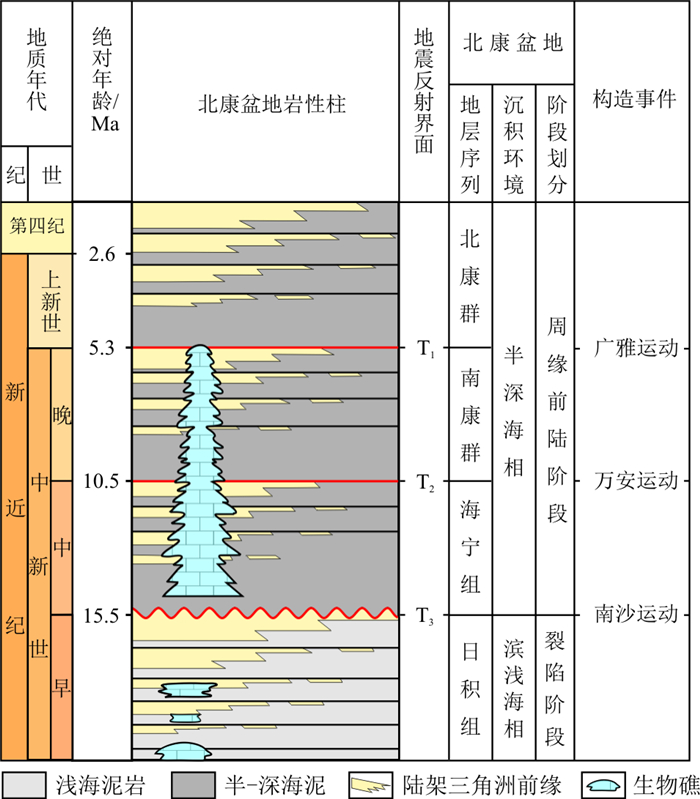
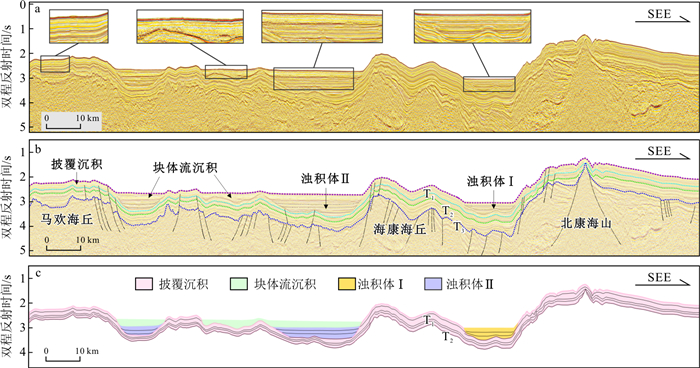
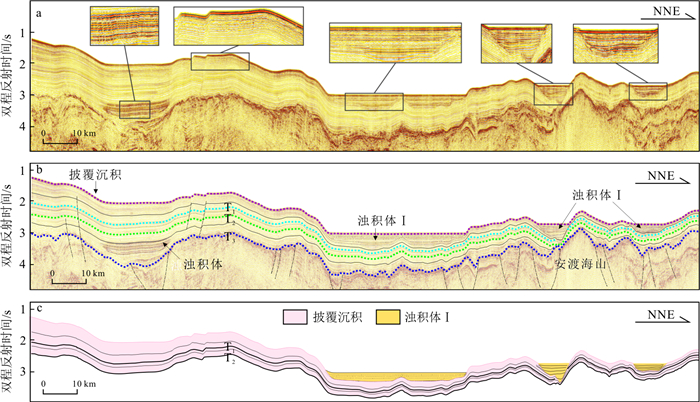
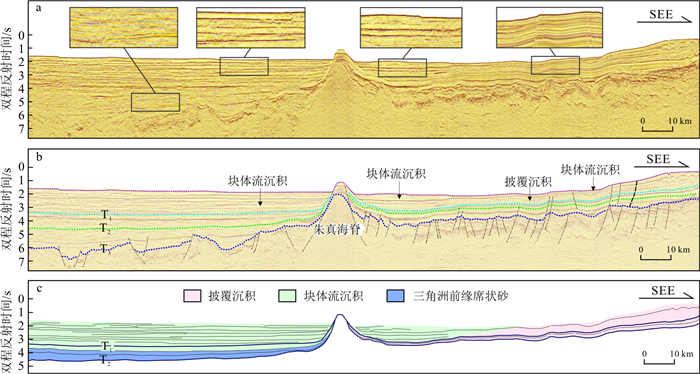
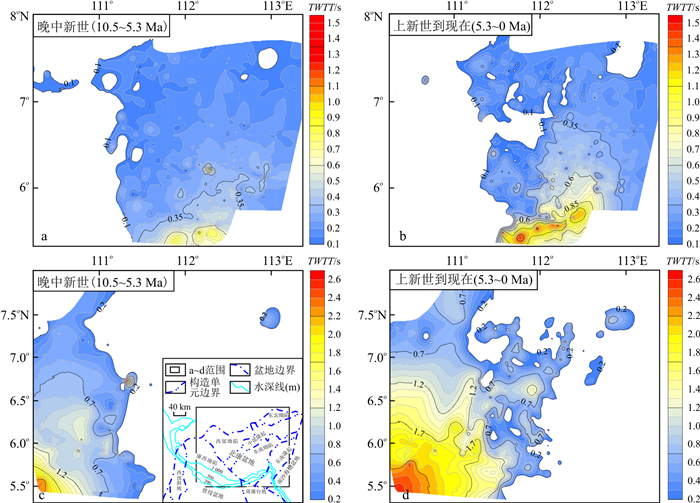
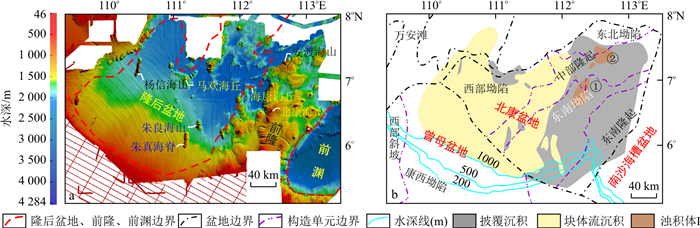
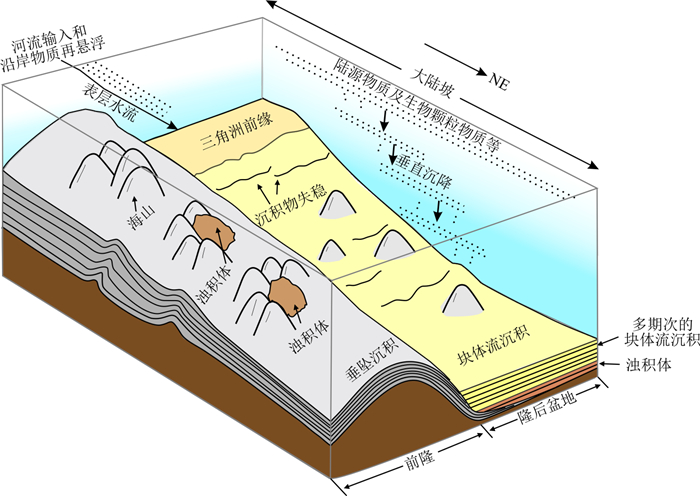
| [1] |
Pickering K, Hiscott R. Deep marine systems: Processes, deposits, environments, tectonics and sedimentation[M]. Washington, DC, USA: Wiley & American Geophysical Union, 2016.
|
| [2] |
Huneke H, Mulder T. Deep-sea sediments[M]. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier, 2011.
|
| [3] |
Rebesco M, Camerlenghi A. Contourites[M]. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier, 2008: 457-489.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
Xie X N, Ren J Y, Wang Z F, et al. Difference of tectonic evolution of continental marginal basins of South China Sea and relationship with SCS spreading[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(1): 77-87(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201501009.htm |
| [6] |
Banerjee A, Salim A M A. Seismic attribute analysis of deep-water dangerous grounds in the South China Sea, NW Sabah Platform region, Malaysia[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2020, 83: 103534. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2020.103534 |
| [7] |
He Y L, Kuang Z G, Xu M J. Seismic reflection characteristics and triggering mechanism of mass transport deposits of Quaternary in Beikang Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(4): 258-268(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2018.0435 |
| [8] |
Liu S, Hernández-Molina F J, Lei Z Y, et al. Fault-controlled contourite drifts in the southern South China Sea: Tectonic, oceanographic, and conceptual implications[J]. Marine Geology, 2021, 433: 106420. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2021.106420 |
| [9] |
Hutchison C S. Marginal basin evolution: The southern South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2004, 21(9): 1129-1148. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2004.07.002 |
| [10] |
Madon M, Ly K C, Wong R. The structure and stratigraphy of deepwater Sarawak, Malaysia: Implications for tectonic evolution[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 76(S1): 312-333.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
Banerjee A, Salim A M A. Stratigraphic evolution of deep-water dangerous grounds in the South China Sea, NW Sabah Platform Region, Malaysia[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 201: 108434. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108434 |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
Lei Z Y, Zhang L, Su M, et al. Middle Miocene deep-water sediments in the Beikang Basin, southern South China Sea: Types, characteristics and implications[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(6): 110-118(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201706013.htm |
| [15] |
王宏斌, 姚伯初, 梁金强, 等. 北康盆地构造特征及其构造区划[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, 21(2): 49-54.
Wang H B, Yao B C, Liang J Q, et al. Tectonic characteristics and division of the Beikang Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2001, 21(2): 49-54(in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [16] |
张莉, 王嘹亮, 易海. 北康盆地的形成与演化[J]. 中国海上油气地质, 2003, 17(4): 23-26.
Zhang L, Wang L L, Yi H. The formation and evolution of Beikang Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2003, 17(4): 23-26(in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [17] |
骆帅兵, 王笑雪, 张莉, 等. 南海南部北康-曾母盆地早中新世层序内部优质砂岩精细刻画[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(2): 111-123.
Luo S B, Wang X X, Zhang L, et al. Study of high-quality sandstone in Early Miocene sequence of Beikang-Zengmu Basin, the southern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(2): 111-123(in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [18] |
Yao Y J, Yang C P, Li X J, et al. The seismic reflection characteristics and tectonic significance of the tectonic revolutionary surface of Mid-Miocene(T 3 seismic interface) in the southern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2013, 56(4): 1274-1286(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201304024.htm |
| [19] |
Koša E. Sea-level changes, shoreline journeys, and the seismic stratigraphy of Central Luconia, Miocene-present, offshore Sarawak, NW Borneo[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 59: 35-55.
|
| [20] |
Madon M, Redzuan A H. West Luconia Province//Anon. The petroleum geology and resources of Malaysia[M]. Kuala Malaysia, Malaysia: Petroliam Nasional Berhad, 1999: 427-436.
|
| [21] |
Petronas. The petroleum geology and resources of malaysia[M]. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: Petronas, 1999.
|
| [22] |
Mitchum R M J, Vail P R, Sangree J B. Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of sea level: Part 6. Stratigraphic interpretation of seismic reflection patterns in depositional sequences[M]//Payton C E. Seismic stratigraphy: Applications to hydrocarbon exploration. Tulsa, USA: AAPG Memoir, 1977: 17-133.
|
| [23] |
Madon M. North Luconia Province//Anon. The petroleum geology and resources of Malaysia[M]. Kuala Lumpur: Petroliam Nasional Berhad, 1999: 441-454.
|
| [24] |
Omosanya K O. Episodic fluid flow as a trigger for Miocene-Pliocene slope instability on the Utgard High, Norwegian Sea[J]. Basin Research, 2018, 30(5): 942-964.
|
| [25] |
Masson D G, Hyggett Q J, Brunsden D. The surface texture of the Saharan debris flow deposit and some speculations on submarine debris flow processes[J]. Sedimentology, 1993, 40(3): 583-598.
|
| [26] |
Steventon M J, Jackson C A L, Hodgson D M, et al. Strain analysis of a seismically imaged mass-transport complex, offshore Uruguay[J]. Basin Research, 2019, 31(3): 600-620.
|
| [27] |
朱本铎, 关水贤, 黄文星, 等. 南海地质地球物理图系(1∶200万)[CM]. 广州: 中国航海图书出版社, 2015.
Zhu B D, Guan S X, Huang W X, et al. Atlas of geology and geophysics of South China Sea(1∶2 000 000)[CM]. Guangzhou: China Navigation Publication Press, 2015(in Chinese).
|
| [28] |
Stow D, Smillie Z. Distinguishing between deep-water sediment facies: Turbidites, contourites and hemipelagites[J]. Geosciences, 2020, 10(2): 68.
|
| [29] |
Stow D, Tabrez A R. Hemipelagites: Processes, facies and model[M]. United Kingdom: Geological Society of London Special Publications, 1998: 317-337.
|
| [30] |
Takano S, Ito M, Nakano T, et al. Sequence-stratigraphic signatures of hemipelagic siltstones in deep-water successions: The Lower Pleistocene Kiwada and Otadai Formations, Boso Peninsula, Japan[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2004, 170(3/4): 189-206.
|
| [31] |
雷振宇, 张莉, 王龙樟, 等. 南海南部北康盆地晚渐新世-中中新世物源变化[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(5): 1855-1864.
Lei Z Y, Zhang L, Wang L Z, et al. The provenance migration in the Beikang Basin of the southern South China Sea during the Oligocene to the Mid-Miocene[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(5): 1855-1864(in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [32] |
张晋, 李安春, 万世明, 等. 南海南部表层沉积物粒度分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(2): 1-10.
Zhang J, Li A C, Wan S M, et al. Grain size distribution of surface sediments in the southern South China Sea and influencing factors[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(2): 1-10(in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [33] |
Wang P, Prell W L, Blum P, et al. Proceedings of the ocean drilling program, Initial Reports 184[R]. Texas: Texas A & M University, 2000.
|
| [34] |
Ding W, Franke D, Li J, et al. Seismic stratigraphy and tectonic structure from a composite multi-channel seismic profile across the entire dangerous grounds, South China Sea[J]. Tectonophysics, 2013, 582: 162-176.
|
| [35] |
Huang J, Jiao W, Liu J, et al. Sediment distribution and dispersal in the southern South China Sea: Evidence from clay minerals and magnetic properties[J]. Marine Geology, 2021, 439: 106560.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
Abdul M M, Robert H, Wong F. Seismic sequence stratigraphy of the Tertiary sediments, offshore Sarawak deep-water area, Malaysia[J]. Geology Society of Malaysia Bulletin, 1995, 57: 545-561.
|
| [38] |
Xu J, Ren J, Luo P. The evolution of a gravity-driven system accompanied by diapirism under the control of the prograding West Luconia Deltas in the Kangxi Depression, southern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geophysical Research, 2019, 40(2): 199-221.
|
| [39] |
Wang H, Chen S, Liu E T, et al. Typical gravity flow sedimentary features and provenance system in Yinggehai-Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 5-18(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0245 |
| [40] |
Pei J X, Zhang C, Wang Y H, et al. Tectonic evolution and depositional response in southern continental marginal basins of South China Sea during period of rift-drift-foreland: A case study from the Liyue Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(2): 42-53(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0205 |
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
Hall R. Reconstructing Cenozoic SE Asia[J]. Geological Society, 1996, 106: 153-184.
|
| [43] |
孙珍, 赵中贤, 周蒂, 等. 南沙海域盆地的地层系统与沉积结构[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2011, 36(5): 798-806.
Sun Z, Zhao Z X, Zhou D, et al. The stratigraphy and the sequence achitecture of the basins in Nansha Region[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2011, 36(5): 798-806(in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [44] |
雷振宇, 刘晓峰, 张莉, 等. 南海南部北康盆地构造样式及构造演化[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(5): 861-874.
Lei Z Y, Liu X F, Zhang L, et al. Structural styles and evolution of Beikang Basin, southern South China Sea[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(5): 861-874(in Chinese with English abstract).
|




 下载:
下载:








 本站查看
本站查看




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: